Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2.0 Seperation Technique 2022 2
Uploaded by
sfOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2.0 Seperation Technique 2022 2
Uploaded by
sfCopyright:
Available Formats
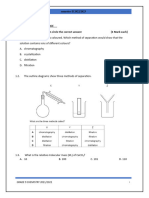
Rf =
known substances distance travelled by solvent
(b) pure and impure substances
Cambridge IGCSE A* Chemistry Notes Ms Joan Yuen|vbest.edu.my
12.4 Separation and purification
Core Supplement
1 Describe and explain methods of separation and
purification using:
(a) a suitable solvent
(b) filtration
(c) crystallisation
(d) simple distillation
(e) fractional distillation
2 Suggest suitable separation and purification
techniques, given information about the
substances involved
3 Identify substances and assess their purity using
melting point and boiling point information
Methods of SEPERATION
12.5 Identification of ions and gases
Core Supplement
1 Describe tests to identify the anions:
(a) carbonate, CO32–, by reaction with dilute acid
and then testing for carbon dioxide gas
(b) chloride, Cl –, bromide, Br –, and iodide, I –, by
acidifying with dilute nitric acid then adding
aqueous silver nitrate
(c) nitrate, NO3–, reduction with aluminium foil
and aqueous sodium hydroxide and then
testing for ammonia gas
(d) sulfate, SO42–, by acidifying with dilute nitric
acid and then adding aqueous barium nitrate
(e) sulfite, SO32–, by reaction with acidified
aqueous potassium manganate(VII)
Mixtures of liquids
36 1. Immiscible liquids can be separated using
www.cambridgeinternational.org/igcse Back to contents page
a ……………………….. ………………………or by decanting (pouring carefully)
