Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Maternal & Child Health Nursing (Pillitteri) Flashcards Quizlet
Uploaded by
Josh Pagnamitan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
38 views1 pageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
38 views1 pageMaternal & Child Health Nursing (Pillitteri) Flashcards Quizlet
Uploaded by
Josh PagnamitanCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Maternal &Study
Child Healthvideos
sets, questions, Nursing (Pillitteri) Study free 7-…
Upgrade:
Science Biology
Maternal & Child Health
Nursing (Pillitteri)
29 studiers today 4.7 (11 reviews)
Get a hint
the cell resulting from the
union of an ovum and a
spermatozoon
Zygote
(including the
organism that develops from
that cell)
21 / 21
Your Memory Score
1 day memory 22%
Flashcards Learn
Test Match
Created by
Share
lauradbrewer
Chapter 9 Terms
Terms in this set (21) Your stats
Still learning (15)
Select these 15
You've started learning these terms. Keep it up!
Decidua the endometrium or lining of
the uterus during pregnancy;
it is shed after giving birth
Embryo the developing human
organism from about 2 weeks
after fertilization through the
second month
EDB, EDC, EDD ...
Fertilization process in sexual
reproduction in which male
and female reproductive
cells join to form a new cell
Fetus the developing human
organism from 9 weeks after
conception to birth
Foramen ovale penetrates interatrial septum
from fifth week of embryonic
development until birth
Hydramnios more than 2000 ml of
amniotic fluid in the uterus.
can cause maternal diabetes;
esophageal atresia
(diminishes or prevents fetal
swallowing); and kidney
disorders that affect kidney
output.
Implantation (embryology) the organic
process whereby a fertilized
egg becomes implanted in
the lining of the uterus of
placental mammals
MdDonald' rule ...
Meconium thick dark green mucoid
material that is the first feces
of a newborn child
Nonstress test test to identify fetal
compromise in conditions
with poor placenta function,
such as hypertension,
diabetes mellitus, or postterm
gestation (pregnancy last
beyond 42 weeks), this test
determines the fetal well-
being, measured by the
ability of the fetus to respond
to its bodymovement by
accelerations of the heart
rate.
Oligohydramnio decreased amniotic fluid.
s increased risk of fetus
because the umbilical cord
does not have enough fluid
to float and may become
compressed.
Surfactant a substance capable of
reducing the surface tension
of a liquid in which it is
dissolved, An amphipathic
molecule secreted by cells in
the alveoli (type 2 alveolar
cells) tha reducs surface
tension on the inside of the
alveolar walls. This prevents
the alveoli from collapsing
upon exhale and sticking
together, thus reducing the
effort required for inspiration.
Trophoblast The outer ring of cells of a
blastocyst. The trophoblast
takes part in the formation of
the placenta.
Umbilical cord a cord or funicle connecting
the embryo or fetus with the
placenta of the mother and
transporting nourishment
from the mother and wastes
from the fetus
Not studied (6)
Select these 6
You haven't studied these terms yet!
Age of viability The age at which a baby can
survive in the event of a
premature birth., Age at
which a preterm newborn
can survive, about 22 weeks,
weight and maturity are
crucial
Amniocentesis (pregnancy) extraction by
centesis of amniotic fluid
from a pregnant woman
(after the 15th week of
pregnancy) to aid in the
diagnosis of fetal
abnormalities
Amniotic The innermost layer which
membrane encloses the fetus and
produces amniotic fluid
Chorionic surround the gestational sac
membrane and extends up and migrates
into the placenta. Outer fetal
membrane
Chorionic villi a procedure in which the
sampling (CVS) chorionic villi to are analyzed
to diagnose fetal genotypes
Zygote the cell resulting from the
union of an ovum and a
spermatozoon (including the
organism that develops from
that cell)
About us For students For teachers Resources
About Quizlet Flashcards Live Help center
How Quizlet works Test Checkpoint Honor code
Careers Learn Blog Community guidelines
Advertise with us Solutions Be the Change Privacy
Get the app Q-Chat Terms
Ad and Cookie Policy
Language
English (USA)
© 2023 Quizlet, Inc.
