Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Microscope Parts and Function
Uploaded by
Rianne Denise Hernandez0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageThe document summarizes the key parts of a compound microscope and their functions:
1) The stage holds the specimen and is where observation takes place.
2) Objective lenses, which are attached to the nosepiece, provide different levels of magnification when combined with the eyepiece magnification.
3) Other important parts include the eyepiece for viewing, illuminator for lighting, diaphragm for adjusting light, and coarse and fine focus knobs for adjusting the specimen view.
Original Description:
.
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes the key parts of a compound microscope and their functions:
1) The stage holds the specimen and is where observation takes place.
2) Objective lenses, which are attached to the nosepiece, provide different levels of magnification when combined with the eyepiece magnification.
3) Other important parts include the eyepiece for viewing, illuminator for lighting, diaphragm for adjusting light, and coarse and fine focus knobs for adjusting the specimen view.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageMicroscope Parts and Function
Uploaded by
Rianne Denise HernandezThe document summarizes the key parts of a compound microscope and their functions:
1) The stage holds the specimen and is where observation takes place.
2) Objective lenses, which are attached to the nosepiece, provide different levels of magnification when combined with the eyepiece magnification.
3) Other important parts include the eyepiece for viewing, illuminator for lighting, diaphragm for adjusting light, and coarse and fine focus knobs for adjusting the specimen view.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
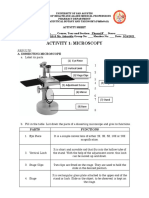
Function of each Microscope Part The stage is where the specimen is placed.
1. Eyepiece or Ocular Lens This place is for observation.
Eyepiece lens magnifies the image of the
specimen. This part is also known 7. Stage Clips
as ocular. Most school microscopes have an Stage clips are the supports that hold the slides
eyepiece with 10X magnification. in place on the stage.
2. Eyepiece Tube or Body Tube 8. Diaphragm (sometimes called the Iris)
The tube hold the eyepiece. The diaphragm controls the amount of light
passing through the slide. It is located below
3. Nosepiece the stage and is usually controlled by a round
Nosepiece holds the objective lenses and is dial. How to set the diaphragm is determined
sometimes called a revolving turret. You by the magnification, transparency of the
choose the objective lens by rotating to the specimen and the degree of contrast you wish
specific lens one you want to use. to have in your image. Also called the
condenser diaphragm.
4. Objective Lenses
Most compound microscopes come with 9. Illuminator
three or four objective lenses that revolve on Most light microscopes use a low voltage bulb
the nosepiece. The most common objective which supplies light through the stage and
lenses have power of 4X, 10X and 40X. onto to the specimen. Mirrors are sometimes
Combined with the magnification of the used instead of a built-in light. If your
eyepiece the resulting magnification is 40X, microscope has a mirror, it provides light
100X and 400X magnification. Total reflected from ambient light sources like
magnification is calculated by multiplying the classroom lights or sunlight if outdoors.
power of the eyepiece by the power of the
objective lens. (10X Eyepiece X 40X 10. Coarse focus
Objective = 400X Total Magnification) Some Coarse focus moves the stage to provide
more advanced microscopes have an general focus on the specimen. When
additional objective lens with 100X power. bringing a specimen into focus, the course
This results in 1,000X magnification. So dial is the first one used.
where do you start? Which objective lens do
11. Fine focus
you need for a particular task? See “How to
Fine focus moves the stage in smaller
Use a Compound Microscope” below.
increments to provide a clear view of the
5. Arm specimen. When bringing a specimen into
The Arm connects the base to the nosepiece and focus, the fine focus dial is the second one
eyepiece. It is the structural part that is also used.
used to carry the microscope.
12. Base
6. Stage The base is the main support of the
microscope. The bottom, where all the other
parts of the microscope stand.
