Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3 Maths Standards ENG
Uploaded by
lang.sophatCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
3 Maths Standards ENG
Uploaded by
lang.sophatCopyright:
Available Formats
RksYgGb;rM yuvCn nig kILa
MATHEMATICS
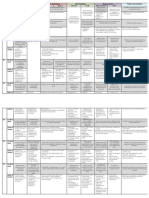
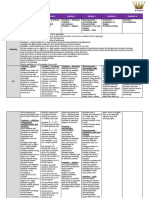
STRAND 3 6 9
• Read, count, write, order and compare whole numbers up to 10,000 in Khmer and Arabic notation. • Read, count, write, order and compare whole numbers not exceeding 7 digits and numbers • Compare, order and carry out four operations with integers, decimals and fractions.
• Use knowledge of whole numbers to read and write accurately everyday numerical information with decimal fractions to two decimal places. • Round off decimal numbers to a specified level of accuracy. (eg the nearest hundredth).
• Read, write, order and compare fractions and mixed numbers.
including house numbers, street numbers, telephone numbers, licence plate numbers and years. • Round decimal numbers to the nearest whole number. • Use degrees up to the power of five to express positive integers (eg 52 = 25; 35 = 243).
• Add and subtract whole numbers where each number is up to 10,000. • Add, subtract, multiply and divide whole numbers using two kinds of brackets. • Recall and use perfect squares and square roots of numbers up to 100, and use sign to represent
• Use mental arithmetic to calculate addition and subtraction of numbers in multiples of 5 up to 100. • Add and subtract fractions with the same denominator. squares (eg 81 = 9).
• Recall and use multiplication tables up to 5 x 10. • Add and subtract decimal numbers with two decimal places.
NUMBER
• Multiply and divide whole numbers up to 3 digits by 1 digit. • Multiply and divide whole numbers up to 4 digits by 2 digits.
• Use estimation strategies to check multiplication, addition and division of whole numbers.
• Use pictures and items to identify fractions from 1/10 to 1. • Rename common fractions (less than one) as decimals and percentages. • Calculate inverse proportions (eg. if 6 workers take 12 days to complete a task, so how many
• Calculate simple ratios and direct proportions (eg 2 people need 4 cups of water so 6 people need 12). days would 9 workers take?).
• Use currency for buying, selling and changing up to R10,000. • Calculate average costs, profit and loss, and write and verify receipts. • Calculate simple interest and discount rates (eg loan of money, sale of goods).
• Use standard measuring instruments and read scales to the nearest gradation to determine: • Express one quantity as a percentage of another (eg 5 girls out of 50 students is 10%).
• Measure and compare everyday objects to determine: • Length from kilometres to millimetres (eg. wood, roads) • Select appropriate metric units for measuring quantities and rates
• length in metres, decimetres or Terks, and centimetres (eg buildings, fields) • Capacity from litres to millilitres (eg. medicine, cooking oil) (eg height of trees in meters, volume of medicine in millilitres).
• weight (mass) in kilograms, grams and Kham (eg rice, fruit, cement) • Weight (mass) from kilograms to grams (eg vegetables, rice and meat)
MEASUREMENT
• capacity in litres (eg water, kerosene). • Time from hours to seconds.
• Read the time in hours and minutes from an analogue clock. • Read and express accurately time in analogue, digital, 12 and 24 hours representations. • Convert the standard units of length, mass, capacity and time to larger and smaller units.
• Carry out the four operations using units of time (hours, minutes and seconds).
• Read a simple timetable accurately. • Interpret a simple scale bar on a map and use the map to calculate distance between places.
• Calculate average travel times using given speeds and distances.
• Identify and draw 2D shapes with up to 4 sides. • Name acute, right, obtuse and straight angles and construct angles using rulers, protractors • Identify axes of symmetry of simple two-dimensional geometric figures in a plane.
and compasses.