You might also like
- Last Minute Embryology: Human embryology made easy and digestible for medical and nursing studentsFrom EverandLast Minute Embryology: Human embryology made easy and digestible for medical and nursing studentsNo ratings yet
- MCHN 3RD LectDocument9 pagesMCHN 3RD LectZahNo ratings yet
- Mother Baby TermsDocument3 pagesMother Baby TermschadnelsonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 The Growing FetusDocument4 pagesChapter 9 The Growing FetusCarrie ANo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physics: Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physics: Reproductive SystemDenise CalderonNo ratings yet
- fertlizationDocument5 pagesfertlizationgallardo.bettinarose.iNo ratings yet
- MCN Lec - Chapter 3Document18 pagesMCN Lec - Chapter 3David LomentigarNo ratings yet
- Maternity and Newborn Nursing ReviewerDocument21 pagesMaternity and Newborn Nursing ReviewerCherubim Lei DC FloresNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Process of Conception and Stage of Fetal DevelopmentDocument25 pagesModule 2 - Process of Conception and Stage of Fetal DevelopmentKatie HolmesNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Prenatal DevelopmentDocument57 pagesUnit 2 Prenatal DevelopmentNurul izwaniNo ratings yet
- Poultry Handouts For Final ExamDocument121 pagesPoultry Handouts For Final Examdaniel,jr BALDOZNo ratings yet
- Maternal & Child Health Nursing Flashcards QuizletDocument1 pageMaternal & Child Health Nursing Flashcards QuizletJosh PagnamitanNo ratings yet
- Reproduction and Development: BIOLOGY: Today and TomorrowDocument60 pagesReproduction and Development: BIOLOGY: Today and Tomorrowmaine pamintuanNo ratings yet
- Fetal Development Nursing CareDocument20 pagesFetal Development Nursing CareiMaibelle BelleNo ratings yet
- REVIEWERDocument7 pagesREVIEWERKhaskie Geneva DumaguinNo ratings yet
- 1-Prenatal & Fetal Development-93666Document45 pages1-Prenatal & Fetal Development-93666Izziddin YassineNo ratings yet
- Fetal Development: Ms - Virgina Varghese and DR - SoniyaDocument37 pagesFetal Development: Ms - Virgina Varghese and DR - Soniyaalmayasa2002No ratings yet
- MCN LectureDocument8 pagesMCN LectureEmily BernatNo ratings yet
- Maternal Health: Pregnancy Signs and StagesDocument9 pagesMaternal Health: Pregnancy Signs and StagesjisooNo ratings yet
- 02 Fertilization & ImplantationDocument24 pages02 Fertilization & ImplantationAugust Ridlof RiwuNo ratings yet
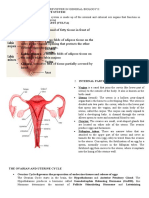
- The Female Reproductive SystemDocument6 pagesThe Female Reproductive SystemKhristin Joy GamponiaNo ratings yet
- GAS-PROCESS-OF-REPRODUCTIONDocument2 pagesGAS-PROCESS-OF-REPRODUCTIONbevienlynpepito10No ratings yet
- Unit 3. (Group 16) Fertilization of Ovum, Embedding of The Blastocyst, Development and Growth of The FetusDocument80 pagesUnit 3. (Group 16) Fertilization of Ovum, Embedding of The Blastocyst, Development and Growth of The FetusKu NiniNo ratings yet
- Human Fertilization Is The Union of A Human Egg and SpermDocument7 pagesHuman Fertilization Is The Union of A Human Egg and Spermoxidalaj100% (1)
- OB 1st SemDocument4 pagesOB 1st SemMai CarbonNo ratings yet
- Note of The ChapterDocument19 pagesNote of The ChapterMotiourNo ratings yet
- NCM 107 Study GuideDocument3 pagesNCM 107 Study GuideJamilah BanglanNo ratings yet
- Reporductive SystemDocument31 pagesReporductive SystemEmma Joel OtaiNo ratings yet
