Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bme2 Week12 Ollinas, Catherine
Uploaded by
Ollinas, Catherine0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesInterrelationship between formulation and implementation of strategies,
Original Title
BME2-WEEK12-OLLINAS,CATHERINE
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentInterrelationship between formulation and implementation of strategies,
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesBme2 Week12 Ollinas, Catherine
Uploaded by
Ollinas, CatherineInterrelationship between formulation and implementation of strategies,
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Catherine D.
Ollinas BME 2 FSA (2:30-4:00 PM)
BSHM – 4A Prof. Anna C. Del Rosario
WEEK 12 - MODULE
INTERRELATIONSHIP BETWEEN FORMULATION AND
IMPLEMENTATION OF STRATEGIES
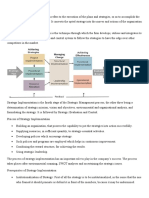
The interrelationship between the formulation and implementation of strategies is a
fundamental concept in the field of strategic management. It emphasizes that the process of
developing and executing strategies is not linear but rather a dynamic and iterative one. The
formulation of a strategy and its subsequent implementation are deeply interconnected and
mutually influence each other. Here's how these two aspects are interrelated:
1. Strategy Formulation Informs Implementation:
• Formulation is the initial step where an organization defines its mission, sets
objectives, and formulates strategies to achieve those objectives.
• The strategies developed during the formulation phase provide a roadmap and a clear
direction for the organization. They serve as a guide for decision-making and resource
allocation during implementation.
2. Alignment and Consistency:
• Successful implementation relies on the alignment of actions with the formulated
strategies. If there is a misalignment, it can lead to confusion and ineffective
execution.
• The formulation phase ensures that strategies are consistent with the organization's
goals, capabilities, and the external environment. This alignment is crucial for
successful implementation.
3. Adaptation and Flexibility:
• As strategies are implemented, organizations often encounter unexpected challenges,
changes in the external environment, or internal limitations. In such cases, the
formulation-implementation interrelationship becomes evident.
• Organizations may need to adapt or adjust their strategies during implementation to
address new information or changing circumstances. This requires a feedback loop
between the two phases.
4. Resource Allocation and Budgeting:
• Implementation involves allocating resources, both human and financial, to specific
projects or initiatives. The resources allocated during implementation must align with
the budget and resource allocation decisions made during formulation.
• If the organization formulates ambitious strategies but fails to allocate adequate
resources for their execution, the implementation is likely to fall short.
5. Monitoring and Control:
• The implementation phase involves continuous monitoring and control to ensure that
the strategies are on track and are producing the desired outcomes.
• The feedback from the implementation phase can inform adjustments in the
formulation phase. If a particular strategy is consistently underperforming, it may
require a revision in the formulation of the strategy.
6. Learning and Improvement:
• The interrelationship between formulation and implementation allows for
organizational learning. Successes and failures during implementation provide
valuable insights that can be used to refine future strategy formulation.
• Organizations can apply lessons learned to improve their strategic planning processes.
7. Communication and Organizational Buy-In:
• Effective communication of the formulated strategy to all levels of the organization is
crucial for successful implementation.
• The formulation phase sets the stage for communicating the strategy's goals,
rationale, and expected outcomes, which can influence the degree of buy-in and
commitment from employees.
You might also like
- Chapter 3 - Strategy ImplementationDocument6 pagesChapter 3 - Strategy Implementationjalaja munirajuNo ratings yet
- MODULE - 4 Strategy ImplementationDocument41 pagesMODULE - 4 Strategy ImplementationRintu RajeshNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management - 4Document30 pagesStrategic Management - 4Pallavi.G.P. pallaviNo ratings yet
- Module2notes - Planning Pharmacy OperationsDocument7 pagesModule2notes - Planning Pharmacy OperationsAaliyah NebresNo ratings yet
- Aspects of Strategy Implementation:-The Different Aspects Involved in Strategy Implementation Cover Practically Everything That IsDocument11 pagesAspects of Strategy Implementation:-The Different Aspects Involved in Strategy Implementation Cover Practically Everything That IsDhiraj Kumar SarafNo ratings yet
