Professional Documents
Culture Documents
TAT1 S2 THANH Eight Word Classes
Uploaded by
Hải LinhOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
TAT1 S2 THANH Eight Word Classes
Uploaded by
Hải LinhCopyright:
Available Formats
WARM-UP
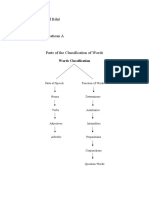
I. THE EIGHT WORD CLASSES / PARTS OF SPEECH:
1. Nouns
2. Pronouns
3. Verbs
4. Adjectives
5. Adverbs
6. Prepositions
7. Conjunctions
8. Determiners
II. Phrases & Clauses
III. Sentence Constituents and Verb Types
IV. Checkup
NUCE. 55 GIAI PHONG
1. NOUNS
Definition: Nouns are all the words that refer to people,
things, animals, plants, ideas, states, actions, etc...
e.g. teacher, book, flower, religion, beauty, swimming, etc.
Two groups of nouns:
- Countable nouns: teachers, books, dogs, flowers
- Uncountable nouns: money, staff, swimming, equipment,
etc.
NUCE. 55 GIAI PHONG
2. PRONOUNS
Definition: A pronoun is the word that is used to replace or refer to
the preceding noun in a passage.
Types of pronouns:
- Personal pronouns: I, you, we, they, he, she, it.
- Indefinite pronouns: any, some, none, nobody, all,
everybody, each, most, etc.
- Demonstrative pronouns: this, that, these, those
- Interrogative pronouns: who, what, how, when, where, why,
which.
- Relative pronouns: who / whom, whose, that, which, what.
NUCE. 55 GIAI PHONG
3. VERBS
Definition: A verb is a word used with a subject to state or describe what
someone or something does, what happens to them, or to give
information about them.
e.g. go, run, love, rise, do, see, tell, make, etc.
Groups of verbs:
- Intransitive verbs: Intransitive verbs do not take an object in a
sentence.
e.g. be, go, rise, sit, become, etc.
The sun always rises in the east
subject verb
- Transitive verbs: transitive verbs do take an object in a sentence:
e.g. make, do, build, watch, tell, see, etc.
People can see the sun in the daytime
subject verb object
NUCE. 55 GIAI PHONG
4. ADJECTIVES
Definition: an adjective is a word that explains or describe features or
states of a noun.
E.g. kind, tall, beautiful, right, difficult, stubborn, etc.
An adjective can modify a noun directly or describe a subject noun as the
complement.
- Attribute: She is a kind teacher
- Predicative: My English teacher is kind
NUCE. 55 GIAI PHONG
5. ADVERBS
Definition: An adverb is a word that describes a state or an action in more
detail by indicating manner, time, place, cause, or degree .
Role: An adverb can modify a verb, an adjective, another adverb, a phrase,
or a clause.
- Modifying a verb: Carolyn really loves spring
- Modifying an adjective: My English teacher is very kind
- Modifying another adverb: Carolyn speaks Korean very well
- Modifying a phrase: She goes home right after class
- Modifying a clause: Finally, she has mastered Spanish.
NUCE. 55 GIAI PHONG
6. PREPOSITIONS
Prepositions: at, in, to, for, on, behind, before, after, through, during, etc.
A preposition comes before a noun, pronoun, or gerund. Together, the
preposition and its object express a time, place, reason, direction, means,
etc.
Roles:
• Expressing a time:
e.g. She always gets dressed up before playing music in front of an audience
• Expressing a place:
e.g. She plays music in the theater
• Expressing a reason
e.g. She plays music for him
NUCE. 55 GIAI PHONG
7. CONJUNCTIONS
Definition: A conjunction is a word that connects words with words, phrases with
phrases, or clauses with clauses. Two major types of conjunctions are coordinating
conjunctions and subordinating conjunctions.
• coordinating conjunctions: for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so
• subordinating conjunctions: though, because, while, until, if, wether, etc.
1. Word with word:
e.g. She loves spring and fall.
2. Phrase with phrase:
e.g. Where is the meeting room, on the second floor or in the basement?
3. Clause with clause:
e.g. I am happy because I can enjoy the fresh green colors of spring.
NUCE. 55 GIAI PHONG
8. DETERMINERS
Definition: A conjunction is a word that gives certain information about a
noun. For example, articles give information about definiteness. Other
determiners include possessive adjectives and quantifiers.
