Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Adobe Scan Nov 06, 2023
Uploaded by
rajtarabap550 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views3 pagesAaa
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAaa
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views3 pagesAdobe Scan Nov 06, 2023
Uploaded by
rajtarabap55Aaa
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
FIRST STAGE SECOND STAGE THIRD STAGE FOURTH STAGE
NEUTRON NEUTRON NEUTRON NEUTRON
Fig. 4.03
2. The neutrons produced in the U235 block leak from the block, if the size of the
block is smaller than the critical size.
The U235 block is said to be of critical size, if the number of neutrons lost per second is just
equal to the number of neutrons produced per second in the block.
The mass of the UZ3 block of critical size is called critical mass. Some neutrons
are also lost due to their absorption by the impurities present in the U block.
So that the fission reaction proceeds smoothly, the number of neutrons
produced per second should be greater than the number of neutrons lost per second
rom the block. It is achieved by having U235 block of size bigger than the critical
size. The loss of neutrons from the U235 block is also minimised by providing alayer
Ofnon-fissionable material over the U3 block. In fact, whether a chain reaction will
Temain steady or accelerate or retard is determined by a factor, called neutron
Teproduction factor (k).
Neutron reproduction factor is defined as the ratio of the rate of production of neutrons
to the rate of loss of neutrons. Thus,
rate of production of neutrons ..(4.02)
k=
rate of loss of neutrons
Anssion reaction will be steady, in case k= 1. In case k>1, the fission reaction
will
laccelerate and it will retard, in case k<1.
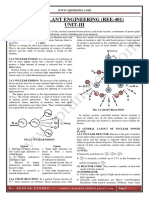
4.07, NUCLEAR REACTOR
Anuclear reactor is a device in which nuclear fission can be carried out through
asustained and a a controlled chain reaction. It is also called an atomicpile. By making
use of uuranium as fuel, the products such as neutrons (useful for causing fission of
uranium), radioisotopes and heat energy (to run turbines)
are produced.
surrounded by
1300
thick blocks ofcarbon nuclear
Construction. Anuclear reactorr
consists of
4.04. The other parts ofthe
shown in Fig.
thick absorbing walls of concrete. as
Teactor areasexplained below: CONTROL
MODERATOR RODS
STEAM TO
COOLANT TURBINE
(WHEN HOT)
00001
WATER
CONCRETE
WALLS
COOLANT
(WHEN GOLD)
CARBON BLOCK
u230 IN ALUMINIUM Watch out
CYLINDERS
Fig.4.04
usedin thereactor is called
nuclearfuel. 99-3% ofuranium
isthe isasgel
0.7% of mixed uranium
ematerial is f
1, Nuclear fuel. The fissionable
sealed in aluminium cylinders. These cylinders are y235 which provides the por
It generallyconsists of o U235 the carbon blocks. normal fission reactor !
inserted in the holes drilledin downthe fastmoving neutrons produced
RModerator. The material used to slow in the fission
nuclear fission is called moderator. The neutrons released energy to
as aresultof order of 2MeV. Moderator reduces their
of uranium possessenergy of the to the thermatmotiön of the neutron. For this reason,
0-0235 eV, which corresponds energy of 0-0235 eV are called thermal neutrons. In
the neutrons slowed down to the either graphite (carbon) or water or heavy water
anuclear reactor, the moderator is
(deuterium oxide).
Research Centre, Trombay uses water as
The Apsra reactor at BhabhaAtomic It is a swimming pool type nuclear
moderator. It was commissioned in the year 1956. of genetic studies in agricultural
reactor. Ithas rendered agreat service in the field Kota and Narora are used for
Kalpakkam,
crops. The nuclear reactors at Tarapur, heavy water is used as moderator.
power production and in these reactors, neutrons are used to control
3. Control rods. The materials that can absorb the used for this purpose. They
the nuclear chain reaction. Cadmium" or boron rods are blocks. When the control
can be moved in or out of the holes drilled in the carbon neutrons to such
rods are completely pushed into the carbon blocks, they absorb the slowly withdrawn,
an extent that the chain reaction comes to a halt. As the rods are
the chain reaction proceeds and more we withdraw the rods, stronger is the intensity
of the chain reaction.
