Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PARTS
Uploaded by
Mary joy Dominguez0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesPARTS
Uploaded by
Mary joy DominguezCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
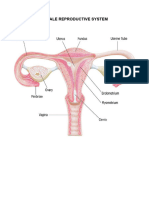
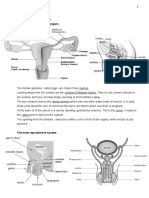
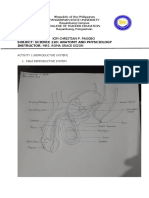
PARTS
FUNCTIONS
They produce the female reproductive cell
Ovaries
called egg or ovum (plural ova)
These are narrow tubes that connect the
ovaries to the uterus. The egg travels
Fallopian tubes down through one of the Fallopian tubes
after ovulation. The sperms travel up to
the Fallopian tubes after contact.
a muscular organ that nourishes and
houses the developing embryo.
Uterus It is also called the womb.
This is where the embryo develops into a
fetus.
It is the lower narrow part of the uterus
Cervix that forms a canal between the uterus and
vagina.
It is the passageway leading from the
Vagina uterus to the outside of the female body.
It is also called as the birth canal.
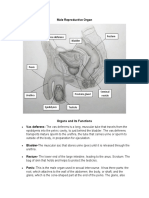
PARTS FUNCTIONS
It is the male external genitalia.
It involves three cylindrical spaces of erectile
Penis
tissue.The foreskin covers the enlarged end
of the penis called glans penis.
It is a sac of thick skin that protects and
surrounds the testes.
controls the temperature of the testes since
Scrotum
they have to be at a slightly lower
temperature than the body temperature for
suitable sperm creation.
Testes are present outside the body in a
pouch called the scrotum.
Testes Generally, the left testis hangs slightly lower
than the right one.
Produces testosterone and sperms.
It is a tube-like structure that connects the
Urethra
urinary bladder to the urinary meatus.
Sac-like pouches that attach to the vas
Seminal vesicles
deferens near the base of the bladder.
long, muscular tube that travels from the
epididymis into the pelvic cavity, just behind
Vas deferens the urinary bladder.
transports mature sperm to the urethra in
preparation for ejaculation.
You might also like
- Presentation 2Document21 pagesPresentation 2ericasinamagNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument8 pagesReproductive SystemaynNo ratings yet
- SXSXDocument27 pagesSXSXJoevany E. BigorniaNo ratings yet
- Ovaries: The Female Gonads, The Ovaries Produce Ova. When One Matures, It Is Released Down Into A Fallopian TubeDocument2 pagesOvaries: The Female Gonads, The Ovaries Produce Ova. When One Matures, It Is Released Down Into A Fallopian TubeCyril AlngogNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive System Female Reproductive SystemDocument1 pageMale Reproductive System Female Reproductive SystemEunimae VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Reproduction 2Document5 pagesReproduction 2CeliaGCNo ratings yet
- Science 5Document26 pagesScience 5barangay89zone9No ratings yet
- MCN LEC (Prelims)Document19 pagesMCN LEC (Prelims)BIANCA ANGELICA GERARDONo ratings yet
- Male and Female Reproductive OrganDocument4 pagesMale and Female Reproductive OrganLawren Ira LanonNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument36 pagesReproductive SystembokkNo ratings yet
- 07 05 Reproductive SystemDocument6 pages07 05 Reproductive SystemOkoye ClappinNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Sa ScienceDocument15 pagesReviewer Sa Sciencecjosh9975No ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument5 pagesReproductive SystemkhakimagdalenaNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System - CompressedDocument109 pagesReproductive System - CompressedNoel Calvo Macarine100% (2)
- Group3 ReproductivesystemDocument19 pagesGroup3 ReproductivesystemLeonie OngNo ratings yet
- Science 5 ReviewerDocument4 pagesScience 5 ReviewerAlexandra Pauline DimayugaNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System: Ingles Medico Ii - Clase 8Document7 pagesReproductive System: Ingles Medico Ii - Clase 8Agustín Bravo ArreyesNo ratings yet
- REPRODUCTIONDocument78 pagesREPRODUCTIONglaizaNo ratings yet