You might also like
- Parasitology Practical HandbookDocument41 pagesParasitology Practical Handbookmaximazarov100% (1)
- ICC Yard - Rathmalana-Model PDFDocument1 pageICC Yard - Rathmalana-Model PDFsajeevi piumikaNo ratings yet
- MicrosDocument4 pagesMicrosShania Guillermo GallardoNo ratings yet
- Microscopy Task A. Draw The Following: Hay Infusion (LPO and HPO)Document5 pagesMicroscopy Task A. Draw The Following: Hay Infusion (LPO and HPO)JASMIN DAMIANNo ratings yet
- Solar PV 2Document18 pagesSolar PV 2nas SNo ratings yet
- Thin-Film Solar CellDocument72 pagesThin-Film Solar CellPraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Biology (Reviewer)Document4 pagesBiology (Reviewer)Claire SerafinNo ratings yet
- MICROSCOPE NOTES - 2018 by LN PDFDocument7 pagesMICROSCOPE NOTES - 2018 by LN PDFLuyando NzalaNo ratings yet
- PhotovoltaicsDocument7 pagesPhotovoltaicsfaraz81No ratings yet
- Buying Your First Telescope PDFDocument14 pagesBuying Your First Telescope PDFTomás RamosNo ratings yet
- SLM Number 2-Grade 7 Science 2nd Quarter-Wet Mount, Focusing and MagnificationDocument20 pagesSLM Number 2-Grade 7 Science 2nd Quarter-Wet Mount, Focusing and MagnificationMaria Fe Vibar100% (3)
- Chem Ass FinalDocument3 pagesChem Ass FinalML GamingNo ratings yet
- Function of Each Microscope PartDocument6 pagesFunction of Each Microscope PartDavid W ReynosoNo ratings yet
- Science7 Q2Document47 pagesScience7 Q2Kc CaymeNo ratings yet
- Compound Light MicroscopeDocument2 pagesCompound Light MicroscopeCIANO, Dellaney Joy A.No ratings yet
- 1 MicrosDocument7 pages1 MicrosJachelle KateNo ratings yet
- Biology Lab Activity 1Document6 pagesBiology Lab Activity 1Adrian Anthony Villaluz GasatayaNo ratings yet
- Specimen: Compound MicroscopeDocument7 pagesSpecimen: Compound MicroscopeAres WellsNo ratings yet
- MOd 1Document2 pagesMOd 1A. MagnoNo ratings yet
- Parts of The Microscope Microscope Part Function Structural Parts of A MicroscopeDocument6 pagesParts of The Microscope Microscope Part Function Structural Parts of A Microscopelarry machonNo ratings yet
- Biochem No. 1Document7 pagesBiochem No. 1Allesa San JoseNo ratings yet
- MicroscopeDocument8 pagesMicroscopeamanda_orbe8504No ratings yet
- Data Sheet Exercise 1 The MicroscopeDocument7 pagesData Sheet Exercise 1 The MicroscopeSohail SaripadaNo ratings yet
- Forensic Chemistry ActivityDocument22 pagesForensic Chemistry ActivityStefanie Puguon Nipahoy100% (1)
- Activity No. 2 The Microscope: Term FunctionDocument5 pagesActivity No. 2 The Microscope: Term FunctionUNSA MANENo ratings yet
- Science 7 q2 m1 - PDF FILEDocument6 pagesScience 7 q2 m1 - PDF FILEEzzel Jan FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Microscope Parts and FunctionsDocument4 pagesMicroscope Parts and FunctionsChris ChanNo ratings yet
- Microscopy Notes and ActivityDocument4 pagesMicroscopy Notes and ActivityMpilwenhle KuneneNo ratings yet
- PareDocument7 pagesPareEloisa LacanilaoNo ratings yet
- Science 7 ScriptDocument3 pagesScience 7 Scriptangeline vacalaresNo ratings yet
- The MicroscopeDocument6 pagesThe MicroscopejustRizzeNo ratings yet
- Ph1F1 PhBioSci1a Activity1 Individual GloriaDocument8 pagesPh1F1 PhBioSci1a Activity1 Individual GloriaAllysa GloriaNo ratings yet