2.0 Separation Technique| Notes v3.18| Google: vbest 1
Cambridge IGCSE A* Chemistry Notes Ms Joan Yuen|vbest.edu.my
Filtration
1. Used to separate an ………………………. solid from a mixture of the solid and liquid / solution
ü e.g. sand from a mixture of sand and salt water
2.0 Separation Technique| Notes v3.18| Google: vbest 2
Cambridge IGCSE A* Chemistry Notes Ms Joan Yuen|vbest.edu.my
Evaporation and Crystallisation
2.0 Separation Technique| Notes v3.18| Google: vbest 3
Cambridge IGCSE A* Chemistry Notes Ms Joan Yuen|vbest.edu.my
Making solid copper(II) sulfate crystal
2.0 Separation Technique| Notes v3.18| Google: vbest 4
Cambridge IGCSE A* Chemistry Notes Ms Joan Yuen|vbest.edu.my
2.0 Separation Technique| Notes v3.18| Google: vbest 5
Cambridge IGCSE A* Chemistry Notes Ms Joan Yuen|vbest.edu.my
Simple Distillation
1. Used to separate …………………………….……………… (solvent) from solution , leaving the solute behind.
ü e.g. water from a solution of salt water
2.0 Separation Technique| Notes v3.18| Google: vbest 6
Cambridge IGCSE A* Chemistry Notes Ms Joan Yuen|vbest.edu.my
Fractional distillation
1. Used to separate two or more liquids that are miscible with one another :
ü With ……………………………….…………… boiling point
2. The solution is heated :
ü the substance with the ………………………………….. boiling point will rise and EVAPORATE first
ü and vapours will pass through a …………………………….….……………..,
ü where they COOL and …………………..,
ü turning into a LIQUID that will be collected in a beaker
2.0 Separation Technique| Notes v3.18| Google: vbest 7
Cambridge IGCSE A* Chemistry Notes Ms Joan Yuen|vbest.edu.my
Q# 3/ iGCSE Chem/2015march/Paper 6/
2.0 Separation Technique| Notes v3.18| Google: vbest 8
Cambridge IGCSE A* Chemistry Notes Ms Joan Yuen|vbest.edu.my
Q# 7/ iGCSE Chem/2014s/Paper 6/
2.0 Separation Technique| Notes v3.18| Google: vbest 9
Cambridge IGCSE A* Chemistry Notes Ms Joan Yuen|vbest.edu.my
Q# 13/ iGCSE Chem/2011s/Paper 6/
2.0 Separation Technique| Notes v3.18| Google: vbest 10
Cambridge IGCSE A* Chemistry Notes Ms Joan Yuen|vbest.edu.my
Q# 23/ iGCSE Chem/2007s/Paper 6/
2.0 Separation Technique| Notes v3.18| Google: vbest 11
Cambridge IGCSE A* Chemistry Notes Ms Joan Yuen|vbest.edu.my
Q# 34/ iGCSE Chem/2003/w/Paper 6/
2.0 Separation Technique| Notes v3.18| Google: vbest 12
Cambridge IGCSE A* Chemistry Notes Ms Joan Yuen|vbest.edu.my
Q# 36/ iGCSE Chem/2003s/Paper 6/
2.0 Separation Technique| Notes v3.18| Google: vbest 13
Cambridge IGCSE A* Chemistry Notes Ms Joan Yuen|vbest.edu.my
Q# 20/ iGCSE Chem/2009s/Paper 6/
2.0 Separation Technique| Notes v3.18| Google: vbest 14
Cambridge IGCSE A* Chemistry Notes Ms Joan Yuen|vbest.edu.my
Q# 22/ iGCSE Chem/2008s/Paper 6/
2.0 Separation Technique| Notes v3.18| Google: vbest 15
Cambridge IGCSE A* Chemistry Notes Ms Joan Yuen|vbest.edu.my
2020 mJ 63 2
1 A sample of rock salt contains sodium chloride and sand.
Sodium chloride is soluble in water. Sand is insoluble in water.
A student obtained dry crystals of pure sodium chloride from a lump of rock salt.
These are some of the steps the student used.
step 1 step 2 step 3
sand
rock salt
A B
grind the rock salt add the rock salt to water and heat filter the mixture
into smaller pieces while stirring with a glass rod
(a) Name the apparatus labelled A in step 1.
.............................................................................................................................................. [1]
(b) Explain why the mixture is heated and stirred in step 2.
.............................................................................................................................................. [1]
(c) (i) Name the apparatus labelled B in step 3.
....................................................................................................................................... [1]
(ii) State the scientific term for the sand left on the filter paper in step 3.
....................................................................................................................................... [1]
(d) Describe what the student must do after step 3 to obtain dry crystals of pure sodium chloride.
....................................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................. [3]
[Total: 7]
© UCLES 2020 0620/63/M/J/20
2.0 Separation Technique| Notes v3.18| Google: vbest 16
Cambridge IGCSE A* Chemistry Notes Ms Joan Yuen|vbest.edu.my
2017 ON 61 2
1 A student reacted dilute hydrochloric acid with zinc oxide to prepare zinc chloride solution.
The diagram shows part of the procedure.
zinc chloride
solution
unreacted
zinc oxide
funnel
.........................................
(a) Complete the box to name the apparatus. [1]
(b) Which of the reactants was in excess?
.............................................................................................................................................. [1]
(c) (i) Name the separation process this apparatus is used for.
....................................................................................................................................... [1]
(ii) Suggest why this apparatus would not work.
.............................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................... [1]
(d) Describe how crystals of zinc chloride could be obtained from the zinc chloride solution.
....................................................................................................................................................
....................................................................................................................................................
.............................................................................................................................................. [3]
[Total: 7]
© UCLES 2017 0620/61/O/N/17
2.0 Separation Technique| Notes v3.18| Google: vbest 17
Cambridge IGCSE A* Chemistry Notes Ms Joan Yuen|vbest.edu.my
2.0 Separation Technique| Notes v3.18| Google: vbest 18
Cambridge IGCSE A* Chemistry Notes Ms Joan Yuen|vbest.edu.my
An important aspect of chemistry is purity and methods of purifi
(a) Give an example of subtacation. used in everyday life which must be pure.
