Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Video Link Notes
Uploaded by
gj.sarrosa0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
0 views2 pagesOriginal Title
Video-Link-Notes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
0 views2 pagesVideo Link Notes
Uploaded by
gj.sarrosaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
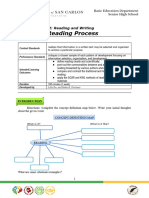
Purposive Communication
CRITICAL READING, LISTENING, VIEWING (VIDEO LINKS)
ACTIVE LISTENING 4. Read Slowly
5. Use of the dictionary and other appropriate reference works
● Passive Listening ( opposite of active listening) 6. Make Notes
7. Keep a reading journal
2 PREREQUISITES OF ACTIVE LISTENING
CONTENT AREA READING
● Commit
● requires more attention of the part of the reader
● Practice
● one goal of content area learning is to get students to
4 QUALITIES OF ACTIVE LISTENING
think as they read (Fober,2015)
● involves non-verbal communication (eye contact,
body posture) TEXT FEATURES
● involves verbal communication ( ask good questions)
● involves responding to what somebody just said According to Faber (2015), authors often organize their text by
● keep the focus on them and me them talk patterns. Common Patterns found in textbooks are:
CRITICAL READING 1. Comparison/Contrast
2. Descriptive Pattern
3. Episode Pattern
2 RECEPTIVE SKILLS
4. Time Sequence
● Reading 5. Process/Cause-effect
● Listening 6. General to specific
WHY DO WE NEED TO READ OR LISTEN? READING STRATEGIES
● entertainment 1. Previewieng
● for a purpose 2. Reading for Main Udeas
3. Using Context Clues for Vocabulary
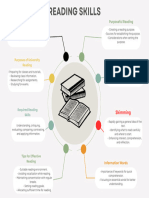
READING + LISTENING SKILLS 4. Scanning for Details
5. Making Interences
● Detailed Reading
6. Drawing Conclusions
● scanning ( specific information)
● skimming (general overview)
SKIMMING
● prediction
● is reading rapidly in order to get a GENERAL
THE RECEPTIVE SKILLS OVERVIEW of the material
1. Critical Reading
SCANNING
2. Critical Viewing
3. Media Literacy ● is reading rapidly in order to find specific facts
4. Critical Listening
CRITICAL LISTENING
CRITICAL READING
HEARING
IMPORTANCE: ● - perception of our ears
● to be fluent in reading not just in speaking
● Level of comprehension LISTENING
● - we have to pay more attention of what is being
STEPS TO BECOMING A CRITICAL READER perceived by our ears.
1. Prepare to become part of the writer’s audience ● - more concentration of the part of the listener
2. Prepare to read with an open mind
3. Consider the Title
DMD 1ST YEAR CANINE- RHYSSA SHAYNE P. REAL 1
TRANS:
5 TYPES OF LISTENING CRITICAL VIEWING
1. DISCRIMINATIVE LISTENING- individuals separate facts
which is provable information from opinion THE 3 METAFUNCTIONS OF LANGUAGE (HALLIDAY)
2. COMPREHENSIVE LISTENING- understanding 1. Interpesonal
messages 2. Ideational
3. CRITICAL OR EVALUATIVE LISTENING- evaluate a 3. Textual
message before accepting or rejecting it
4. THERAPEUTIC LISTENING- allows the individual to listen
without judging
5. APPRECIATIVE LISTENING- listen for entertainment or
enjoyment
ACTIVE OR REFLECTIVE LISTENING
● we are able to have a deeper understanding of the
information that we hav recieved
● Relational or Dialogic listening
● entails two or more participants
● seek face to face interaction
WHAT IS CRITICAL LISTENING
● this requires you not only to exercise skills yo
comprehend information but also assessments and
decisions about what you hear.
