Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Haloalkanes and Haloarenes QNA
Uploaded by
tanishasainits2Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Haloalkanes and Haloarenes QNA
Uploaded by
tanishasainits2Copyright:
Available Formats
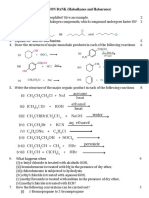
Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
1. A HYDROCARBON C5H10 does not react with chlorine in dark but gives a single monochloro compound C5H9Cl in
bright sunlight. Identify the hydrocarbon.
2. What are ambident nucleophiles? Explain with an example.
3. Which compound in each of the following pairs will react faster in SN2 reaction with –OH?
(i) CH3Br or CH3I
(ii) (CH3)3CCl or CH3Cl
How will you bring about the following conversions? (i) Ethanol to but-1-yne
(ii) Ethane to bromoethene
(iii) Propene to 1-nitropropane
(iv) Toluene to benzyl alcohol
4. alkyl halides, though polar, are immiscible with water.
Grignard reagents should be prepared under anhydrous conditions.
5. Give the uses of freon 12, DDT, carbon tetrachloride and iodoform.
6. Arrange the compounds of each set in order of reactivity towards SN 2 displacement:
(i) 2-Bromo-2-methylbutane, 1-Bromopentane, 2-Bromopentane
7. Out of C6H5CH2Cl and C6H5CHClC6H5, which is more easily hydrolysed by aqueous KOH?
8. How can the following conversions be carried out?
(i) Propene to propan-1-ol
(ii) Ethanol to but-1-yne
(iii) 1-Bromopropane to 2-bromopropane
(iv) Toluene to benzyl alcohol
(v) Benzene to 4-bromonitrobenzene
(vi) Benzyl alcohol to 2-phenylethanoic acid
(vii) Ethanol to propanenitrile
(viii) Aniline to chlorobenzene
9. The treatment of alkyl chlorides with aqueous KOH leads to the formation of alcohols but in the presence of
alcoholic KOH, alkenes are major products. Explain.
10. Primary alkyl halide C4H9Br (a) reacted with alcoholic KOH to give compound (b). Compound (b) is reacted with
HBr to give (c) which is an isomer of (a). When (a) is reacted with sodium metal it gives compound (d), C 8H18 which
is different from the compound formed when n-butyl bromide is reacted with sodium. Give the structural formula
of (a) and write the equations for all the reactions.
You might also like
- Class 12 Chemistry PYQs Shobhit NirwanDocument68 pagesClass 12 Chemistry PYQs Shobhit NirwanDron Pande83% (12)
- Pdf-Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument159 pagesPdf-Haloalkanes and HaloarenesOmkar Singh Shekhawat100% (2)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Revision Sheet HaloalkaneDocument3 pagesRevision Sheet HaloalkaneSahil PandeyNo ratings yet
- QB - Haloalkane and HaloareneDocument2 pagesQB - Haloalkane and HaloareneSameer KumarNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument1 pageHaloalkanes and HaloarenesPES 21No ratings yet
- Reasoning Based Questions (6 Marks) Section-ADocument4 pagesReasoning Based Questions (6 Marks) Section-ARishi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument3 pagesHaloalkanes and HaloarenesRAUNAK DEYNo ratings yet
- Class 12th Chemistry Haloalkenes and HaloarenesDocument1 pageClass 12th Chemistry Haloalkenes and Haloarenes10A / 33 / Soham DwivediNo ratings yet
- Alcohol, Phenols and Ethers PDFDocument13 pagesAlcohol, Phenols and Ethers PDFRahul JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Very Short Answer Type Questions (1 Mark)Document10 pagesVery Short Answer Type Questions (1 Mark)Ꮢupesh YadavNo ratings yet
- Leep511 PDFDocument14 pagesLeep511 PDFSubhabrata MabhaiNo ratings yet
- The Reaction Gives Pure Alkyl HalidesDocument8 pagesThe Reaction Gives Pure Alkyl HalidesMohammed IliasNo ratings yet
- Class-Xii Haloalkanes and Haloarenes (Assignment-2)Document4 pagesClass-Xii Haloalkanes and Haloarenes (Assignment-2)Hardik GulatiNo ratings yet
- Chapter - Haloalkanes and Haloarenes: Subject: Chemistry Class: XII Worksheet: IDocument3 pagesChapter - Haloalkanes and Haloarenes: Subject: Chemistry Class: XII Worksheet: IPathan MohsinNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Org Che CHAPTER 10Document10 pagesClass 12 Org Che CHAPTER 10DeekshaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Class Xii - Chemistry Chapter - Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument3 pagesWorksheet Class Xii - Chemistry Chapter - Haloalkanes and Haloarenesjiya jainNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Class Xii - Chemistry Chapter - Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument3 pagesWorksheet Class Xii - Chemistry Chapter - Haloalkanes and HaloarenesApratim NagNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Class Xii - Chemistry Chapter - Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument3 pagesWorksheet Class Xii - Chemistry Chapter - Haloalkanes and Haloarenesjiya jainNo ratings yet
- Revision - HaloalkanesDocument4 pagesRevision - HaloalkanessafaaNo ratings yet
- Unit-10 HaloalkanesDocument2 pagesUnit-10 HaloalkanesVIDHI CHORDIANo ratings yet
