Professional Documents
Culture Documents
WEEK 1 - Introduction To Mental Health Nursing Copy 2
Uploaded by
John WallaceOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
WEEK 1 - Introduction To Mental Health Nursing Copy 2
Uploaded by
John WallaceCopyright:
Available Formats
people of all ages suffer from depression. It is a major contributor to the overall global burden of disease.
◦More women are affected by depression than men.
◦It can lead to suicide.
• There are effective psychological and pharmacological treatments for moderate and severe depression.
◦Recurrent depressive disorder: 2 week period mild moderate severe Cannot carry on with usual activities.
◦Bipolar affective disorder: this type of depression typically consists of both manic and depressive episodes separated by
periods of normal mood.
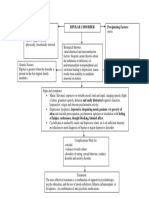
The Stuart Stress Adaptation Model of Psychiatric Nursing Care
• is a model of psychiatric nursing care.
• which integrates aspects of patient care into a unified framework for practice.
◦biological
◦psychological
◦socio-cultural
◦environmental
◦legal-ethical
• Developed by Gail Stuart as a synthesis of diverse bodies of knowledge from the perspective of psychiatric nursing and as an
application of this knowledge to clinical practice
Importance of using a conceptual model
• provide a structure for thinking, observing, and interpreting what is seen.
• are frames of reference within which patients, their environment and health states, and nursing activities are described.
• Nursing models can explain a person’s response to stress and the process and desired outcomes of nursing interventions
• Psychiatric nurses enhance their practice by basing their actions on a model of psychiatric nursing care that is:
◦Inclusive
◦Holistic
◦Relevant to the needs of it, families, groups and communities
Assumption of the Model
• Nature is ordered as a social hierarchy from the simplest unit to the most complex
◦Each level of this hierarchy is an organized whole.
◦Each level is also is a part of all of the other levels, so nothing exists in isolation.
◦Thus the individual is a part of the family, group, community, society, & the larger
biosphere.
◦Material and information flow across levels, and each level is influenced by all the others.
◦The most basic level of nursing intervention is the individual. However, in working with the
individual, the nurse also must consider how the individual relates to the whole.
• Nursing care is provided within a biological, psychological, sociocultural, legal, ethical, policy
and advocacy context.
◦Each of these aspects of care is described in detail in Chapters 5 through 9.
◦The nurse must understand each of them in order to provide competent, holistic
psychiatric nursing care.
◦The theoretical basis for psychiatric nursing practice is derived from nursing science as
well as from the behavioral, social, and biological sciences.
◦The range of theories used by psychiatric nurses includes:
‣ nursing, developmental psychology, neurobiology, pharmacology, psychopathology,
learning, sociocultural, cognitive, behavioral, economic, organizational, political, legal,
ethical, interpersonal, group, family, and milieu.
You might also like
- Lesson 1 The Stuart Stress Adaptation ModelDocument50 pagesLesson 1 The Stuart Stress Adaptation ModelMaria Victoria A. PraxidesNo ratings yet
- Psychiatry UNIT WISE NOTESDocument126 pagesPsychiatry UNIT WISE NOTESvijayvk8749No ratings yet
- Multimodal Treatment of Acute Psychiatric Illness: A Guide for Hospital DiversionFrom EverandMultimodal Treatment of Acute Psychiatric Illness: A Guide for Hospital DiversionNo ratings yet
- Seminar On Current Issues and Trends in Psychiatry. Mental Health Services in Kerala India and GlobalDocument34 pagesSeminar On Current Issues and Trends in Psychiatry. Mental Health Services in Kerala India and GlobalGopika SNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric and Mental Health NursingDocument4 pagesPsychiatric and Mental Health Nursingedomilies524100% (1)
