Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Nervous System (Notes)
Uploaded by
Trisha LaidenOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Nervous System (Notes)
Uploaded by
Trisha LaidenCopyright:
Available Formats
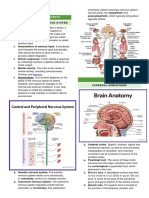
Nervous system Right Hemisphere
Coordinates actions by transmitting signals to Creative, intuition, imagination
and from the different parts of the body
Detect environmental changes and tandem with 4 lobes
endocrine system. 1. Frontal
Purpose 2. Parietal
3. Temporal
Coordinates all activities 4. Occipital
Body’s respond and adapt changes both inside
and out Frontal
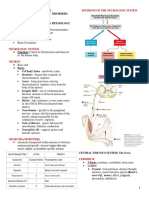
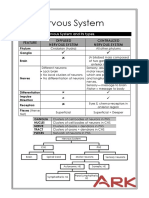
3 Major Division of the BRAIN - Reasoning and thoughts
1. Hindbrain Parietal
2. Midbrain - Integrates sensory information
3. Forebrain
Temporal
Hindbrain
- Processes auditory information from ears
Located at the posterior portion of the brain
Medulla, Pons, Cerebellum Occipital
Brain Stem - Processing visual information from eyes
Medulla and other central structures of the brain Cerebral Cortex
Medulla Oblongata Cellular layers on the outer surface
Divided into 2 halves & joined 2 bundle of axon
Located at the bottom of the brainstem 1. Corpus Callosum
Connects to the spinal cord 2. Anterior Commissure
Damaged (paralyzed, respiratory failure)
Corpus Callosum
Pons
Both side of brain communicate and send signals
Located below the midbrain (brainstem) If damage, it delays motor and language skills
Responsible for certain reflex action Ex.
Relays sensory information to cerebellum
Connects to forebrain and midbrain Split brain Syndrome (callosal disconnection syndrome)
Controls of sleep cycle
- Unusual behavior concerns with speech and
Cerebellum object recognition.
Muscle coordination, Balance, Posture, and Aphaxia
Muscle tone
- inability to respond and command with
Midbrain motor activity.
Located below the cerebrum Aphasia
Responsible for eye and auditory reflexes
- Comprehension and expression of language
Tegmentum
Broca’s Aphasia (Anterior)
Prevent unwanted movement
- Cannot speak
reflex/ pain processing
- When damage the person’s stutter
Forebrain
Wernicke’s Aphasia (Posterior)
Most anterior and prominent part of brain
- Can’t comprehend
Consist of 2 cerebral hemispheres
- Hard to understand speech
1. Outer Cortex (Cerebral Cortex)
2. Subcortical Regions Forebrain Structure
Sides receives information and contols motor
of the opposite (contralateral) side of the body Olfactory
Left Hemisphere - Sensory receptor
- Electrical activity transmitted to CNS
Language, analytical thinking
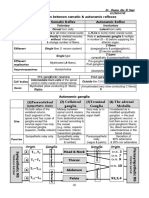
Thalamus Efferent Sensory Neurons (
- Relay station - Takes information from the CNS to the
- Passes information to and from celebral cortex muscle fibers throughout the body
Hypothalamus Sympathetic Nervous System
- Associated with behavior such as - “fight or flight”
eating,drinking, sexual behavior - revs up the body either responds or defend to
- Pituitary gland to release hormones escaped threats
Hippocampus Parasympathetic Nervous System
- Responsible for memory function - brings all system of the body back to normal
- Encodes and store memory into cerebral
cortex
If damage it leads to amnesia
Retrograde- can’t form new memory
Anterograde – can’t remember past memory
Amygdala
- Behavioral coordination
- Fear and anxiety center
- Make memories through emotions
Cingulate gyrus
- Message carrier
- Regulates pain and emotion
- Negative consequences
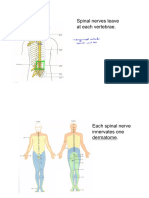
Spinal Cord
- Link between the brain and the nerves in the
rest of the body
4 regions
1. Cervical
2. Thoracic
3. Lumbar
4. Spinal Nerves
Afferent (Sensory Division)
- Carries information from the body to brain
Efferent (Motor Division)
- Carries information from the brain to the
body
Peripheral Nervous System
1. Somatic
2. Autonomic
Somatic Nervous System
- Carrying motor and sensory information
- Nerves that connect to skin, sensory organs,
skeletal muscles
- Responsible for all muscle movements
- Process sensory information from external
stimuli.
