Professional Documents
Culture Documents
03aacm Licyayo
03aacm Licyayo
Uploaded by
Mohamidin Mamalapat0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageThe document discusses amino acids, peptides, and polypeptides. It describes how amino acids have an amino group, carboxyl group, hydrogen, and a side chain. Peptides are formed when the carboxyl group of one amino acid binds to the amino group of another, releasing a water molecule. Polypeptides consist of two or more amino acids linked together. The document also lists the 20 common amino acids and groups them into nonpolar, polar, acidic, and basic categories based on their side chain properties.
Original Description:
Original Title
03AACM-LICYAYO
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses amino acids, peptides, and polypeptides. It describes how amino acids have an amino group, carboxyl group, hydrogen, and a side chain. Peptides are formed when the carboxyl group of one amino acid binds to the amino group of another, releasing a water molecule. Polypeptides consist of two or more amino acids linked together. The document also lists the 20 common amino acids and groups them into nonpolar, polar, acidic, and basic categories based on their side chain properties.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 page03aacm Licyayo
03aacm Licyayo
Uploaded by
Mohamidin MamalapatThe document discusses amino acids, peptides, and polypeptides. It describes how amino acids have an amino group, carboxyl group, hydrogen, and a side chain. Peptides are formed when the carboxyl group of one amino acid binds to the amino group of another, releasing a water molecule. Polypeptides consist of two or more amino acids linked together. The document also lists the 20 common amino acids and groups them into nonpolar, polar, acidic, and basic categories based on their side chain properties.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
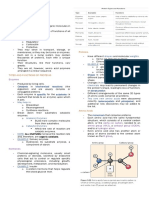
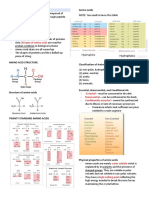
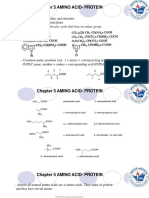
LICYAYO, MICHEL PAULETTE CHAPTER 3: AMINO ACID AND
Chem 2065 AY2022-23 PEPTIDE BONDS
PEPTIDES
- α-carboxyl group of one amino
General structure:
acid and the α-amino group of the
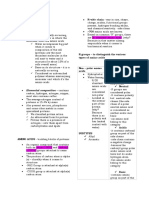
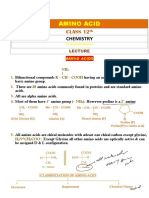
-AMINO GROUP AMINO ACIDS PEPTIDES other amino acid covalently bonds.
-CARBOXYL GROUP
During this process, water is lost,
- HYDROGEN
- SIDE CHAIN GROUP (R) – and residues of the linked amino
which determines the identities of UNCOMMON AMNO ACID acid remain
the amino acid - derived from common amino acids
and are produced by modification of POLYPEPTIDES - A peptide consisting of 2
the parent amino acid or more amino acids.
20 COMMON AMINO ACIDS
Example is the acidic amino acid
- are "common" because they
glutamate plays a significant role in
are proteinogenic in nature.
mediating excitatory transmission
(the generation of EPSPs).
Some small peptides with
physiological activity
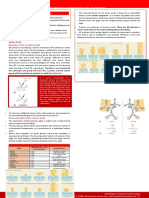
A. NONPOLAR (HYDROPHOBIC)
- has non-polar side chains
- side chains are usually
aliphatic or aromatic 1. OXYTOCIN – induces labor in
hydrocarbons pregnant women
2. VASOPRESSIN – controls blood
pressure
3. INSULIN – maintains glucose
B. POLAR (UNCHARGED) level in the body
- side chains are hydrophilic C. ACIDIC
- polar side chains that are D. BASIC - have carboxyl group in their side
electrically neutral or uncharged at - have basic side chains , and chain
neutral pH. their side chain is positively
charged at or nearly neutral pH
level.