• Use the following terms to describe 2D shapes: base, sides, length, width, top, height, diagonal. • Construct and label circles using the following terms: radius, centre, diameter and circumference. • Use formulae to find the circumference, radius, diameter and area of a circle.
• Construct and label triangles and simple quadrilaterals from given data.
GEOMETRY
• Identify the following simple 3D shapes in daily life: cube, cuboid, cylinder. • Make models of prisms, cones, pyramids and cylinders. • Calculate unknown angles formed with parallel lines cut by a transversal.
• Calculate unknown angles using angle properties of triangles and parallelograms.
• Find side, hypotenuse and height lengths of right angled triangles using Pythagoras’ theorem
or similar triangles.
• Identify the area of rectangles and squares using pictorial representations. • Measure the perimeter and find the area of triangles, squares, and rectangles. • Use formulae to find the areas of triangle, square, rectangle, trapezium, parallelogram and rhombus.
• Find the volume of solids made up of unit cubes. • Sketch and find the volume and surface area of cubes, cuboids and cylinders.
Work in groups to construct a simple survey and collect data from up to three sources. Find mean, median and mode from data sets, including frequency distribution tables, and
STATISTICS
• •
distinguish the purpose of each.
• Interpret and construct picture graphs. • Construct and interpret data presented in tables, line graphs, bar charts and simple pie charts. • Estimate the probability of an event on the basis of repeated trials of a simple experiment
(eg repeated tossing of dice).
• Find patterns from given examples and supply missing elements in a pattern. • Find the value of simple algebraic expressions using substitution methods involving addition • Express information provided in words in simple equations and inequalities using >; < and = signs
( eg. ; ; ... ) and subtraction (eg. 3 + b =?; 8 - b= ? where b is 4). (eg the sum of two numbers must be between 6 and 20 becomes 6 < x + y < 20).
x-2
PATTERNS
Simplify simple algebraic expressions using addition and subtraction method. (eg. 4x + 2x = ?). = 6 ).
ALGEBRA
• • Solve linear fractional equations with one unknown and none in the denominator (eg
12
AND
• Solve a system of first degree equations with two unknowns
(eg if person A buys 2kg of fish and 6kg of rice for R29,000, and person B buys 1kg fish and
1kg rice for R11,600, what is the cost of fish per kg?).
• Construct the graph of the line y = ax + b ( where a and b are integers).
REASONING
• Make decisions about how to approach simple two-step problems by deciding which • Explain a short chain of reasoning used to approach and solve a problem that involves an • Develop a problem in a real life situation and develop a solution using a range of mathematical
mathematics techniques to use and breaking a problem into parts. analysis of data through the selection and use of mathematical techniques. techniques.
You might also like
- GCSE Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- g3 May 20 1Document6 pagesg3 May 20 1api-293518100No ratings yet
- Year 10 Curriculum Coverage For Year End 2022-23Document12 pagesYear 10 Curriculum Coverage For Year End 2022-23Romesa ZahraNo ratings yet
- Geometry 16 Hrs SHAPES and SPATIAL UNDERDocument2 pagesGeometry 16 Hrs SHAPES and SPATIAL UNDERPiyush AgrahariNo ratings yet