Afferent Sensory Neurons (conducting inwards)
- Takes information form the nerves to the CNS
You might also like
- EL Husseiny's Guide to Cell Death, Calcification, and Ischemic InjuryDocument92 pagesEL Husseiny's Guide to Cell Death, Calcification, and Ischemic InjurySara Alsubaie100% (1)
- Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesNervous SystemEllanny GloriaNo ratings yet
- Biological MindDocument25 pagesBiological MindQuesiah González100% (1)
- Brain Anatomy Function Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesBrain Anatomy Function Cheat SheetJo PigarNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Study GuideDocument11 pagesCardiac Study Guidesurviving nursing school100% (2)
- Brain Anatomy and Function Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesBrain Anatomy and Function Cheat SheetminaNo ratings yet
- Neurological AssessmentDocument13 pagesNeurological AssessmentLorenz Jude CańeteNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Neuroscience. Anatomy of The BrainDocument11 pagesCognitive Neuroscience. Anatomy of The BrainKryzhel CuachonNo ratings yet
- 2 Human Body Nervous SystemDocument24 pages2 Human Body Nervous SystemRain HuntsdaleNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lec Midterm ReviewerDocument39 pagesAnaphy Lec Midterm ReviewerphoebeNo ratings yet
- Arterial Blood PressureDocument46 pagesArterial Blood PressureRupasi KathiravanNo ratings yet
- Nervous System: A Tutorial Study GuideFrom EverandNervous System: A Tutorial Study GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Human Anatomy and Physiology MCQ With Answers PDFDocument4 pagesHuman Anatomy and Physiology MCQ With Answers PDFPrince Maurya88% (8)
- COGNITION IN THE BRAINDocument8 pagesCOGNITION IN THE BRAINShekinah Pearl Niog100% (1)
- Unit 1 Gastro Intestinal SystemDocument53 pagesUnit 1 Gastro Intestinal SystemPlatypus proNo ratings yet
- Presentation of Neurogenic Shock Within The Emergency Department - TaylorDocument6 pagesPresentation of Neurogenic Shock Within The Emergency Department - TaylorAnprtma kaunangNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing Review NotesDocument75 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing Review NotesMary Ann Comia RañolaNo ratings yet
- HumanEye PDFDocument16 pagesHumanEye PDFsneha Mary AntonyNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Kel 4Document10 pagesNervous System Kel 4Talitha FatihahNo ratings yet
- Equine Applied and Clinical Nutrition (VetBooks - Ir)Document673 pagesEquine Applied and Clinical Nutrition (VetBooks - Ir)Lu MarfiaNo ratings yet
- Understanding the Neurologic System in 40 CharactersDocument10 pagesUnderstanding the Neurologic System in 40 CharactersMeryville Jacildo100% (1)
- HANDOUTSDocument3 pagesHANDOUTSElaiza Eline LaguaNo ratings yet
- Midterm #1 Neuro Anatomy and Physiology ReviewDocument15 pagesMidterm #1 Neuro Anatomy and Physiology ReviewMonica JubaneNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Psychology TopicsDocument11 pagesCognitive Psychology TopicsJulia AlforteNo ratings yet
- PT Neuro Intro NotesDocument13 pagesPT Neuro Intro NotesSusan K100% (1)
- BIOLOGY 10: Brain Stem and Sacral Regions of the Central Nervous SystemDocument9 pagesBIOLOGY 10: Brain Stem and Sacral Regions of the Central Nervous System12 Dy NicoleNo ratings yet
- Personal Development Reviewer: © Angelica GarciaDocument14 pagesPersonal Development Reviewer: © Angelica GarciaFat AjummaNo ratings yet
- Brain Anatomy Function Handout 2023Document3 pagesBrain Anatomy Function Handout 2023xtralargee.mbaNo ratings yet
- Functions of the Nervous System in 40 CharactersDocument5 pagesFunctions of the Nervous System in 40 CharactersXandra BasnilloNo ratings yet