You might also like
- Biochemistry Amino AcidsDocument13 pagesBiochemistry Amino AcidsApril Aram100% (1)
- AMINO ACIDS (Slides)Document6 pagesAMINO ACIDS (Slides)cessNo ratings yet
- Techniques in Molecular Biology and Dna TechnologyDocument104 pagesTechniques in Molecular Biology and Dna TechnologyMd Shahroz AlamNo ratings yet
- BOOK Gene TherapyDocument210 pagesBOOK Gene TherapyCarla GomesNo ratings yet
- Notes Lesson 6 To 9 Botany LecDocument23 pagesNotes Lesson 6 To 9 Botany LecMohamidin MamalapatNo ratings yet
- Biochem Midterm ReviewerDocument19 pagesBiochem Midterm ReviewerERIKA ROSE ALEJONo ratings yet
- Essentials of Molecular BiologyDocument770 pagesEssentials of Molecular BiologyTuan Lam Ngoc86% (7)
- Molecular GeneticsDocument3 pagesMolecular GeneticsPRINTDESK by DanNo ratings yet
- CMS in MaizeDocument29 pagesCMS in Maizeswati_meghaNo ratings yet
- Methods of Identification in Forensic MedicineDocument53 pagesMethods of Identification in Forensic MedicineSusi Rutmalem80% (5)
- BIOCHEM - Amino AcidsDocument7 pagesBIOCHEM - Amino AcidsAlyssa Nicole PadillaNo ratings yet
- Proteins (Lec)Document3 pagesProteins (Lec)Dashi MeiNo ratings yet
- Coupling ReagentsDocument20 pagesCoupling ReagentsVaibhav DafaleNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Topical Past Papers Biology P4 C1 - C7Document63 pagesIGCSE Topical Past Papers Biology P4 C1 - C7이지후No ratings yet
- 03aamo LicyayoDocument6 pages03aamo LicyayoMohamidin MamalapatNo ratings yet
- ProteinsDocument6 pagesProteinsAlliyah Gail LoraniaNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids Peptides ProteinsDocument9 pagesAmino Acids Peptides Proteinsshane.surigaoNo ratings yet
- FOOD20003 NotesDocument42 pagesFOOD20003 NotescallensciberNo ratings yet
- (Chapter 3) Amino Acids and PeptidesDocument2 pages(Chapter 3) Amino Acids and PeptidesGicaraya, Ariana Raine FlorencelNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Notes MidtermDocument13 pagesBiochemistry Notes MidtermCeline Ricci AbrahamNo ratings yet
- 03AACM ProvidoDocument1 page03AACM ProvidoYUAN PROVIDONo ratings yet
- Coupling ReagentsDocument20 pagesCoupling ReagentsciuccototaNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Amino Acids and ProteinDocument9 pagesWeek 3 Amino Acids and Protein2F - MACAO, KHALILANo ratings yet
- Coupling ReagentsDocument20 pagesCoupling ReagentsSneh LataNo ratings yet
- Proteins NotesDocument12 pagesProteins NotesAshley SaronNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid and ProteinDocument15 pagesAmino Acid and ProteinHưng LiêuNo ratings yet
- Proteins: Amylase Lipase Pepsin Trypsin LigaseDocument8 pagesProteins: Amylase Lipase Pepsin Trypsin LigaseGin HuangNo ratings yet
- 03 - Intro UNIT 2Document24 pages03 - Intro UNIT 2Elena OlmedoNo ratings yet
- Biochem 101 Midterm Part3Document25 pagesBiochem 101 Midterm Part3saudiamaemalang7No ratings yet
- Activity 3 - Amino Acids and PeptidesDocument7 pagesActivity 3 - Amino Acids and PeptidesKate MendozaNo ratings yet
- Amino AcidDocument64 pagesAmino AcidGon FreecssNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids - Importance (Buffering Ability) and Problems (Cystinuria)Document10 pagesAmino Acids - Importance (Buffering Ability) and Problems (Cystinuria)ANAND sNo ratings yet
