Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Adobe Scan 28 Dec 2022
Uploaded by
Sumit SorenOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Adobe Scan 28 Dec 2022
Uploaded by
Sumit SorenCopyright:
Available Formats
9.
CLEANING OF SOAP IN
HARD AND SOFT WATER
Experiment 9
OAIM
of the
Study of comparative cleani
comparative
cleaning capacity of a sample of soap in soft and hard water.
MATERIALS REQUIRED
nles of hard water, soft water (distilled water), calcium chloride, magnesium sulphate, physical or digital balance,
Sample.
box, two test tubes, a test tube stand, five beakers (100 ml), a glass rod, burner, tripod stand, wire gauze, a
weight
asuringcylinder (50 ml) and a measuring scale (6 inch).
THEORY
when
When
soap is shaken in soft water which does not contain Ca" and Mg ions, lot of lather is formed which helps in
cleaning clothes.
wWhen soap is shaken with hard water which contains Ca and Mg* ions, very less lather is formed and cleaning of
clothes does not take place.
Hard water contains hydrogen carbonates, sulphates and chlorids of calcium and magnesium, which are soluble inwater
Soaps are sodium or potassium salts of fatty acids which react with Ca and Mg* to form calcium and magnesium
salts of fatty acids which are called "scum". It is insoluble in water, so soap goes waste.
Ca+2C,H COONa- (C,H COO), Ca +2Na
Sodium stearate Calcium stearate
(soap) (scum)
Mg" +2C,,H,COONa (CH CO0), Mg +2Na
Magnesium stearate
(scum)
PROCEDURE
Take a 100 ml beaker.
Weight 1 g of sample of soap with the help of balance and put in the beaker.
Add 20 ml of distilled water in the beaker. Dissolve the soap by stirring the mixture with the help of glass rod.
Warm a little if soap does not dissolve.
Take a test tube stand and place four test tubes in it and label them as 'A', B, C'and D'.
Take four beakers 'A', B, C and TD of 100 ml each.
Take 20 ml of distilled water in 'A', 20 ml of tap water in 'B, 20 ml of distilled water in which 1 g of MgS0, is
dissolved in C and take 20 ml of distilled water in which 1g of MgS0, and 1 g of CaCl, both are dissolved in 'D'.
Add 10 ml of each type of water in test tubes 'A', B, 'C and D' respectively.
Add 2 ml each ofsoap solution prepared in corresponding test tube.
Measure the initial length ofsolution in 'A", B, 'C'and D'.
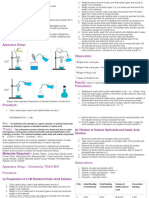
Take the test tube 'A and shake it 10 times by placing thumb over it as shown in diagram.
Foam will be formed. Measure the final length ofsoap solution and foam produced immediately with the help of
Scale and record in observation table.
Repeat the same procedure with other three test tubes and note down the length offoam in observation table.
) Mass of soap taken =
.
Science Lab Skills-X 67
dissolved =
l l
ml.
,
which soap was
(11) Volume of distilled water in
IMI,
i ) Volume ofsoap solution added to each test tube . .
mi.
(1) Volume of each
water added to each test tube....
sample
(v) Number of times each test tube shaken = . mes.
Test tube
Movement of the test tube
Soap solution
(A) Test tubes containing different samples of water (B) Shaking of the test tube
(C) To compare the foaming capacity of soap in different samples of water
Fig. 9.1 Comparative cleaning capacity of soap
ev OBSERVATION TABLE
Sample Initial length Final length Length of foam produced Inference
of water in cm in cm in cm in cm
1.
e 2
3.
4.
e RESULT
The sample of water 'A' produces maximum length of foam, therefore, it is soft water. B' produces less foam, it is han
water. C produces even less foam, it is more hard water than 'B. Sample D' produces minimum foam, it is most hart
water.