4.Coolant. The material used to absorb the heat generated as a consequence
of chainreaction is called coolant. The coolant releases the heat energy to the water
and the water is thus converted into super-heated steam, which is used to runthe
urbines. These turbines in turn are used to operate the machines, say electric
generator. Liquid sodium may also be used as coolant. Sometimes heavý water is
used as coolant.
5. Protective shield. To prevent the spreading of the radioactive effect to the
space around the nuclear reactor, it is enclosed in thick Concrete watts catted
protective shield. The protective shieldmay be 10 m thick.
Working. Asingle slowneutron causes the fission of , U235 nucleus, with the
release of 200 MeV energy and three fast neutrons. The cadmium rods partially
Rnrh the neutrons and the moderator slows down the remaining neutrons. The
Sow neutrons carry out the fission of other gUnuclei and so on. In order to step
un the reaction, the cadmium rods are slowly withdrawn, while to step Own the
eaction. the cadmium rods are slowly introduced. In addition to control rods, the
reactors are provided with safety rods. For the fair functioning of a nuclear reactor, Watch out !
its k-factor is kept close to unity by moving the cadmium rods in or out. nuclear
ofa
The k-factor is defined as the ratio of the number of fissions The operation
k-factor
produced
oPneration of neutrons to the numiber of jisstoMs of the preceeding generation by a given
of neutrons. It critical, as its
is also called reproduction factor.
*Cadmium has high cross-section for neutron absorption
NCLEARREACTIONS
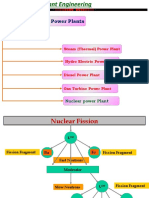
Uses. 1. Nuclear reactors are used in electric Power generation.
2They are used to produce radioactive isotopesfor their use in medical science,
agricultureand industry.
3.They areresearch.
allso used to produce neutron beamns of very high intensity for their
INe in nuclear
4.08. NUCLEARFUSION
Whentwo or more than tuo light nucleifuse together to form heavy nucleus with the
liberation of energy, the process is called nuclear fusion.
For example, two deutrons çan fusetogether to form a helium nucleus releasing
24 MeV of energy. The fusion reaction may be expressed as below:
H'+H’He+ 24 MeV
The above nuclear fusion reaction isenergetically possible, only if the mass of the
He nucleus is less than the sum of the masses of the two deutron nuclei. The
difference in the initialmass and the final mass of the product nuclei is liberated as
he energy of fusion reaction. It may be pointed out that the fusion of two light nuclei
akes place in an attempt to achieve greater stability. It is because, the high value of the
DInding energy per nucleon is one of the factors responsible for the greater stability of
Anucleus. It follows from the binding energy curve that in the low mass number region,
Mie binding energy per nucleon increases with the mass number. When two lighter
Mucei fuse together to form a heavier nucleus, the net mass defect and hence the binding
nergy of the nucleus so formed will be more.
To carry out the fusion of two nuclei, they must be brought so much close to each
other that they overcome the electrostatic repulsion and come within the attractive
of the nuclear forces. This is possible only, when they approach each other with
Kinetic energy of the order of 0-1 MeV or more. This is best obtained by raising the
emperature of the two nuclei to about 10 K.At this temperature, the thermal motion
atoms is with kinetic energy of the order of 0-1 MeV. For this reason, nuclear fusion
Teactionis also termed as themonuclear reaction.