● the ability to distinguish information vs.
misinformation
● ability to distinguish which messages are false and
misleading
CHARACTERISTICS OF A CRITICAL LISTENER
1. Engaged
2. Fully Attentive
3. Systemically Analytical
4. Focused on Clarity
5. Responsive
6. Empathetic
7. Collaborative
A COMPETENT LISTENER
● - uses eye contact appropriately
● - ask questions in a non threatening tone
● - paraphrase, restates, or summarizes what the
speaker says
● - open minded
● - does not criticize, non judgmental
AN INEFFECTIVE LISTENER
- changes the subject
- judgmental
- close minded
- talks too much
- self pre occupied
- gives unwanted advice
DMD 1ST YEAR CANINE- RHYSSA SHAYNE P. REAL 2
You might also like
- Unit 2 Week 4 Fluency Assessment-3Document370 pagesUnit 2 Week 4 Fluency Assessment-3api-47536388189% (9)
- Book Wondersfluency PDFDocument368 pagesBook Wondersfluency PDFZendo KansaNo ratings yet
- Course Contents of Super LearningDocument7 pagesCourse Contents of Super LearningAhtsham AhmadNo ratings yet
- Strategies To Improve Reading SkillDocument7 pagesStrategies To Improve Reading SkillTri Kurniawati MarjadiantoNo ratings yet
- District Pamphlet 1 Junior EnglishDocument62 pagesDistrict Pamphlet 1 Junior EnglishBricious Mulimbi87% (31)
- RPS Intermediate ReadingDocument8 pagesRPS Intermediate ReadingRirin HarmilaNo ratings yet
- Reading and Writing Skills PDFDocument14 pagesReading and Writing Skills PDFPauline Juliana TiradoNo ratings yet
- Induction: Course ObjectivesDocument36 pagesInduction: Course ObjectivesQuyền Huỳnh TuấnNo ratings yet
- Determining ImportanceDocument16 pagesDetermining Importancejenom35100% (7)
- Speed Reading.Document28 pagesSpeed Reading.M WaseemNo ratings yet
- Reading and WritingDocument2 pagesReading and WritingAdhel Lucas Pascual83% (6)
- Skimming/Reading For Gist Tasks: Skyteach@oillDocument4 pagesSkimming/Reading For Gist Tasks: Skyteach@oillKate100% (2)
- Types of ReadingDocument39 pagesTypes of ReadingRabia KhanNo ratings yet
- Cornell NotesDocument5 pagesCornell NotesDonna Claire AngusNo ratings yet
- Q2 English NotesDocument6 pagesQ2 English NoteshannahmarieandalanNo ratings yet
- Kabigting, Marielle CDocument3 pagesKabigting, Marielle CAngela Louise SmithsNo ratings yet
- Q1.L5-Reading Strategies To Meet One's PurposeDocument13 pagesQ1.L5-Reading Strategies To Meet One's Purposeauhsoj raluigaNo ratings yet
- Reading and WritingDocument7 pagesReading and WritinglexieNo ratings yet
- Finals enDocument32 pagesFinals enae859562No ratings yet
- Oral CommDocument9 pagesOral CommCAMILLE JELLA ALZOLANo ratings yet
- Technical Writing MidtermDocument8 pagesTechnical Writing MidtermMayraniel RuizolNo ratings yet
- 1 What Are The Types of Reading That We Saw in Class?: Oral Reading Silent. ReadingDocument2 pages1 What Are The Types of Reading That We Saw in Class?: Oral Reading Silent. ReadingRana ArslanNo ratings yet
- DLP Student TeachersDocument7 pagesDLP Student TeachersJofer PadrinaoNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Good Readers: Multiple Rereading of More Difficult Texts Help BroadenDocument6 pagesCharacteristics of Good Readers: Multiple Rereading of More Difficult Texts Help BroadenANNA MAE PANONo ratings yet
- Module 1 - The Reading Process Ay 2023-2024Document10 pagesModule 1 - The Reading Process Ay 2023-202419010031No ratings yet
- BabitaDocument8 pagesBabitaDuho ChristopherNo ratings yet
- Dyn EdDocument11 pagesDyn Edlsrys1130No ratings yet
