Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Aldehyde Ketones and Carboxylic Acid
Uploaded by
sarthakyedlawar04Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Aldehyde Ketones and Carboxylic Acid
Uploaded by
sarthakyedlawar04Copyright:
Available Formats
CARBOXYLIC ACIDS ALDEHYDES AND KETONES
ALDEHYDE, KETONES AND
CARBOXYLIC ACID
STRUCTURE USES GENERAL FORMULA CLASSIFICATION
R - C - OH
. Rubber, Textiles.
O . Food Industry. Aldehyde: Ketones
Aliphatic Aromatic
. Manufacture of O O
Soap and Detergent.
CLASSIFICATION R-C-H R - C - R'
where R is alkyl and H is where R and R' can be
Hydrogen. same or different.
Aliphatic Aromatic
CH3COOH PREPARATIONS CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
COOH CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
PREPARATIONS . Esterification . Oxidation of alcohol Aldehyde > Ketones
RCOOH + R ' OH
RCOOR '+ H 2 O K 2 Cr2 O 7 + H 2 SO 4
1° Alcohol
→ Aldehyde 1
Re activity ∝
. Ring Substitution in Aromatic Acids: K Cr O + H SO
2° Alcohol
2 2 7 2 4
→ Ketone stearic factor and
Odour: Lower Aldehyde have an
. Oxidation of 1° alcohols COOH group is deactivating and K 2 Cr2 O 7 + H 2 SO 4 impleasant odour. electronic factror
(i)alk. KMnO
R − CH 2 OH
→ RCHO + H 2 O
RCH 2 OH
+
4 → R − COOH meta directing. COOH K Cr O + H SO
(ii) H 3 O R − CH(OH)R '
2 2 7 2 4
→ R − CO − R '+ H 2 O
2° alcohol
Br2 Physical State: HCHO is a gas. All Nucleophilic Addition-reaction
. Hydrolysis of Nitriles and Amides
+ COOH ∆ . Ozonolysis of alkenes other aldehyde and ketone upto C11
H or
R − C ≡ N + 2H 2 O → RCOOH + NH 3
FeBr3,
Br OH
− H 2 O, Zn are volatile liquids. C=O + CN C
OH CH 3 − CH = CH − CH 3 + O 3
→ 2CH 3 CHO CN
COOH
. Hydrolysis of Esters . From Gem-Dihalides:
H+ Solubility: Larger Carbonyl compounds SO2Na
RCOOR '+ H 2 O → RCOOH + R ' OH R' C=O + NaHSO3 C
Conc. HNO3 aq. KOH
R' are soluble in water due to the OH
NO2 R-C-Cl →
. From Grignard Reagent Conc. H2SO4 ∆ Or Ba(OH) 2
R-C=O formation of H-bond.
. Reduction of Carboxylic Acid Cl C=O + H2N-Z C=N-z+H2O
Dry ether
CO 2 + RMgBr → RCOOH + Mg(OH)Br (Aldehyde when Boiling Point and Melting Point: Boiling
+ H , H2O
O R' = H Ketone when Point or Melting point ∝ Molecular
(i) LiAlH /ether R' = alkyl group) weight
R-C-OH
4
+
→ R − CH 2 OH
(ii) H 3 O
. Hydroboration Oxidation of Alkynes 1 Clemmensen Reduction:
∝
Branching
. Decarboxylation of Carboxylic Acid B2H6
→ R-C=C-H Zn − Hg
O
R-C≡C-H THF C=O →
HCl
CH2 + H2O
Terminal alkyne H BH2 Eue to electron donating alkyl group
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES NaOH or
R-C-OH
CaO
→ R − H + Na 2 CO 3 -
group ketones have higher boiling point
H2O2 OH-
than aldehye.
. Reaction involving cleavage of
R-CH2=C-H R-C=C-H
-OH group Reactivity: It depends on the nature Wolff-kishner reduction
O O H OH of alkyl group. Smaller the group,
. Physical State: Polar Substances soluble in (i) NH − NH
R-C-NH2 . Rosenmund Reduction more reactive will be compound. C=O
2 2
KOH/ethyl glycol
→ CH2 + N2
organic solvents.
O O
. Acidity: The acidic character is due to the H , Pd-BaSO
R-C-OH R-COCl R-C-Cl
2 4
→ R-C-H
presence of resonance.