- Articles: a, an, the
- Possessive adjectives: my, your, his, her, its, our, their
- Quantifiers: each, every, some, most , etc.
I likes to live in a place, where I can enjoy fresh things and be myself.
Unfortunately, I haven’t found any so far!
NUCE. 55 GIAI PHONG
II. PHRASES & CLAUSES
Definition:
- when more than two words are combined and represent a chunk of
meaning but don’t build the relationship between a subject and a verb,
the combination of words is called a phrase.
- When more than two words are combined that present a chunk of
meaning and one of those words is used as a subject and another is used
as a verb, it is called a clause.
NUCE. 55 GIAI PHONG
II. PHRASES & CLAUSES (cont.)
Three different roles of phrases and clauses:
- Acting as a noun:
She wants to drink a cup of coffee.
a phrase playing the role of object
I know that she wants to drink a cup of coffee.
a clause playing the role of object
- Acting as an adjective:
The coffee from the cafe tastes good.
An adjective phrase appearing after and modifying a noun
The coffee that he made for her tastes good.
An adjective clause appearing after and modifying a noun
- Acting as an adverb:
She drinks her coffee on the sofa
an adverbial phrase appearing after and modifying a verb
She drinks her coffee while she listens to music.
an adverbial clause appearing after and modifying a verb
NUCE. 55 GIAI PHONG
III. SENTENCE CONSTITUENTS & VERB TYPES
In any sentence, at least one of the words in the sentence should play the role
of a subject and another the role of a verb. Other words also have their own
roles in the sentence. These roles are called the constituents of a sentence. In
English, there are five basic constituents of sentences: subjects, verbs, objects,
complements, and modifiers.
NUCE. 55 GIAI PHONG
III. SENTENCE CONSTITUENTS & VERB TYPES (cont.)
Main Elements of a Sentence in English
There are five main elements of a sentence in English: subject, verb, object,
complement, and modifier.
• Subject (chủ ngữ) is who or what does the action in a sentence.
• Verb (động từ) refers to the action or state of the subject.
• Object (tân ngữ) is the receiver of the action in a sentence. There are
indirect (gián tiếp) object and direct (trực tiếp) object.
• Complement (bổ ngữ) completes the meaning of a verb and adds more
information to the subject or object in a sentence. There are subject
complement and object complement.
• Modifier (trạng từ) is a word or a group of words that modify nouns,
verbs, adjectives, or a whole sentence. It is not a must, but it adds more
information to a sentence.
NUCE. 55 GIAI PHONG
III. SENTENCE CONSTITUENTS & VERB TYPES (cont.)
FIVE MAIN SENTENCE TYPES:
NUCE. 55 GIAI PHONG
1. Sentence Structure – Structure 1
What is Structure 1?
This is the most basic structure formed by only a subject and a verb.
You are likely to see common verbs such as go, work, live, come,
arrive, sleep, rise, walk, etc. in Structure 1.
Subject + Verb
Mr. White / came.
Structure 1
The seminar / ended.
The plane / arrived.
NUCE. 55 GIAI PHONG
1. Sentence Structure – Structure 1
Sometimes, in Structure 1, a modifier may be added to
make the sentence longer and more informative.
• Some employees / work / at home.
(Subject + verb + modifier)
• The train / left / three hours ago.
(Subject + verb + modifier)
• The museum / opens / every day.
(Subject + verb + modifier)
NUCE. 55 GIAI PHONG
A. Identify the elements in each of the following sentences and mark
below the subject, below the verb, and below the modifier.
1. The store closed 30 minutes ago.
2. I work near downtown.
3. Mr. Wilson returned from his business trip.
4. The door opens automatically.
close: đóng cửa
5. Ms. Johnson works eight hours a day. near: gần
downtown: trung tâm thành phố
return: trở lại
6. The bus leaves around noon. business trip: chuyến đi công tác
automatically: tự động
leave: rời đi
around noon: khoảng trưa
NUCE. 55 GIAI PHONG
B. Look at the elements in each of the following sentences and
choose one correct option to complete the sentence.
1. The new employee ________ near the office.
Subject Modifier
A. he B. lives C. him D. living
2. The strategy meeting _________ in an hour.
Subject Modifier
A. they B. in the room C. it D. starts
employee: nhân viên
strategy meeting: cuộc họp chiến lược
in an hour: trong khoảng một giờ sau
NUCE. 55 GIAI PHONG
2. Sentence Structure – Structure 2
What is Structure 2?