- K4 Maths Syllabus Tags 2023-24Document1 pageK4 Maths Syllabus Tags 2023-24tehreemali864No ratings yet
- Tp2 M 2678928 Y6 Measurement Planit Maths Steps To Progression Overview English Ver 1Document10 pagesTp2 M 2678928 Y6 Measurement Planit Maths Steps To Progression Overview English Ver 1Ritah NantezaNo ratings yet
- In Maths A Year 6 Child Is Expected To Know:: NumberDocument3 pagesIn Maths A Year 6 Child Is Expected To Know:: NumbermrvaughanNo ratings yet
- In Maths A Year 5 Child Is Expected To KnowDocument5 pagesIn Maths A Year 5 Child Is Expected To KnowmrvaughanNo ratings yet
- Higher Maths Syllabus GCSEDocument3 pagesHigher Maths Syllabus GCSEtakenalrNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Foundation Syllabus: 1. NumbersDocument2 pagesMathematics Foundation Syllabus: 1. NumbersSmita NagNo ratings yet
- In Maths A Year 4 Child Is Expected To KnowDocument3 pagesIn Maths A Year 4 Child Is Expected To KnowmrvaughanNo ratings yet
- Number and Place Value: Subject: Math Year: 2Document7 pagesNumber and Place Value: Subject: Math Year: 2madeehaNo ratings yet
- Class 8Document130 pagesClass 8Ajmal NayabNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Lower School Syllabus 2021Document12 pagesMathematics Lower School Syllabus 2021Sakshi NijhawanNo ratings yet
- Year 2 Maths Assessment Targets Colouring Sheet: Page 1 of 2Document2 pagesYear 2 Maths Assessment Targets Colouring Sheet: Page 1 of 2TaylorNo ratings yet
- Class-6 Maths WorkbookDocument12 pagesClass-6 Maths Workbookneomatrix70No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 IntroductionDocument45 pagesChapter 1 IntroductionHunde AdamuNo ratings yet
- SAT T1 Syllabus - Y8H - JAN 2021-22Document6 pagesSAT T1 Syllabus - Y8H - JAN 2021-22Usman TanveerNo ratings yet
- 15 TET Syllabus Paper 2 Mathematics & ScienceDocument34 pages15 TET Syllabus Paper 2 Mathematics & ScienceMohankumar P KNo ratings yet
- Perimeter Are A VolumeDocument37 pagesPerimeter Are A VolumeAdrian CayabyabNo ratings yet
- Maths FrameworkDocument1 pageMaths FrameworkSamion AwaldinNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Framework, Year 8Document6 pagesMathematics Framework, Year 8Raluca MoldovanNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Mathematics Topics Based On NSC CurriculumDocument3 pagesGrade 8 Mathematics Topics Based On NSC CurriculumGarth GreenNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Syllabus - Year 6: Properties of Numbers and Number SequencesDocument9 pagesMathematics Syllabus - Year 6: Properties of Numbers and Number SequencesAnonymous X5rzmINo ratings yet
- Home Letters CH 9Document5 pagesHome Letters CH 9Mile GomezNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Primary Maths Curriculum Outline PDFDocument6 pagesCambridge Primary Maths Curriculum Outline PDFRe MarkNo ratings yet
- Bha Maths POIDocument2 pagesBha Maths POIDave Secomb100% (5)
- Cambridge Primary Maths (0845) Curriculam SyllabusDocument3 pagesCambridge Primary Maths (0845) Curriculam SyllabusJK EduNotes100% (5)
- NCERT Syllabus For Class 2 Maths 2023-24: Geometry (13 HRS.)Document3 pagesNCERT Syllabus For Class 2 Maths 2023-24: Geometry (13 HRS.)monishapanniNo ratings yet
- In Maths A Year 3 Child Is Expected To KnowDocument3 pagesIn Maths A Year 3 Child Is Expected To KnowmrvaughanNo ratings yet
- LS CheckpointDocument15 pagesLS CheckpointBhavishyaNo ratings yet