⊕ O DISTINCTION TEST FOR Aldol Condensation
: :
R-C-O-H R-C-OH
(R-CO)2O ALDEHYDE 2CH3CHO CH3CH(OH)CH2CHO
:O O . Hell-volhard Zelinsky Reaction
:
(i) X , Re d P
R-CH 2 -OH
2 → R − CH(x)COOH TEST ALDEHYDE KETONES ∆-H2O
. Boiling Points: High boiling point due to (ii)H O 2
intermolecular hydrogen bonding. DISTINCTION TEST Schiff's Pink No colour
FOR CARBOXYLIC ACID reagent Colour CH3-CH=CH-CHO
COMPARISON OF METLING AND BOILING POINT OF ACIDIC ORDER
Fehling's Red ppt. No ppt.
AROMATIC AND ALIPHATIC ACID
. Brisk effervescence of CO2 gas with solution Cannizaro reaction
NaHCO3
. Melting Point and Boiling Point of aromatic Tollen's Silver No ppt.
acid greater than aliphatic acid. Caboxylic Acid > Phenol > Alcohol . Gives buff coloured ppt. with FeCl3
Conc. KOH
2HCHO → CH3OH + HCOOK
reagent Mirror
You might also like
- ProjectDocument16 pagesProjectDebashis Ghosh50% (2)
- Biology Project-Drugs and Alcohol AbuseDocument23 pagesBiology Project-Drugs and Alcohol AbuseDeepika78% (18)
- Bio Investigatory ProjectDocument18 pagesBio Investigatory ProjectJhilik ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ProjectDocument18 pagesChemistry ProjectAnurup ChattopadhyayNo ratings yet
- Oxalate Ions Presenant in Guava Fruit Other Stages of Ripening.Document24 pagesOxalate Ions Presenant in Guava Fruit Other Stages of Ripening.अभय भधौरीयाNo ratings yet
- Jayen BioDocument16 pagesJayen BioJayenNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Potash AlumDocument11 pagesPreparation of Potash AlumIsha .SNo ratings yet
- Investigatory Project ChemistryDocument22 pagesInvestigatory Project Chemistryakshaya100% (1)
- Chemistry Investigatory ProjectDocument4 pagesChemistry Investigatory ProjectSiddharth NagarajNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Investigatory On Presence of Oxlate Ion in GuavaDocument16 pagesChemistry Investigatory On Presence of Oxlate Ion in GuavaMaanChavan100% (1)
- Chemistry Investigatory ProjectDocument15 pagesChemistry Investigatory ProjectAishwarya BabuNo ratings yet
- Study of Quantity of Casein Present in Different Samples of Milk Chemistry Investigatory Project Class Xii Cbse SanjibDocument10 pagesStudy of Quantity of Casein Present in Different Samples of Milk Chemistry Investigatory Project Class Xii Cbse Sanjibavishekthakur9091100% (2)
- Chemistry ProjectDocument9 pagesChemistry ProjecttripathiNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Shampoo - 12Document20 pagesAnalysis of Shampoo - 12Faima A.50% (2)
- Bio Investigatory ProjectDocument18 pagesBio Investigatory ProjectJhilik Choudhury100% (3)
- Kendriya Vidhyalay NO. 2 Biology Investigatory Project: Topic-Microbes in Human WelfareDocument25 pagesKendriya Vidhyalay NO. 2 Biology Investigatory Project: Topic-Microbes in Human WelfareVaishnavi SongaraNo ratings yet
- Class 12 ProjectDocument22 pagesClass 12 Projectkunal goswamiNo ratings yet
- Drug AdiictionDocument17 pagesDrug AdiictionRahul PatelNo ratings yet
- Guava Fruitguava Fruitguava Fruitguava Fruitguava Fruitguava Fruitguava Fruitguava Fruitguava Fruitguava Fruitguava Fruitguava Fruitguava Fruitguava Fruitguava Fruitguava FruitDocument19 pagesGuava Fruitguava Fruitguava Fruitguava Fruitguava Fruitguava Fruitguava Fruitguava Fruitguava Fruitguava Fruitguava Fruitguava Fruitguava Fruitguava Fruitguava Fruitguava FruitAditya Soni100% (3)
- Study of Oxalate Ion Content in Guava Fruit - VelDocument15 pagesStudy of Oxalate Ion Content in Guava Fruit - VelSubbukbalaji LakshmiNo ratings yet
- To Study The Quantity Case in Present in Different Sample of MilkDocument7 pagesTo Study The Quantity Case in Present in Different Sample of Milkbelly4u100% (2)
