Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Vu Phan Huyen Chi 11230034
Uploaded by
ahnheeyeon500 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views4 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views4 pagesVu Phan Huyen Chi 11230034
Uploaded by
ahnheeyeon50Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Vu Phan Huyen Chi – 11230034 – EBBA 15.
2 – Microeconomic assignment
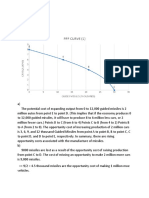
Ex 1: a)
- A => B = 3/2 = 1,5
- B => C = 6/2 = 3
- C => D = 9/2 = 4,5
- D => E = 12/2 = 6
The opportunity costs for producing guide missiles increase.
b) At point C
- If one million more cars be produced, point C will move gradually to point D. The
opportunity cost ratio from C to D is 4,5.
=> 1 million more cars will cost 4500 missiles.
- If one thousand more guided missiles be produced, point C will move gradually to
point B. The opportunity ratio from C to B is 1/3
=> 1 thousand more missiles will cost 1/3 million cars.
c) The point G inside the curve of the graph indicate that the amount of these products
that were produced is ineffective with the resources that were provided at that
moment.
d)
- The point H outside the curve shows that it is impossible to produce these amounts
of cars and missiles with the current provided resources.
- Before attaining the point H, more and better inputs or labor resources, higher
technology… must be occurred.
e)
: The original PPF curve
: The PPF curve indicates that there is improvement occurs in the technology of
producing guided missiles but not in the production of cars.
: The PPF curve that reflects technological improvement in the production of both
products.
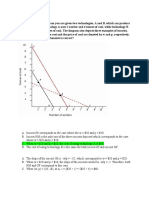
Ex 2:
a)
E
D
b) Productive efficiency: (using the lowest cost production method)
- If the output of wheat and cloth is 9 tons of wheat and 4000 sets of cloth → this
economy is inefficient. The main reason is this point which represents 2 objects (wheat
and cloths) will meet at a point lying inside the production possibility of frontier.
(Besides, we can produce more goods with that amount of input. For example, the
company produces 9 tons of wheat, the clothes they can produce is 9000 set of that or it
4000 set of cloths are created → the most of wheat that can product is 20 tons → this
way is more effective)
c) With a production complex (20,10 ) which represents a point outside the line (PPF)
means the process of production has exceeded allowed economic resources. On the
other hand, if the company produces 20 tons of wheat, the most set of clothes they
can reach is 4000 sets. Therefore, it is impossible to produce 20 tons of wheat and
10000 set of clothes.
d) The opportunity cost of wheat and set of clothes:
- From A-B the opportunity cost of producing 1000 more sets of clothes is 5/4 tons of
wheat.
→ From B-A the opportunity cost of producing 1 more ton of wheat is 4/5
thousand sets of clothes.
- From B to C the opportunity cost of producing 1000 more sets of clothes is 5/3 tons of
wheat.
→From C to B the opportunity cost of producing 1 more tons of wheat is 3/5
thousand set of clothes
- From C to D the opportunity cost of producing 1000 more sets of clothes is 3 tons of
wheat.
→From D to C the opportunity cost of producing 1 more of wheat is 2/6 = 1/3
thousand set of clothes
- From D to E the opportunity cost of producing 1000 more sets of clothes is 9 tons of
wheat.
→From E to D the opportunity cost of producing 1 more ton of wheat is 1/9000
sets of clothes.