- Intro English Cefr Form 1Document15 pagesIntro English Cefr Form 1AdzlinaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Teaching ListeningDocument25 pagesPrinciples of Teaching ListeningDemayy ChuanNo ratings yet
- InterpretationDocument10 pagesInterpretationSri wahyuningsihNo ratings yet
- Listening and Critical ThinkingDocument11 pagesListening and Critical Thinkinglsrys1130No ratings yet
- HO (Art of Listening)Document1 pageHO (Art of Listening)Korhina GaliaNo ratings yet
- EFAPDocument10 pagesEFAPZenaida FeliasNo ratings yet
- CRITICAL READING - WPS OfficeDocument28 pagesCRITICAL READING - WPS OfficefrezelenrubioNo ratings yet
- Facilitator Handbook 4Document207 pagesFacilitator Handbook 4Md AmirNo ratings yet
- An Effective Way To Teaching Reading at Junior High SchoolDocument9 pagesAn Effective Way To Teaching Reading at Junior High SchoolersonefendiNo ratings yet
- CRWT Week 5Document31 pagesCRWT Week 5Honey marquezNo ratings yet
- CRWT Week 5Document31 pagesCRWT Week 5JULIE ANN ABAYONNo ratings yet
- Public Speaking and Persuasion FinalDocument23 pagesPublic Speaking and Persuasion Finalgostephanie247No ratings yet
- Colorful Calm Corporate Clean Mind MapDocument1 pageColorful Calm Corporate Clean Mind MapAzul Vazquez MaldonadoNo ratings yet
- English Reviewer QatDocument2 pagesEnglish Reviewer QatJames Darren TadeoNo ratings yet
- English Lesson On Listening SkillsDocument8 pagesEnglish Lesson On Listening SkillsAristotle BongoNo ratings yet
- Act of Looking at Printed Words and Understanding or Comprehending What They Mean or What They Are SayingDocument4 pagesAct of Looking at Printed Words and Understanding or Comprehending What They Mean or What They Are Sayingmabea dediosNo ratings yet
- CRWT111 Prelim Lec 4-Reading-StrategiesDocument2 pagesCRWT111 Prelim Lec 4-Reading-Strategiesjonna delNo ratings yet
- Tugas Manajemen Minggu 3Document30 pagesTugas Manajemen Minggu 3Erna NanaNo ratings yet
- Teacher: 4th Grade School: Subject: Reading/ElaDocument5 pagesTeacher: 4th Grade School: Subject: Reading/ElaKO GINNo ratings yet
- Assignnment No. 4 - Reading Writing MethodsDocument6 pagesAssignnment No. 4 - Reading Writing MethodsNazareth de leonNo ratings yet
- Bu I 1 Critical - Active ReadingDocument2 pagesBu I 1 Critical - Active ReadingNgô HươngNo ratings yet
- Eapp Lesson 3 Reading Acad TextDocument39 pagesEapp Lesson 3 Reading Acad TextKathleenNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5: 3 Components of AttitudeDocument2 pagesLesson 5: 3 Components of AttitudeMhiramae RoxasNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Lesson Part 1Document16 pagesModule 1 Lesson Part 1Nicole DeusNo ratings yet
- Week 3 - 8 July 2021Document13 pagesWeek 3 - 8 July 2021Nazmin Binti Abdullah IPG KDANo ratings yet
- English ReviewerDocument10 pagesEnglish ReviewerKyla PrincipeNo ratings yet
- Reading StrategiesDocument3 pagesReading StrategiesDe Leon, Austine Sydney D.No ratings yet
- Oral Communications NotesDocument6 pagesOral Communications NotesSeraphina LopezzNo ratings yet
- Great BooksDocument19 pagesGreat BooksKitNo ratings yet
- The Art of ListeningDocument32 pagesThe Art of Listeningcessy castilloNo ratings yet
- ZFacilitator Handbook 5 (2018)Document198 pagesZFacilitator Handbook 5 (2018)mohdaqil595No ratings yet
- RWS Week7 Critical ReadingDocument5 pagesRWS Week7 Critical Readingdeejaycarpio05No ratings yet
- Capstone Research: Basic Research Applied ResearchDocument2 pagesCapstone Research: Basic Research Applied ResearchTapnio Glezel GolongNo ratings yet