.............................................................................................................................................. [1]
(b) A list of techniques used to separate mixtures is given below.
chromatography rystall diffusion
evaporation filtratio
ltrationn fractional dis illatio simple distillation
(i) From the list, choose the most suitable technique to separate the following.
water from sea-water ..........................................................................................................
helium from a mixture of helium and methane ...................................................................
ethanol from a mixture of ethanol and propanol .................................................................
iron filings from a mixture of iron filings and water .............................................................
a mixture of two amino acids, glycine and alanine .............................................................
[5]
(ii) Describe how you would obtain a pure sample of copper(II) sulfate-5-water crystals from
a mixture of copper(II) sulfate-5-water with copper(II) oxide using some of the techniques
A list oflisted
techniques
above. used to separate mixtures is given
below. filtration
.............................................................................................................................................
diffusion
.............................................................................................................................................
fractional distillation
.............................................................................................................................................
simple distillation
.............................................................................................................................................
crystallisation
chromatography
....................................................................................................................................... [4]
From this list, choose the most suitable technique to separate the following mixtures. [Total: 10]
A technique may be used once, more than once or not at all.
(a) butane from a mixture of propane and butane ........................................................... [1]
(b) oxygen from liquid air ................................................................................................. [1]
(c) water from aqueous magnesium sulfate ..................................................................... [1]
(d) potassium chloride from aqueous potassium chloride ................................................ [1]
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com
(e) silver chloride from a mixture of silver chloride and water .......................................... [1]
(f) glucose from a mixture of glucose and maltose ......................................................... [1]
[Total: 6]
2.0 Separation Technique| Notes v3.18| Google: vbest 19
Cambridge IGCSE A* Chemistry Notes Ms Joan Yuen|vbest.edu.my
The following techniques are used to separate mixtures.
A simple distillation B fractional distillation C evaporation
D chromatography E filtration F diffusion
From this list, choose the most suitable technique to separate the following.
(a) methane from a mixture of the gases, methane and ethane .................. [1]
(b) water from aqueous magnesium sulfate .................. [1]
(c) glycine from a mixture of the amino acids, glycine and lysine ................... [1]
(d) iron filings from a mixture of iron filings and water .................. [1]
(e) zinc sulfate crystals from aqueous zinc sulfate .................. [1]
(f) hexane from a mixture of the liquids, hexane and octane .................. [1]
[Total: 6]
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com