Structure 2 is formed by Subject + verb + subject complement. The
subject complement can be an adjective or a noun/noun phrase.
Subject + verb + subject complement
Structure 2
She / is / the new manager.
His speech / was / helpful.
The project / seemed / impossible.
NUCE. 55 GIAI PHONG
2. Sentence Structure – Structure 2
• Common verbs in Structure 2.
Generally, you can see such linking verbs as be, become, look, seem,
remain, taste, etc. in Structure 2.
Verbs Examples
be / become The job became easy.
look / sound / feel The report looks difficult.
seem The new product seems expensive.
NUCE. 55 GIAI PHONG
A. Identify the elements in each of the following sentences and
mark below the subject and below the subject complement.
1. The workshop sounds boring.
2. They were customers.
3. His idea seems useless.
4. Some items in the store looked expensive. workshop: xưởng
customer: khách hàng
boring: tẻ nhạt, nhàm
5. Her presentation was very useful. chán
useless: vô dụng
item: món đồ
6. Mr. Lee became the president of the company. expensive: đắt tiền
presentation: màn
thuyết trình
useful: hữu dụng
president: chủ tịch
B. Look at the elements in each of the following sentences and
choose one correct option to complete the sentence.
1. Mr.Kim suggestion about the problem ________ practical.
Subject Subject complement
A. the B. seemed C. very D. useful
2. The relocation of the office wasn’t _________ at first.
Subject Verb Modifier
A. easy B. easily C. seemed D. became
suggestion: đề nghị
practical: thực tế
relocation: việc di dời
NUCE. 55 GIAI PHONG
3. Sentence Structure – Structure 3
What is Structure 3?
Structure 3 is formed by Subject + verb + object. The object can be a
pronoun or a noun/noun phrase.
Subject + verb + object
Structure 3
We / met / him.
The team / finished / the project.
The conference room / has / three tables.
NUCE. 55 GIAI PHONG
3. Sentence Structure – Structure 3
• Confusing verbs in Structure 3.
Learners are usually confused about the verbs attend, mention, and
discuss. Be careful! An object, not a preposition, must follow right
after these verbs.
Verbs Examples
attend He attended the meeting. (o)
He attended to the meeting. (x)
mention I mentioned it. (o)
I mentioned about it. (x)
discuss They will discuss the problem. (o)
They will discuss about the problem. (x)
A. Put the words and phrases in brackets in the correct order to make
complete sentences.
1. (they, the issue, discussed)
• They discussed the issue.
2. (the contract, our team, finished)
• Our team finished the contract.
3. (my suggestion, the HR manager, liked)
• The HR manager liked my suggestion.
4. (some packages, Mr. Green, sent)
• Mr. Green sent some packages.
5. (the conference, will attend, Sam and Sara)
• Sam and Sara will attend the conference.
6. (an invitation, received, yesterday, we)
• We received an invitation yesterday.
• / Yesterday, we received an invitation.
B. Look at the elements in each of the following sentences and
choose one correct option to complete the sentence.
1. TeleCom ______ cellular phone at low prices.
Subject Verb Object Modifier
A. its B. us C. sells D. selling
2. Some of the executives will discuss ________ later this week.
Subject Verb Modifier
A. they B. them C. doing D. effective
cellular phone: điện thoại di động
executive: ban quản lý
NUCE. 55 GIAI PHONG
4. Sentence Structure – Structure 4
What is Structure 4?
Structure 4 is formed by Subject + verb + indirect object + direct
object.
Subject + verb + indirect object + direct object
The headquarters / sent / us / the form.
Structure 4
He / gave / her / a copy of the sales report.
The secretary / offered / me / some help.
NUCE. 55 GIAI PHONG
4. Sentence Structure – Structure 4
Transform Structure 4 to Structure 3
You can change Structure 4 into Structure 3 by reordering the indirect
object and direct object, then adding a preposition before the indirect
object.
• Verbs followed by the preposition TO: give, send, offer, show,
teach, tell, etc.
• Verbs followed by the preposition FOR: get, make, buy, find, etc.
NUCE. 55 GIAI PHONG
A. Choose the correct option given in brackets to complete
each sentence.
