Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ge Elec M3
Uploaded by
Lorenz Vicente0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views3 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views3 pagesGe Elec M3
Uploaded by
Lorenz VicenteCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
LESSON 3:
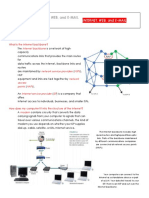
THE INTERNET AND WORLD WIDE WEB THE INTERNET
Who Uses the Internet?
THE INTERNET Teachers and Students at Universities,
THE INTERNET is defined as a Community Colleges.
worldwide network connecting to a Professors and Research at Universities
million of computers via dedicated and in Research Division
routers and servers. It is a network of Corporation
networks that consist of private, public, Professionals in Businesses Large and
academic, business and government Small.
networks of local to global scope, linked State and Local Government Officials
by a broad array of electronic, wireless, Reporters
and optical network technologies. Celebrities
The INTERNET, also called the Net, is a
worldwide collection of networks that What Things Can Do on The Internet?
links millions of businesses, Conduct Collaborative Research
government agencies, educational Conduct Free Telephone Calls
institutions, and individuals. Visit many major Museums and
The INTERNET has its roots in Galleries Worldwide
ARPANET, a network started in 1969 to Provide a Forum for Exchanging
link scientific and academic researchers Opinions and Information
across the United States. In 1986, the Send and Receive Messages and
National Science Foundation connected Documents around the world at low or
its huge network, called NSFnet, to no cost.
ARPANET, creating a configuration of
complex networks and hosts that
became known as the Internet. Today, TYPES OF INTERNET CONNECTION
more than 550 million host computers DIAL-UP
connect to the Internet. access is cheap but slow. A modem
(internal or external) connects to the
internet after the computer dials a
HISTORY OF THE INTERNET phone number.
THE HISTORY OF THE INTERNET
begins with the development of DSL (Digital Subscriber Line)
electronic computers in the 1950’s. It is an Internet connection that is
Initial concepts of wide area networking always “on”. DSL uses a router to
originated in several computer science transport data and the range of
laboratories in the United States, United connection speed, depending on the
Kingdom, and France. service offered.
Before it became known as the Internet,
ARPANET (Advanced Research Projects SATELLITE
Agency Network) served universities, accesses the internet via a satellite in
defense contractors, and a few Earth’s orbit. The enormous distance
government agencies. ARPANET initially that a signal travels from earth to
served as a backbone for satellite and back again, provides a
interconnection of regional academic delayed connection compared to cable
and military networks in the 1980’s. and DSL.
VINT CERF (VINTON GRAY) CELLULAR
Is an American computer scientist, who provides wireless Internet access
is recognized as one of the “fathers of through cell phones.
the internet,” sharing this title with
American computer scientist Bob Kahn.
ISP (Internet Service Provider) WEB BROWSER
Is an organization that provides services is application software that allows users
for accessing, using, or participating in to access and view Web pages or access
the internet. Internet services typically Web 2.0 programs.
provided by ISPs include Internet With an Internet connection
access, Internet transit, domain name established, you start a Web browser,
registration, web hosting, Usenet which then retrieves and displays a
service, and colocation. starting Web page, sometimes called a
home page.
CONNECTING TO THE INTERNET
SERVICES OF INTERNET
REQUIREMENTS FOR CONNECTING TO E-Mail (Electronic Mail)
THE INTERNET is a paperless method of sending
Internet service provider - provides messages, notes or letters from one
you with a connection to the internet person to another or even many people
and the software you will need to at the same time via the Internet. E-
navigate. mail is very fast compared to the
Telecommunication line - a telephone normal post. E-mail messages usually
line is required to connect you to the take only few seconds to arrive at their
internet service provider. destination. One can send messages
Modem - converts a digital signal anytime of the day or night and it will
received from a computer into an get delivered immediately.
analogue signal that can be sent along
ordinary telephone lines, and back to Features of E-mail:
digital at the other end. One-to-one or one-to-many
Web browser - is software used to view communications
and download Web pages and various Instant communications
types of files such as text, graphics and Physical presence of recipient is not
video. required.
Most inexpensive mail service, 24-hours
a day and seven days a week
The Purpose of an IP Address Its Encourages informal communication.
Relationship to a Domain Name
FTP (File Transfer Protocol)
An IP address (Internet Protocol address) It is an Internet utility software used
is a number that uniquely identifies to upload and download files. It gives
each computer or device connected to access to directories or folders on
the Internet. remote computers and allows software,
data, and text files to be transferred
The Internet relies on IP addresses to
between different kinds of computers.
send data to computers at specific
FTP works based on same principle as
locations.
that of Client/Server.