The order of hardness of water is B <C<D whereas A' is soft water.
e
PRECAUTIONS
1. Use distilled water for dissolving soap.
2. Stir the mixture carefully so as to avoid spilling.
3. Take same quantity of water in each beaker.
ey
4. Use digital balance for weighing if available.
5. Shake every test tube equal number of times.
6. Measure the length immediately after production of foam.
7. Use wire gauze for warming beaker containing soap solution if needed.
You might also like
- Cleaning Capacity of A Sample of SoapDocument2 pagesCleaning Capacity of A Sample of Soap21- VARNIKA DALALNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 9Document3 pagesExperiment No. 9mayankroy9431No ratings yet
- Class-XI CHEMISTRY SAMPLE COPY FOR PROJECT WORKDocument10 pagesClass-XI CHEMISTRY SAMPLE COPY FOR PROJECT WORKkushanyadav3848No ratings yet
- Chemistry Project RemovedDocument6 pagesChemistry Project Removeddevk09911No ratings yet
- Determination of The Amount of Hardness in Water Using Soap SolutionDocument3 pagesDetermination of The Amount of Hardness in Water Using Soap SolutionlokeshjoshimjNo ratings yet
- Foaming Capacity Of-Soap: Tarun TejaDocument16 pagesFoaming Capacity Of-Soap: Tarun Tejatarunteja859No ratings yet
- Chemistry Investigatory ProjectDocument16 pagesChemistry Investigatory ProjecthgvgNo ratings yet
- Project On Foaming Capacity of Soaps XiiDocument16 pagesProject On Foaming Capacity of Soaps XiiDeepanshu RajputNo ratings yet
- S. No. Page No. 1 1 2 Experiment 1 2 3 Experiment 2 4 4 Bibliography 6Document9 pagesS. No. Page No. 1 1 2 Experiment 1 2 3 Experiment 2 4 4 Bibliography 6Lakshay BairwaNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument6 pagesChemistryvishrutha karunaharanNo ratings yet
- Testing The Hardness of WaterDocument3 pagesTesting The Hardness of Wateralexduart01No ratings yet
- Foaming Capacity of SoapDocument16 pagesFoaming Capacity of SoapAnonymous D5g37JjpGB100% (1)
- Chemistry Investigatory ProjectDocument15 pagesChemistry Investigatory ProjectHimanshu mishraNo ratings yet
- Foaming Capacity of SoapsDocument4 pagesFoaming Capacity of SoapsHemant Patra100% (1)
- Forming Capacit-WPS OfficeDocument10 pagesForming Capacit-WPS OfficeSanskritiNo ratings yet
- Foaming Capacity of Soaps: Chemistry Project OnDocument12 pagesFoaming Capacity of Soaps: Chemistry Project OnNilabha Das100% (2)
- Chemistry ProjectDocument11 pagesChemistry ProjectNavnith ReddyNo ratings yet
- Foaming Capacity of SoapDocument9 pagesFoaming Capacity of SoapPrince of PersiaNo ratings yet
- Mukesh LamgariyaDocument11 pagesMukesh LamgariyaSakshi KiroulaNo ratings yet
- Question #2 Answers: Therefore, Volume of Bar A 5×2×3 30cmDocument9 pagesQuestion #2 Answers: Therefore, Volume of Bar A 5×2×3 30cmlakadia taylorNo ratings yet
- Testing The Hardness of WaterDocument3 pagesTesting The Hardness of WatersmitpiyushpatelNo ratings yet
- Monicaa Chemistry Project EditedDocument15 pagesMonicaa Chemistry Project Editedvix lunaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project Class 11thDocument10 pagesChemistry Project Class 11thpiyushchand457No ratings yet
- New Ajay Blue Illustrated Modern Group Project PresentationDocument21 pagesNew Ajay Blue Illustrated Modern Group Project PresentationNawaraj RokayaNo ratings yet
- Foaming Capacity of SoapsDocument4 pagesFoaming Capacity of SoapsAvinash Dwivedi60% (5)
- Foaming Capacity of SoapsDocument5 pagesFoaming Capacity of SoapsGurbaaz GillNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ProjectDocument14 pagesChemistry ProjectAkshara KathribailNo ratings yet
- WashingDocument19 pagesWashingNitish DebbarmaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project On Foaming Capacity of Soaps2Document8 pagesChemistry Project On Foaming Capacity of Soaps2Shaila BhandaryNo ratings yet
- Cleansing Action of SoapDocument3 pagesCleansing Action of SoapYeshwanth K PNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ProjectDocument20 pagesChemistry Projectbineeshbgopal71% (24)