1. They (gave us / us gave) some documents.
2. Genie Electronics will (she offer / offer her) the
position.
3. The company sent (us some chairs / some chairs us).
4. The store offers (a free coupon new customers /
new customers a free coupon).
5. My coworker teaches computer language (for me /
to me).
NUCE. 55 GIAI PHONG
B. Look at the elements in each of the following sentences and
choose one correct option to complete the sentence.
1. The sales clerk sold ______ the copy machine.
Subject Verb Direct object
A. hers B. our C. me D. he
2. The boss _______ his staff some helpful tips.
Subject Indirect Object Direct object
A. was B. gave C. provided D. talked
sales clerk: nhân viên bán hàng
tip: lời khuyên, mẹo
NUCE. 55 GIAI PHONG
5. Sentence Structure – Structure 5
What is Structure 5?
Structure 5 is formed by Subject + verb + object + object
complement. The object can be a pronoun or a noun/noun phrase.
The object complement can be an adjective, a noun/noun phrase, a
to-infinitive, or a bare infinitive.
Subject + verb + object + object complement
The resort / makes / guests / very comfortable.
Structure 5
They / called / it / a big success.
He / helped / me / to finish the project.
The boss / made / us / work overtime.
NUCE. 55 GIAI PHONG
5. Sentence Structure – Structure 5
• Common verbs in Structure 5.
Common verbs in Structure 5 include make, let, have, keep, find, etc.
Verbs Examples
make / let / have The new policy will make the job hard.
keep We keep the desks clean.
find They found the machine useless.
NUCE. 55 GIAI PHONG
A. Write which type (1-5) the sentence is.
1. The chairs in the meeting room looked new.
• Structure 2 ( S+V+OC)
2. The engineer made his colleagues an effective device.
• Structure 4 ( S+V+IO+DO)
3. I found the discussion useful.
• Structure 5 (S+V+O+OC)
4. The printer over there is not working.
• Structure 1 (S+V)
5. The company announced a new policy.
• Structure 3 (S+V+O)
6. The new cleaning company keeps the office clean every day.
• Structure 5 (S+V+O+OC)
meeting room: phòng họp work: làm việc
colleagues: đồng nghiệp announce: thông báo
device: thiết bị policy: chính sách
discussion: cuộc thảo luận cleaning company: công ty lau dọn
NUCE. 55 GIAI PHONG
B. Look at the elements in each of the following sentences and
choose one correct option to complete the sentence.
1. He ______ the company profitable.
Subject Object Object Complement
A. looked B. was C. made D. seemed
2. The employee in the Accounting Department _______ the job
Subject Object
impossible.
Object Complement
A. seemed B. worked C. became D. found
profitable: có lợi
accounting department: ban kế toán
impossible: bất khả thi
NUCE. 55 GIAI PHONG
IV. CHECKUP
A. Write the word class for the highlighted word.
e.g. This corporation employs more than a thousand people. (noun)
1. Clara attends a weekly meeting. (Verb)
2. How many books do you read every month? (Noun)
3. She looks beautiful. (Adjective)
4. He speaks so fast. (Adverb)
5. I love spring because I can see flowers. (Conjunction)
NUCE. 55 GIAI PHONG
IV. CHECKUP
B. Write whether the underlined words are a phrase or a clause and
what role they play in the sentence.
e.g. The woman at the front desk was helpful. (phrase/adjective)
1. She bought a fancy skirt at the shop. (Phrase/ adverb)
2. It would be hard for me to write a book. (Phrase / noun)
3. I’m happy because I’m healthy. (Clause/adverb)
4. The man on the right side is my English teacher. (Phrase/ adjective)
5. He knows that I am from Korea. (Clause/ noun)
NUCE. 55 GIAI PHONG
IV. CHECKUP (cont.)
C. Write which kind of sentence constituent the highlighted words are.
Then write which type (1-5) the sentence is.
