Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Working Principle of A Tube Light
Uploaded by
Mahak Kumrawat0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views4 pagesworking principle of tubelight
Original Title
Working Principle of a Tube Light
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentworking principle of tubelight
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views4 pagesWorking Principle of A Tube Light
Uploaded by
Mahak Kumrawatworking principle of tubelight
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Working Principle of a Tube Light
What is Tube Light?
Tube shaped fluorescent lamp is termed as tube light. Tube light is a lamp that
works on low pressure mercury vapor discharge phenomenon and converts ultra
violate ray into visible ray with the help of phosphor coated inside glass tube.
Material Used Inside the Tube Light
The materials used to build a tube light are given below.
1. Filament coils as electrodes
2. Phosphor coated glass bulb
3. Mercury drop
4. Inert gases (argon)
5. Electrode shield
6. End cap
7. Glass stem
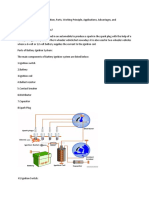
Auxiliary Electrical Components along with Tube Light
The tube light does not work directly on power supply. It needs some auxiliary
components to work. They are-
● Ballast: It may be electromagnetic ballast or electronic ballast.
● Starter: The starter is a small neon glow up lamp that contains a fixed
contact, a bimetallic strip and a small capacitor.
Working Principle of Tube Light
● When the switch is ON, full voltage will come across the tube light
through ballast and fluorescent lamp starter. No discharge happens
initially i.e. no lumen output from the lamp.
● At that full voltage first the glow discharge is established in the starter.
This is because the electrodes gap in the neon bulb of starter is much
lesser than that of inside the fluorescent lamp.
● Then gas inside the starter gets ionized due to this full voltage and
heats the bimetallic strip that is caused to be bent to connect to the
fixed contact. Current starts flowing through the starter. Although the
ionization potential of the neon is little bit more than that of the argon
still due to small electrode gap high voltage gradient appears in the
neon bulb and hence glow discharge is started first in starter.
● As voltage gets reduced due to the current causing a voltage drop
across the inductor, the strip cools and breaks away from the fixed
contact. At that moment a large L di/dt voltage surge comes across the
inductor at the time of breaking.
● This high valued surge comes across the tube light electrodes and
strike penning mixture (mixture argon gas and mercury vapor).
● Gas discharge process continues and current gets path to flow through
the tube light gas only due to low resistance as compared to resistance
of starter.
● The discharge of mercury atoms produces ultra violet radiation which in
turn excites the phosphor powder coating to radiate visible light.
● Starter gets inactive during operation of tube light.
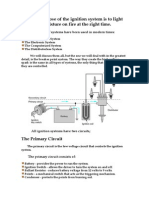
Automobile Ignition System: Mechanism, Components and
Working
An ignition system is used in internal combustion engines to create an electric spark
in the engine combustion chamber to ignite a petrol and air mixture. It is an integral
component of automobiles often treated as the sub-section of the
engine-management system.
What Is the Function of Ignition Systems in Automobiles?
The main function of a vehicle's ignition system is to ignite the air-fuel mixture in its internal
combustion engine. To do this, it creates a high-voltage spark using its spark plugs which
makes a car fuel burn, causing its pistons to turn its wheels.
An automobile ignition system must work in tandem with all other parts of an engine. So,
igniting the fuel at the right time is necessary to make a vehicle function smoothly. The timing
of a high-voltage electric spark depends on a vehicle’s load, speed and other factors.
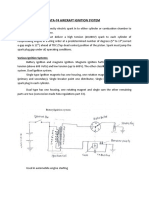
How Do Automobile Ignition Systems Work?
● In a conventional ignition system, there are two main sets of
windings/circuits—primary and secondary. The primary circuit works on
battery current and is responsible for carrying low voltage. Some breaker
points and an ignition switch control this primary circuit. When a driver turns
on the ignition key of a vehicle, its battery supplies 12 volts of current to its
ignition coil through the contact breaker points. This flow of current creates a
magnetic field around this coil.