- Cbse Class - 6 SyllabusDocument9 pagesCbse Class - 6 SyllabusAnkita SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Decimals PDFDocument5 pagesLesson Plan Decimals PDFDivinegRace tanOarezaNo ratings yet
- Design Topic: Place Value, Fractions & Decimals Subject(s) : Math Grade(s) : 4 Designer(s) Samantha Miller Understanding by DesignDocument12 pagesDesign Topic: Place Value, Fractions & Decimals Subject(s) : Math Grade(s) : 4 Designer(s) Samantha Miller Understanding by Designapi-369706033No ratings yet
- Reviewer Teaching Math in The PrimarygradesDocument9 pagesReviewer Teaching Math in The PrimarygradesShaira CainlangNo ratings yet
- Term 1 - End of Unit Math Topic ListDocument2 pagesTerm 1 - End of Unit Math Topic ListMáxima BrunoNo ratings yet
- Math Answers Lesson 2Document3 pagesMath Answers Lesson 2Maria Victoria Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Revision Checklist For o Level Mathematics 4024 FinalDocument15 pagesRevision Checklist For o Level Mathematics 4024 FinalHussain TafazzulNo ratings yet
- Summary of Curriculum SpecificationDocument4 pagesSummary of Curriculum SpecificationNoratiqa LahadiNo ratings yet
- Maths Curriculum Year 6Document3 pagesMaths Curriculum Year 6soe myatmonNo ratings yet
- Maths IGCSE Scheme of Work 0580 - 2010Document6 pagesMaths IGCSE Scheme of Work 0580 - 2010Yenny TigaNo ratings yet
- GCSE 9-1 Mathematics Parent-Student GuideDocument24 pagesGCSE 9-1 Mathematics Parent-Student GuideTawanda ChibweNo ratings yet
- Mathematics RevisedCurriculum 2021-2022Document9 pagesMathematics RevisedCurriculum 2021-2022iqra darNo ratings yet
- OBPS Math t4Document13 pagesOBPS Math t4yentriNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 Target Sheet For Term 1Document2 pagesGrade 6 Target Sheet For Term 1manilaNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 Handover Tool Mathematics 2024Document12 pagesGrade 6 Handover Tool Mathematics 2024Fatima Ally100% (1)
- (MEP Year 2) (MEP Year 2) - (MEP Year 2)Document9 pages(MEP Year 2) (MEP Year 2) - (MEP Year 2)Cristian Andrés Delgado CalderónNo ratings yet
- U017 Edexcel GCSE Maths Chart P2Document1 pageU017 Edexcel GCSE Maths Chart P2al-gazNo ratings yet
- BiostatisticsDocument12 pagesBiostatisticsAyesha SanaNo ratings yet
- Teaching Place-Value Concepts: Purpose and Overview of GuideDocument7 pagesTeaching Place-Value Concepts: Purpose and Overview of GuideSaraNo ratings yet
- Maths - Syllabus Class 1Document24 pagesMaths - Syllabus Class 1Saravana PerumalNo ratings yet
- Sample MAT0501Document16 pagesSample MAT0501JenNo ratings yet
- Number Topics: Functional Skills Maths L1/L2 Topic OutlineDocument3 pagesNumber Topics: Functional Skills Maths L1/L2 Topic OutlinejohnNo ratings yet
- DraftingDocument44 pagesDraftingrubsNo ratings yet
- 7th G PPT - Concept of Area & CircumferenceDocument43 pages7th G PPT - Concept of Area & Circumferencehaniebalm100% (1)
- CBSE Syllabus For Class 6 Maths 2023 24Document3 pagesCBSE Syllabus For Class 6 Maths 2023 24codingsikho2026No ratings yet
- Presenting Data For The EPQDocument34 pagesPresenting Data For The EPQHenry LubingaNo ratings yet
- Measurement: First Year ScienceDocument26 pagesMeasurement: First Year Scienceapi-406307933No ratings yet
- DraftingDocument44 pagesDraftingRoxanne Eve Ferranco ZamoraNo ratings yet
- A Year 2 Child Is Expected To KnowDocument3 pagesA Year 2 Child Is Expected To KnowmrvaughanNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Grade 11Document122 pagesMathematics: Grade 11dilshanhNo ratings yet