- CoversionDocument12 pagesCoversionSunil KumarNo ratings yet
- All ORGANIC Q ADocument55 pagesAll ORGANIC Q AkunalNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 10 (Test Paper - Haloalkane and Haloarene) : Saint S.R.S School Class-Xii Chemistry (Theory)Document2 pagesChapter - 10 (Test Paper - Haloalkane and Haloarene) : Saint S.R.S School Class-Xii Chemistry (Theory)Shivank KurmiNo ratings yet
- Reasoning OrganicDocument31 pagesReasoning OrganicBlack IceNo ratings yet
- Wa0003 PDFDocument3 pagesWa0003 PDFaPP bOssNo ratings yet
- Assignment Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument2 pagesAssignment Haloalkanes and HaloarenesBasant KothariNo ratings yet
- J Yxqlmzkdh CTX 5 EKst 7 PDocument10 pagesJ Yxqlmzkdh CTX 5 EKst 7 PNew GmailNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Halo Alkanes and Halo Arenes Ws-2Document2 pagesClass 12 Halo Alkanes and Halo Arenes Ws-2Chintu RajNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - AlcoholDocument14 pagesWorksheet - AlcoholHarshu BhaiyaNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Exemplar Chapter 11Document11 pages12 Chemistry Exemplar Chapter 11Priya dharshiniNo ratings yet
- Class XII Alcohols Phenols EthersDocument7 pagesClass XII Alcohols Phenols EthersvartikasinghNo ratings yet
- Important Questions On Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Class 12Document3 pagesImportant Questions On Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Class 12justtryingtoghostNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questio11Document14 pagesMultiple Choice Questio11Achiket Anand DesaiNo ratings yet
- Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution-03-Assignments (New)Document18 pagesElectrophilic Aromatic Substitution-03-Assignments (New)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Alcohol, Phenols and EtherDocument4 pagesAlcohol, Phenols and EtherShayaan & friend's vlogNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes AssignmentDocument3 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenes AssignmentManaswini JhaNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument2 pagesHaloalkanes and HaloarenesJeremiah ShibuNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols and EthersDocument3 pagesAlcohols, Phenols and EthersCJ's Music GalleryNo ratings yet
- CH-10 Halogen DerivativeDocument9 pagesCH-10 Halogen DerivativeKirtan Singh RaoNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument5 pagesUntitledAnurag DubeyNo ratings yet
- Class: Xii Max. Marks: 50 Subject: Chemistry. TIME: 2 HoursDocument2 pagesClass: Xii Max. Marks: 50 Subject: Chemistry. TIME: 2 HoursPrerak Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Leep 511Document14 pagesLeep 511Sanjeev KumarNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument14 pagesHaloalkanes and HaloarenesHarshitha GowdaNo ratings yet
- 12th Ch.7 Alcohols Phenols and EthersDocument4 pages12th Ch.7 Alcohols Phenols and EthersjusttryingtoghostNo ratings yet
- Alcohol, Phenol EtherDocument1 pageAlcohol, Phenol EtherSomu Yashawant ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Class Test 1 Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument1 pageClass Test 1 Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and HaloarenesPoovaraahan RaghuveeranNo ratings yet
- HaloDocument2 pagesHalonawfalredxNo ratings yet
- Alcohol & Phenol Markswise QuestionsDocument9 pagesAlcohol & Phenol Markswise QuestionsSachin GuptaNo ratings yet
- Test - Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers - 28.8.2023Document3 pagesTest - Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers - 28.8.2023jayaprasanthsinghNo ratings yet
- Alcohols Phenols and Ethers Holiday TestDocument3 pagesAlcohols Phenols and Ethers Holiday TestSruthiNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes QDocument35 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenes QAbhinav BishtNo ratings yet
- Alcohols Phenols and EthersDocument18 pagesAlcohols Phenols and EthersFurious AGARWALNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Worksheet-1Document2 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenes Worksheet-1viiNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes-Imp QNSDocument3 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenes-Imp QNSjamesNo ratings yet
- Eamcet Part Test - 5Document6 pagesEamcet Part Test - 5udaysrinivasNo ratings yet
- Ch6 HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES HHW WORKSHEETDocument4 pagesCh6 HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES HHW WORKSHEETAaditya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Halo Alkanes and Halo ArenesDocument23 pagesHalo Alkanes and Halo Arenesaleena'No ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Impq CH10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes 01Document10 pages12 Chemistry Impq CH10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes 01gadhaNo ratings yet