- Biology Summary Modules 5+6+7 CompleteDocument70 pagesBiology Summary Modules 5+6+7 Complete1811ameliaNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Health Nursing: Pregnancy StagesDocument8 pagesMaternal and Child Health Nursing: Pregnancy StagesBing58No ratings yet
- Fertilization 1 1Document219 pagesFertilization 1 1Edwin TiuNo ratings yet
- 2600 - Module 3 - PregnancyDocument14 pages2600 - Module 3 - Pregnancymegan.abbinkNo ratings yet
- Der To Properly Care About The Offspring and Keep It Safe.: ImplantationDocument2 pagesDer To Properly Care About The Offspring and Keep It Safe.: ImplantationChristine AguilarNo ratings yet
- 100 most important D&GA conceptionsDocument250 pages100 most important D&GA conceptionsRa ViNo ratings yet
- NSD With Iufd PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesNSD With Iufd Pathophysiologykaye040382% (11)
- Reviewer (HumanRep) : MIDTERMDocument6 pagesReviewer (HumanRep) : MIDTERMHazel GeronimoNo ratings yet
- Foetal DevelopmentDocument50 pagesFoetal Developmentdipendrakumarkushawaha44No ratings yet
- Stages of Fetal DevelopmentDocument42 pagesStages of Fetal DevelopmentKara Ashleigh0% (1)
- Huma JoshDocument17 pagesHuma JoshBenny AgassiNo ratings yet
- 178 Anatomy Reproductive SystemDocument25 pages178 Anatomy Reproductive SystemJUVY ANN PATOSANo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child (Healthy Pregnancy)Document37 pagesMaternal and Child (Healthy Pregnancy)Lenny SucalditoNo ratings yet
- MCN Midterm 1Document12 pagesMCN Midterm 1sherelyn legaspiNo ratings yet
- Fertilization and DevelopmentDocument23 pagesFertilization and Developmentjoshua.brussell100% (3)
- Fertilization and Implantation StagesDocument47 pagesFertilization and Implantation StagesTan DesmondNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 AnswerDocument20 pagesNCM 109 AnswerBiway RegalaNo ratings yet
- Human Embryology: Dr. Anushri MukhopadhyayDocument61 pagesHuman Embryology: Dr. Anushri MukhopadhyaySabyasachi MukhopadhyayNo ratings yet
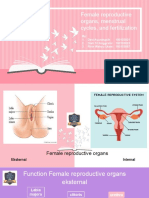
- Female reproductive organs, menstrual cycles, and fertilization explainedDocument13 pagesFemale reproductive organs, menstrual cycles, and fertilization explainedNurinnisa ShiddiqiyahNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 Human ReproductionDocument8 pagesChapter-3 Human ReproductionbpmbhamoraNo ratings yet
- Estoras Neil Vincent Module 2Document9 pagesEstoras Neil Vincent Module 2Christine ElnasNo ratings yet
- OB - Abortion (NER)Document6 pagesOB - Abortion (NER)gellie gellesNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - Conception NOTESDocument4 pagesModule 5 - Conception NOTESKisha BethelNo ratings yet
- Esquema Unit 3 SciencesDocument4 pagesEsquema Unit 3 SciencesALBANo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System GlossaryDocument4 pagesFemale Reproductive System GlossaryHASSAM KHANNo ratings yet
- Basic Maternity ConceptsDocument14 pagesBasic Maternity ConceptsDivine Grace Arreglo AbingNo ratings yet
- COURSE UNIT WEEK 4 MaternalDocument9 pagesCOURSE UNIT WEEK 4 Maternalesmactal8408antNo ratings yet
- Hormone Feedback & PregnancyDocument11 pagesHormone Feedback & Pregnancymaricaruba9No ratings yet
- THE GROWING FETUSDocument11 pagesTHE GROWING FETUSGwyneth ManioNo ratings yet
- Diversity in Living Organisms Notes For Class 10 Download in PDFDocument3 pagesDiversity in Living Organisms Notes For Class 10 Download in PDFgooodeNo ratings yet
- 1 - Introduction To Clinical Hematology IDocument26 pages1 - Introduction To Clinical Hematology IJulliene DadoleNo ratings yet