The IP address usually consists of four
groups of numbers, each separated by a
The basic objectives of FTP
period.
• To give flexibility and promote sharing of
domain name - is the text version of an
computer programs, files and data
IP address.
• to transfer data reliably and more
efficiently over network
• to encourage implicit or indirect use of
remote computers using internet
• to shield a user from variations in file
The Purpose of a Web Browser and the
storage systems among hosts.
Components of a Web Address
Telnet (Remote Computing)
is telecommunication utility NETIQUETTE
software, which uses available which is short for Internet etiquette,
telecommunication facility and allows is the code of acceptable behaviors
you to become a user on a remote users should follow while on the
computer. Once you gain access to the Internet.
remote computer, you can use it for the
intended purpose. Netiquette rules include:
Keep messages short,
Be polite,
WORLD WIDE WEB Avoid sending flames or spam,
WWW is the acronym for the World Use emoticons and acronyms,
Wide Web. Clearly identify a spoiler,
The WWW is a system that we use to Read the FAQ,
access the Internet. The WWW is Do not assume material is accurate or
hypertext-based information retrieval up to date,
tool, it uses the hypertext to access the And never read someone’s private e-
various forms of information available mail.
on the world’s different networks. One
can easily surf the Web by jumping
from one document to another using the
links in those documents.
You might also like
- Chapter 2 - IT ERADocument3 pagesChapter 2 - IT ERAJulie Ann ParicaNo ratings yet
- CRM – Domestic Voice: Types of Internet ConnectionsDocument20 pagesCRM – Domestic Voice: Types of Internet Connectionsakhil kottediNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document5 pagesChapter 2seulgi kangNo ratings yet
- Internet Basics - Unit1Document30 pagesInternet Basics - Unit1Bash MonacoNo ratings yet
- WwwDocument5 pagesWwwRehman AliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Communication TechnologiesDocument21 pagesChapter 6 Communication TechnologiesTsepiso MohaleNo ratings yet
- Internet Fundamentals ExplainedDocument20 pagesInternet Fundamentals Explaineddiosdada mendozaNo ratings yet
- E-commerce and internet marketing fundamentalsDocument25 pagesE-commerce and internet marketing fundamentalsStephanie AndalNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document8 pagesModule 2bscomputersciencelsstiNo ratings yet
- Janta Shikshana Samiti'S: Vidyagiri, Dharwad - 580 004Document41 pagesJanta Shikshana Samiti'S: Vidyagiri, Dharwad - 580 004Santosh ShirodkarNo ratings yet
- E-Commerce 3Document3 pagesE-Commerce 3Princess Jem C. TamayoNo ratings yet
- Computer Group 4Document9 pagesComputer Group 4beingmarilyn naëlNo ratings yet
- Living in It Era Midterm ModuleDocument10 pagesLiving in It Era Midterm ModuleRhodz Banan86% (14)
- Unit 5 Internet Basics: 5.0 Learning OutcomesDocument15 pagesUnit 5 Internet Basics: 5.0 Learning OutcomesPreethi PrakashNo ratings yet
- Internet PresentationDocument27 pagesInternet Presentationkamolideen07026No ratings yet
- The Internet and World Wide Web: Which Came First - Internet or WWW?Document38 pagesThe Internet and World Wide Web: Which Came First - Internet or WWW?mubarak idrissNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Introduction To InternetDocument73 pagesModule 1 Introduction To InternetAkshay ßabyNo ratings yet
- Internet and Email: ArpanetDocument11 pagesInternet and Email: ArpanetMir HussainNo ratings yet
- DMC1935Document338 pagesDMC1935Kajendran KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Internet Infrastructure and Email BasicsDocument4 pagesInternet Infrastructure and Email BasicsJambres DelacruzNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Web Technology: Introduction and Web Development StrategiesDocument29 pagesUnit 1 Web Technology: Introduction and Web Development StrategieshemantNo ratings yet
- What Is InternetDocument40 pagesWhat Is InternetADSRNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Internet, WWW and Web Browsers PDFDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Internet, WWW and Web Browsers PDFQuennie Kate Yvonne PatacsilNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Internet:: 323Document17 pagesFundamentals of Internet:: 323sachinNo ratings yet
