Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Research Reviewer
Uploaded by
Joseline SisonCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Research Reviewer
Uploaded by
Joseline SisonCopyright:
Available Formats
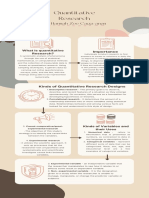
Nature of Inquiry on Research 2.
Causal-comparative Research
QUANTITATIVE RESEARCH - attempts to establish cause-effect relationships among
the variables of the study.
- The process of collecting and analyzing numerical data.
It can be used to find patterns and averages, make 3. Experimental Research
predictions, test causal relationships, and generalize - also measures the effect of the independent variable
results to wider populations. (cause) to the dependent variable (effect); however, the
researcher can control the independent variables in the
- Is an objective, systematic, empirical investigation of study, wherein the participants are randomly assigned.
observable phenomena through the use of computational A. True experimental
techniques. B. Quasi-experimental
- It uses numbers in stating generalizations about a given IMPORTANCE OF RESEARCH
problem or inquiry in contrast.
Research is essential for the following reasons:
- It highlights the numerical analysis of data hoping that 1. Knowledge is established.
the numbers yield unbiased results that can be generalized 2. Perceptions are corrected.
to some larger population and explain a particular 3. Phenomena are validated.
observation. 4. Present solutions are tested for effectivity.
5. Problems are solved.
- The research instrument used in this kind of research is
in the form of surveys and closed-ended questionnaires.
CONSTRUCTS AND VARIABLES
- The data usually obtained from a large sample of the
population and is analyzed using statistical techniques Constructs
ensuring that the conclusions drawn from quantitative - are mental abstractions derived from the combination of
research are valid and are representative of the population. concepts, or your mental representation of the world
around you.
STRENGTHS OF A QUANTITATIVE RESEARCH
- Involves greater number of subjects & enables a broader Variables
study. - are constructs that can be understood differently because
- Results are more objective and accurate. of their differences in values
-When the right procedure is used, it can be replicated.
- Can summarize vast sources of information & make 1. Independent variables – manipulated variables that
comparisons across categories.
cause a change in another variable.
- Personal bias can be avoided.
2. Dependent variables – those that are affected by
WEAKNESSES OF A QUANTITATIVE RESEARCH
independent variables.
- Quantitative data, while they can test a hypothesis, may
be limited in explaining their context. 3. Confounding or extraneous variables – variables
- The research is often conducted in an artificial setting,
usually indicated in an experimental research.
where a certain level of control is exercised.
4. Discrete variables – quantitative or numeric variables
TYPES OF QUANTITATIVE RESEARCH
that are obtained by counting.
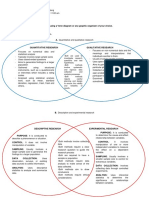
1. Descriptive Research 5. Continuous variables - quantitative or numeric
- involves the collection of data either test a hypothesis or
variables that are obtained by measuring or computation.
describe the variables mentioned in the study.
a. Correlational Research 6. Quantitative variables – variables that give details
- attempts to determine the level of relationship between
regarding the number or level of something.
two or more variables.
b. Survey 7. Qualitative variable – variables that represent kinds or
types of objects.
8. Categorical variables – those that characterize and 1. Nominal scales – just concerned with the names and
describe the quality of data. categories of responses. (e.g. nationality, hair color)
2. Ordinal Scales – used for data that intends to be
Level of measurement – the association of the values that
ranked. (e.g. first, second, third)
are linked to a variable.
3. Interval Scales – use equal units of measurement and
Importance
intervals to know the distance between them more than the
• Proper interpretation of data related to the variable.
• Decisions about the proper statistical analysis to be used. sequence. (e.g. temperature, IQ)