emperature of the order of 10Kis very difficult to obtain. However, this can be
You might also like
- Nuclear Power Engineering: Aiub Dr. M. Tanseer Ali NPWR Lec 09/1Document27 pagesNuclear Power Engineering: Aiub Dr. M. Tanseer Ali NPWR Lec 09/1Toaha HasnainNo ratings yet
- Lec - 10 PP - Nuclear Power PlantsDocument41 pagesLec - 10 PP - Nuclear Power PlantsLog XNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power PlantsDocument7 pagesNuclear Power Plantsb200102No ratings yet
- Power Plant Engineering Lab Sheet 7 PDFDocument3 pagesPower Plant Engineering Lab Sheet 7 PDFMd. Mehadi Hasan Shamim 171-33-422No ratings yet
- Notes Unit IIDocument14 pagesNotes Unit IIAloke RajkishoreNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 PowerDocument12 pagesChapter 10 PowerAliciaDawnNo ratings yet
- Lec-11 - MCE 4805 - Nuclear Power PlantDocument37 pagesLec-11 - MCE 4805 - Nuclear Power PlantWinden CaveNo ratings yet
- Nuclearpowerplant 170804051105Document31 pagesNuclearpowerplant 170804051105Carlos WilliamsonNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power Plant I: Chernobyl Reactor Meltdown: CH320 - Seminar IIIDocument47 pagesNuclear Power Plant I: Chernobyl Reactor Meltdown: CH320 - Seminar IIIGokul SinghNo ratings yet
- Classification of Power Plants: Steam (Thermal) Power Plant Hydro Electric Power PlantDocument10 pagesClassification of Power Plants: Steam (Thermal) Power Plant Hydro Electric Power PlantAd Man GeTigNo ratings yet
- Unit Iii Power Plant Engineering Ree 401Document5 pagesUnit Iii Power Plant Engineering Ree 401vlogs 4 youNo ratings yet
- Ppe AnswersDocument54 pagesPpe AnswersAditya SinghNo ratings yet
- Part 1 - General Introduction (Saroja Saibaba)Document31 pagesPart 1 - General Introduction (Saroja Saibaba)Arnav ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power plantDocument9 pagesNuclear Power plantMridul krishna bhardwajNo ratings yet
- Applications of Nuclear PhysicsDocument76 pagesApplications of Nuclear PhysicsultimuNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power Plant: Course ContentsDocument15 pagesNuclear Power Plant: Course ContentsSheh NazNo ratings yet
- Nuclear PowerDocument6 pagesNuclear PowerAiman SaufiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9. Nuclear Power PlantDocument24 pagesChapter 9. Nuclear Power Plantdiana tahaNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Fission and Fusion Lesson 16Document6 pagesNuclear Fission and Fusion Lesson 16Angel Alyza SisonNo ratings yet
- L3 - RadioActivityDocument54 pagesL3 - RadioActivityAmita SurNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Physics: Fission & FusionDocument46 pagesNuclear Physics: Fission & FusionFraser McGillNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Energy (5.4) (Sebenar)Document13 pagesNuclear Energy (5.4) (Sebenar)Mohamad AfiqNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Fission: Understanding the Process and DebateDocument15 pagesNuclear Fission: Understanding the Process and DebateDina ThebianNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power Plant Question BankDocument7 pagesNuclear Power Plant Question BanksriramrpselvamNo ratings yet
- Ppe M4Document13 pagesPpe M4AnexmechNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Energy Conversion1Document112 pagesUnit 4 Energy Conversion1Shevaniga SridharNo ratings yet
- 10sep2014 Nuclear Fuel Cycle Notes Balakrishna PalankiDocument52 pages10sep2014 Nuclear Fuel Cycle Notes Balakrishna PalankiBalakrishna PalankiNo ratings yet
- Thermo ProjectDocument9 pagesThermo Projectmohamed mustafaNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power PlantDocument21 pagesNuclear Power PlantAshvani ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power PlantDocument50 pagesNuclear Power PlantBLACK GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Part - I (General) : Rajasthan Atomic Power StationDocument28 pagesPart - I (General) : Rajasthan Atomic Power StationjbsoniNo ratings yet