2.0 Separation Technique| Notes v3.18| Google: vbest 20
You might also like
- Inorganic Reactions and Methods, Formation of CeramicsFrom EverandInorganic Reactions and Methods, Formation of CeramicsJim D. AtwoodNo ratings yet
- 0620 w02 QP 6 PDFDocument12 pages0620 w02 QP 6 PDFHendrawan SaputraNo ratings yet
- A Practical Approach to Water Conservation for Commercial and Industrial FacilitiesFrom EverandA Practical Approach to Water Conservation for Commercial and Industrial FacilitiesNo ratings yet
- B2 6.2.5 Organic Synthesis 2020-21Document27 pagesB2 6.2.5 Organic Synthesis 2020-21noornhhhNo ratings yet
- Full Thesis PDFDocument83 pagesFull Thesis PDFNewaz KabirNo ratings yet
- Nanotechnology Applications for Clean Water: Solutions for Improving Water QualityFrom EverandNanotechnology Applications for Clean Water: Solutions for Improving Water QualityNo ratings yet
- Durability Study of Low Calcium Fly Ash GeopolymerDocument8 pagesDurability Study of Low Calcium Fly Ash GeopolymerARNABNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Analysis of Flavor and Fragrance Volatiles by Glass Capillary Gas ChromatographyFrom EverandQualitative Analysis of Flavor and Fragrance Volatiles by Glass Capillary Gas ChromatographyNo ratings yet
- Final Project Report NayanaDocument40 pagesFinal Project Report NayanaNayana P BabuNo ratings yet
- Geological Sequestration of Carbon Dioxide: Thermodynamics, Kinetics, and Reaction Path ModelingFrom EverandGeological Sequestration of Carbon Dioxide: Thermodynamics, Kinetics, and Reaction Path ModelingNo ratings yet
- Determination of Carbon Dioxide Concentration of WaterDocument6 pagesDetermination of Carbon Dioxide Concentration of WaterShoumik LemonNo ratings yet
- Analisis Kation Dan Anion - 084 - Tri Ayu Sukma NingsihDocument82 pagesAnalisis Kation Dan Anion - 084 - Tri Ayu Sukma NingsihBani AsrorNo ratings yet
- SL PAPER 3 MockDocument24 pagesSL PAPER 3 MockIda Bagus Alit ManuabaNo ratings yet
- Fejiro Final Year ProjectDocument116 pagesFejiro Final Year ProjectOluwatobiloba IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Bioremediation of Heavy Metal in Crude Oil Contaminated Soil Using Isolated Indigenous Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Culture With e Coli De3 Bl21Document46 pagesBioremediation of Heavy Metal in Crude Oil Contaminated Soil Using Isolated Indigenous Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Culture With e Coli De3 Bl21omotola ayotundeNo ratings yet
- The Usage of Domestic Water Filtration Systems in MalaysiaDocument132 pagesThe Usage of Domestic Water Filtration Systems in MalaysiaAmirahNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Analysis of Urine Polluted Environment in FpnoDocument41 pagesBacterial Analysis of Urine Polluted Environment in FpnoekojamichaelNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 2ND Semester Final Exam Paper 2Document14 pagesGrade 9 2ND Semester Final Exam Paper 2dodoNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 2ND Semester Final Exam Paper 1Document14 pagesGrade 9 2ND Semester Final Exam Paper 1dodoNo ratings yet
- Ap Chem Lab 2Document8 pagesAp Chem Lab 2123123ᄋNo ratings yet
- Curtin Flyash GC-2Document107 pagesCurtin Flyash GC-2api-3850604No ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/62Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/62taimurmalik5562No ratings yet
- Ea Ceb 2093 Jan 2020 PDFDocument4 pagesEa Ceb 2093 Jan 2020 PDFDanial AimanNo ratings yet
- Univeristy of The Punjab, Lahore Chemistry (Sample Paper) Part-II A/2020Document2 pagesUniveristy of The Punjab, Lahore Chemistry (Sample Paper) Part-II A/2020MuhammadQasimNo ratings yet
- FYP Report-Finalized PDFDocument137 pagesFYP Report-Finalized PDFwong zhi chengNo ratings yet