- Science Process Skills - MicroscopeDocument2 pagesScience Process Skills - MicroscopeCharina May Lagunde-SabadoNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Explain Arial 11Document2 pagesModule 2 Explain Arial 11eryan binsentNo ratings yet
- Activity 1A MicroscopeDocument4 pagesActivity 1A MicroscopeClarito ManaayNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - MicroscopeDocument4 pagesModule 1 - MicroscopeGoogle BackupNo ratings yet
- I. Microscope Parts and FunctionsDocument1 pageI. Microscope Parts and FunctionsRowie WanawanNo ratings yet
- Instruction: Using The Video On Microscope Working in AnimationDocument3 pagesInstruction: Using The Video On Microscope Working in AnimationCyndel TindoyNo ratings yet
- The Compound Light MicroscopeDocument2 pagesThe Compound Light MicroscopeIsabela MartinezNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 1 The Use and Care of The MicroscopeDocument7 pagesActivity No. 1 The Use and Care of The MicroscopeRheal P EsmailNo ratings yet
- Parts of Microscope and Their FunctionsDocument3 pagesParts of Microscope and Their FunctionsAlfina SafiraNo ratings yet
- Parts of A MicroscopeDocument3 pagesParts of A Microscopeazaanhasnat345No ratings yet
- Microlab Activity 2 The Microscopes - DHAWELL ANN F. CARPIODocument6 pagesMicrolab Activity 2 The Microscopes - DHAWELL ANN F. CARPIODhawell AnnNo ratings yet
- Micp Lab Act # 01 MicrosDocument6 pagesMicp Lab Act # 01 MicrosEdel GapasinNo ratings yet
- Microscope DefinitionsDocument3 pagesMicroscope DefinitionsJessica ThomasNo ratings yet
- Microscope Overview PDFDocument10 pagesMicroscope Overview PDFMIKAELA TINGNo ratings yet
- MicroscopeDocument3 pagesMicroscopeJannette Jane DavidNo ratings yet
- CMB Laboratory Activity 3 BORJA JAYVEN CDocument5 pagesCMB Laboratory Activity 3 BORJA JAYVEN CJboar TbenecdiNo ratings yet
- Compound MicroscopeDocument2 pagesCompound MicroscopeditucalanshanmichaelvNo ratings yet
- Q2 W2Document2 pagesQ2 W2B20Taroy, Miguel BernarteNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 - MicroscopeDocument4 pagesActivity 1 - MicroscopeYousra Mae CadienteNo ratings yet
- PMLS 2 MicrosDocument2 pagesPMLS 2 MicrosYlyza MarquezNo ratings yet
- Microscopically DetailsDocument6 pagesMicroscopically DetailsAnonymous TCbZigVqNo ratings yet
- Demonstration of Microscope and Its PartsDocument5 pagesDemonstration of Microscope and Its PartsSujoy Tontubay100% (1)
- Zoology LaboratoryDocument11 pagesZoology LaboratoryGIDEON MARK ABEJO RABINo ratings yet
- How To Use A Light MicroscopeDocument4 pagesHow To Use A Light MicroscopebasondesaNo ratings yet
- MicroPara Lab Activity 2Document5 pagesMicroPara Lab Activity 2BernardMarkMateoNo ratings yet
- Microscopy ManualDocument11 pagesMicroscopy ManualozlemNo ratings yet
- Microscope Usage and Handling Procedures: A. IntroductionDocument5 pagesMicroscope Usage and Handling Procedures: A. Introductiongrafei pennaNo ratings yet
- CASNS 1a Laboratory - Module 1Document12 pagesCASNS 1a Laboratory - Module 1Maxi VellasNo ratings yet
- Detailed Explanation of MicroscopeDocument3 pagesDetailed Explanation of MicroscopestsrinidiNo ratings yet