● The secondary circuit is not electrically connected to the primary circuit. It has
secondary windings in its coil and high tension lead between the distributor
and coil wire on external coil distributors. Furthermore, it also consists of a
distributor rotor, a distributor cap, spark plug leads and spark plugs. The
engine's rotation turns the distributor shaft cam which separates the breaker
points, which, in turn, stops the current flow. This leads to a collapse of the
magnetic field around this coil.
● When these contacts break, a high voltage current of 20,000-25,000 volts
passes through the secondary winding. Then, the current flows through the
high-tension cable and reaches the distributor cap, which moves along the
drive shaft’s direction. Its movements are aligned with the high-tension cables
corresponding to each spark plug. This alignment enables the cam lobes to
open all contact points after each compression stroke of the cylinder. This lets
the high-voltage current pass to the respective spark plug, ultimately creating
a spark.
You might also like
- Sec7a SmootherDocument219 pagesSec7a SmootherJipsonCueva100% (15)
- Electronics for Artists: Adding Light, Motion, and Sound to Your ArtworkFrom EverandElectronics for Artists: Adding Light, Motion, and Sound to Your ArtworkRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- A Guide to the Home Electric System: Home Guide Basics Series, #2From EverandA Guide to the Home Electric System: Home Guide Basics Series, #2No ratings yet
- Free Energy GeneratorsDocument3 pagesFree Energy GeneratorsYogesh25% (4)
- Defination of Ignition SystemDocument28 pagesDefination of Ignition SystemDawood KhanNo ratings yet
- Automotive Ignition SystemDocument8 pagesAutomotive Ignition SystemA A.DevanandhNo ratings yet
- Ignition System FundamentalsDocument22 pagesIgnition System FundamentalsGin Laguitao100% (2)
- 3.study of Ignition SystemDocument10 pages3.study of Ignition SystemShridhar RaskarNo ratings yet
- 05-737-800 Ramp & Transit FuelDocument90 pages05-737-800 Ramp & Transit FuelNicolas SalNo ratings yet
- Motoring Catalogue 2021Document108 pagesMotoring Catalogue 2021cegb81No ratings yet
- P - Automotive Ignition System Service RevisedDocument29 pagesP - Automotive Ignition System Service Reviseddmc constructionNo ratings yet
- Worldwide Engineering Standards: Corrosion Performance SpecificationDocument8 pagesWorldwide Engineering Standards: Corrosion Performance SpecificationAkmal Nizametdinov100% (1)
- Ignition SystemDocument43 pagesIgnition SystemHAMZA YOUSAFNo ratings yet
- Perkins Parts BookDocument54 pagesPerkins Parts BookKoppertPower83% (23)
- Ignition SystemDocument5 pagesIgnition SystemPankaj GauravNo ratings yet
- Starting and IgnitionDocument9 pagesStarting and IgnitionshyamsundarsrNo ratings yet
- TM 9-6115-464-12 Mep-004a, Mep-103a, Mep-113aDocument365 pagesTM 9-6115-464-12 Mep-004a, Mep-103a, Mep-113aAdvocate100% (1)
- Ignition SystemSDocument18 pagesIgnition SystemSADKMARNo ratings yet
- Fluorescent Lighting FixtureDocument17 pagesFluorescent Lighting FixtureelyNo ratings yet
- Components of The Ignition SystemDocument5 pagesComponents of The Ignition SystemJaston MwicheNo ratings yet
- Ignition SystemDocument10 pagesIgnition SystemParag100% (1)
- Working Principle of A Tube LightDocument3 pagesWorking Principle of A Tube LightYassir ButtNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.10213Document6 pagesExperiment No.10213nithinNo ratings yet