- Harper's Biochemistry - C3 Amino Acids & PeptidesDocument2 pagesHarper's Biochemistry - C3 Amino Acids & PeptidesKim LlamasNo ratings yet
- Biochem Midterms Review Ni QTDocument17 pagesBiochem Midterms Review Ni QTAlyssa MacaraigNo ratings yet
- PHR109 Lec19Document23 pagesPHR109 Lec19saminshamserNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Ii Chapter 7Document34 pagesChemistry Ii Chapter 7Nur AthirahNo ratings yet
- Biochem Lec Proteins and EnzymesDocument7 pagesBiochem Lec Proteins and EnzymesLyra Denise LlidoNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids and ProteinsDocument5 pagesAmino Acids and ProteinsGrace FernandoNo ratings yet
- General Biology ReviewerDocument7 pagesGeneral Biology ReviewerGenne kayeNo ratings yet
- Elemental Composition - ContainsDocument31 pagesElemental Composition - ContainsGabriel RamosNo ratings yet
- (BioE 402) MolBio Lecture 3 Amino AcidsDocument8 pages(BioE 402) MolBio Lecture 3 Amino AcidsJhun Lucky Sadsad100% (1)
- Amino AcidsDocument10 pagesAmino AcidsHaneen HafizNo ratings yet
- ProteinDocument6 pagesProteinAbdullah Al MamunNo ratings yet
- Protein Structure and FunctionDocument176 pagesProtein Structure and FunctionbanyacskijuliusNo ratings yet
- 05 - Amino Acids and ProteinDocument56 pages05 - Amino Acids and ProteinFauzia SavitriNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids and Proteins ReviewerDocument5 pagesAmino Acids and Proteins ReviewerDaine MarconNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Week 7 - ProteinsDocument6 pagesBiochemistry Week 7 - ProteinsMicah JadeNo ratings yet
- 2.0 Amino AcidsDocument57 pages2.0 Amino AcidsGURPARABJOT KAURNo ratings yet
- Medicinal Chemistry of Beta-Lactam AntibioticsDocument13 pagesMedicinal Chemistry of Beta-Lactam AntibioticsJosiah O OmobaNo ratings yet
- Proteins: DR Sonam Chhoden RDocument33 pagesProteins: DR Sonam Chhoden RTob JurNo ratings yet
- Lippincott ProteinDocument10 pagesLippincott ProteinCAMILLE MAGNONo ratings yet
- Biochem Lesson 1Document2 pagesBiochem Lesson 1hello baiNo ratings yet
- Proteins TransesDocument10 pagesProteins TransesGwyn CaigoyNo ratings yet
- Structure of Amino AcidsDocument32 pagesStructure of Amino AcidswithneyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document143 pagesChapter 5Vân Anh Nguyễn ThịNo ratings yet
- BCH 3066 English Amino Acids - 1655284742280Document15 pagesBCH 3066 English Amino Acids - 1655284742280mistic JayNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ProteinsDocument1 pageIntroduction To ProteinsShheeeeeshhNo ratings yet
- Bochemistry - Introduction To Proteis: The Primary Level of ProteinDocument1 pageBochemistry - Introduction To Proteis: The Primary Level of ProteinALEXANDRA COLLEEN ALEGRENo ratings yet
- Im-4 Genbiochem1Document14 pagesIm-4 Genbiochem1izzy9zyzyNo ratings yet
- JLSRGDNDocument13 pagesJLSRGDNjamiegayleditaNo ratings yet
- AS ProteinsDocument2 pagesAS ProteinsAraijan AbaiNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids PDFDocument9 pagesAmino Acids PDFShreyashNo ratings yet
- 3 Amino AcidsDocument45 pages3 Amino AcidsBereket Agumas KegneNo ratings yet