- Chemistry Project Class 12Document13 pagesChemistry Project Class 12chemistry projectNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project On Study of Effect of Potassium Bisulphite As Food Pre Servative Under Various ConditionsDocument21 pagesChemistry Project On Study of Effect of Potassium Bisulphite As Food Pre Servative Under Various ConditionsAnurag YadavNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Investigatory ProjectDocument13 pagesChemistry Investigatory ProjectAshrayee Wasnik100% (1)
- Krish Presence-of-oxalate-ions-in-Guava-Chemistry-Investigatory-ProjectDocument10 pagesKrish Presence-of-oxalate-ions-in-Guava-Chemistry-Investigatory-ProjectAman TripathiNo ratings yet
- Presence of Oxalate Ions in Guava ChemisDocument10 pagesPresence of Oxalate Ions in Guava ChemispunyanshNo ratings yet
- Mbs Public School: Topic: Study The Presence of Oxalate Ions in Guava Fruit at Different Stages of RipeningDocument15 pagesMbs Public School: Topic: Study The Presence of Oxalate Ions in Guava Fruit at Different Stages of RipeningSwaraj Patel100% (1)
- Presence of Oxalative Ions in GuavaDocument11 pagesPresence of Oxalative Ions in GuavaGaurav Chaudhary100% (3)
- INVETIGATORY Project Chemistry Preparation of Soymilk and Comparison With Real MilkDocument16 pagesINVETIGATORY Project Chemistry Preparation of Soymilk and Comparison With Real MilkShobhit mishra100% (1)
- Chem Investigatory ProjectDocument27 pagesChem Investigatory ProjectRoshini Gopusankar100% (1)
- Chemistry GuavaDocument13 pagesChemistry GuavaAnbuNo ratings yet
- To Determine The Amount of Casein in Different Samples of MilkDocument14 pagesTo Determine The Amount of Casein in Different Samples of MilkDETECTIVE100% (1)
- Chemistry Project On Study of Rate of Fermentation of JuicesDocument9 pagesChemistry Project On Study of Rate of Fermentation of JuicesAlexis Trevino75% (4)
- Study of Quantity of Casein Present in Various Sample of MilkDocument12 pagesStudy of Quantity of Casein Present in Various Sample of MilkAman RoyNo ratings yet
- "To Find The Quantity of Caesin in Different Samples of Milk" Chemistry Investigatory ProjectDocument16 pages"To Find The Quantity of Caesin in Different Samples of Milk" Chemistry Investigatory ProjectShivendra Tripathi100% (2)
- Preparation of Potash AlumDocument14 pagesPreparation of Potash AlumXI-A Vishal BishnoiNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study of Rate of Fermentation of Fruit JuicesDocument27 pagesComparative Study of Rate of Fermentation of Fruit Juicesajay qureshi0% (1)
- Chemistry ProjectDocument19 pagesChemistry ProjectAmarjeet Singh0% (1)
- Chemistry Project Class XIIDocument11 pagesChemistry Project Class XIIPherands Pherands0% (1)
- Presence of Oxalate Ions in Guava Chemistry Investigatory ProjectDocument11 pagesPresence of Oxalate Ions in Guava Chemistry Investigatory ProjectRonit GauravNo ratings yet
- Presence of Oxalative Ions in GuavaDocument11 pagesPresence of Oxalative Ions in GuavaAbhishek SinghNo ratings yet
- Preparation of An Alum From Scrap Aluminium PDFDocument11 pagesPreparation of An Alum From Scrap Aluminium PDFshiv payasi0% (1)
- Chem ProjectDocument17 pagesChem ProjectMayankNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Investigatory Project ABSDocument18 pagesChemistry Investigatory Project ABS11th Batch LegendzNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project Class XIIDocument15 pagesChemistry Project Class XIIAadarsh MishraNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study of Rate of Fermentation of Fruit JuicesDocument30 pagesComparative Study of Rate of Fermentation of Fruit JuicesSubrat KumarNo ratings yet
- Study of Quantity of Casein in Different Sample of MilkssDocument16 pagesStudy of Quantity of Casein in Different Sample of MilkssManan Jain71% (7)