4. Ratio scales – the highest level of measurement. (e.g.
height, weight, age)
You might also like
- Topic 1 Assignment: Navigating GCU Resources & Writing ExpectationsDocument7 pagesTopic 1 Assignment: Navigating GCU Resources & Writing ExpectationsBlake ChambersNo ratings yet
- Oxford Solutions Intermediate Cumulative Test Answer Keys ADocument5 pagesOxford Solutions Intermediate Cumulative Test Answer Keys AAleks50% (2)
- Sharp J. Exam Ref AI-900 Microsoft Azure AI Fundamentals 2022 PDFDocument366 pagesSharp J. Exam Ref AI-900 Microsoft Azure AI Fundamentals 2022 PDFKoos SerfonteinNo ratings yet
- 02 NetNumen U31 Software Installation - 54PDocument54 pages02 NetNumen U31 Software Installation - 54PAppolenaire Alexis86% (7)
- D0117 RB XEO Service ManualDocument217 pagesD0117 RB XEO Service ManualYuriko MartinezNo ratings yet
- Study Guide for Practical Statistics for EducatorsFrom EverandStudy Guide for Practical Statistics for EducatorsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Iso 21504 2022Document11 pagesIso 21504 2022Olga MorenoNo ratings yet
- MTCO - Tapping Into Digital BrainDocument13 pagesMTCO - Tapping Into Digital BrainRuby Singla100% (1)
- Research 2 (Quantitative Research) ResearchDocument3 pagesResearch 2 (Quantitative Research) ResearchAbie Joyce RemoNo ratings yet
- Research Paper (Quantitative Research) ResearchDocument3 pagesResearch Paper (Quantitative Research) ResearchLerie MendozaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document1 pageChapter 1Quincy Joy SarioNo ratings yet
- STATISTICS ANALYSIS - Reviewer Week 1Document5 pagesSTATISTICS ANALYSIS - Reviewer Week 1Lovely De SalasNo ratings yet
- Research in Daily Life 2Document5 pagesResearch in Daily Life 2Mike Reyes (XxMKExX)No ratings yet
- Lessons#1 - Characteristics, Strengths, Weaknesses, and Kinds of Qiantitative ResearchDocument17 pagesLessons#1 - Characteristics, Strengths, Weaknesses, and Kinds of Qiantitative Researchjerikbenito46No ratings yet
- Practical Research 2 Midterms ReviewerDocument4 pagesPractical Research 2 Midterms ReviewerRyan GañaNo ratings yet
- Resesarch ReviewerDocument3 pagesResesarch ReviewerMa Jollie Mae BereNo ratings yet
- STATPSY ReviewerDocument15 pagesSTATPSY ReviewerVincent Miguel BastieroNo ratings yet
- Research: Scientific Methods of Research Importance of ResearchDocument4 pagesResearch: Scientific Methods of Research Importance of ResearchSai RillNo ratings yet
- StatisticsDocument5 pagesStatisticsMachi KomacineNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Practical Research 2Document3 pagesReviewer in Practical Research 2Elmo Vincent Bernardo MurosNo ratings yet
- 4q Capstone ReviewerDocument14 pages4q Capstone Reviewerlheyne lopezNo ratings yet
- Nature of Inquiry and ResearchDocument51 pagesNature of Inquiry and ResearchCorpin Ian RoyNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in PR2, (QUARTER 2)Document4 pagesReviewer in PR2, (QUARTER 2)Jv OlegarioNo ratings yet
- Lectures Ni SheineDocument42 pagesLectures Ni SheineZedekiah HaloNo ratings yet
- Practical Research II Nature and Inquiry of ResearchDocument62 pagesPractical Research II Nature and Inquiry of ResearchRolando Jose CachoperoNo ratings yet
- Statistics, and The Relationships Between Events/Numbers: Collection of Quantitative InformationDocument4 pagesStatistics, and The Relationships Between Events/Numbers: Collection of Quantitative Informationanon_853164953No ratings yet
- Research Quiz 1Document5 pagesResearch Quiz 1Ellen CatedralNo ratings yet
- Psychological Statistics (Notes)Document9 pagesPsychological Statistics (Notes)Faith Hannah OroNo ratings yet
- Research ReviewerDocument5 pagesResearch ReviewermaeesotoNo ratings yet
- Research NotesDocument5 pagesResearch NotesLadyrose SalazarNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2Document4 pagesPractical Research 2Ace Andrie AbarabarNo ratings yet
- 9 ResearchDocument15 pages9 ResearchGrace PascualNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Its Role in Psychological ResearchDocument2 pagesStatistics and Its Role in Psychological ResearchAlexandra San PedroNo ratings yet
- Res - NotesDocument14 pagesRes - NotesYuri YapNo ratings yet
- PR ReviewerDocument3 pagesPR ReviewerVictoria Lourdes Mesias LoquinteNo ratings yet
- PR2 ReviewerDocument4 pagesPR2 ReviewerThe HowlNo ratings yet
- Statistics Mod 1Document4 pagesStatistics Mod 1Jannelle TanNo ratings yet
- Terms To Learn: Notes in StatisticsDocument13 pagesTerms To Learn: Notes in StatisticsMichael JubayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction PDFDocument6 pagesChapter 1 Introduction PDFDaniela ArceoNo ratings yet
- Notes No. 1 Stat and Prob 11 D 2024Document4 pagesNotes No. 1 Stat and Prob 11 D 2024nikkigabanto.24No ratings yet
- Infographics GEN CHEMDocument1 pageInfographics GEN CHEMKhing NanaaagacNo ratings yet