- Detailed Explanation of MicroscopeDocument3 pagesDetailed Explanation of MicroscopestsrinidiNo ratings yet
- 1 MicroscopeDocument3 pages1 MicroscopeMary Jane TiangsonNo ratings yet
- The MicroscopeDocument4 pagesThe MicroscopeRyz DoctoraNo ratings yet
- Weg Industries (India) Pvt. Ltd. - Physical Layout-1.5mwDocument1 pageWeg Industries (India) Pvt. Ltd. - Physical Layout-1.5mwDIVAKARNo ratings yet
- Zeiss OPMI LUMERA 300 Surgical MicroscopeDocument2 pagesZeiss OPMI LUMERA 300 Surgical Microscopedavood salkhordehNo ratings yet
- GE Fluorescent Lamps Types & Sizes Overview 1-64Document4 pagesGE Fluorescent Lamps Types & Sizes Overview 1-64Alan MastersNo ratings yet
- Title Card: Lesson 12: Mirror Images Are Laterally InvertedDocument16 pagesTitle Card: Lesson 12: Mirror Images Are Laterally InvertedNathan Francis Enzo NicolasNo ratings yet
- Specxyfy Blog 3Document2 pagesSpecxyfy Blog 3NishantNo ratings yet
- 2 - Low Intensity Discharge Lamps Part 3Document41 pages2 - Low Intensity Discharge Lamps Part 3Miko F. RodriguezNo ratings yet
- NSIT Solar Car Brochure 2013-14Document13 pagesNSIT Solar Car Brochure 2013-14Videt JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Draft Explanatory Memorandum Solar Power ProjectsDocument16 pagesDraft Explanatory Memorandum Solar Power ProjectsPushkar ShahNo ratings yet
- Syska Led Price List RLP Jan 23Document4 pagesSyska Led Price List RLP Jan 23e98210659fe209100% (1)
- LUMsearch CMd0QYrTSxy0JgNs7F5Upg PDFDocument1 pageLUMsearch CMd0QYrTSxy0JgNs7F5Upg PDFAlberto Ordoñez TrujilloNo ratings yet
- The Maksutov Revolution: Equipment RoundupDocument5 pagesThe Maksutov Revolution: Equipment RoundupLeonardo ColomboNo ratings yet
- Glass Manufacturing Process and Application of Glass (1) - 1Document21 pagesGlass Manufacturing Process and Application of Glass (1) - 1Ved PatelNo ratings yet
- Uno MindaDocument3 pagesUno MindaRohit JindalNo ratings yet
- Vandal VNR11Document1 pageVandal VNR11EliasNo ratings yet
- Boq 20KW Panel 24KW Hybrid Inv 3PH With MeteringDocument10 pagesBoq 20KW Panel 24KW Hybrid Inv 3PH With MeteringOrly, Jr. PalomarNo ratings yet
- Ezgi Bengü Durak - Miraç Daşkin - Semiramis Oğuz - Elif ŞenyuvaDocument21 pagesEzgi Bengü Durak - Miraç Daşkin - Semiramis Oğuz - Elif ŞenyuvaSơnNo ratings yet
- Bushnell's Tac Optics Lil P (Rism) 1x Prism SightDocument4 pagesBushnell's Tac Optics Lil P (Rism) 1x Prism SightTwobirds Flying PublicationsNo ratings yet
- MS 360-380Wp 9BB 166 PERC 120cells Mono Solar Panel SpecificationDocument2 pagesMS 360-380Wp 9BB 166 PERC 120cells Mono Solar Panel SpecificationZsolt SzabóNo ratings yet
- 520Document2 pages520Hugo BossNo ratings yet
- Ray OpticsDocument6 pagesRay OpticsshardaviharphysicsNo ratings yet
- AE Solar SpécificationsDocument2 pagesAE Solar SpécificationsBoudaouara Med ChafikNo ratings yet
- MT8Document2 pagesMT8fahsaiiNo ratings yet
- Lighting: Interior Design by John F. PileDocument22 pagesLighting: Interior Design by John F. PileBhuvanaNo ratings yet
- Royal Arts Complex: Stage 3B - Design DevelopmentDocument1 pageRoyal Arts Complex: Stage 3B - Design DevelopmentDan SarmientoNo ratings yet