e.g. The movie starts at 7:00 in the evening. (subject/type 1)
1. We finally found our lost cat.(object/type 3)
2. She let the patient go home early.(Verb/ type 5)
3. My sister became a nurse at a dental clinic. (Subject complement/ type 2)
4. He received the package yesterday. (Modifier/ type 3)
5. My father bought me a new smartphone. (Indirect object / type 4)
NUCE. 55 GIAI PHONG
You might also like
- Latin Natural Method 1 - Most PDFDocument191 pagesLatin Natural Method 1 - Most PDFMichael HunterNo ratings yet
- The Parts of Speech: By: Syeda Rifa AnjumDocument39 pagesThe Parts of Speech: By: Syeda Rifa AnjumaNo ratings yet
- The Sentences and Parts of The SpeechDocument22 pagesThe Sentences and Parts of The SpeechVirginia GarciaNo ratings yet
- Gramar Grade Ingles 3Document45 pagesGramar Grade Ingles 3Aline Constanza BrunaNo ratings yet
- Meta Language Notes (VCE)Document4 pagesMeta Language Notes (VCE)AtifNo ratings yet
- Categorical Proposition 1Document5 pagesCategorical Proposition 1Muhammad Waqas100% (1)
- Parts of Speech: GrammarDocument8 pagesParts of Speech: GrammarAmalia InfanteNo ratings yet
- Lec Writing The Sentence 3 1Document22 pagesLec Writing The Sentence 3 1SERVICES SUBNo ratings yet
- Connectors of Addition and ContrastDocument3 pagesConnectors of Addition and ContrastAlex8mR100% (1)
- Week 2 - Part of Speech (Noun, Pronoun, Verb, Adjective)Document39 pagesWeek 2 - Part of Speech (Noun, Pronoun, Verb, Adjective)Anisa LarasNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Parts of SpeechDocument8 pagesLesson 2 Parts of Speechkuranji ruriNo ratings yet
- Teacher English Id 3Document192 pagesTeacher English Id 3Cornius Terranova100% (2)
- Milton Erickson - Language SkillsDocument13 pagesMilton Erickson - Language SkillsSorin LaurNo ratings yet
- Book Level A1.1Document114 pagesBook Level A1.1Luis Benitez100% (1)
- (Jaakko Hintikka Selected Papers 3) Jaakko Hintikka (Auth.) - Language, Truth and Logic in Mathematics-Springer Netherlands (1998)Document256 pages(Jaakko Hintikka Selected Papers 3) Jaakko Hintikka (Auth.) - Language, Truth and Logic in Mathematics-Springer Netherlands (1998)E. Goldstajn100% (2)
- Phrases & Sentence TypesDocument34 pagesPhrases & Sentence Typeseaonyinye13No ratings yet
- De Juan - Written Activity No. 1 (English)Document15 pagesDe Juan - Written Activity No. 1 (English)J.L Gaming YTNo ratings yet
- VHU - Syntax ContextDocument22 pagesVHU - Syntax ContextkhangtammedNo ratings yet
- Syntax-Bao NDocument87 pagesSyntax-Bao NHàn TínNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Parts of Speech Module OutcomesDocument4 pagesModule 1 Parts of Speech Module OutcomesKieziah VillegasNo ratings yet
- Lcture 2 On Phrse ClseDocument75 pagesLcture 2 On Phrse ClseMahmudur RahmanNo ratings yet
- English Language StudiesDocument10 pagesEnglish Language StudiesMiguel Yáñez LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Module 3 and 4Document10 pagesModule 3 and 4MelNo ratings yet
- English Syntax I Facultad de Filosofía Y Letras UNT - Año 2020Document24 pagesEnglish Syntax I Facultad de Filosofía Y Letras UNT - Año 2020Victoria del Rosario MaidanaNo ratings yet
- The SentenceDocument5 pagesThe SentenceBediako EzekielNo ratings yet
- 3rdQEnglish 10 Week 7Document62 pages3rdQEnglish 10 Week 7arshpogi123No ratings yet
- Grammar 2Document8 pagesGrammar 2الشيخة جمانةNo ratings yet
- Structure IiDocument6 pagesStructure Iidelima kranjiNo ratings yet
- Basic Grammar Notes For B.Tech (1st Years)Document17 pagesBasic Grammar Notes For B.Tech (1st Years)jayNo ratings yet