- Reactor Operation Without Feedback Effects: 22.05 Reactor Physics - Part Twenty-SixDocument16 pagesReactor Operation Without Feedback Effects: 22.05 Reactor Physics - Part Twenty-SixmsakowskNo ratings yet
- Prepared by Hasin Mussayab Ahmed, Lecturer, Dept of EEE, UU: Power Plant Engineering Lecture On Nuclear Power PlantDocument26 pagesPrepared by Hasin Mussayab Ahmed, Lecturer, Dept of EEE, UU: Power Plant Engineering Lecture On Nuclear Power Plantহাসিন মুসাইয়্যাব আহমাদ পুণ্যNo ratings yet
- Nlenvirte 5174Document6 pagesNlenvirte 5174api-244168124No ratings yet
- The Physics Behind The Working Of: Made By-Taniya Gupta B.SC Phy (H) II Yr. Miranda HouseDocument19 pagesThe Physics Behind The Working Of: Made By-Taniya Gupta B.SC Phy (H) II Yr. Miranda HouseTaniya GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1: Nuclear Power PlantDocument14 pagesChapter-1: Nuclear Power PlantMohammad AmmarNo ratings yet
- A2 Unit5 Nuclear 15 The Thermal Nuclear ReactorDocument27 pagesA2 Unit5 Nuclear 15 The Thermal Nuclear ReactorPawanMatabadulNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Energy - 2022FDocument23 pagesNuclear Energy - 2022FNdapiwa KengaletsweNo ratings yet
- Unit-II Nuclear Physics & Electron BalisticsDocument10 pagesUnit-II Nuclear Physics & Electron BalisticsAloke Rajkishore100% (1)
- Unit - Iii Nuclear Power PlantsDocument10 pagesUnit - Iii Nuclear Power Plantsrsankarganesh MECH-HICETNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Fission and FusionDocument32 pagesLecture 2 - Fission and FusionSahil MakwanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4-Nuclear Power PlantDocument28 pagesChapter 4-Nuclear Power PlantbaseakelNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Fission and Reactor Types ExplainedDocument13 pagesNuclear Fission and Reactor Types Explainedhafeez khanNo ratings yet
- 11-Nuclear Power PlantsDocument86 pages11-Nuclear Power PlantsSaif YounusNo ratings yet
- Pearson Chemistry 25.3Document6 pagesPearson Chemistry 25.3Jack LualdiNo ratings yet
- NSE L1-2 Basic Layout22fDocument38 pagesNSE L1-2 Basic Layout22fabdul hakimNo ratings yet
- Why a Nuclear Reactor Cannot Explode Like an Atom BombDocument4 pagesWhy a Nuclear Reactor Cannot Explode Like an Atom BombMarlind3No ratings yet
- Unit 2 power plantDocument36 pagesUnit 2 power plantlekoringoeNo ratings yet
- Nuclear 2Document37 pagesNuclear 2Dan NiloNo ratings yet
- E=mc2 Einstein's Mass-Energy EquationDocument17 pagesE=mc2 Einstein's Mass-Energy EquationSukhwinder Singh GillNo ratings yet
- Nikhil Gaurav MSESP75010Document23 pagesNikhil Gaurav MSESP75010RabinNo ratings yet
- Physics Fission and FusionDocument20 pagesPhysics Fission and FusionhamdaNo ratings yet
- Nuclear TechnologyDocument18 pagesNuclear Technologysipun acharyaNo ratings yet
- 2017 - Ali - Nuclear Fission and Nuclear Power StationsDocument76 pages2017 - Ali - Nuclear Fission and Nuclear Power StationsrjostNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Reactors: Presented To: Sir Aiman ShabbirDocument33 pagesNuclear Reactors: Presented To: Sir Aiman Shabbirabubakar chohaanNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Engineering 2Document35 pagesNuclear Engineering 2rajeshNo ratings yet
- ME 5129 - Principles of Thermal Energy Conversion: Introduction To Nuclear Power ReactorsDocument12 pagesME 5129 - Principles of Thermal Energy Conversion: Introduction To Nuclear Power ReactorsAnandNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document8 pagesChapter 1zjutt sabNo ratings yet
- The Stopping and Ranges of Ions in Matter: Handbook of Stopping Cross-Sections for Energetic Ions in All ElementsFrom EverandThe Stopping and Ranges of Ions in Matter: Handbook of Stopping Cross-Sections for Energetic Ions in All ElementsNo ratings yet