- Name: NIM: Class:: Medical InstrumentsDocument9 pagesName: NIM: Class:: Medical InstrumentsNessyaa SyahnaNo ratings yet
- FISA Engl DISCIPLINA FIZIOLOGIE I MODUL LIMBA ENGLEZADocument8 pagesFISA Engl DISCIPLINA FIZIOLOGIE I MODUL LIMBA ENGLEZAAbdallah Darwish100% (1)
- Gua ShaDocument24 pagesGua Shaprince190071% (7)
- The Emotion Code Has Helped Trapped EmotionsDocument2 pagesThe Emotion Code Has Helped Trapped Emotionsmagdalena0% (1)
- 5-Neuro MCQs Final UnsolvedDocument29 pages5-Neuro MCQs Final UnsolvedOsman Somi0% (2)
- Cryo SurgeryDocument8 pagesCryo SurgeryninroseNo ratings yet
- Acute Gastroenteritis Individual TaskDocument5 pagesAcute Gastroenteritis Individual TaskMaria Lourdes ManganarNo ratings yet
- Microbiology & Parasitology Module 1 Part 2Document7 pagesMicrobiology & Parasitology Module 1 Part 2BARRERAS Aubrey Eden Faye G.No ratings yet
- Histopathological and Biochemical, BhawnaDocument8 pagesHistopathological and Biochemical, BhawnaBhaskar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Curs Ia. Anemia AplasticaDocument10 pagesCurs Ia. Anemia Aplasticaalina2009No ratings yet
- Colonoscopy Screening GuideDocument52 pagesColonoscopy Screening GuideRisal WintokoNo ratings yet
- 674-Article Text-5409-1-10-20210430Document6 pages674-Article Text-5409-1-10-20210430Rizca Cholidatun Ni'mahNo ratings yet
- NCP - Risk For Impaired Skin Integrity R/T Dry Skin and Behaviors That May Lead To Skin Integrity Impairment AEB Scratching of ScabsDocument1 pageNCP - Risk For Impaired Skin Integrity R/T Dry Skin and Behaviors That May Lead To Skin Integrity Impairment AEB Scratching of ScabsCarl Elexer Cuyugan Ano100% (4)
- The History of Surgical Suturing TechniquesDocument5 pagesThe History of Surgical Suturing TechniquesfaizalmasoodiNo ratings yet
- Fluid and electrolyte homeostasis comprehensive studyDocument5 pagesFluid and electrolyte homeostasis comprehensive studyAchmat riyadiNo ratings yet
- Proposal ThesisDocument6 pagesProposal ThesisJemarse GumpalNo ratings yet
- Family Planning Semester VDocument82 pagesFamily Planning Semester Vduaabdullah33No ratings yet
- Alcohol DementiaDocument3 pagesAlcohol DementiaHenok Moges KassahunNo ratings yet
- Management of Reproductive Health and DysmenorrheaDocument33 pagesManagement of Reproductive Health and DysmenorrheaIntan Permatasari Putri SNo ratings yet
- English For Nursing Topic 13 Reinforcing A Dietary ProgramDocument7 pagesEnglish For Nursing Topic 13 Reinforcing A Dietary ProgramAyu AndiniiNo ratings yet
- Effects of Low Versus High Volume High Intensity Interval - 2023 - Journal of EDocument10 pagesEffects of Low Versus High Volume High Intensity Interval - 2023 - Journal of ESherriNo ratings yet
- 1611220033Document337 pages1611220033JORGENo ratings yet
- Lactulose Drug StudyDocument4 pagesLactulose Drug StudyAgronaSlaughterNo ratings yet
- Implant-Related Complications and FailuresDocument91 pagesImplant-Related Complications and FailuresSaman MohammadzadehNo ratings yet
- Assessment On Respiratory ProblemsDocument7 pagesAssessment On Respiratory ProblemsSetiaty PandiaNo ratings yet
- NCLEX Questions: Nursing Care, Medication Administration & Client EducationDocument3 pagesNCLEX Questions: Nursing Care, Medication Administration & Client EducationkxviperNo ratings yet
- ACOG All About Exercise During PregnancyDocument4 pagesACOG All About Exercise During PregnancyriasahNo ratings yet
- Praktek Essentials: Tanda Dan GejalaDocument5 pagesPraktek Essentials: Tanda Dan GejalaElvis HusainNo ratings yet
- PneumoniaDocument27 pagesPneumoniamameekasim75No ratings yet