- Information Sheet 5.1 Fluorescent Lighting FixturesDocument17 pagesInformation Sheet 5.1 Fluorescent Lighting FixturesJhobhel Christopher GalivoNo ratings yet
- Battery Ignition SystemDocument2 pagesBattery Ignition SystemAmit Singh DehuryNo ratings yet
- Ignition SystemDocument43 pagesIgnition SystemBreech EdubasNo ratings yet
- BEE Lab Manual - Exp-4-NewDocument11 pagesBEE Lab Manual - Exp-4-NewImchaulNo ratings yet
- Secondary CircuitDocument4 pagesSecondary CircuitIrfan Khan0% (1)
- Chapter 9 New 1Document81 pagesChapter 9 New 1Minn Nyi SheinNo ratings yet
- Artificial Sources of LightDocument3 pagesArtificial Sources of LightjdipbhadraNo ratings yet
- Conventional Ignition SystemrevDocument20 pagesConventional Ignition SystemrevSuparman St0% (2)
- ECNG Design Project - Year 1Document38 pagesECNG Design Project - Year 1kurmakkNo ratings yet
- Working Principle of Arc LampDocument8 pagesWorking Principle of Arc LamphimNo ratings yet
- 12 Volt Fluorescent Lamp DriversDocument8 pages12 Volt Fluorescent Lamp DriversDedy SuhendraNo ratings yet
- Ignition SystemDocument8 pagesIgnition SystemAsraNo ratings yet
- Battery Coil Ignition SystemDocument4 pagesBattery Coil Ignition Systemaravinth53n_72539869No ratings yet
- Tle 9Document3 pagesTle 9Lilian Laurel Cariquitan50% (2)
- Electronic Ballast Fundamentals: Dr. Bryan M.H. Pong Hong Kong UniversityDocument23 pagesElectronic Ballast Fundamentals: Dr. Bryan M.H. Pong Hong Kong UniversityoneratoNo ratings yet
- The Purpose of The Ignition System Is To Light The FuelDocument25 pagesThe Purpose of The Ignition System Is To Light The FuelNuno CunhaNo ratings yet
- A Fuse Tubelight Glower Without Any Electric ChokeDocument25 pagesA Fuse Tubelight Glower Without Any Electric ChokePrints BindingsNo ratings yet
- Parts of Ignition SystemDocument16 pagesParts of Ignition SystemAnthony ArgandaNo ratings yet
- Ignition SystemDocument37 pagesIgnition SystemDhanu MalarNo ratings yet
- Electronic Ignition1 Ed.15-06-18Document27 pagesElectronic Ignition1 Ed.15-06-18collins arogoNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument5 pagesIntroductionHarsh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Ignition System Video (STUDENTS)Document4 pagesIgnition System Video (STUDENTS)9hhhhgxbzxNo ratings yet
- Camera Flash WorkDocument10 pagesCamera Flash WorkajgoluNo ratings yet
- Iiiumination4 Tube LightDocument11 pagesIiiumination4 Tube LightPushpendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Working of TubelightDocument2 pagesWorking of Tubelightjsrilakshmi42720% (2)
- Electronic Ballast FundamentalsDocument23 pagesElectronic Ballast Fundamentalshyu2123No ratings yet
- Tube Light WordDocument21 pagesTube Light WordMuniyasamyNo ratings yet
- Types of Fluorescent LightsDocument3 pagesTypes of Fluorescent LightsTowfiqNo ratings yet
- Ignition SystemDocument8 pagesIgnition Systemgood friendNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document89 pagesChapter 9Si Thu AungNo ratings yet
- 12 - IgnitonDocument18 pages12 - IgnitonBharath Kumar GoudNo ratings yet
- Illumination 2Document20 pagesIllumination 2Waqas AhmadNo ratings yet
- Distributor CamDocument3 pagesDistributor CamJovy0% (1)
- Laser Ignition SystemDocument26 pagesLaser Ignition Systemkrishnasinghrs4546No ratings yet
- Group-2 Two and Three Wheeled Vehicle Assignment PresentationDocument20 pagesGroup-2 Two and Three Wheeled Vehicle Assignment PresentationTäð Œvê MîðNo ratings yet
