Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ohm's Law Im
Uploaded by
Mary Queen TeroOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ohm's Law Im
Uploaded by
Mary Queen TeroCopyright:
Available Formats
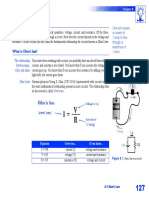
Ohm’s Law
Ohm’s Law was given by German physicist Georg Simon Ohm. It
states the relationship between current, resistance, and voltage across an
electrical circuit. This relationship between current I, voltage V, and
resistance R was given by famous German scientist Georg Simon Ohm in
1827. He found conducting his experiment that the product of the current
flowing through the conductor and the resistance of the conductor
determines the voltage drop over that conductor in the circuit.
Ohm’s law states that the voltage across a conductor is directly
proportional to the current flowing through it, provided all physical
conditions and temperatures remain constant, i.e. V ∝ I. Thus, it is
considered as the basic law which helps us in dealing electric circuit.
Ohm’s Law Unit
There are three physical quantities that are associated with the Ohms Law
that include,
Current
Voltage
Resistance
The table added below shows the various symbol and their unit used.
Physical Quantity Unit of Measurement Unit Abbreviation
Current(C) Ampere A
Voltage(V) Volt V
Resistance(R) Ohm Ω
Ohm’s Law Equations
Ohm’s law provides three equations which are:
V=I×R (Voltage = Current x Resistance)
I=V/R (Current = Voltage / Resistance)
R=V/I (Resistance = Voltage / Current)
You might also like
- Complete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsFrom EverandComplete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Ohm's LawDocument24 pagesOhm's LawIrish de LeonNo ratings yet
- Principles and Definition of Ohms LawDocument36 pagesPrinciples and Definition of Ohms LawIrfanNo ratings yet
- OhmsDocument2 pagesOhmsMaria Sofia SalasNo ratings yet
- Ohm's Acoustic LawDocument1 pageOhm's Acoustic LawBenjamin Duallo FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Lecture On Ohm's LawDocument2 pagesLecture On Ohm's LawJanxi Carlisle ChuaNo ratings yet
- BasicElecOhmsLawDocument16 pagesBasicElecOhmsLawRichard del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument2 pagesOhm's LawDon't Know EverythingNo ratings yet
- Ohms Law ReviewerDocument4 pagesOhms Law ReviewerwannieNo ratings yet
- Btle Ia 3 Fundamentals of Electronics Technology Learning ModuleDocument7 pagesBtle Ia 3 Fundamentals of Electronics Technology Learning ModuleLorenzo RamosNo ratings yet
- Ohms Law Formula WheelDocument2 pagesOhms Law Formula WheelTesda SfistNo ratings yet
- Ohm S Law TutorialDocument17 pagesOhm S Law Tutorialchristopher pazmiño panchanaNo ratings yet
- Ohm S Law TutorialDocument17 pagesOhm S Law Tutorialchristopher pazmiño panchanaNo ratings yet
- Series Parallel CircuitDocument13 pagesSeries Parallel Circuitelvis mendezNo ratings yet
- Ohms Law To Find The Third Missing Value. Ohms Law Is Used Extensively in ElectronicsDocument3 pagesOhms Law To Find The Third Missing Value. Ohms Law Is Used Extensively in ElectronicsDarius Dave CruzNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument3 pagesNotesmikko decenaNo ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument2 pagesOhm's LawBelly JoeNo ratings yet
- Ohm's Law States That The Current Through A Conductor Between Two Points Is Directly Proportional ToDocument1 pageOhm's Law States That The Current Through A Conductor Between Two Points Is Directly Proportional ToGary NugasNo ratings yet
- Computation and Relations of VariablesDocument2 pagesComputation and Relations of Variablesrurucj08No ratings yet
- Ohms LawDocument1 pageOhms LawAvinash UdupaNo ratings yet
- IntroDocument1 pageIntroMARREN JEIRELLE PENAFLORNo ratings yet
- Introduction Objectives Equipment Steps Results CommentsDocument8 pagesIntroduction Objectives Equipment Steps Results CommentsRalph EvidenteNo ratings yet
- Document 43Document20 pagesDocument 43bumbadiyaviralNo ratings yet
- Electronic CircuitsDocument13 pagesElectronic CircuitsAbhisek PagadNo ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument12 pagesOhm's LawMK BarrientosNo ratings yet
- Unit IDocument27 pagesUnit IPratap VeerNo ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument23 pagesOhm's Lawmini2268100% (1)