- Protein FileDocument7 pagesProtein FilePhia JesalvaNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids, Proteins, and EnzymesDocument62 pagesAmino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymesendale gebregzabherNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument2 pagesBiomoleculesririNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12. Amino Acid Composition AnalysisDocument6 pagesLecture 12. Amino Acid Composition Analysisnpthaonhi12No ratings yet
- Enantioselective Synthesis of Beta-Amino AcidsFrom EverandEnantioselective Synthesis of Beta-Amino AcidsEusebio JuaristiNo ratings yet
- EXERCISE 5. Molecular Basis of Heredity Structure of The Genetic MaterialDocument3 pagesEXERCISE 5. Molecular Basis of Heredity Structure of The Genetic MaterialMohamidin MamalapatNo ratings yet
- Activity 4 - Energy Flow and Food WebDocument4 pagesActivity 4 - Energy Flow and Food WebMohamidin MamalapatNo ratings yet
- EXERCISE 9. Karyotype AnalysisDocument2 pagesEXERCISE 9. Karyotype AnalysisMohamidin MamalapatNo ratings yet
- Act. 3B Staining Methods For Microorganisms 2023Document8 pagesAct. 3B Staining Methods For Microorganisms 2023Mohamidin MamalapatNo ratings yet
- Activity 3 - Microbial MetabolismDocument1 pageActivity 3 - Microbial MetabolismMohamidin MamalapatNo ratings yet
- 12TrlAMO LicyayoDocument9 pages12TrlAMO LicyayoMohamidin MamalapatNo ratings yet
- Chap. 3 Microbial ObservationsDocument8 pagesChap. 3 Microbial ObservationsMohamidin MamalapatNo ratings yet
- Proteins 2Document4 pagesProteins 2Mohamidin MamalapatNo ratings yet
- Pre - Lectio 1-Seven Wonders in The Microbe World Video Worksheet 2023Document1 pagePre - Lectio 1-Seven Wonders in The Microbe World Video Worksheet 2023Mohamidin MamalapatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Microbial GrowthDocument18 pagesChapter 5 Microbial GrowthMohamidin MamalapatNo ratings yet
- 06Enz1AMO LICYAYODocument11 pages06Enz1AMO LICYAYOMohamidin MamalapatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Microbial MetabolismDocument9 pagesChapter 4 Microbial MetabolismMohamidin MamalapatNo ratings yet
- Chap. 2 Cell Structure and Function Student NotesDocument10 pagesChap. 2 Cell Structure and Function Student NotesMohamidin MamalapatNo ratings yet
- 03AAMO MamalapatDocument8 pages03AAMO MamalapatMohamidin MamalapatNo ratings yet
- Reporting TitrationCurve DumagpiDocument6 pagesReporting TitrationCurve DumagpiMohamidin MamalapatNo ratings yet
- 09NucAMO MamalapatDocument7 pages09NucAMO MamalapatMohamidin MamalapatNo ratings yet
- 08LipAMO MamalapatDocument14 pages08LipAMO MamalapatMohamidin MamalapatNo ratings yet
- 06Enz1AMO MamalapatDocument14 pages06Enz1AMO MamalapatMohamidin MamalapatNo ratings yet
- 07Enz2AMO MamalapatDocument8 pages07Enz2AMO MamalapatMohamidin MamalapatNo ratings yet
- Compilation of The ScriptDocument14 pagesCompilation of The ScriptMohamidin MamalapatNo ratings yet
- Prayer For StudyingDocument1 pagePrayer For StudyingMohamidin MamalapatNo ratings yet
- Notes Lesson 7 To 10 Botany LecDocument2 pagesNotes Lesson 7 To 10 Botany LecMohamidin MamalapatNo ratings yet
- 04ProAMO MamalapatDocument6 pages04ProAMO MamalapatMohamidin MamalapatNo ratings yet
- MAMALAPAT LearningContract PDFDocument2 pagesMAMALAPAT LearningContract PDFMohamidin MamalapatNo ratings yet
