Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PD 12 Overloading
PD 12 Overloading
Uploaded by
RD0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views3 pagesOriginal Title
PD_12_overloading
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views3 pagesPD 12 Overloading
PD 12 Overloading
Uploaded by
RDCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
// ===========================================================================
// Operator Overloading
// ===========================================================================
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
using namespace std;
// class definition of MyVector
class MyVector
{
friend const MyVector operator+(const MyVector& v, double d);
private:
int n;
double* m;
public:
MyVector();
MyVector(int n, double m[]);
MyVector(const MyVector& v);
~MyVector();
void print() const;
bool operator==(const MyVector& v) const;
bool operator!=(const MyVector& v) const;
bool operator<(const MyVector& v) const;
double operator[](int i) const;
double& operator[](int i);
const MyVector& operator=(const MyVector& v);
const MyVector& operator+=(const MyVector& v);
};
// end of class definition of MyVector
// global function headers
const MyVector operator+(const MyVector& v, double d);
const MyVector operator+(double d, const MyVector& v);
const MyVector operator+(const MyVector& v1, const MyVector& v2);
// MyVector's instance functions
MyVector::MyVector(): n(0), m(NULL)
{
}
MyVector::MyVector(int n, double m[])
{
this->n = n;
this->m = new double[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
this->m[i] = m[i];
}
MyVector::MyVector(const MyVector& v)
{
this->n = v.n;
this->m = new double[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
this->m[i] = v.m[i];
}
MyVector::~MyVector()
{
delete [] m;
}
void MyVector::print() const
{
cout << "(";
for(int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
cout << m[i] << ", ";
cout << m[n-1] << ")\n";
}
// end of MyVector's instance functions
// MyVector's overloaded operators
bool MyVector::operator==(const MyVector& v) const
{
if(this->n != v.n)
return false;
else
{
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if(this->m[i] != v.m[i])
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
bool MyVector::operator!=(const MyVector& v) const
{
return !(*this == v);
}
bool MyVector::operator<(const MyVector& v) const
{
if(this->n != v.n)
return false;
else
{
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if(this->m[i] >= v.m[i])
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
double MyVector::operator[](int i) const
{
if(i < 0 || i >= n)
exit(1);
return m[i];
}
double& MyVector::operator[](int i)
{
if(i < 0 || i >= n)
exit(1);
return m[i];
}
const MyVector& MyVector::operator=(const MyVector& v)
{
if(this != &v)
{
if(this->n != v.n)
{
delete [] this->m;
this->n = v.n;
this->m = new double[this->n];
}
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
this->m[i] = v.m[i];
}
return *this;
}
const MyVector& MyVector::operator+=(const MyVector& v)
{
if(this->n == v.n)
{
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
this->m[i] += v.m[i];
}
return *this;
}
// end of MyVector's overloaded operators
// global functions
const MyVector operator+(const MyVector& v, double d)
{
MyVector sum(v);
for(int i = 0; i < v.n; i++)
sum[i] += d;
return sum;
}
const MyVector operator+(double d, const MyVector& v)
{
return v + d;
}
const MyVector operator+(const MyVector& v1, const MyVector& v2)
{
MyVector sum(v1);
sum += v2;
return sum;
}
// end of global functions
// ===========================================================================
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5819)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- PD 06 Algorithms Practice AnswerDocument8 pagesPD 06 Algorithms Practice AnswerRDNo ratings yet
- PD 10 SelfTypeDocument7 pagesPD 10 SelfTypeRDNo ratings yet
- PD 08 PointerDocument9 pagesPD 08 PointerRDNo ratings yet
- C Exercise Example5Document4 pagesC Exercise Example5RDNo ratings yet
- C Exercise Example3Document7 pagesC Exercise Example3RDNo ratings yet
- Computer Organization Exercise AnswerbDocument5 pagesComputer Organization Exercise AnswerbRDNo ratings yet
- Computer Organization Exercise Answer6Document5 pagesComputer Organization Exercise Answer6RDNo ratings yet
- Computer Organization Exercise Answer8Document7 pagesComputer Organization Exercise Answer8RDNo ratings yet
- C Exercise Example1Document4 pagesC Exercise Example1RDNo ratings yet
- 第04章 Ac Ac变换器Document55 pages第04章 Ac Ac变换器RDNo ratings yet
- Computer Organization Exercise Answer5Document7 pagesComputer Organization Exercise Answer5RDNo ratings yet
- Received May 3, 2010 First Revision Oct 7, 2010 Second Revision Jan 28, 2011 Third Revision Apr 28, 2011 Accepted May 4, 2011Document16 pagesReceived May 3, 2010 First Revision Oct 7, 2010 Second Revision Jan 28, 2011 Third Revision Apr 28, 2011 Accepted May 4, 2011RDNo ratings yet
- Computer Organization Exercise Answer8Document6 pagesComputer Organization Exercise Answer8RDNo ratings yet
- Computer Organization Exercise Answer7Document7 pagesComputer Organization Exercise Answer7RDNo ratings yet
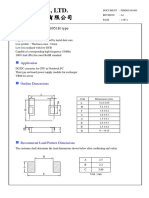
- Cyntec Co., LTD.: Power Choke Coil PIMB051H TypeDocument4 pagesCyntec Co., LTD.: Power Choke Coil PIMB051H TypeRDNo ratings yet
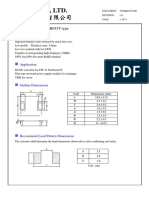
- Cyntec Co., LTD.: Power Choke Coil PCMB053T TypeDocument3 pagesCyntec Co., LTD.: Power Choke Coil PCMB053T TypeRDNo ratings yet
- The Influence of Online Product Reviews On Consumer Purchase Intentions: The Moderating Roles of Cognitive Need and Product KnowledgeDocument4 pagesThe Influence of Online Product Reviews On Consumer Purchase Intentions: The Moderating Roles of Cognitive Need and Product KnowledgeRDNo ratings yet
- Fdpc8016S: Powertrench Power Clip 25V Asymmetric Dual N-Channel MosfetDocument12 pagesFdpc8016S: Powertrench Power Clip 25V Asymmetric Dual N-Channel MosfetRDNo ratings yet
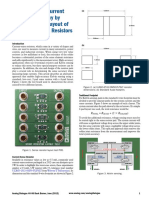
- Optimize High-Current Sensing Accuracy by Improving Pad Layout of Low-Value Shunt ResistorsDocument3 pagesOptimize High-Current Sensing Accuracy by Improving Pad Layout of Low-Value Shunt ResistorsRDNo ratings yet
- Specification For Approval: Page 1 of 8Document8 pagesSpecification For Approval: Page 1 of 8RDNo ratings yet
- Verilog Primer SlidesDocument42 pagesVerilog Primer SlidesRDNo ratings yet
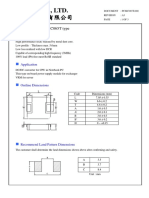
- Cyntec Co., LTD.: Power Choke Coil PCMC065T TypeDocument3 pagesCyntec Co., LTD.: Power Choke Coil PCMC065T TypeRDNo ratings yet
- Electric Power System, Syllabus - Fall 2016Document3 pagesElectric Power System, Syllabus - Fall 2016RDNo ratings yet