- Optical Spectra of Transparent Rare Earth CompoundsFrom EverandOptical Spectra of Transparent Rare Earth CompoundsS. HufnerNo ratings yet
- 2019 Implementasie-SamsatdiBaliDocument10 pages2019 Implementasie-SamsatdiBaliDiannita SusantiNo ratings yet
- A Generation of Contradictions-Unlocking Gen Z 2022 China FocusDocument25 pagesA Generation of Contradictions-Unlocking Gen Z 2022 China FocusCindy Xidan XiaoNo ratings yet
- 1-2 COGS Vs SALESDocument3 pages1-2 COGS Vs SALESRenato GilbonioNo ratings yet
- Temenos Brochure - FormpipeDocument5 pagesTemenos Brochure - FormpipeDanial OngNo ratings yet
- FMAI - Ch04 - Stock MarketDocument105 pagesFMAI - Ch04 - Stock Marketngoc duongNo ratings yet
- What Is Your Road, Man?Document232 pagesWhat Is Your Road, Man?Oana AndreeaNo ratings yet
- USP FriabilityDocument2 pagesUSP Friabilityshdph100% (1)
- Coffee TestDocument6 pagesCoffee TestAmit Satyen RaviNo ratings yet
- SMC Dialog Plus Conversion To Another SMC 8 - 22 - 2014Document15 pagesSMC Dialog Plus Conversion To Another SMC 8 - 22 - 2014vivek kumarNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document50 pagesUnit 1vaniphd3No ratings yet
- 01 A Brief Introduction To Cloud ComputingDocument25 pages01 A Brief Introduction To Cloud ComputingfirasibraheemNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Accounting 2 - CL NCL Lecture NotesDocument2 pagesIntermediate Accounting 2 - CL NCL Lecture NotesRacheel SollezaNo ratings yet
- Forecast Time Series-NotesDocument138 pagesForecast Time Series-NotesflorinNo ratings yet
- Etherpad Text-Based TutorialDocument5 pagesEtherpad Text-Based Tutorialapi-437836861No ratings yet
- Finding The Answers To The Research Questions (Qualitative) : Quarter 4 - Module 5Document39 pagesFinding The Answers To The Research Questions (Qualitative) : Quarter 4 - Module 5Jernel Raymundo80% (5)
- Factory Test Report For OPzS 800 EED-20041724 2VDocument3 pagesFactory Test Report For OPzS 800 EED-20041724 2VmaherNo ratings yet
- Mark Wildon - Representation Theory of The Symmetric Group (Lecture Notes) (2015)Document34 pagesMark Wildon - Representation Theory of The Symmetric Group (Lecture Notes) (2015)Satyam Agrahari0% (1)
- Trial BalanceDocument2 pagesTrial BalanceJoseph Bayo BasanNo ratings yet
- Shooting ScriptDocument12 pagesShooting Scriptapi-544851273No ratings yet
- A New Aftercooler Is Used On Certain C9 Marine Engines (1063)Document3 pagesA New Aftercooler Is Used On Certain C9 Marine Engines (1063)TASHKEELNo ratings yet
- Board Question Paper: March 2018: Geography and EconomicsDocument2 pagesBoard Question Paper: March 2018: Geography and EconomicsVishvajit PatilNo ratings yet
- Red Lion Edict-97 - Manual PDFDocument282 pagesRed Lion Edict-97 - Manual PDFnaminalatrukNo ratings yet
- Effect of Upstream Dam Geometry On Peak Discharge During Overtopping Breach in Noncohesive Homogeneous Embankment Dams Implications For Tailings DamsDocument22 pagesEffect of Upstream Dam Geometry On Peak Discharge During Overtopping Breach in Noncohesive Homogeneous Embankment Dams Implications For Tailings DamsHelvecioNo ratings yet
- Rolls-Royce M250 FIRST Network: 2015 Customer Support DirectoryDocument76 pagesRolls-Royce M250 FIRST Network: 2015 Customer Support Directoryale11vigarNo ratings yet
- Why it's important to guard your free timeDocument2 pagesWhy it's important to guard your free timeLaura Camila Garzón Cantor100% (1)
- A Report On Kantajew MandirDocument21 pagesA Report On Kantajew MandirMariam Nazia 1831388030No ratings yet
- Consumer Behavior PP Chapter 4Document36 pagesConsumer Behavior PP Chapter 4tuongvyvyNo ratings yet
- Cisco Series SWCFG Xe 16 12 XDocument416 pagesCisco Series SWCFG Xe 16 12 XWagner SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document10 pagesLesson 2angeliquefaithemnaceNo ratings yet
- Engr2227 Apr03Document10 pagesEngr2227 Apr03Mohamed AlqaisiNo ratings yet