- Brain Structure and Function Explained in 40 CharactersDocument4 pagesBrain Structure and Function Explained in 40 CharactersPem TNo ratings yet
- Nervous System OverviewDocument4 pagesNervous System OverviewEds SyNo ratings yet
- Neurologic System Functions and StructuresDocument9 pagesNeurologic System Functions and StructuresBianx Flores DosdosNo ratings yet
- Nervous System: Skull Cerebrospinal FluidDocument1 pageNervous System: Skull Cerebrospinal FluidVincent Franciz T. FernandezNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Disorders PresentationDocument70 pagesCognitive Disorders PresentationWasiu AfoloabiNo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy of the Central and Peripheral Nervous SystemDocument88 pagesNeuroanatomy of the Central and Peripheral Nervous SystemAchenk BarcelonistaNo ratings yet
- The Brain: Key Terms-DefinitionsDocument12 pagesThe Brain: Key Terms-DefinitionsPem TNo ratings yet
- The Whole Brain Theory in 40 CharactersDocument2 pagesThe Whole Brain Theory in 40 CharactersgirlsalwayswinNo ratings yet
- Cognitive PsychologyDocument5 pagesCognitive Psychologymain.22001454No ratings yet
- 8B Coordination in Animals and Plants 8B Checkpoint: 8B.1 The Central Nervous SystemDocument8 pages8B Coordination in Animals and Plants 8B Checkpoint: 8B.1 The Central Nervous SystemsalmaNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument6 pagesNervous System Anatomy and PhysiologyNadia AbdurasidNo ratings yet
- Module 2: Biology and PsychologyDocument23 pagesModule 2: Biology and Psychologyshain aldovinoNo ratings yet
- Sleep Physiology 1st YrDocument45 pagesSleep Physiology 1st YrJeffrey RamosNo ratings yet
- How the Nervous System Controls the BodyDocument7 pagesHow the Nervous System Controls the BodyAltheaNo ratings yet
- Neurological System Assessment Part 1 - NCM 101 H.ADocument5 pagesNeurological System Assessment Part 1 - NCM 101 H.ALexie KepnerNo ratings yet
- Psy 119 Lec 2Document2 pagesPsy 119 Lec 2Angelo SumaoyNo ratings yet
- CH 2 CnotesDocument11 pagesCH 2 Cnotesvalcobacl.681.studNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument8 pagesNervous SystemBSLMS1D - Depasupil, Laurice Ann A.No ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument6 pagesNervous SystemAndrea RicamaraNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document8 pagesModule 1laaraybmehmood1503No ratings yet
- Psychology Summary of Brain Anatomy and FunctionsDocument6 pagesPsychology Summary of Brain Anatomy and FunctionssisilNo ratings yet
- Assessing the Neurologic SystemDocument7 pagesAssessing the Neurologic Systemjanikkakristal100% (1)
- Perdev The BrainDocument4 pagesPerdev The BrainJL BautistaNo ratings yet
- Physiological Psychology - Midterm - ReviewerDocument4 pagesPhysiological Psychology - Midterm - ReviewerAudije, John Michael M.No ratings yet
- Nervous System CNS 1481841Document5 pagesNervous System CNS 1481841Jglacier godNo ratings yet
- Module 3.2 The Cerebral CortexDocument3 pagesModule 3.2 The Cerebral CortexChriscelle Ann PimentelNo ratings yet
- 116 - Concept of Perception and CoordinationDocument3 pages116 - Concept of Perception and Coordinationalaisahmae02No ratings yet
- Brain Structures and Functions ExplainedDocument2 pagesBrain Structures and Functions ExplainedAmanda LeeNo ratings yet
- Neuro Week 1Document6 pagesNeuro Week 1Sheryhan BayleNo ratings yet
- 03 Nervous System BDocument41 pages03 Nervous System BBalew KassieNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous System (CNS) Neuroanatomy &Document26 pagesCentral Nervous System (CNS) Neuroanatomy &Asaad JawedNo ratings yet