- MHN, I (U), 6Document51 pagesMHN, I (U), 6akilaNo ratings yet
- Positive Qualities and Values of A Community Health Nurse, Public Health Nursing CompetenciesDocument27 pagesPositive Qualities and Values of A Community Health Nurse, Public Health Nursing CompetenciesMary Dale Omanea Almodal100% (1)
- Mind Magic: Building a Foundation for Emotional Well-BeingFrom EverandMind Magic: Building a Foundation for Emotional Well-BeingNo ratings yet
- NURSING CONCEPTS Exam GuideDocument24 pagesNURSING CONCEPTS Exam Guide2016114427No ratings yet
- Conceptual and Philosophical Foundations of Professional Nursing PracticeDocument36 pagesConceptual and Philosophical Foundations of Professional Nursing PracticeDip Ayan MNo ratings yet
- 117 FoundationsDocument4 pages117 FoundationsGabrielle AcaboNo ratings yet
- Summary SMIDocument116 pagesSummary SMIsophlounyNo ratings yet
- Ngoa, Jose Troy - Sas1Document9 pagesNgoa, Jose Troy - Sas1Ella AroNo ratings yet
- Diploma in NursingDocument10 pagesDiploma in NursinglilianNo ratings yet
- Week One (1) - PPN 201 A Theoretical Orientation To Nursing Practical Relational InquiryDocument8 pagesWeek One (1) - PPN 201 A Theoretical Orientation To Nursing Practical Relational InquiryLuya WeiNo ratings yet
- Community Mental Health Nursing, Community Mental Health-1Document65 pagesCommunity Mental Health Nursing, Community Mental Health-1Patel Hasmukh Dhanjibhai100% (1)
- Assessment ModelsDocument36 pagesAssessment ModelsNaxliceNo ratings yet
- Session #1 SAS - Funda (Lec)Document8 pagesSession #1 SAS - Funda (Lec)Mary Maxiluch TabudlongNo ratings yet
- Mental Health &mental Illness PPT (1) - 2Document75 pagesMental Health &mental Illness PPT (1) - 2N.a.s.r EbaidNo ratings yet
- Multidisciplinary TeamDocument8 pagesMultidisciplinary TeamBinu MathewNo ratings yet
- Critical Issues in PsychotherapyDocument8 pagesCritical Issues in PsychotherapyYoshita AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Concept of PsychoeducationDocument22 pagesConcept of PsychoeducationAli100% (3)
- Psychiatric Nursing Notes: History, AsylumsDocument62 pagesPsychiatric Nursing Notes: History, Asylumssurviving nursing school100% (1)
- CMH - Merged End Term PDFDocument320 pagesCMH - Merged End Term PDFSrishti KumarNo ratings yet
- Hildgard PeplauDocument31 pagesHildgard PeplauHazel LezahNo ratings yet
- BPSS AnalysisDocument5 pagesBPSS AnalysisVictor VeraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Continuum of Care: Keltner: Psychiatric Nursing, 5 EditionDocument7 pagesChapter 3: Continuum of Care: Keltner: Psychiatric Nursing, 5 EditionWarrenPeaceNo ratings yet
- Theories and Models For CommunityDocument5 pagesTheories and Models For CommunitychandratappyNo ratings yet
- 122 Lecture 1 Milieu TherapyDocument7 pages122 Lecture 1 Milieu TherapyDENNIS N. MUÑOZNo ratings yet
- TFNDocument5 pagesTFNkem00000No ratings yet
- TFN SES 3 - Chap8 - 9Document54 pagesTFN SES 3 - Chap8 - 9Prince Charles AbalosNo ratings yet
- Ch.1+2 CMHNDocument48 pagesCh.1+2 CMHNMohammed Taysier QudaihNo ratings yet
- Integrative Pathways: Navigating Chronic Illness with a Mind-Body-Spirit ApproachFrom EverandIntegrative Pathways: Navigating Chronic Illness with a Mind-Body-Spirit ApproachNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Intervention & ManagementDocument19 pagesUnit 4 Intervention & ManagementSwarnaNo ratings yet
- Behavioral Health Specialist - The Comprehensive Guide: Vanguard ProfessionalsFrom EverandBehavioral Health Specialist - The Comprehensive Guide: Vanguard ProfessionalsNo ratings yet
- Role - Responsibilities of Psychiatry Health NurseDocument3 pagesRole - Responsibilities of Psychiatry Health NurseDhAiRyA ArOrANo ratings yet
- PrintedFundamentals of NursingDocument23 pagesPrintedFundamentals of NursingAaron EspirituNo ratings yet