You might also like
- Consulting Agreement Fund Raising SampleDocument6 pagesConsulting Agreement Fund Raising Sampleredynsfier91% (11)
- International Relations: A Simple IntroductionFrom EverandInternational Relations: A Simple IntroductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (9)
- Bafb1023 Microeconomics (PPF)Document6 pagesBafb1023 Microeconomics (PPF)Hareen JuniorNo ratings yet
- Budget Cycle Both LGU and National Government AgenciesDocument41 pagesBudget Cycle Both LGU and National Government AgenciesKrizzel Sandoval100% (1)
- Recent Trends in Operations ManagementDocument5 pagesRecent Trends in Operations Managementmechidream100% (12)
- Corporate Social Responsibility A New Way of Doing Business..FINALDocument21 pagesCorporate Social Responsibility A New Way of Doing Business..FINALRavi Gupta100% (1)
- Financial Accounting and Reporting Iii (Reviewer) : Name: Date: Professor: Section: ScoreDocument18 pagesFinancial Accounting and Reporting Iii (Reviewer) : Name: Date: Professor: Section: ScoreAnirban Roy ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Linear Programming: Basic Concepts Solution To Solved ProblemsDocument15 pagesLinear Programming: Basic Concepts Solution To Solved ProblemsVibhuti BatraNo ratings yet
- Indian Coffee House: History and Growth of a Popular Cafe ChainDocument47 pagesIndian Coffee House: History and Growth of a Popular Cafe ChainSalman RazaNo ratings yet
- Production Possibilities Frontier - WorksheetDocument2 pagesProduction Possibilities Frontier - WorksheetMr. Powers100% (2)
- Practical 1Document7 pagesPractical 1s10024426No ratings yet
- Agricultural and Biosystems Engineering Licensure Exam 2021 Recalled QuestionsDocument41 pagesAgricultural and Biosystems Engineering Licensure Exam 2021 Recalled QuestionsJake BalilaNo ratings yet
- Mul 1Document6 pagesMul 1Đan KimNo ratings yet
- Group Assignment Presentation 1Document4 pagesGroup Assignment Presentation 1Liinh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- VI Mô 1Document5 pagesVI Mô 1Nguyen DzungNo ratings yet
- COBU 210 Chapter 2 Review QuestionsDocument6 pagesCOBU 210 Chapter 2 Review QuestionsDemetrius Roach100% (1)
- EconomicsDocument15 pagesEconomicsTahreen HasanNo ratings yet
- Economics Exam MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDocument11 pagesEconomics Exam MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionManal Al-MoatazNo ratings yet
- ECON+2105+Exam+ 1+study+guide Chapters+2-3 Exam+date+02112015Document34 pagesECON+2105+Exam+ 1+study+guide Chapters+2-3 Exam+date+02112015BlackBunny103No ratings yet
- The Economic Problem: 1) The Production Possibilities Frontier Is The Boundary BetweenDocument8 pagesThe Economic Problem: 1) The Production Possibilities Frontier Is The Boundary Betweenhantu hantuNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1: Microeconomics - Group 10Document13 pagesAssignment 1: Microeconomics - Group 10Hải LêNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics Canadian 3rd Edition Krugman Test BankDocument38 pagesMicroeconomics Canadian 3rd Edition Krugman Test Bankjaydenur3jones100% (13)
- Practice Sheet - Production Possibility CurvesDocument16 pagesPractice Sheet - Production Possibility CurvesNahid FaizyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Problem Set 3Document4 pagesChapter 2 Problem Set 3Rayan RabbiNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Macroeconomics 3rd Canadian Edition Paul Krugman Robin Wells Iris Au Jack ParkinsonDocument71 pagesTest Bank For Macroeconomics 3rd Canadian Edition Paul Krugman Robin Wells Iris Au Jack ParkinsonDianeBoyerqmjs100% (38)
- Test 1 2020Document10 pagesTest 1 2020Buyisile NyongwanaNo ratings yet
- Study Guide Ps 01Document10 pagesStudy Guide Ps 01chensikaiNo ratings yet