- Internet Basics FullDocument12 pagesInternet Basics FullTECNICAL ADITYANo ratings yet
- Introduction to the Internet and World Wide WebDocument6 pagesIntroduction to the Internet and World Wide WebLeighton KendelyNo ratings yet
- UC-CIT Empowerment Technologies ModuleDocument6 pagesUC-CIT Empowerment Technologies ModuleLalaine Cababa Opsima-JoveNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Internet: 242:: Data Entry OperationsDocument20 pagesIntroduction To Internet: 242:: Data Entry Operationsshishay GebreNo ratings yet
- Internet Defined: A Concise History and OverviewDocument23 pagesInternet Defined: A Concise History and OverviewRoman clashNo ratings yet
- E Commerce Chap 2Document21 pagesE Commerce Chap 2CloudKitNo ratings yet
- Section 4: Computer NetworksDocument11 pagesSection 4: Computer NetworksfatehkiaNo ratings yet
- Internet and The World Wide WebDocument14 pagesInternet and The World Wide WebOloka George OkwirNo ratings yet
- Gee-1 SG2Document9 pagesGee-1 SG2hokai hokaiNo ratings yet
- Internet: Ravi BhushanDocument53 pagesInternet: Ravi Bhushangparekh4uNo ratings yet
- The Internet: Lesson 2Document12 pagesThe Internet: Lesson 2Xivaughn SebastianNo ratings yet
- Getting Connected: What The IsDocument3 pagesGetting Connected: What The Ismoney shmoneyNo ratings yet
- Background Information, Part 1: Growth of The InternetDocument6 pagesBackground Information, Part 1: Growth of The InternetbiyaNo ratings yet
- The Internet Websites and MediaDocument48 pagesThe Internet Websites and Mediafairuz hafizieNo ratings yet
- Internet and Web Development FundamentalsDocument9 pagesInternet and Web Development FundamentalsAyele MitkuNo ratings yet
- Internet and Wordl Wide WebDocument6 pagesInternet and Wordl Wide WebSabir AliNo ratings yet
- Uses of InternetDocument8 pagesUses of Internetigwe nnabuikeNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Lesson 2 Living in The IT EraDocument6 pagesModule 2 Lesson 2 Living in The IT EraCaleb Jedel OlivoNo ratings yet
- ClassX CA NotesDocument75 pagesClassX CA NotesAshutosh TripathiNo ratings yet
- Meaning of internet, brief history and basic internet termsDocument25 pagesMeaning of internet, brief history and basic internet termsShipraNo ratings yet
- Meaning of Internet, Brief History and Basic Internet TermsDocument25 pagesMeaning of Internet, Brief History and Basic Internet TermsShipraNo ratings yet
- Internet / EmailDocument19 pagesInternet / EmailAdvait NigudkarNo ratings yet
- Internet ServicesDocument49 pagesInternet ServicesDexie Joy JaimeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2: The Internet ExplainedDocument12 pagesLesson 2: The Internet ExplainedJAEHYUK YOONNo ratings yet
- InternetDocument67 pagesInternetJeneillaNo ratings yet
- Computer Communication & Networking AssignmentDocument3 pagesComputer Communication & Networking AssignmentSoni DellaNo ratings yet
- History of the Internet RodrigoDocument34 pagesHistory of the Internet RodrigoJerelyn MalacasteNo ratings yet
- Module-1: Web ProgrammingDocument50 pagesModule-1: Web ProgrammingAtharv KarnekarNo ratings yet
- Submodule Internet and E-mailDocument19 pagesSubmodule Internet and E-mailmohamedmwakuzimu9966No ratings yet
- IIT Lecturer 3 & 4Document60 pagesIIT Lecturer 3 & 4awais mehmoodNo ratings yet
- Evolution of the InternetDocument13 pagesEvolution of the Internetpraful1737No ratings yet
- Graphical Design of Information: Important Persons: Vint CerfDocument2 pagesGraphical Design of Information: Important Persons: Vint CerfShianne RacadioNo ratings yet
- MIS-6112 Module on ISPs and Internet ConnectionsDocument6 pagesMIS-6112 Module on ISPs and Internet ConnectionsDaniel NasolNo ratings yet
- GNS312 Chapter 5 (Module 5) SlidesDocument17 pagesGNS312 Chapter 5 (Module 5) SlidesJosephNo ratings yet
- Internet Science IIS NelliadyDocument48 pagesInternet Science IIS NelliadyprabhahrnNo ratings yet