- 2 Human Body Nervous System - PPT Grade12 Ch29 Lesson 2Document24 pages2 Human Body Nervous System - PPT Grade12 Ch29 Lesson 2kheloudmamdouhNo ratings yet
- REVIEWER Neurological SystemDocument5 pagesREVIEWER Neurological SystemKeren GaciasNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous System (CNS)Document10 pagesCentral Nervous System (CNS)Ma Roni Paula VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Biological Psychology (BRAIN AND ITS DISEASES)Document16 pagesBiological Psychology (BRAIN AND ITS DISEASES)Shenne Ann MaghuyopNo ratings yet
- Biological PsychologyDocument9 pagesBiological PsychologyShenne Ann MaghuyopNo ratings yet
- The Brain and The Nervous SystemDocument17 pagesThe Brain and The Nervous SystemElena-Andreea MutNo ratings yet
- Nervous System1Document76 pagesNervous System1ahmed jeylaaniNo ratings yet
- REVIEWERDocument6 pagesREVIEWERLeihMinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Basics: Created by Last Edited TagsDocument21 pagesChapter 1: Basics: Created by Last Edited TagsWendy TanNo ratings yet
- Physiology, Catecholamines: Stephen Paravati Alan Rosani Steven J. WarringtonDocument2 pagesPhysiology, Catecholamines: Stephen Paravati Alan Rosani Steven J. WarringtonVincent Paul SantosNo ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetics: PharmacodynamicsDocument22 pagesPharmacokinetics: PharmacodynamicsRoseline Adebisi100% (1)
- Comparing somatic and autonomic reflexesDocument4 pagesComparing somatic and autonomic reflexesahmed yousefNo ratings yet
- APPENDIX A B GlossaryDocument15 pagesAPPENDIX A B GlossaryaddiramonaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument10 pagesEndocrine SystemEthel May AlabastroNo ratings yet
- PharmaDocument77 pagesPharmaP.T ShunmiNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Pharmacology of the Eye/TITLEDocument23 pagesAutonomic Pharmacology of the Eye/TITLERomaine-Ricardo FrancisNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument19 pagesAutonomic Nervous SystemAnuvabNo ratings yet
- Biology NotesDocument102 pagesBiology Notesajabgul123493No ratings yet
- 1031 Autonomic Nervous System-BSDocument20 pages1031 Autonomic Nervous System-BSBunny KumarNo ratings yet
- Case Study Wearing On Her NervesDocument42 pagesCase Study Wearing On Her Nervesapi-460556390No ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Nervous SystemDocument12 pagesChapter 8 - Nervous SystemlalaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Nervous System and Nervous TissueDocument37 pagesFundamentals of Nervous System and Nervous Tissue차지형No ratings yet
- Anatomy 1st Semester ReviewDocument23 pagesAnatomy 1st Semester ReviewMonia AliNo ratings yet
- Lecture DPT 4 NEURO ANATOMY 'Autonomic Nervous System'Document57 pagesLecture DPT 4 NEURO ANATOMY 'Autonomic Nervous System'CHANGEZ KHAN SARDARNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 AnswersDocument3 pagesChapter 14 AnswersdanielNo ratings yet
- Int Endodontic J - 2020 - Zhan - Dental Nerves A Neglected Mediator of PulpitisDocument15 pagesInt Endodontic J - 2020 - Zhan - Dental Nerves A Neglected Mediator of PulpitisDevin KwanNo ratings yet
- Terminologia NeuroanatomicaDocument144 pagesTerminologia Neuroanatomicamatteo_vavassoriNo ratings yet
- Human Body Systems ProjectDocument9 pagesHuman Body Systems ProjectmrdornNo ratings yet
- Pages From Histology - A Text and Atlas With Correlated Cell and Molecular Biology - 7th Edition (2015)Document48 pagesPages From Histology - A Text and Atlas With Correlated Cell and Molecular Biology - 7th Edition (2015)v-sant100% (1)
- K00429 - 20190428163910 - Blanded Learning - Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesK00429 - 20190428163910 - Blanded Learning - Nervous SystemNixon ErnestNo ratings yet