- Cost Analysis of Cloth Production TechnologiesDocument9 pagesCost Analysis of Cloth Production TechnologiesSiraj AhmadNo ratings yet
- MicroeconomicsDocument19 pagesMicroeconomicsTa Thi Thu VanNo ratings yet
- International trade questionsDocument7 pagesInternational trade questionsNiha KhanNo ratings yet
- Economics 4th Edition Krugman Test Bank DownloadDocument76 pagesEconomics 4th Edition Krugman Test Bank DownloadHarriet Mikels100% (23)
- Exercise 3-12Document44 pagesExercise 3-12api-3769920No ratings yet
- HW1mutiple Choice Solution (A)Document6 pagesHW1mutiple Choice Solution (A)Marc DessauvageNo ratings yet
- Sultan Mahmud: Road To BB Ad 2020Document4 pagesSultan Mahmud: Road To BB Ad 2020TAWHIDNo ratings yet
- Seminar Assignments Multiple Choice Questions Why Do Cities Exist PDFDocument4 pagesSeminar Assignments Multiple Choice Questions Why Do Cities Exist PDFminlwintheinNo ratings yet
- ECON Exercise2Chap02Document5 pagesECON Exercise2Chap02ying huiNo ratings yet
- MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDocument14 pagesMULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The One Alternative That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionTrung Kiên NguyễnNo ratings yet
- The Art of ReviewDocument11 pagesThe Art of ReviewDiamante GomezNo ratings yet
- MUN ECON 1010 Sample Ques CH 01 2020 21fDocument8 pagesMUN ECON 1010 Sample Ques CH 01 2020 21fnotjeremyhallNo ratings yet
- PPC PDFDocument6 pagesPPC PDFSelvaNo ratings yet
- Introduction For EconomicDocument36 pagesIntroduction For Economicsky lewNo ratings yet
- Nanda Mam PPFDocument13 pagesNanda Mam PPFAditya ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- ECON2113 MC PracticeDocument44 pagesECON2113 MC Practicefish LNo ratings yet
- Part A: (See Figure Below.) The Assumptions Are Full Employment, Fixed Supplies ofDocument3 pagesPart A: (See Figure Below.) The Assumptions Are Full Employment, Fixed Supplies ofDESI BillNo ratings yet
- 2013 Trade Mid Term 1Document5 pages2013 Trade Mid Term 1rkqls3286663No ratings yet
- Understanding opportunity cost and production possibility frontierDocument3 pagesUnderstanding opportunity cost and production possibility frontierAbrar FaiyazNo ratings yet
- Cma-Fdn LT P4-Economics We-4 QP1 KeyDocument3 pagesCma-Fdn LT P4-Economics We-4 QP1 KeyDhruv AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Economicsproject 180215173919Document28 pagesEconomicsproject 180215173919Bhavya GoelNo ratings yet
- Assignment GroupDocument12 pagesAssignment GroupFadzli YusofNo ratings yet
- Yanata Reylend CA1 ASSIGNMENTDocument7 pagesYanata Reylend CA1 ASSIGNMENTReylend YanataNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument24 pagesDocumentCeline YoonNo ratings yet
- For Revision Multiple Choice Question PPFDocument7 pagesFor Revision Multiple Choice Question PPFbkjanetNo ratings yet
- ERU 2.1 Z01 Soluciones OSullivan Cap 2Document3 pagesERU 2.1 Z01 Soluciones OSullivan Cap 2Lautaro De LaurentiisNo ratings yet
- Practice Set 4 DEM GSCM 2022Document6 pagesPractice Set 4 DEM GSCM 2022Romit BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Economics 1A Revison Unit 1 Unit 9Document7 pagesEconomics 1A Revison Unit 1 Unit 9Tman LetswaloNo ratings yet
- The Transportation Model - FormulationsDocument26 pagesThe Transportation Model - FormulationsPotnuru VinayNo ratings yet
- Mixed-Integer Optimization Problems Formulated and SolvedDocument5 pagesMixed-Integer Optimization Problems Formulated and SolvedMacarena González GuerreroNo ratings yet
- ECON1054 Chapter 1 Practice MCQsDocument10 pagesECON1054 Chapter 1 Practice MCQslamx100% (1)
- Chapter 2 Test BankDocument18 pagesChapter 2 Test Bankhesham50ahmed2001No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Why Do Cities ExistDocument6 pagesChapter 2 Why Do Cities ExistMoayed Mohamed100% (2)