- Cmca 1Document5 pagesCmca 1Erika Mae Sta. MariaNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology: 1. PenisDocument7 pagesMale Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology: 1. PenisMhiahLine TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Humans: SMPK 6 PenaburDocument24 pagesReproduction in Humans: SMPK 6 PenaburOKTAVIANI HAPSARINo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Male and Female Rep. SystemDocument21 pagesLesson 3 Male and Female Rep. SystemHye JinNo ratings yet
- Organism Hormones Organ Systems FitnessDocument10 pagesOrganism Hormones Organ Systems FitnessAnonymous 0iY2p9FdNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System - Bio 2 - 12 Stem - l11Document4 pagesReproductive System - Bio 2 - 12 Stem - l11Lyka Lobido CabeltesNo ratings yet
- Biomedicalperspective in Gender and Sexuality: Anatomy and Physiology of ReproductionDocument29 pagesBiomedicalperspective in Gender and Sexuality: Anatomy and Physiology of ReproductionBrian CastañedaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of ReproductionDocument27 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of ReproductionÆRO YT CHANNELNo ratings yet
- S10 Q3 WEEK1 Reproductive System LECTUREDocument35 pagesS10 Q3 WEEK1 Reproductive System LECTUREREGLOS, Marie Nhelle K.No ratings yet
- Science Presentation: By: Beam BorachoDocument33 pagesScience Presentation: By: Beam BorachoPEMAR ACOSTANo ratings yet
- Abdalla MostafaDocument8 pagesAbdalla MostafaDr. Mohammad JamaliNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Science 10Document22 pagesReproductive Science 10palicpicbea50No ratings yet
- Gender & Society Lo4Document6 pagesGender & Society Lo4Mark Eugene DeocampoNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument32 pagesReproductive SystemPrincess Nicole HernaezNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument17 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemYsthanamhire TolentinoNo ratings yet
- The Male Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesThe Male Reproductive SystemHoney MalabuteNo ratings yet
- Physics Class 10 ICSEDocument5 pagesPhysics Class 10 ICSEmohammedumar7864521No ratings yet
- Bahan UASDocument4 pagesBahan UASislamiah sybNo ratings yet
- 2 The Reproductive SystemDocument122 pages2 The Reproductive SystemBryan Lloyd Ballestar RayatNo ratings yet
- Review of Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument8 pagesReview of Anatomy and PhysiologyRuthangela GarciaNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in HumansDocument3 pagesReproduction in HumansYolanda JesslinaNo ratings yet
- SG 5 Anaphy ActivityDocument4 pagesSG 5 Anaphy Activitykim christianNo ratings yet
- Ana Physio ReprodDocument8 pagesAna Physio ReprodTeodoro Lemuel Ramos Gaela100% (1)
- MCHDocument3 pagesMCHReniella HidalgoNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System 1Document56 pagesReproductive System 1zekesergmanuedenina08No ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Male Reproductive SystemDocument8 pagesAnatomy of The Male Reproductive SystemSejuta AdaNo ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument14 pagesHuman ReproductionANA MARY JOY PEPENo ratings yet
- The Reproductive SystemDocument17 pagesThe Reproductive SystemRye ManosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16. The Reproductive SystemDocument6 pagesChapter 16. The Reproductive SystemScianna Christel LastimosaNo ratings yet
- Final LectureDocument162 pagesFinal Lecturemohmmad-0-50No ratings yet
- Reproductive System Power Point AckroydDocument19 pagesReproductive System Power Point AckroydTrung Ngô Lê BảoNo ratings yet
- REPRODUCTIVEDocument89 pagesREPRODUCTIVEJohn MichaelMackayNo ratings yet
- The Human Reproductive System: By: Blessing Guzman & Jay MerilanDocument14 pagesThe Human Reproductive System: By: Blessing Guzman & Jay MerilanMark Anthony Evangelista CabrietoNo ratings yet
- Delamide, Reproductive System Anaphy LabDocument5 pagesDelamide, Reproductive System Anaphy LabKristine Lorainne DelamideNo ratings yet