- Speed of Light Communications and the Internet Protocol (IP)From EverandSpeed of Light Communications and the Internet Protocol (IP)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Console Setup GuideDocument11 pagesConsole Setup GuideMichaelNo ratings yet
- M1 Blockchain TechnologyDocument115 pagesM1 Blockchain TechnologyBijith MarakarkandyNo ratings yet
- Test Assignment Class14Document7 pagesTest Assignment Class14Mijan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Zhenya Antić - Python Natural Language Processing Cookbook - Over 50 Recipes To Understand, Analyze, and Generate Text For Implementing Language Processing Tasks-Packt Publishing (2021)Document285 pagesZhenya Antić - Python Natural Language Processing Cookbook - Over 50 Recipes To Understand, Analyze, and Generate Text For Implementing Language Processing Tasks-Packt Publishing (2021)Jonathan Vielma100% (1)
- CavalazziMarcoCarlo TESIDocument275 pagesCavalazziMarcoCarlo TESIchiruNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 ICT A Platform For ChangeDocument3 pagesChapter 9 ICT A Platform For ChangeSyrill CayetanoNo ratings yet
- Dogecoin wallet guide for online and offline storageDocument1 pageDogecoin wallet guide for online and offline storagelauraNo ratings yet
- Networking Academy Digital Badges FAQ PDFDocument6 pagesNetworking Academy Digital Badges FAQ PDFdaniel fernandezNo ratings yet
- Changing Quickr Theme ColorsDocument7 pagesChanging Quickr Theme ColorsAshish DagaNo ratings yet
- The Indoor Unit of The RTN: Web LCT Configuration - Logging in To An NEDocument12 pagesThe Indoor Unit of The RTN: Web LCT Configuration - Logging in To An NEethosgrNo ratings yet
- SAP Cloud Platform Solution Diagrams & Icons: Guidelines v06Document93 pagesSAP Cloud Platform Solution Diagrams & Icons: Guidelines v06Rahul YadavNo ratings yet
- Install Athena HubDocument7 pagesInstall Athena HubEriberto AlvaresNo ratings yet
- PuraSeva Super APP DocumentationDocument11 pagesPuraSeva Super APP DocumentationRaghu RamNo ratings yet
- FortiGate Inf 06 FSSODocument52 pagesFortiGate Inf 06 FSSOIgoFernandesNo ratings yet
- Nanny NowDocument7 pagesNanny NowDavi SpilleirNo ratings yet
- DDT Contract Template 20Document2 pagesDDT Contract Template 20Abonie BlountNo ratings yet
- Unified IMS Configuration For Linux Android Devices Using MPSS - DI.4.x/MPSS - DPM.2.x/MPSS - BO.2.x and GDR 2.0Document23 pagesUnified IMS Configuration For Linux Android Devices Using MPSS - DI.4.x/MPSS - DPM.2.x/MPSS - BO.2.x and GDR 2.0burdun777No ratings yet
- Dashboard / Courses / BLENDED 1923T.B / BL-CS-301-LEC-1923T / Week 1: Introduction to JavaScript / Quiz 001 (15:38Document3 pagesDashboard / Courses / BLENDED 1923T.B / BL-CS-301-LEC-1923T / Week 1: Introduction to JavaScript / Quiz 001 (15:38katherine anne ortizNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Language Identification MethodsDocument24 pagesEvaluation of Language Identification MethodsIskandar AbdurraniNo ratings yet
- CompTIA A+ 1001 Practice Questions - Sample Questions - Training - CompTIADocument5 pagesCompTIA A+ 1001 Practice Questions - Sample Questions - Training - CompTIAMarielis GermanNo ratings yet
- Fast Detection of DATA TRANSFERDocument88 pagesFast Detection of DATA TRANSFERDharshini AnbazhaganNo ratings yet
- Procedural Guide - Concur Expense Submitter and DelegateDocument38 pagesProcedural Guide - Concur Expense Submitter and Delegatepsp210295No ratings yet
- MonitoringDocument2 pagesMonitoringVaibhav MittalNo ratings yet
- Influencer Study Finalv2Document5 pagesInfluencer Study Finalv2Souptik MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Autobiography of A Yogi in Tamil PDF Free PDFDocument2 pagesAutobiography of A Yogi in Tamil PDF Free PDFLava Loon86% (7)
- Chapyer 2Document37 pagesChapyer 2Samer AlsumaryNo ratings yet
- Corneliu Diaconovici - Enciclopedia Romana-Tomul I Sibiu, 1898 PDFDocument925 pagesCorneliu Diaconovici - Enciclopedia Romana-Tomul I Sibiu, 1898 PDFGeorge MarcuNo ratings yet
- Haxorware ManualDocument23 pagesHaxorware ManualVivianandEnrique Garibay100% (1)
- Online Platform Picture SizeDocument11 pagesOnline Platform Picture SizeKingHungTingNo ratings yet
- L3 Cascading Style SheetsDocument59 pagesL3 Cascading Style Sheetsdmwale2003No ratings yet