- Reviewer PR2Document10 pagesReviewer PR2Jhon Laurence DumendengNo ratings yet
- PR2 ReviewerDocument3 pagesPR2 ReviewerJeysel CarpioNo ratings yet
- Math 4Document4 pagesMath 4Arceta, Alia Mae M.No ratings yet
- Reviewer PRDocument4 pagesReviewer PRLaisan SantosNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER-1-PR2 Quantitative ResearchDocument3 pagesCHAPTER-1-PR2 Quantitative ResearchAnonymousNo ratings yet
- PR Module 1Document18 pagesPR Module 1Aprilyn Martelino ObregonNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Research 2Document8 pagesModule 1 - Research 2Jayvee Ken Celis RocillaNo ratings yet
- Handouts No. 01: Quantitative Research (Pr2)Document3 pagesHandouts No. 01: Quantitative Research (Pr2)Alvin Ray GarciaNo ratings yet
- Nature and Inquiry of ResearchDocument2 pagesNature and Inquiry of ResearchDach McIvan CalunsagNo ratings yet
- Stat Prelim ExamDocument4 pagesStat Prelim ExamSTEPHANIE ASONo ratings yet
- Scientific TraitsDocument6 pagesScientific Traitsaxel angelus zerimar garinaNo ratings yet
- Statistical Analysis - MODULES 1,2 & 3Document19 pagesStatistical Analysis - MODULES 1,2 & 3Allana MierNo ratings yet
- Stats Vid Lecture NotesDocument3 pagesStats Vid Lecture NotesPeaches PHNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in PRDocument8 pagesReviewer in PRCatherine SalasNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2Document6 pagesPractical Research 2Jihane TanogNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Quiz 1Document3 pagesLesson 3 Quiz 1VANESSA MOLUDNo ratings yet
- PR2 - Nature - of Inquiry - and - ResearchDocument2 pagesPR2 - Nature - of Inquiry - and - ResearchGailNo ratings yet
- PR ReviewerDocument15 pagesPR ReviewerSean OrolaNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Approach: 3. Quasi-Experimental DesignDocument3 pagesQuantitative Approach: 3. Quasi-Experimental DesignDior EstrellaNo ratings yet
- pr2 NotesDocument8 pagespr2 Notesjclmaeramonal23No ratings yet
- PR2 ReviewerDocument3 pagesPR2 ReviewerGabby GargantosNo ratings yet
- ? What Is Statistics: Descriptive and Inferential StatisticsDocument5 pages? What Is Statistics: Descriptive and Inferential StatisticsKawthar 2002No ratings yet
- PR2 HeDocument12 pagesPR2 HeJay-r MatibagNo ratings yet
- Summary Topic Coverage For Prelim Grading PeriodDocument20 pagesSummary Topic Coverage For Prelim Grading PeriodfabyunaaaNo ratings yet
- ManageEngine Desktop CentralDocument629 pagesManageEngine Desktop CentralCarlos RamirezNo ratings yet
- Ose 12 Twin Ose Boxer OkDocument2 pagesOse 12 Twin Ose Boxer OkOrlando Rojas PintoNo ratings yet
- Canada CC TopupDocument22 pagesCanada CC TopupFree RobuxNo ratings yet
- 560CMR02 DS enDocument4 pages560CMR02 DS enBhageerathi SahuNo ratings yet
- BateDocument3 pagesBateNadiaNo ratings yet
- Objectives of StudyDocument3 pagesObjectives of Studysehaj01100% (2)
- Assignment On ERPDocument3 pagesAssignment On ERPMithan BhowmickNo ratings yet
- User Interaction Design: Information Technology and Information Systems DepartmentDocument23 pagesUser Interaction Design: Information Technology and Information Systems DepartmentArnold Adriel TarregaNo ratings yet
- Aplikasi Alat Ukur Indeks Massa Tubuh Untuk Evaluasi Gizi Balita Berbasis AndroidDocument5 pagesAplikasi Alat Ukur Indeks Massa Tubuh Untuk Evaluasi Gizi Balita Berbasis Androidsri lestariNo ratings yet
- NM8 (S) DatasheetDocument53 pagesNM8 (S) Datasheetcalvin gninguiNo ratings yet
- Umwd 06516 0DHDocument3 pagesUmwd 06516 0DHИван ФиличевNo ratings yet
- Tabla RH 3RHDocument1 pageTabla RH 3RHJhon SuarezNo ratings yet
- Company Name - Ashok Leyland. Company Code - Ashok Leyland Nissan VehicleDocument1 pageCompany Name - Ashok Leyland. Company Code - Ashok Leyland Nissan VehicleDevendra ShahNo ratings yet
- Stihl 211 Chainsaw ManualDocument60 pagesStihl 211 Chainsaw ManualwaltoiNo ratings yet
- Technical Support Engineer - JDDocument2 pagesTechnical Support Engineer - JDKshitiz SagarNo ratings yet
- NM-238 GBDocument27 pagesNM-238 GBShania GintingNo ratings yet
- Description: Packag eDocument4 pagesDescription: Packag eVicenteAlvarezNo ratings yet
- Humber Battery Charger - CDHD-60-24III4-J0说明书 (中英文)Document13 pagesHumber Battery Charger - CDHD-60-24III4-J0说明书 (中英文)Clarence ClarNo ratings yet
- TM354 - Final Essay (Units 6-11) - Waleed OmarDocument31 pagesTM354 - Final Essay (Units 6-11) - Waleed OmarChristina FingtonNo ratings yet
- Monthly Grocery List Maligai Provision ListDocument9 pagesMonthly Grocery List Maligai Provision ListmayalogamNo ratings yet
- CS103 Syllabus: Date Topics Readings Assignments M January 8Document3 pagesCS103 Syllabus: Date Topics Readings Assignments M January 8Dupla PaltaNo ratings yet
- NF - Apple EUADocument2 pagesNF - Apple EUAgustavogko01100% (1)
- Solar PV Methodology - BRIDocument20 pagesSolar PV Methodology - BRI2020dlb121685No ratings yet