- English For Academic and Professional Purposes HandoutDocument7 pagesEnglish For Academic and Professional Purposes HandoutDiamond frosty guyNo ratings yet
- 2023-01 SCC Scope and Sequence MaglpuDocument6 pages2023-01 SCC Scope and Sequence MaglpukempeNo ratings yet
- Reading & Listening (Communication Skills 6th Form)Document32 pagesReading & Listening (Communication Skills 6th Form)Cass EssentialsNo ratings yet
- GEC324 - Module 6Document8 pagesGEC324 - Module 6AIDYNo ratings yet
- Ee Dealing Difficult People Handout PacketDocument7 pagesEe Dealing Difficult People Handout PacketWasif UllahNo ratings yet
- Public Speaking and Persuasion REVIEWERDocument5 pagesPublic Speaking and Persuasion REVIEWERTini GarciaNo ratings yet
- Reading and TOEIC Test Preparation: A Task-Based Approach For UnderpreparedDocument27 pagesReading and TOEIC Test Preparation: A Task-Based Approach For UnderpreparedAgus MiantaNo ratings yet
- Route To Academic English 2 - Unit 1Document71 pagesRoute To Academic English 2 - Unit 1Eda ALDAŞNo ratings yet
- Photo ReadingDocument14 pagesPhoto Readingtrung voNo ratings yet
- Thành Trung - Pre - Prep - L2Document6 pagesThành Trung - Pre - Prep - L2Thành TrungNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet Lesson 4: Researching Topic Using Multiple SourcesDocument4 pagesLearning Activity Sheet Lesson 4: Researching Topic Using Multiple SourcesGexie Siaron-VillamorNo ratings yet
- Updated - FLL Eii Course OutlineDocument6 pagesUpdated - FLL Eii Course OutlineMUNIB CHOHANNo ratings yet
- English (1st Quarter)Document46 pagesEnglish (1st Quarter)JC Azurin100% (1)
- Writing Effective STUDY Methods UESI APDocument8 pagesWriting Effective STUDY Methods UESI APJoe Clement CNo ratings yet
- PDF (SG) - Eap 11 - 12 - Unit 3 - Lesson 1 - What Is A SummaryDocument21 pagesPDF (SG) - Eap 11 - 12 - Unit 3 - Lesson 1 - What Is A SummaryMayNo ratings yet
- Functional Writing: Mwalukombe Evaluation Examination - 2021 English Paper Form 1 February Series Marking SchemeDocument7 pagesFunctional Writing: Mwalukombe Evaluation Examination - 2021 English Paper Form 1 February Series Marking SchemeHaron HB WritersNo ratings yet
- S Ing 034588 Chapter2Document22 pagesS Ing 034588 Chapter2Kim CoolinerNo ratings yet
- Skimming: General Information - The Plot of A Book: Key Words Quick ReadingDocument6 pagesSkimming: General Information - The Plot of A Book: Key Words Quick ReadingLaura Yolanda Calderon BenitezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 - Speed ReadingDocument18 pagesLesson 8 - Speed ReadingJamille NguyenNo ratings yet
- BSC Civil EngineeringDocument4 pagesBSC Civil EngineeringKamran AliNo ratings yet
- Education Network - Epc 1 - Reading and Reflecting On Texts PDFDocument11 pagesEducation Network - Epc 1 - Reading and Reflecting On Texts PDFSHIVAM CHOPRA100% (1)
- Unit 1 PDFDocument32 pagesUnit 1 PDFAman DesaiNo ratings yet
- Reading and WritingDocument2 pagesReading and WritingJumar FernandezNo ratings yet
- Teaching ReadingDocument27 pagesTeaching ReadingMunavvar SoliyevaNo ratings yet
- Close and Critical Reading: Guiding PrinciplesDocument6 pagesClose and Critical Reading: Guiding PrinciplesNel BorniaNo ratings yet
- Communications Skills PDFDocument337 pagesCommunications Skills PDFKairu KiharaNo ratings yet
- Unit 13 (Final) PDFDocument16 pagesUnit 13 (Final) PDFआई सी एस इंस्टीट्यूटNo ratings yet
- GIÁO TRÌNH ĐỌC 3 CHÍNH THỨC bản cuốiDocument151 pagesGIÁO TRÌNH ĐỌC 3 CHÍNH THỨC bản cuốiThuỳ MaiNo ratings yet