- SCIENCEDocument4 pagesSCIENCEMa. Isabel AtanesNo ratings yet
- Science 10Document4 pagesScience 10Dawn April sanoyNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Science Handout Third QuarterDocument7 pagesGrade 10 Science Handout Third QuarterJumarie ypilNo ratings yet
- Biomedical PerpectiveDocument22 pagesBiomedical Perpectiveedmaration 2002No ratings yet
- Concept Block - NamocoDocument4 pagesConcept Block - NamocoGladys NamocoNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument39 pagesReproductive SystemCenando Bodanio100% (1)
- Coordinated Functions of The Nervous, Endocrine, and Reproductive SystemsDocument30 pagesCoordinated Functions of The Nervous, Endocrine, and Reproductive SystemsSarah CruzNo ratings yet
- Pre Operative Planning For Total Hip ArthroplastyDocument78 pagesPre Operative Planning For Total Hip ArthroplastyJulio EspinozaNo ratings yet
- TractionDocument45 pagesTractionMISS. COMNo ratings yet
- A Method For Visual Determination of Sex, Using The Human Hip BoneDocument12 pagesA Method For Visual Determination of Sex, Using The Human Hip Bonede4thm0ng3rNo ratings yet
- 1992 - Bridgman's Complete Guide To Drawing From LifeDocument346 pages1992 - Bridgman's Complete Guide To Drawing From LifeJulia Ramos95% (82)
- Pelvic Floor Exercises For WomenDocument3 pagesPelvic Floor Exercises For Womenreza.7868910100% (2)
- Leg Length Discrepancy: ReviewDocument12 pagesLeg Length Discrepancy: ReviewGusti TettaNo ratings yet
- N227F - 2004 - OBS Lecture 1 - Introduction To Obstetric Nursing Lecture NotesDocument17 pagesN227F - 2004 - OBS Lecture 1 - Introduction To Obstetric Nursing Lecture NotesPriscilla NgNo ratings yet
- 2) QuestionsDocument95 pages2) Questionsgita safiraNo ratings yet
- Functional Neuromuscular AnatomyDocument56 pagesFunctional Neuromuscular AnatomyΒασίλης Βασιλείου100% (3)
- Tap Ghi Chep 1Document85 pagesTap Ghi Chep 1vutuyen519No ratings yet
- Interview With Prof. GracovetskyDocument5 pagesInterview With Prof. GracovetskyWhisperer BowenNo ratings yet
- Ido's Seminar NotesDocument15 pagesIdo's Seminar NotesAndrei FCFNo ratings yet
- High Riding ProstateDocument13 pagesHigh Riding ProstateHendry DimasNo ratings yet
- Prenatal Care: Muthia MutmainnahDocument77 pagesPrenatal Care: Muthia MutmainnahBima NetNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Skeletal System 1Document18 pagesChapter 6 Skeletal System 1M GarciaNo ratings yet
- OSCE On 14/3/2008: Describe Gynaecoid PelvisDocument82 pagesOSCE On 14/3/2008: Describe Gynaecoid PelvisKahing LiNo ratings yet
- Core & Pelvis - The Anterior Oblique SystemDocument4 pagesCore & Pelvis - The Anterior Oblique Systemryan9871No ratings yet
- Acetabular Fracture PostgraduateDocument47 pagesAcetabular Fracture Postgraduatekhalidelsir5100% (1)
- BSC Medical Sociology PDFDocument24 pagesBSC Medical Sociology PDFmchakra72100% (2)
- WWW Slideshare Net SurajDhara2 Forensic Medicine Mcqs PDFDocument19 pagesWWW Slideshare Net SurajDhara2 Forensic Medicine Mcqs PDFShrutiNo ratings yet
- 9 Somatic Breath TechniquesDocument12 pages9 Somatic Breath TechniquesOVVCMOULI100% (6)
- Sexual A&PDocument37 pagesSexual A&PnissashiblyNo ratings yet
- Gray Institute Work SheetsDocument39 pagesGray Institute Work Sheetskokoliu liu100% (2)
- Cobra Snake or Serpent Pose: HujangasanaDocument15 pagesCobra Snake or Serpent Pose: HujangasanaLomombNo ratings yet
- Intermediate ABS Routine PDFDocument20 pagesIntermediate ABS Routine PDFadityavermabm89% (9)
- Pelvic InjuriesDocument35 pagesPelvic InjuriesJavier Saad100% (1)
- StretchFit Ebook V2Document16 pagesStretchFit Ebook V2Rukaphuong100% (1)
- Biomechanics of RunningDocument19 pagesBiomechanics of RunningJaviera Paz VegaNo ratings yet
- Lower Back Exercise Guide by Dr. Walter SalubroDocument37 pagesLower Back Exercise Guide by Dr. Walter SalubroBeaulah Hunidzarira100% (1)
- Cosmetic Gynecology Booklet - Dr. Michael Tahery in Los AngelesDocument16 pagesCosmetic Gynecology Booklet - Dr. Michael Tahery in Los AngelesMichael TaheryNo ratings yet