- Planning-Engineering-Management For PostingDocument23 pagesPlanning-Engineering-Management For PostingChristian J SebellinoNo ratings yet
- Importance of Organizational Structures To Strategic ImplementationDocument6 pagesImportance of Organizational Structures To Strategic ImplementationShashank Dohrey100% (2)
- Strategic ImplementationDocument14 pagesStrategic Implementationharshit8bp19No ratings yet
- Assignment On Strategy ImplementationDocument20 pagesAssignment On Strategy ImplementationGeetinder Singh100% (2)
- Eng Managemet - Ass 2Document4 pagesEng Managemet - Ass 2pollypew333No ratings yet
- Strategic Mangement 4Document45 pagesStrategic Mangement 4kritikachhapolia100% (1)
- Management AssignmentDocument5 pagesManagement AssignmentSohil VhoraNo ratings yet
- Concept of Obj., Mission & VisionDocument18 pagesConcept of Obj., Mission & VisionPadmini KandulaNo ratings yet
- Management 9th Edition Daft Solutions Manual DownloadDocument15 pagesManagement 9th Edition Daft Solutions Manual DownloadGloria Jones100% (18)
- Unit 5 Final Business Research MethodDocument22 pagesUnit 5 Final Business Research MethodAccurate Health Care CenterNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 SummaryDocument3 pagesChapter 8 SummaryMinh AnhNo ratings yet
- Strategy Implementation & ControlDocument71 pagesStrategy Implementation & ControlPriyesh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Strategy ImplementationDocument12 pagesStrategy ImplementationGracey KinimoNo ratings yet
- Types of BudgetDocument13 pagesTypes of Budgetmustefa ademNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management 4 TH ModDocument10 pagesStrategic Management 4 TH ModShiju ShajiNo ratings yet
- Uc2 For Level IVDocument12 pagesUc2 For Level IVGizaw TadesseNo ratings yet
- Principles of Planning BootcampDocument25 pagesPrinciples of Planning BootcampmominNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document41 pagesChapter 5AgatNo ratings yet
- Bryson Chapter 10 Implementing Strategies and Plans SuccessfullyDocument13 pagesBryson Chapter 10 Implementing Strategies and Plans Successfullyමිලන්100% (1)
- Implementing Strategies: Management and Operations Issues: Key PointsDocument11 pagesImplementing Strategies: Management and Operations Issues: Key Pointskhurram. khurshidNo ratings yet
- SBADocument4 pagesSBAJoanah TayamenNo ratings yet
- Strategy Implementation - ClassDocument56 pagesStrategy Implementation - ClassM ManjunathNo ratings yet
- Subject: Strategic Management: Submitted To: Submitted byDocument30 pagesSubject: Strategic Management: Submitted To: Submitted byAbhi ShriNo ratings yet
- Strategy Implementation and ControlDocument71 pagesStrategy Implementation and Controlmilee0005100% (1)
- Chapter-8 Strategic Implementation and Control: Si No ParticularsDocument20 pagesChapter-8 Strategic Implementation and Control: Si No ParticularsakashNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document9 pagesChapter 6Fisseha KebedeNo ratings yet
- 1 3 7-RevisionDocument38 pages1 3 7-RevisionPrashantNo ratings yet
- SM Strategy ImplementationDocument7 pagesSM Strategy ImplementationHafiz DanialNo ratings yet
- Strategy ImplementationDocument5 pagesStrategy ImplementationOneof TNNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management Individual Assignment of Berhe Teklehaymanot Section DDocument11 pagesStrategic Management Individual Assignment of Berhe Teklehaymanot Section DAwetahegn HagosNo ratings yet
- DuduDocument25 pagesDuduCatherine SayolangangtinginNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 Strategy Implementation and Organisational Culture, Leadership and RewardsDocument12 pagesTopic 6 Strategy Implementation and Organisational Culture, Leadership and Rewardsfrancis MagobaNo ratings yet
- BPSMDocument28 pagesBPSMBasudev SahooNo ratings yet
- Strategic Planning Process: Steps in Developing Strategic Plans I. Strategic Planning Process DefinedDocument22 pagesStrategic Planning Process: Steps in Developing Strategic Plans I. Strategic Planning Process Definednavinm87No ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Planning1Document71 pagesLecture 4 Planning1Mark Paul Marquez IINo ratings yet
- Strategy Implementation AssignmentDocument4 pagesStrategy Implementation AssignmentHafiz DanialNo ratings yet
- Strategy Implementation: UNIT-4Document19 pagesStrategy Implementation: UNIT-4VIVEK KUMAR SINGH 13No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3-5 MGT (1) .OdtDocument38 pagesCHAPTER 3-5 MGT (1) .OdtBehailu TejeNo ratings yet
- Management Asia Pacific 5th Edition Samson Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument42 pagesManagement Asia Pacific 5th Edition Samson Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFirisdavid3n8lg100% (12)
- A Systematic Approach To Organizational DevelopmentDocument2 pagesA Systematic Approach To Organizational DevelopmentMUHAMMAD KALEEMNo ratings yet
- Management Asia Pacific 5th Edition Samson Solutions ManualDocument21 pagesManagement Asia Pacific 5th Edition Samson Solutions Manualcamamabeljnk9100% (21)