- Section 1 - MicroeconomicsDocument6 pagesSection 1 - MicroeconomicsUyên TrầnNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Two-1Document9 pagesTutorial Two-1Gift MoyoNo ratings yet
- EMGT 501 HW Solutions Linear Programming ProblemsDocument12 pagesEMGT 501 HW Solutions Linear Programming Problemsroberto tumbacoNo ratings yet
- Ch2 HandoutsDocument13 pagesCh2 HandoutsFernando FlorinioNo ratings yet
- Modern Cotton Spinning Machinery, Its Principles and ConstructionFrom EverandModern Cotton Spinning Machinery, Its Principles and ConstructionNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4Document21 pagesLesson 4Đoàn Ngọc DũngNo ratings yet
- Consumer Promotions Event Time Type (p3, Last Paragraph) CostDocument8 pagesConsumer Promotions Event Time Type (p3, Last Paragraph) CostDuyên NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Maruti Suzuki Internship ReportDocument19 pagesMaruti Suzuki Internship ReportShashikant kumar 21ME15No ratings yet
- TG Calling Data Excel FileDocument6 pagesTG Calling Data Excel FileVISHAL WARULENo ratings yet
- Sony and Zee Ink Merger DealDocument2 pagesSony and Zee Ink Merger DealMr PicaedNo ratings yet
- Nakama Special PolvoronDocument9 pagesNakama Special PolvoronAlmayda AndrewNo ratings yet
- 2021 Directory of Full Professors in The Nigerian University System FINALDocument978 pages2021 Directory of Full Professors in The Nigerian University System FINALnicodemus.usehNo ratings yet
- HidadfrDocument55 pagesHidadfrArvind JSNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 The Nineteenth Century Philippine Economy Society and The Chinese MestizosDocument27 pagesChapter 5 The Nineteenth Century Philippine Economy Society and The Chinese MestizosJuMakMat Mac50% (2)
- The Impact of COVID-19 in The Construction Sector and Its Remedial MeasuresDocument12 pagesThe Impact of COVID-19 in The Construction Sector and Its Remedial MeasuresdamithNo ratings yet
- Graham Mayor: Word Variables, Properties and Content Controls and Bookmarks Editor Add-In For Word 2007/2010/2013Document11 pagesGraham Mayor: Word Variables, Properties and Content Controls and Bookmarks Editor Add-In For Word 2007/2010/2013Sumith VkNo ratings yet
- New Tablet Menu Project CharterDocument3 pagesNew Tablet Menu Project CharterBasit Ali QureshiNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation Group - 10 Company's Overview Growth StrategyDocument6 pagesCase Presentation Group - 10 Company's Overview Growth StrategyMaan MehtaNo ratings yet
- Letter of Enquiry and Response EditedDocument5 pagesLetter of Enquiry and Response EditedMugdhaNo ratings yet
- Nmims Interview FinalDocument6 pagesNmims Interview FinalYagyansh KapoorNo ratings yet
- Slice N' Craft Marketing PlanDocument10 pagesSlice N' Craft Marketing PlanMaria Gella PerezNo ratings yet
- ATS9900 V100R006C00 Feature List FTDocument14 pagesATS9900 V100R006C00 Feature List FTaranibarmNo ratings yet
- Bobble.AI Internship Offer LetterDocument3 pagesBobble.AI Internship Offer LetterNilesh Sukhdeve IINo ratings yet
- Bussiness Ethics Responsibility of StakeholdersDocument34 pagesBussiness Ethics Responsibility of StakeholdersNalin GuptaNo ratings yet
- Role Soft Switch in NGNDocument6 pagesRole Soft Switch in NGNHung Nguyen HuyNo ratings yet
- Ashley Brockhausen: EducationDocument1 pageAshley Brockhausen: Educationapi-432823755No ratings yet
- PressRelease-Project Nickel 20220405Document3 pagesPressRelease-Project Nickel 20220405Rama Usaha MandiriNo ratings yet
- CV Firli - Application Letter 2017 - PT - Nana Yamano TeknikDocument5 pagesCV Firli - Application Letter 2017 - PT - Nana Yamano TeknikBambang PermanaNo ratings yet
- Mode of Expression: Chabahar Port, IranDocument16 pagesMode of Expression: Chabahar Port, IranUmair MumtazNo ratings yet