- Edited DramaturgyDocument4 pagesEdited DramaturgyMohamidin MamalapatNo ratings yet
- DramaturgyDocument4 pagesDramaturgyMohamidin MamalapatNo ratings yet
- Expt#1-Lab ReportDocument11 pagesExpt#1-Lab ReportMohamidin MamalapatNo ratings yet
- Expt 1 Cal of PipetteDocument3 pagesExpt 1 Cal of PipetteMohamidin MamalapatNo ratings yet
- Notes Lesson 1 To 5 Botany LecDocument7 pagesNotes Lesson 1 To 5 Botany LecMohamidin MamalapatNo ratings yet
- BLOSUM - Dot Plot - Needleman & Wunch - Smith & Waterman Matrix FillingDocument41 pagesBLOSUM - Dot Plot - Needleman & Wunch - Smith & Waterman Matrix FillingAyush zalaNo ratings yet
- MCB 253 Protein QuantitationDocument13 pagesMCB 253 Protein Quantitationrobomunkey12345No ratings yet
- Elicobactoe Real-Time PCR KitDocument10 pagesElicobactoe Real-Time PCR KitAmitNo ratings yet
- Bcsci 10 Unit 1 Topic1 1Document16 pagesBcsci 10 Unit 1 Topic1 1DemisNo ratings yet
- Nutrition, Metabolism, and Body Temperature RegulationDocument60 pagesNutrition, Metabolism, and Body Temperature RegulationJudy UrciaNo ratings yet
- Protokol Hiei-KomariDocument11 pagesProtokol Hiei-KomariMuchdar DavisNo ratings yet
- Assignment PDFDocument6 pagesAssignment PDFaubrey yangzonNo ratings yet
- Fvets 09 975726Document13 pagesFvets 09 975726Maria MountrihaNo ratings yet
- Enzymes Organic ChemistryDocument6 pagesEnzymes Organic Chemistryمحمد الكبيسيNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis Practice (Sidney Berjamin)Document3 pagesProtein Synthesis Practice (Sidney Berjamin)sidney berjaminNo ratings yet
- (Doi 10.1007 - 978!3!662-05204-4) Mirsky, Vladimir M. - (Springer Series On Chemical Sensors and Biosensors) Ultrathin Electrochemical Chemo - and Biosensors Volume 2Document367 pages(Doi 10.1007 - 978!3!662-05204-4) Mirsky, Vladimir M. - (Springer Series On Chemical Sensors and Biosensors) Ultrathin Electrochemical Chemo - and Biosensors Volume 2Al AmeenNo ratings yet
- Gene Tech - Set 1 A2 Biology: by Akram SirDocument17 pagesGene Tech - Set 1 A2 Biology: by Akram SirMuhammad AkramNo ratings yet
- By1 Jan 2010 QPDocument13 pagesBy1 Jan 2010 QPFreyaaMichelleNo ratings yet
- Video Recap of Cell Transport by Amoeba SistersDocument2 pagesVideo Recap of Cell Transport by Amoeba Sisters5zhrbrtbwdNo ratings yet
- A Simple Two-Stage PCR Based Method To Construct Gene Disruption CassetteDocument4 pagesA Simple Two-Stage PCR Based Method To Construct Gene Disruption CassetteMakesh KumarNo ratings yet
- This Learning Competency Is Extracted From The Deped Curriculum GuideDocument6 pagesThis Learning Competency Is Extracted From The Deped Curriculum GuideZuzuNo ratings yet
- Summer 2018 Answer PaperDocument36 pagesSummer 2018 Answer PaperJayesh DesaleNo ratings yet
- PlasmodesmataDocument3 pagesPlasmodesmataTan ShunYaoNo ratings yet
- Differences Between Mitosis and MeiosisDocument8 pagesDifferences Between Mitosis and MeiosisNanashiNo ratings yet
- 1743 7075 8 75 PDFDocument16 pages1743 7075 8 75 PDFPutri Wulan SukmawatiNo ratings yet
- SIM Biochemistry ULO6Document28 pagesSIM Biochemistry ULO6Darl MalazarteNo ratings yet
- Welch Et AlDocument2 pagesWelch Et AlStephanie SmithNo ratings yet
- DNA RecombinationDocument42 pagesDNA RecombinationAkashDebNo ratings yet