- Grammar 3Document49 pagesGrammar 3ABDELLAH RGUIBINo ratings yet
- Word Classes (Noun To Verb)Document8 pagesWord Classes (Noun To Verb)floz fowneNo ratings yet
- English 7Document4 pagesEnglish 7MA.RESA M.GALIDONo ratings yet
- 5 - Living Words School - GRAMATICADocument11 pages5 - Living Words School - GRAMATICAShalomPC SystemsNo ratings yet
- ELT122-Week 1-3 (pg.14-19)Document38 pagesELT122-Week 1-3 (pg.14-19)Becira LiNo ratings yet
- The Eight Parts of Speech: NounsDocument17 pagesThe Eight Parts of Speech: NounsValensia SumampouwNo ratings yet
- The Eight Parts of Speech: NounsDocument17 pagesThe Eight Parts of Speech: NounsSTENLY PONTOLONDONo ratings yet
- Naoual Derraz - GrammarDocument28 pagesNaoual Derraz - GrammarfatimernitNo ratings yet
- (123doc) - De-Cuong-On-Thi-Mon-Ngu-Phap-Tieng-Anh-Hay-Ngan-GonDocument20 pages(123doc) - De-Cuong-On-Thi-Mon-Ngu-Phap-Tieng-Anh-Hay-Ngan-GonPhạm Kim HiềnNo ratings yet
- Grammar 3 (Complete Course)Document26 pagesGrammar 3 (Complete Course)Abdelouahed El AbiNo ratings yet
- 7 Phrases and ClausesDocument27 pages7 Phrases and Clausesjangauci123No ratings yet
- Mid TermDocument13 pagesMid Termelsa lestariNo ratings yet
- 2q Eng5 PointersDocument34 pages2q Eng5 PointersAbigail DizonNo ratings yet
- Verbs Gerunds and Infinitive FinishDocument10 pagesVerbs Gerunds and Infinitive FinishYoga NurzamanNo ratings yet
- For Example A) Noun Phrase As SubjectDocument20 pagesFor Example A) Noun Phrase As SubjectMarcusKlahnTokoeJr.No ratings yet
- Midterm Exam SerranoDocument4 pagesMidterm Exam SerranoNolan G. SerranoNo ratings yet
- Activity 3: Writing Task ForumDocument9 pagesActivity 3: Writing Task ForumYorman Hernan Medina RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Makalah Bahasa Inggris Ega 4Document16 pagesMakalah Bahasa Inggris Ega 4Sri MursalinaNo ratings yet
- Lee Esto Primero... !Document13 pagesLee Esto Primero... !Orlando Chandía OchoaNo ratings yet
- Grammatical-Categories 2.5Document12 pagesGrammatical-Categories 2.5arl somarNo ratings yet
- Maulana Rifki Hidayat - 2021SE024 B.INGGRISDocument12 pagesMaulana Rifki Hidayat - 2021SE024 B.INGGRISselvia anggrainiNo ratings yet
- Welcome To English 7!Document33 pagesWelcome To English 7!Abigail DizonNo ratings yet
- Ept Preparation Chapter - 2Document21 pagesEpt Preparation Chapter - 2TiwoqPoenyaNo ratings yet
- Basic Grammar TermsDocument6 pagesBasic Grammar TermsSamuel JosephNo ratings yet
- WHLP-1ST Quarter-English7-Week 5-6Document6 pagesWHLP-1ST Quarter-English7-Week 5-6Ernest De Mesa MendozaNo ratings yet
- Gramatical UnitsDocument15 pagesGramatical Unitsvanesa121084No ratings yet
- Lecture 1 (Com Skills)Document52 pagesLecture 1 (Com Skills)ernestafriyie04No ratings yet
- Mubarak Use of English GNS 301Document18 pagesMubarak Use of English GNS 301Mubarak AdamuNo ratings yet
- English Grammar and Its Basic ConceptsDocument123 pagesEnglish Grammar and Its Basic Conceptsblitzkrig007No ratings yet
- Morphology Unit4Document25 pagesMorphology Unit4ferasORVNo ratings yet
- English Comprehension and CompositionDocument28 pagesEnglish Comprehension and CompositionDaniyal khanNo ratings yet
- Objectives: San Pedro Integrated SchoolDocument8 pagesObjectives: San Pedro Integrated SchoolEljean LaclacNo ratings yet
- Name: Buya Ahmad Bilal Nim:200502502015 Class: English Educatioan ADocument17 pagesName: Buya Ahmad Bilal Nim:200502502015 Class: English Educatioan ABilal BuyaNo ratings yet