- Esterification and SaponificationDocument2 pagesEsterification and SaponificationbookeleahNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Ongc Panvel: Chemistry Investigatory Project SESSION 2018-2019Document14 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Ongc Panvel: Chemistry Investigatory Project SESSION 2018-2019tlgNo ratings yet
- Khue Le - Lab 6. Preparation and Cleaning Action of Soaps (3%)Document13 pagesKhue Le - Lab 6. Preparation and Cleaning Action of Soaps (3%)Thanh Khuê LêNo ratings yet
- Practical Book Analytical ChemistryDocument14 pagesPractical Book Analytical Chemistrysalman ahmedNo ratings yet
- WWW Seminarsonly Com Engineering Projects Chemistry Investigation of Foaming Capacity of Different Washing Soap PHPDocument4 pagesWWW Seminarsonly Com Engineering Projects Chemistry Investigation of Foaming Capacity of Different Washing Soap PHPdeepankar mishraNo ratings yet
- JulebrusDocument9 pagesJulebrusSandra JonssonNo ratings yet
- Simulaltion Lab - Ryan TeckDocument4 pagesSimulaltion Lab - Ryan Teck2021155224No ratings yet
- AnaChem Lec 1-2Document42 pagesAnaChem Lec 1-2Richmond Paul RiveraNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project On Foaming Capacity of SoapsDocument4 pagesChemistry Project On Foaming Capacity of SoapsSri50% (2)
- This Study Resource Was: Titration Level 1Document4 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Titration Level 1Camaya RumbleNo ratings yet
- Sudharsanam VidyaashramDocument11 pagesSudharsanam VidyaashrammanojNo ratings yet
- II PU Chemistry Lab Manual (Part - A+B) Final - 10!09!22 (File)Document39 pagesII PU Chemistry Lab Manual (Part - A+B) Final - 10!09!22 (File)RajanNo ratings yet
- AyushDocument11 pagesAyushAYUSH KUMAR RAJDEEPNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Grade 12 PracticalsDocument6 pagesChemistry Grade 12 PracticalsFadil AliNo ratings yet
- Foaming Capacity of SoapDocument10 pagesFoaming Capacity of SoapAnonymous D5g37JjpGBNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Cbse ProjectDocument24 pagesChemistry Cbse ProjectTanvi PahwaNo ratings yet
- Investigatory File On Foaming Capacity of SoapsDocument16 pagesInvestigatory File On Foaming Capacity of SoapsAditya Pratap Singh Sengar86% (7)
- Vikas Bharati Public School Rohini ChemiDocument11 pagesVikas Bharati Public School Rohini Chemiprashant sharmaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project On Foaming Capacity of SoapsDocument13 pagesChemistry Project On Foaming Capacity of SoapsNeeraj100% (1)
- Chem ProjectDocument10 pagesChem ProjectSampriti MadhukulyaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Investigatory ProjectDocument16 pagesChemistry Investigatory Projectmangroliyajenil0No ratings yet
- Making A Standrad SolutionDocument2 pagesMaking A Standrad SolutionFaridaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project NewDocument16 pagesChemistry Project NewStudyNo ratings yet
- PRACTICAL CLASS 11 CHEMISTRY NewDocument11 pagesPRACTICAL CLASS 11 CHEMISTRY Newbaghelanuragsingh09No ratings yet
- MT Lab Manual (1) - 29-39Document11 pagesMT Lab Manual (1) - 29-39Ajin JayanNo ratings yet
- Vol Expt 2 ChemistryDocument4 pagesVol Expt 2 ChemistryVrisanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Investigatory ProjectDocument24 pagesChemistry Investigatory ProjectYakshithChinnappa100% (2)
- The Chemistry of Fertilisers and Manure - Including Information on the Chemical Constituents and Types of Fertilisers and ManuresFrom EverandThe Chemistry of Fertilisers and Manure - Including Information on the Chemical Constituents and Types of Fertilisers and ManuresRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Chemistry of Dairy Products - A Chemical Analysis of Milk, Cream and ButterFrom EverandThe Chemistry of Dairy Products - A Chemical Analysis of Milk, Cream and ButterNo ratings yet