- Adsorption Studies of Dyes Using Clay-Based and Activated CaDocument47 pagesAdsorption Studies of Dyes Using Clay-Based and Activated Camendoaja100% (1)
- CO Sequestration by Chlorella Vulgaris: Master of Technology in Chemical EngineeringDocument49 pagesCO Sequestration by Chlorella Vulgaris: Master of Technology in Chemical EngineeringR_M_M_No ratings yet
- Microbiologically Induced Calcium Carbonate Precipitation (Micp)Document35 pagesMicrobiologically Induced Calcium Carbonate Precipitation (Micp)Anandhu VenugopalNo ratings yet
- Ana Chem Practice Questions With AnswersDocument22 pagesAna Chem Practice Questions With AnswersMark Anthonni Masumpad100% (2)
- UntitledDocument60 pagesUntitled22ME38 yash PatilNo ratings yet
- 2019 Oct 2 IGCSE 27 2 PDFDocument16 pages2019 Oct 2 IGCSE 27 2 PDFnnnjafghnNo ratings yet
- 0620 - TQ - P3 - U3 - v2 - 3 Air and WaterDocument10 pages0620 - TQ - P3 - U3 - v2 - 3 Air and WaterShubhra MoreNo ratings yet
- 0653 s16 QP 62Document20 pages0653 s16 QP 62yuke kristinaNo ratings yet
- Lec2Jan0922Sedimentation PDFDocument41 pagesLec2Jan0922Sedimentation PDFABHIJEET NONDANo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument93 pagesUntitledijeoma NwajuakuNo ratings yet
- Major Project ReportDocument49 pagesMajor Project ReportMohini BhartiNo ratings yet
- Anal Chem Practice-1 - KeyDocument24 pagesAnal Chem Practice-1 - KeyARLIE JAY DACION100% (1)
- Analytical Chemistry Practice Questions 0001Document22 pagesAnalytical Chemistry Practice Questions 0001JasonTenebroso100% (4)
- Effects of High Water Reducing Admixtures On The Properties of Concrete Made With Quarry Dust As The Sole Fine AggregatesDocument61 pagesEffects of High Water Reducing Admixtures On The Properties of Concrete Made With Quarry Dust As The Sole Fine AggregatesEKWUE ChukwudaluNo ratings yet
- Map Induction Cel SolarDocument154 pagesMap Induction Cel SolarFernando LegendsNo ratings yet
- Science Final X 1mcqDocument51 pagesScience Final X 1mcqbhagyapatel9723No ratings yet
- 5070 s17 QP 41Document12 pages5070 s17 QP 41Waleed Bin AhmadNo ratings yet
- Acids and Alkali - 1 QSDocument4 pagesAcids and Alkali - 1 QSMr. SuitNo ratings yet
- Engineering Chemistry PDFDocument39 pagesEngineering Chemistry PDFYash NaiwarNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/61Document12 pagesCambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/61Jahangir KhanNo ratings yet
- Modified Guidelines For Geopolymer Concrete Mix Design Using Indian StandardDocument13 pagesModified Guidelines For Geopolymer Concrete Mix Design Using Indian StandardDl Divakar LNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument8 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Educationsarrah asgarNo ratings yet
- Barnett 2010Document55 pagesBarnett 2010Chris StillNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/62Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/62zoyaNo ratings yet
- DE 4th Sem ProjectDocument34 pagesDE 4th Sem Projectashish hingu100% (1)
- HL PAPER 3 MockDocument37 pagesHL PAPER 3 MockIda Bagus Alit ManuabaNo ratings yet
- Final - 1nd Semesterالدور الثانيDocument12 pagesFinal - 1nd Semesterالدور الثانيAli aliraqiNo ratings yet
- TEST BKC4543 Sem 1 20192020Document5 pagesTEST BKC4543 Sem 1 20192020mustaf mohamedNo ratings yet
- Artigo 4Document11 pagesArtigo 4nayaraprado22No ratings yet
- Carbon-Dot Project - IIDocument31 pagesCarbon-Dot Project - IIMAHIMA BAIDNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual For Engineering Chemistry Practical: First / Second Semester B.EDocument50 pagesLaboratory Manual For Engineering Chemistry Practical: First / Second Semester B.EDaizy GillNo ratings yet
- EE Labsheet 2020 SCCDocument6 pagesEE Labsheet 2020 SCCzeeshan arifNo ratings yet
- 10 Science Cbse Sample Paper MCQ 07Document6 pages10 Science Cbse Sample Paper MCQ 07Sucharita NahaNo ratings yet