- Q1 Week 6 Grade 7 LAS Phrases Clauses SentencesDocument5 pagesQ1 Week 6 Grade 7 LAS Phrases Clauses SentencesVeronica Almera ManuelNo ratings yet
- Parts of SentencesDocument14 pagesParts of SentencesAkirun HarahapNo ratings yet
- Sentence Constituents & Word Order: Muthia Andini Rinawati Pelawi Sri Susanti Trihartina Tampubolon Weby YolannisaDocument88 pagesSentence Constituents & Word Order: Muthia Andini Rinawati Pelawi Sri Susanti Trihartina Tampubolon Weby YolannisaWeby YolannisaNo ratings yet
- Midterms: Week 1: 1. Topic: Pronouns (Overview) DescriptionDocument9 pagesMidterms: Week 1: 1. Topic: Pronouns (Overview) DescriptionLara Mae CabangonNo ratings yet
- Final Presentation300Document30 pagesFinal Presentation300Aisha RehnumaNo ratings yet
- Adverbs and Adverbial ClausesDocument13 pagesAdverbs and Adverbial ClausesStefania OrtizNo ratings yet
- Interjection: Aha! An Interjection Definition!Document2 pagesInterjection: Aha! An Interjection Definition!TESL10621 Shameen Farah Binti Mohd AminNo ratings yet
- 11 20Document24 pages11 20анастасияNo ratings yet
- SAT Writing Subject VerbDocument3 pagesSAT Writing Subject VerbimsungbaekNo ratings yet
- Scientific Writing Word UsageDocument10 pagesScientific Writing Word UsageRebecca PotterNo ratings yet
- Gerund: To, To Take To, To Be Accustomed To, To Get Around To, & To Be Used To. It Is Important To Recognise ThatDocument4 pagesGerund: To, To Take To, To Be Accustomed To, To Get Around To, & To Be Used To. It Is Important To Recognise ThatASTINo ratings yet
- Horseshit: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument3 pagesHorseshit: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediawalteryNo ratings yet
- Translation Procedures - Modulation EquivalenceDocument2 pagesTranslation Procedures - Modulation EquivalenceMaría Agustina Aquino García100% (1)
- Alfabetul KoreanDocument6 pagesAlfabetul Koreangeo_dragutzicaNo ratings yet
- Eng Rev ReviewerDocument8 pagesEng Rev ReviewerBabe'sNo ratings yet
- Academic Shrine Series - English Language (SHS) (Autorecovered)Document152 pagesAcademic Shrine Series - English Language (SHS) (Autorecovered)pkademangNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4-Tangmuan, Wenie RoseDocument15 pagesLesson 4-Tangmuan, Wenie Rosewenie rose tangmuanNo ratings yet
- Copi Instructor Manual 130631 PDF FreeDocument106 pagesCopi Instructor Manual 130631 PDF FreeCarlos VargasNo ratings yet
- Pacte 2000Document13 pagesPacte 2000Littleone8No ratings yet
- Tugas Bahasa Inggris: Nama:Irawan Chandra NO: 17 Kelas:XII-A!Document9 pagesTugas Bahasa Inggris: Nama:Irawan Chandra NO: 17 Kelas:XII-A!irawanNo ratings yet
- Errata: The Syntax Workbook: A Companion To Carnie's Syntax (2013)Document7 pagesErrata: The Syntax Workbook: A Companion To Carnie's Syntax (2013)ralphNo ratings yet
- Semantic S: Kiara Pichis Freitas Lucy Torres OjanamaDocument12 pagesSemantic S: Kiara Pichis Freitas Lucy Torres OjanamaHeidy Teresa MoralesNo ratings yet
- Paradigmatic Sense Relations of Inclusion and IdentityDocument4 pagesParadigmatic Sense Relations of Inclusion and IdentityAlmedina Tokić Zornić100% (1)
- Atividade Língua Inglesa IiDocument4 pagesAtividade Língua Inglesa IiFrancisco De Assis NetoNo ratings yet
- Unit-I Mathematical Logic: Statements and NotationsDocument24 pagesUnit-I Mathematical Logic: Statements and NotationsADRIAN EMMANUEL CLEMENTENo ratings yet
- Seallagain-Catriona ParsonsDocument112 pagesSeallagain-Catriona Parsonswaymac007No ratings yet
- Unity Vocab Quick ReferenceDocument2 pagesUnity Vocab Quick ReferenceJustin WalkerNo ratings yet