- Policy and Strategy FormulationDocument12 pagesPolicy and Strategy FormulationRahul BaruahNo ratings yet
- Strategy ImplementationDocument6 pagesStrategy Implementationswatisingla786No ratings yet
- The Nature of Strategy ImplementationDocument3 pagesThe Nature of Strategy ImplementationDusty Rose100% (4)
- Chapter 2 Managerial EconomicsDocument10 pagesChapter 2 Managerial EconomicsMaye PilapilNo ratings yet
- Planning 1Document8 pagesPlanning 1Mwangy PinchezNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management - 3Document12 pagesStrategic Management - 3Helen FernandesNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes Topic 1Document5 pagesLecture Notes Topic 1Lawrence PascualNo ratings yet
- 7 Process of Strategic ManagementDocument3 pages7 Process of Strategic ManagementOkorafor ChikezirimNo ratings yet
- Strategy Implementation: UNIT-4Document19 pagesStrategy Implementation: UNIT-4VIVEK KUMAR SINGH 13No ratings yet
- Strategic Implementation, Evaluation and ControllingDocument14 pagesStrategic Implementation, Evaluation and ControllingtatekNo ratings yet
- Module 7 HandoutsDocument4 pagesModule 7 HandoutsvivianNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Planning: CorollaryDocument28 pagesUnit 2 Planning: CorollaryransdkasjNo ratings yet
- REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE FTF LearningDocument6 pagesREVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE FTF LearningHuolynehb TiagoNo ratings yet
- Asch 1951 Jenness 1932 Sheriff 1936Document1 pageAsch 1951 Jenness 1932 Sheriff 1936FolorunshoEmNo ratings yet
- Wiley - Calculus - Single and Multivariable, 2nd Edition - 978-0-470-45360-5Document3 pagesWiley - Calculus - Single and Multivariable, 2nd Edition - 978-0-470-45360-5Omar Al-MoughrabiNo ratings yet
- Time, Temporality, and History in Process Organization StudiesDocument324 pagesTime, Temporality, and History in Process Organization StudiesGust100% (1)
- Pentaksiran Autentik 2020Document12 pagesPentaksiran Autentik 2020azriNo ratings yet
- Theories of Management - PPTDocument31 pagesTheories of Management - PPTJoy Paloma100% (1)
- 10 - Constructivism and Conflict ResolutionDocument20 pages10 - Constructivism and Conflict Resolutionimam100% (1)
- Course Outline - Cognitive PsychDocument4 pagesCourse Outline - Cognitive PsychJeng Mun SamNo ratings yet
- ResearchDocument26 pagesResearchmarian alamagNo ratings yet
- MY Significant ExperiencesDocument8 pagesMY Significant ExperiencesJennelyn DuranNo ratings yet
- Roblem ET: Deadline: 09/09/2020 at Midnight (COT)Document4 pagesRoblem ET: Deadline: 09/09/2020 at Midnight (COT)Alexa Contreras CristanchoNo ratings yet
- Chazan2022 PrinciplesAndPedagogiesInJewisDocument103 pagesChazan2022 PrinciplesAndPedagogiesInJewisDanna GilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document58 pagesChapter 3david AbotsitseNo ratings yet
- Budgeted Lesson/Topic Allocation Curriculum AuditDocument4 pagesBudgeted Lesson/Topic Allocation Curriculum AuditAgnes RamoNo ratings yet
- Deped Order 36Document22 pagesDeped Order 36Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- Finals Reviewer Reading and WritingDocument73 pagesFinals Reviewer Reading and WritingGemmadel Galang DuaquiNo ratings yet
- Perfeval Prob 6MO PDFDocument2 pagesPerfeval Prob 6MO PDFAnonymous KwzVdSVOILNo ratings yet
- Viewing ComprehensionDocument15 pagesViewing ComprehensionQuemmy AyingNo ratings yet
- 518022A - 1391 - Phase 4 - Juan David Peraza BuitragoDocument5 pages518022A - 1391 - Phase 4 - Juan David Peraza BuitragoJuan David Peraza BuitragoNo ratings yet
- UNITDocument1 pageUNITsaritalodhi636No ratings yet
- Lecturer: MR Abd Razak: Circle The Correct Answer For The Following StatementsDocument4 pagesLecturer: MR Abd Razak: Circle The Correct Answer For The Following Statementssarah sharilNo ratings yet
- Edwin Guthrie Contiguity Theory and One Trial LearningDocument3 pagesEdwin Guthrie Contiguity Theory and One Trial Learningjuan JNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 - Context of Con Art - Lesson SummaryDocument22 pagesCHAPTER 2 - Context of Con Art - Lesson SummaryCherrymae GeraldezNo ratings yet
- CPU's & GenderDocument1 pageCPU's & GenderJohn R. Adler100% (11)
- SHRM BoCK-2016Document52 pagesSHRM BoCK-2016duediligence365No ratings yet
- Spatial Perspective in The United StatesDocument7 pagesSpatial Perspective in The United Statesapi-251996345No ratings yet
- Whay Do We Mean by Reading Readines 21.47.19Document2 pagesWhay Do We Mean by Reading Readines 21.47.19Andrea Josefa SotoNo ratings yet
- DLP 2 (Grade10) TTDocument3 pagesDLP 2 (Grade10) TTGunther Pedrano RosimaNo ratings yet
- Radically Open Dialectical Therapy Ro DBT 323Document213 pagesRadically Open Dialectical Therapy Ro DBT 323yeet masterNo ratings yet
- Alpabeto Diksyunaryo FinalDocument12 pagesAlpabeto Diksyunaryo FinalLadymae Barneso SamalNo ratings yet