- Removal of Heavy Metals From Electroplating Wastewater Using RiceDocument100 pagesRemoval of Heavy Metals From Electroplating Wastewater Using RicebagusdwipayanaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 - Time Dose Fractionation TDF ConceptsDocument3 pagesAssignment 1 - Time Dose Fractionation TDF Conceptsapi-299138743No ratings yet
- Tle 10 Agricrop Production Quarter 2 Week 8 Summative TestDocument5 pagesTle 10 Agricrop Production Quarter 2 Week 8 Summative TestRosalieMarCuyaNo ratings yet
- Section 2Document6 pagesSection 2Ancuta DanielaNo ratings yet
- AEIEDocument6 pagesAEIEarijit_ghosh_18No ratings yet
- Modi Bus Wale BrochureDocument15 pagesModi Bus Wale BrochureVeeresh RathodNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Power Bi TrainingDocument2 pagesMicrosoft Power Bi TrainingYazanMohamedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 The Hamsa (Udhav Gita)Document7 pagesChapter 13 The Hamsa (Udhav Gita)Vishnu Prakash NangathNo ratings yet
- ZXCTN Seamless MPLS (BGP LU) Principles and Applications - R1.1Document24 pagesZXCTN Seamless MPLS (BGP LU) Principles and Applications - R1.1kyi lwinNo ratings yet
- The Negative Impact of Cigarette Smoking: Mapeh (Health) 8-Quarter 4Document60 pagesThe Negative Impact of Cigarette Smoking: Mapeh (Health) 8-Quarter 4JOHN FRITS GERARD MOMBAYNo ratings yet
- Grabar FTPDocument6 pagesGrabar FTPSergio Martín CorderoNo ratings yet
- Activity Based CostingDocument30 pagesActivity Based CostingBalakrishna ChakaliNo ratings yet
- Diklofenac DietilaminDocument12 pagesDiklofenac DietilaminAnnisa FitrianaNo ratings yet
- Choose The Best Answer A, B, C, D, or E To Each Question.: Text 1: Questions No. 1 - 7Document8 pagesChoose The Best Answer A, B, C, D, or E To Each Question.: Text 1: Questions No. 1 - 7Wx Gaming100% (1)
- Literature ReviewDocument14 pagesLiterature Reviewniftiangautam70% (2)
- Individual Learning Monitoring PlanDocument2 pagesIndividual Learning Monitoring PlanJohnArgielLaurenteVictorNo ratings yet
- ArchitectureDocument268 pagesArchitectureAndrijaNo ratings yet
- Sarah Plain and Tall BookfileDocument63 pagesSarah Plain and Tall Bookfilexinying94100% (1)
- 7 - Modified Slenderness Ratio For Built-Up MembersDocument13 pages7 - Modified Slenderness Ratio For Built-Up Membersخوێندن لە ئەوروپاNo ratings yet
- Charlie-Rose Evans ResumeDocument3 pagesCharlie-Rose Evans Resumeapi-309085679No ratings yet
- Grade 6 PollutionDocument3 pagesGrade 6 PollutionNermine Mouallem75% (4)
- Cisco Catalyst Blade Switch 3020 For HP Getting Started GuideDocument36 pagesCisco Catalyst Blade Switch 3020 For HP Getting Started GuideAlgor333No ratings yet
- Blessed Is He, Who Has Seen' - The Power of Ritual-Viewing and Ritual Framing in EleusisDocument34 pagesBlessed Is He, Who Has Seen' - The Power of Ritual-Viewing and Ritual Framing in EleusisAndre Bambu100% (1)
- Self-Learning Home Task (SLHT) : KG Given To HelperDocument4 pagesSelf-Learning Home Task (SLHT) : KG Given To HelperCatherine AbabonNo ratings yet
- Ritual of LilithDocument0 pagesRitual of LilithDarely Sabbati100% (3)
- Chapter 5 Pallet Storage and Handling SystemsDocument40 pagesChapter 5 Pallet Storage and Handling SystemsPachm GrinsNo ratings yet
- Fee Circular 12Document2 pagesFee Circular 12ilyaskureshiNo ratings yet
- 3RD QUARTER SCIENCE 6 FRICTION Lesson ExemplarDocument5 pages3RD QUARTER SCIENCE 6 FRICTION Lesson ExemplarMargie RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Riph ReviewerDocument16 pagesRiph ReviewerREVECA AVIGAIL JOY SAMINNo ratings yet
- Preboring Works To DWall With Air-Lift & RCD Core Barrer - 17.6.14 PDFDocument18 pagesPreboring Works To DWall With Air-Lift & RCD Core Barrer - 17.6.14 PDFErick SmithNo ratings yet
- Corelli Trio Sonata Op.4 No.3 in A-major-HarpsichordDocument4 pagesCorelli Trio Sonata Op.4 No.3 in A-major-HarpsichordMatteo MignolliNo ratings yet