- Conductors Electric Current Voltage Microscopic View of Ohm's Law ResistanceDocument2 pagesConductors Electric Current Voltage Microscopic View of Ohm's Law ResistanceKatrina Zoi ApostolNo ratings yet
- Here We'll Attempt To Explain Ohm's Law Basics!: WaterDocument2 pagesHere We'll Attempt To Explain Ohm's Law Basics!: WaterRoy Axel HabocNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Elctricity and Electronics Week 3Document13 pagesFundamentals of Elctricity and Electronics Week 3richie cuizonNo ratings yet
- Ohm's Law: Presented By: Shantell Limjoco Tonet Sy Viana AngDocument12 pagesOhm's Law: Presented By: Shantell Limjoco Tonet Sy Viana AngViana Celina AngNo ratings yet
- Ohm LawDocument1 pageOhm LawmadexsystechNo ratings yet
- OHM LawDocument5 pagesOHM LawSeanie ReyesNo ratings yet
- Ohms LawDocument5 pagesOhms LawCyber MagicNo ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument11 pagesOhm's LawMarifer RamirezNo ratings yet
- What Is Ohm's Law?Document6 pagesWhat Is Ohm's Law?mohsenNo ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument1 pageOhm's LawAdrielNo ratings yet
- برزنتيشن طرق قياس اكوادDocument13 pagesبرزنتيشن طرق قياس اكوادMomen SalahNo ratings yet
- Ohm's Law (Lab Report)Document7 pagesOhm's Law (Lab Report)yuta titeNo ratings yet
- Lab 2Document4 pagesLab 2api-3720469No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electricity and ElectronicsDocument26 pagesFundamentals of Electricity and ElectronicsBryan AremadoNo ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument1 pageOhm's Lawcute_arvina13163No ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument32 pagesOhm's LawDezz Balleta-BonaNo ratings yet
- Ohm LawDocument12 pagesOhm LawJessica ZarateNo ratings yet
- Current Voltace Resistance: Study in This ExperimentDocument1 pageCurrent Voltace Resistance: Study in This ExperimenterzaNo ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument2 pagesOhm's Lawabuzar12533No ratings yet
- Ohm's Law: This Article Is About The Law Related To Electricity. For Other Uses, SeeDocument10 pagesOhm's Law: This Article Is About The Law Related To Electricity. For Other Uses, SeeAditya Singh BaisNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 Ohms LawDocument5 pagesExperiment 2 Ohms LawnatlasNo ratings yet
- The Ohm's Law EquationDocument3 pagesThe Ohm's Law EquationLalinjaman L MarionNo ratings yet
- The Relationship Among Basic Quantities VoltageDocument9 pagesThe Relationship Among Basic Quantities VoltagechristiankenthusaNo ratings yet
- Electronic Circuit: Ohm's Law CircuitDocument2 pagesElectronic Circuit: Ohm's Law CircuithasnaNo ratings yet
- Presentation of Applied PhysicsDocument9 pagesPresentation of Applied PhysicsFarooq TariqNo ratings yet
- Ohms LawDocument10 pagesOhms Lawlindre00267% (3)
- Introduction To Ohms LawDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Ohms LawJoshteKunNo ratings yet
- Module 7Document15 pagesModule 7Laiza GranaNo ratings yet
- كرار جاهرDocument4 pagesكرار جاهرkararalzide2005No ratings yet
- OhmssDocument2 pagesOhmssMark SantillanNo ratings yet
- His Article Is About The Law Related To ElectricityDocument22 pagesHis Article Is About The Law Related To ElectricitySandeep GuptaNo ratings yet
- (Ohm's Law) Tutorial 2 For ElectricalsDocument5 pages(Ohm's Law) Tutorial 2 For ElectricalsPraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Resistance FormulaDocument14 pagesResistance FormulaCarl Kristopher PeloniaNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Log Q3 WK 1Document4 pagesDaily Lesson Log Q3 WK 1Mary Queen TeroNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson LogDocument4 pagesDaily Lesson LogMary Queen TeroNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Log 2024 WK 1Document5 pagesDaily Lesson Log 2024 WK 1Mary Queen TeroNo ratings yet
- Storm ClassificationDocument18 pagesStorm ClassificationMary Queen TeroNo ratings yet
- ATTENDANCEDocument1 pageATTENDANCEMary Queen TeroNo ratings yet
- Heat Vs TemperatureDocument1 pageHeat Vs TemperatureMary Queen TeroNo ratings yet
- Q1S2 Back PageDocument1 pageQ1S2 Back PageMary Queen TeroNo ratings yet
- OutputDocument23 pagesOutputMary Queen TeroNo ratings yet
- Homeroom Meeting Ppt2Document21 pagesHomeroom Meeting Ppt2Mary Queen Tero100% (1)