- Nonpharmacological Management of Schiz (1) JPDocument50 pagesNonpharmacological Management of Schiz (1) JPRupinder Gill100% (1)
- Model of PreventionDocument14 pagesModel of Preventionsudeepminz15No ratings yet
- Community Mental Health NursingDocument76 pagesCommunity Mental Health Nursinggopscharan92% (25)
- NSG As A PRFSN Set 1Document20 pagesNSG As A PRFSN Set 1saranya amuNo ratings yet
- BORINGOT, Aliah Marie - MAON, Marry Elordy - RIVERA, Mara Ysabel PERPETUA, Anne Dominique - SANCHEZ, Aubrey MhilesDocument32 pagesBORINGOT, Aliah Marie - MAON, Marry Elordy - RIVERA, Mara Ysabel PERPETUA, Anne Dominique - SANCHEZ, Aubrey MhilesAebee Velasco AlcarazNo ratings yet
- Nursing As Profession PDFDocument115 pagesNursing As Profession PDFArchana Sahu100% (3)
- Weathering the Storm: A Guide to Understanding and Overcoming Mood DisordersFrom EverandWeathering the Storm: A Guide to Understanding and Overcoming Mood DisordersNo ratings yet
- Concept of Mental Health - MKU-1Document35 pagesConcept of Mental Health - MKU-1Favour Joshua MpumurijeNo ratings yet
- MHN ReflectionDocument6 pagesMHN ReflectionKeep smileNo ratings yet
- The Value of Peplau's Theory For Mental Health Nursing.: Jones ADocument13 pagesThe Value of Peplau's Theory For Mental Health Nursing.: Jones AmejulNo ratings yet
- Blueprint Exam 1+studyDocument37 pagesBlueprint Exam 1+studyNatasha DrummondNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document27 pagesChapter 1seyfelizelihaNo ratings yet
- What Is PsychotherapyDocument28 pagesWhat Is PsychotherapybatuhihihiNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Health - IllnessDocument45 pagesConcepts of Health - IllnessadiNo ratings yet
- Palliative Care: Basic TerminologiesDocument7 pagesPalliative Care: Basic TerminologiesDagmawit GirmaNo ratings yet
- 01 Introduction To FMDocument35 pages01 Introduction To FMahmad aminNo ratings yet
- Nursing TheoriesDocument10 pagesNursing TheoriesfinazkyaloNo ratings yet
- Clo 20Document4 pagesClo 20Kit LaraNo ratings yet
- Final Exam - VA - VERADocument4 pagesFinal Exam - VA - VERAVictor VeraNo ratings yet
- Week 3 - Therapeutic Relationship 2Document1 pageWeek 3 - Therapeutic Relationship 2John WallaceNo ratings yet
- Environmental HealthDocument47 pagesEnvironmental HealthJohn WallaceNo ratings yet
- Notability Notes KDocument1 pageNotability Notes KJohn WallaceNo ratings yet
- Food SafetyDocument81 pagesFood SafetyJohn Wallace100% (1)
- Energy SourcesDocument33 pagesEnergy SourcesJohn WallaceNo ratings yet
- Notability Notes 22Document1 pageNotability Notes 22John WallaceNo ratings yet
- Notability Notes 23 PDFDocument1 pageNotability Notes 23 PDFJohn WallaceNo ratings yet
- WEEK 3 - Climate and BiodiversityDocument63 pagesWEEK 3 - Climate and BiodiversityJohn WallaceNo ratings yet
- WEEK 4-Sustaining BiodiversityDocument108 pagesWEEK 4-Sustaining BiodiversityJohn WallaceNo ratings yet
- Notability Notes 21Document1 pageNotability Notes 21John WallaceNo ratings yet
- WEEK 1-Introduction To Enviromental ScienceDocument21 pagesWEEK 1-Introduction To Enviromental ScienceJohn WallaceNo ratings yet
- WEEK 2 - Ecology How Do They WorkDocument40 pagesWEEK 2 - Ecology How Do They WorkJohn WallaceNo ratings yet
- Mindfulness Based Interventions For Anxiety and DepressionDocument13 pagesMindfulness Based Interventions For Anxiety and DepressionStefan SanduNo ratings yet
- Life Event Dimensions of Loss, Humiliation, Entrapment, and Danger in The Prediction of Onsets of Major Depression and Generalized AnxietyDocument8 pagesLife Event Dimensions of Loss, Humiliation, Entrapment, and Danger in The Prediction of Onsets of Major Depression and Generalized AnxietyMariaIoanaTelecanNo ratings yet
- Lifestyle and Health Books - CatalogDocument16 pagesLifestyle and Health Books - CatalogRafael Machuca100% (1)
- Students Depression SuicidingDocument5 pagesStudents Depression SuicidingWendel NuguidNo ratings yet