- The Light Bulb: The Concept of LighteningDocument15 pagesThe Light Bulb: The Concept of LighteningOmar Reda Abdel Hakim El saaedNo ratings yet
- EXP5Document4 pagesEXP5Rajesh GangwarNo ratings yet
- What Is The Use of Choke in Florescent TubesDocument7 pagesWhat Is The Use of Choke in Florescent Tubessumanta1981100% (2)
- Battery Ignition SystemDocument4 pagesBattery Ignition SystemJenamae Ashly HernandezNo ratings yet
- Handbook: E LightingDocument1 pageHandbook: E LightingreacharunkNo ratings yet
- Citation CJ4 - Checklist Working TitleDocument3 pagesCitation CJ4 - Checklist Working TitlePhilippe MagnoNo ratings yet
- Xylo MumbaiDocument5 pagesXylo Mumbaibwroy100% (2)
- Wireless Automation - ABBDocument16 pagesWireless Automation - ABBajit_ahuja1737No ratings yet
- M15.16 Turbo Prop Engines Tham KhaoDocument7 pagesM15.16 Turbo Prop Engines Tham KhaoMinh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Supra 6xx - 7xx Mod 99 (62-10483) PDFDocument33 pagesSupra 6xx - 7xx Mod 99 (62-10483) PDFj_gabrielflores100% (2)
- Autocar UK TruePDF-13 May 2020 PDFDocument84 pagesAutocar UK TruePDF-13 May 2020 PDFRemus P. PecilaNo ratings yet
- FM-Mazda PDF-23 06 08Document2 pagesFM-Mazda PDF-23 06 08Felix AustenNo ratings yet
- Marketing Management (Chapter 7)Document26 pagesMarketing Management (Chapter 7)Hamidul IslamNo ratings yet
- Volvo V40 Owner's ManualDocument8 pagesVolvo V40 Owner's ManualFábio MagnoNo ratings yet
- 070.450-IOM XJF 2013-11 Rev 2022-03Document38 pages070.450-IOM XJF 2013-11 Rev 2022-03Mohamed HeshamNo ratings yet
- Capability Statement 1638383760Document8 pagesCapability Statement 1638383760Ryan AldermanNo ratings yet
- Automotive ResistancesDocument13 pagesAutomotive ResistancesSweetiSharmaNo ratings yet
- Stagecoach East Midlands: (PB0001484, PF0001611, PF0007038)Document18 pagesStagecoach East Midlands: (PB0001484, PF0001611, PF0007038)Nathan AmaizeNo ratings yet
- Warn Xd9000 Winch Replacement Parts List Warn Xd9000 Winch Replacement Parts ListDocument2 pagesWarn Xd9000 Winch Replacement Parts List Warn Xd9000 Winch Replacement Parts ListTegal jatiNo ratings yet
- Nano Over ViewDocument15 pagesNano Over ViewNaveen BansalNo ratings yet
- Passive-voice#1901010030#Muhammad Ziad AlfianDocument3 pagesPassive-voice#1901010030#Muhammad Ziad Alfianyusuf hijriahNo ratings yet
- Datasheet Grupo Generador C700D5Document3 pagesDatasheet Grupo Generador C700D5hrsciberNo ratings yet
- XC-G Series Servo BrochureDocument3 pagesXC-G Series Servo Brochurejohnsuca81100% (1)
- Digital MarketinggDocument14 pagesDigital Marketinggtanya singhNo ratings yet
- Wilden PS820 Pump SpecificationDocument28 pagesWilden PS820 Pump SpecificationSergey KichenkoNo ratings yet
- World Series: Conforms To Power Supply Voltages in Asia Induction Motors Reversible Motors Electromagnetic Brake MotorsDocument33 pagesWorld Series: Conforms To Power Supply Voltages in Asia Induction Motors Reversible Motors Electromagnetic Brake MotorsdikdikNo ratings yet
- Development of A New Traction ControlDocument12 pagesDevelopment of A New Traction ControlMozãoFragaNo ratings yet
- TVC - 315+000 7 Days Hourly WiseDocument14 pagesTVC - 315+000 7 Days Hourly Wiseprabhu chand alluriNo ratings yet
- Harley Davidson: Motorcycle Manufacturer or Financing Company? Case StudyDocument5 pagesHarley Davidson: Motorcycle Manufacturer or Financing Company? Case StudyHarsh MNo ratings yet