- M10-3rd TOPIC - Division of PolynomialsDocument54 pagesM10-3rd TOPIC - Division of PolynomialsClara ChuNo ratings yet
- SES - Nora D. Herrera - Grade 6 - 2nd ST - San Rafael EastDocument4 pagesSES - Nora D. Herrera - Grade 6 - 2nd ST - San Rafael EastNora HerreraNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 Math Scopeand Sequence GuideDocument6 pagesGrade 5 Math Scopeand Sequence GuideDev MauniNo ratings yet
- 1st Term s2 MathematicsDocument38 pages1st Term s2 MathematicsBarbaraNo ratings yet
- Book For Practice V2.01 Quantitative AbilityDocument112 pagesBook For Practice V2.01 Quantitative AbilityRutuja JadhavNo ratings yet
- AIMO 2017 Trial G7 PaperDocument4 pagesAIMO 2017 Trial G7 PaperHary PurbowoNo ratings yet
- MG - DCCM-DLHTM Math 4,5 & 6 Q1 - W2Document5 pagesMG - DCCM-DLHTM Math 4,5 & 6 Q1 - W2REZA TAGLENo ratings yet
- DLL - Math 6 - Q3 - W1Document7 pagesDLL - Math 6 - Q3 - W1mary rose cornitoNo ratings yet
- Teaching Numbers AdvancedDocument30 pagesTeaching Numbers Advancedsantiago cortes castroNo ratings yet
- Maths InterviewDocument6 pagesMaths InterviewKeamogetse BoitshwareloNo ratings yet
- Operations On SurdsDocument3 pagesOperations On SurdsKomal PatelNo ratings yet
- Math 6 DLP 24 - Forming Equivalent Fractions Solving The Missing Number in A Pair of Equivalent FDocument9 pagesMath 6 DLP 24 - Forming Equivalent Fractions Solving The Missing Number in A Pair of Equivalent FSheena Marie B. AnclaNo ratings yet
- Class 5 Mathematics Worksheet 2021Document2 pagesClass 5 Mathematics Worksheet 2021Hussain KhanNo ratings yet
- Pre Board 2Document32 pagesPre Board 2S.N. SwamiNo ratings yet
- Math 6 - Q1 - W3.docx EditedDocument11 pagesMath 6 - Q1 - W3.docx EditedShaine Dzyll KuizonNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 Decimals and Fractions CSEC Revision TestDocument3 pagesUNIT 1 Decimals and Fractions CSEC Revision TestNicola Nichelle100% (1)
- Holiday Homework For Class 12 MathsDocument8 pagesHoliday Homework For Class 12 Mathscfja0ewh100% (2)
- Las Math 7 Q1-W4 2021-2022Document3 pagesLas Math 7 Q1-W4 2021-2022Angela Camille PaynanteNo ratings yet
- Content Code Learning Competencies References: First Mathematics SIX 2017 - 2018Document7 pagesContent Code Learning Competencies References: First Mathematics SIX 2017 - 2018Geneven Hermosa OlasimanNo ratings yet
- Sasmo 2017 Grade 05Document10 pagesSasmo 2017 Grade 05SamrongNo ratings yet
- ACT Math-Ultimate Formula Sheet.Document6 pagesACT Math-Ultimate Formula Sheet.Waheed ShaabanNo ratings yet
- Python For Beginners: OpensapDocument32 pagesPython For Beginners: OpensapAbhishekBNo ratings yet
- College Algebra 11th Edition Gustafson Test BankDocument74 pagesCollege Algebra 11th Edition Gustafson Test BankCalvinMataazscm100% (12)
- LONG TEST - Business MathDocument3 pagesLONG TEST - Business MathJohn Philip EchevarriaNo ratings yet
- Maths Colour by NumbersDocument87 pagesMaths Colour by NumbersJoleneNo ratings yet
- Math Modern WorldDocument25 pagesMath Modern WorldZsef IryshNo ratings yet
- Standard Sample Paper XyzDocument7 pagesStandard Sample Paper XyzMaurya Sachin100% (1)
- M101Algebra Week 05Document4 pagesM101Algebra Week 05Jovelyn Deloria EspañolNo ratings yet
- 01a Algebraic Fractions - H - Question Paper v2Document13 pages01a Algebraic Fractions - H - Question Paper v2Umama UbaidiNo ratings yet