- Sleep Predictors and Sleep Patterns - CarskadonDocument29 pagesSleep Predictors and Sleep Patterns - CarskadonScarlettBlondeNo ratings yet
- Lavender Oil For Anxiety and DepressionDocument19 pagesLavender Oil For Anxiety and DepressionYary SandovalNo ratings yet
- The Big Four by Rolf GordonDocument40 pagesThe Big Four by Rolf GordonArcanistNo ratings yet
- ADHD and DepressionDocument8 pagesADHD and DepressionVicki B VeeNo ratings yet
- Mohandas Et Al-2013-British Journal of Dermatology PDFDocument7 pagesMohandas Et Al-2013-British Journal of Dermatology PDFEdu SajquimNo ratings yet
- Comment: How Social Media Affects Teen Mental Health: A Missing LinkDocument3 pagesComment: How Social Media Affects Teen Mental Health: A Missing LinkWilliam Hernandez GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Medical BooksDocument20 pagesMedical Booksapi-385347264% (14)
- World Psychiatry June 2017Document112 pagesWorld Psychiatry June 2017Marco Macavilca CruzNo ratings yet
- Mock Congress Bill Research EssayDocument9 pagesMock Congress Bill Research Essayapi-302890064No ratings yet
- 2.e.case Ctudy On BPADDocument9 pages2.e.case Ctudy On BPADManisa Parida100% (1)
- Diagnosis of Alzheimer's Disease From EEG Signals Where Are We StandingDocument43 pagesDiagnosis of Alzheimer's Disease From EEG Signals Where Are We StandingElvis Josip EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Pyche Lecture : The Johari Window" (Joseph Luft/Harry Ingham, 1963) A Model For SELF-AWARENESS"Document29 pagesPyche Lecture : The Johari Window" (Joseph Luft/Harry Ingham, 1963) A Model For SELF-AWARENESS"mhayaNo ratings yet
- Teaching ManualDocument43 pagesTeaching ManualAli RezayiNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Mental Health and Psychosocial Support Interventions On People Affected by Humanitarian Emergencies: A Systematic ReviewDocument210 pagesThe Impact of Mental Health and Psychosocial Support Interventions On People Affected by Humanitarian Emergencies: A Systematic ReviewOxfamNo ratings yet
- A New Potential Target For The Treatment of Alcohol-Withdrawal Induced Depression - EurekAlert! Science NewsDocument2 pagesA New Potential Target For The Treatment of Alcohol-Withdrawal Induced Depression - EurekAlert! Science Newssupraja.bommalaNo ratings yet
- About DysphoriaDocument5 pagesAbout DysphoriaCarolina GómezNo ratings yet
- Bipolar CaseDocument41 pagesBipolar CaseEmariel Dulana25% (4)
- Pathophysiology of Bipolar 1 DisorderDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Bipolar 1 DisorderFloriejane Marata100% (2)
- HammenDocument18 pagesHammenAndreia AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Yakeley 2018 Psychoanalysis in Modern Mental Health PracticeDocument8 pagesYakeley 2018 Psychoanalysis in Modern Mental Health PracticeJonathan RiveraNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 - ResearchDocument31 pagesCHAPTER 1 - ResearchRea Genela ChuaNo ratings yet
- Design and Planning of Puzzle Games To Prevent and Intervene in The Elderly With Alzheimer's DiseaseDocument4 pagesDesign and Planning of Puzzle Games To Prevent and Intervene in The Elderly With Alzheimer's DiseaseInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Massman, 1992 Cortical y SubcorticalDocument21 pagesMassman, 1992 Cortical y SubcorticalRicardo Jose De LeonNo ratings yet
- Marchand - Neurobiology of Mood DisordersDocument11 pagesMarchand - Neurobiology of Mood DisordersDanaNo ratings yet
- Theoretical FoundationsDocument24 pagesTheoretical FoundationsMariana FarinasNo ratings yet
- (Compact Research - Diseases and Disorders) Scott Barbour - Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder-ReferencePoint Press (2012)Document104 pages(Compact Research - Diseases and Disorders) Scott Barbour - Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder-ReferencePoint Press (2012)NOBELDINo ratings yet