- Chemistry Investigatory ProjectDocument14 pagesChemistry Investigatory ProjectIshita Singh100% (1)
- ChemistryDocument12 pagesChemistrySouptik Pal100% (1)
- Amount of Casein in Milk Chemistry Project (FINAL)Document15 pagesAmount of Casein in Milk Chemistry Project (FINAL)Brijesh Kandolkar100% (3)
- Chemistry Investigatory Project 2020-2021Document23 pagesChemistry Investigatory Project 2020-2021S100% (1)
- Aahil's Project PDFDocument13 pagesAahil's Project PDFDhanush KumarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project (XII)Document21 pagesChemistry Project (XII)Anwesha Kar, XII B, Roll No:110% (4)
- Study of Rates of Fermentation (Autorecovered)Document9 pagesStudy of Rates of Fermentation (Autorecovered)SreyasNo ratings yet
- Aim Is To Find The Determination of Contents of Tooth PowderDocument4 pagesAim Is To Find The Determination of Contents of Tooth PowderHargur Bedi71% (7)
- Chemistry ProjectDocument15 pagesChemistry ProjectArjun Chauhan50% (2)
- Class 12th Chemistry Project On Investigatory Test On GuavaDocument21 pagesClass 12th Chemistry Project On Investigatory Test On GuavaSulogna Dutta0% (1)
- Chemistry Project: Rusting of IronDocument27 pagesChemistry Project: Rusting of IronLateka GopiNo ratings yet
- Determination of The Oxalate Ions in Guava Fruit at Different Stages of Its RipeningDocument5 pagesDetermination of The Oxalate Ions in Guava Fruit at Different Stages of Its RipeningSachidanand Singh44% (9)
- Aldehyde, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidDocument1 pageAldehyde, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidGargi PathakNo ratings yet
- CLS ENG 23 24 XII Che Target 1 Level 1 Chapter 2Document43 pagesCLS ENG 23 24 XII Che Target 1 Level 1 Chapter 2TirthNo ratings yet
- P - Ch-28 - Communication SystemsDocument8 pagesP - Ch-28 - Communication Systemssarthakyedlawar04No ratings yet
- Rotational MotionDocument1 pageRotational Motionsarthakyedlawar04No ratings yet
- AIATS For First Step JEE (ADV) - Phase-3&4 Test-2A-P2 Code-H Sol 10-03-2024Document7 pagesAIATS For First Step JEE (ADV) - Phase-3&4 Test-2A-P2 Code-H Sol 10-03-2024sarthakyedlawar04No ratings yet
- Newton - S LawDocument1 pageNewton - S Lawsarthakyedlawar04No ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument1 pageChemical Bonding and Molecular Structuresarthakyedlawar04No ratings yet
- A3 Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties MinDocument1 pageA3 Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties MinKarthikeyan LakshmananNo ratings yet
- Oscillations MindmapDocument1 pageOscillations Mindmapsarthakyedlawar04No ratings yet
- Thermodynamics-1 MindmapDocument1 pageThermodynamics-1 Mindmapsarthakyedlawar04No ratings yet
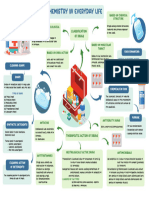
- Chemistry in Everyday LifeDocument1 pageChemistry in Everyday Lifesarthakyedlawar04No ratings yet
- Environmental Chemistry.Document1 pageEnvironmental Chemistry.sarthakyedlawar04No ratings yet
- 6 General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements 1Document1 page6 General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements 1Raunak JayaswalNo ratings yet
- EquilibriumDocument1 pageEquilibriumsarthakyedlawar04No ratings yet
- Alcohol, Phenol - EthersDocument1 pageAlcohol, Phenol - Etherssarthakyedlawar04No ratings yet
- Offline Exam CBT Exam: For Any Queries Email Us At: Dlp@allen - Ac.in or Call Us: 0744-3510275/2750275Document1 pageOffline Exam CBT Exam: For Any Queries Email Us At: Dlp@allen - Ac.in or Call Us: 0744-3510275/2750275Varun ChandelNo ratings yet
- Section - E: Subjective Type: G V T GT VDocument32 pagesSection - E: Subjective Type: G V T GT Vsarthakyedlawar04No ratings yet