Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Digestive Quiz
Uploaded by
Salina SalujaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Digestive Quiz
Uploaded by
Salina SalujaCopyright:
Available Formats
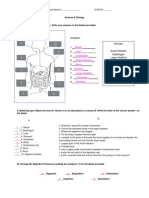
Human Body Series
Digestive System
Name: Date:
Quiz
Instructions: Answer each question.
1. Your digestive system works on the foods you eat for about: 8. A flexible flap of tissue called the
a. 5 hours ________________________ reflexively closes over the
windpipe when we swallow to prevent choking.
b. 10 hours
c. 15 hours 9. Waves of muscle contractions called
d. 20 hours ________________________ force food down through the
esophagus to the stomach.
2. The digestive system breaks down food into:
10. The inner wall of the small intestine is covered with
a. nutrients millions of microscopic, finger-like projections called
b. amylase ________________________, through which nutrients can
c. saliva be absorbed into the body.
d. sphincters Extra credit
The small intestine is made up of three parts:
3. During the process of absorption, nutrients from food go from: the c-shaped first part called the
a. the intestines into the bladder ________________________, the coiled midsection called
the ________________________, and the final section
b. the blood into the organs
that leads into the large intestine called the
c. the intestines into the bloodstream ________________________.
d. the mouth into the stomach
4. The alimentary canal, or digestive tract, is made up of the:
a. pancreas, liver, and gallbladder
b. esophagus, stomach, and intestines
c. colon, rectum, and anus
d. mouth, esophagus, and stomach
5. These move food through the digestive system:
a. digestive fluids
b. enzymes
c. mucous membranes
d. smooth muscles
6. In the stomach:
a. muscles churn and mix the food with acids and enzymes
b. glands make 3 quarts of digestive juices each day
c. food leaves as a thick liquid called chyme
d. all of the above
7. The pancreas, liver, and gallbladder help digestion in these ways, respectively:
a. making enzymes; making bile and processing nutrients; and storing bile
b. producing saliva; digesting carbohydrates; and eliminating waste
c. producing hormones; producing enzymes; and eliminating waste
d. making acids; producing digestive juices; and storing enzymes
© 2016 The Nemours Foundation/KidsHealth. Reproduction permitted for individual classroom use.
You might also like
- 2nd Dexes Science 4 2022-2023Document3 pages2nd Dexes Science 4 2022-2023Jessie SandanNo ratings yet
- Name: GRADE AND SECTION: - DATEDocument2 pagesName: GRADE AND SECTION: - DATEnimfa t. plazaNo ratings yet
- Final Exam in ScienceDocument2 pagesFinal Exam in ScienceMarilou VirtudazoNo ratings yet
- Reviewe Scie Self MadeDocument2 pagesReviewe Scie Self MadeMANUEL LUIS JR. TAYAONo ratings yet
- Section Quiz: Section: The Digestive SystemDocument1 pageSection Quiz: Section: The Digestive SystemDavid GiraldoNo ratings yet
- Science 4th Quarter PrelimDocument5 pagesScience 4th Quarter PrelimRey Ann RubioNo ratings yet
- Grade 10mDocument5 pagesGrade 10mSameh NoorNo ratings yet
- Science Test Digesty and RespiratoryDocument1 pageScience Test Digesty and RespiratoryANDREA PAOLA DIAZ ANDRADENo ratings yet
- Taking Care of The Digestive SystemDocument8 pagesTaking Care of The Digestive SystemamaniNo ratings yet
- Gen. Zoology Multiple Choice TestDocument2 pagesGen. Zoology Multiple Choice TestCedrick MatibagNo ratings yet
- B g8 Digestive SystemDocument3 pagesB g8 Digestive SystemnoorlailyNo ratings yet
- Unlock SGCh12Document6 pagesUnlock SGCh12Silax100% (1)
- Q2 - Summative Test No 3 - ELSDocument2 pagesQ2 - Summative Test No 3 - ELSMARIZA MAPALONo ratings yet
- DigestionDocument3 pagesDigestionmuneeza dueveshNo ratings yet
- ExamDocument2 pagesExamAbegail SajoniaNo ratings yet
- Digestive System LaboratoryDocument6 pagesDigestive System LaboratoryValeria ReinaNo ratings yet
- MODULE 3 2ND QUARTER Science 6 EDITDocument6 pagesMODULE 3 2ND QUARTER Science 6 EDITEmie PonceNo ratings yet
- Long Test in Digestive SystemDocument2 pagesLong Test in Digestive SystemThess Curayag FernandezNo ratings yet
- Science SummDocument1 pageScience SummArrabelle Tamayo-PableNo ratings yet
- Bio More PracticeDocument6 pagesBio More PracticemeromoNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Animals Class 7 WsDocument2 pagesNutrition in Animals Class 7 WsShweta RathiNo ratings yet
- Chloe Reviewer SCienceDocument3 pagesChloe Reviewer SCienceKim Carlo AglinaoNo ratings yet
- Science 4 1st Summative TestDocument2 pagesScience 4 1st Summative TestEmz FloresNo ratings yet
- Science: Good LuckDocument11 pagesScience: Good LuckAnnabelle Mangilit Corpuz BonaNo ratings yet
- Eternity Christian School and InstituteDocument4 pagesEternity Christian School and Instituteronald.cardonaNo ratings yet
- St. John Adaptive Montessori School Magsaysay, Alicia, Isabela Monthly Exam in Science September Grade VI Name: - DateDocument3 pagesSt. John Adaptive Montessori School Magsaysay, Alicia, Isabela Monthly Exam in Science September Grade VI Name: - Date渡辺正平No ratings yet
- Tutorial Digestive SystemDocument2 pagesTutorial Digestive SystemNur Shahirah Nasir Faculty of Social Science and FoundationNo ratings yet
- St. Columban's InstituteDocument2 pagesSt. Columban's InstituteOhmark VeloriaNo ratings yet
- Cordillera Administrative Region Division of Kalinga PASIL NATIONAL HIGH SCHOOL 4th Periodical Exam in Science 8Document3 pagesCordillera Administrative Region Division of Kalinga PASIL NATIONAL HIGH SCHOOL 4th Periodical Exam in Science 8Kimeo Bagyon100% (1)
- SCIENCE DIGESTIONDocument4 pagesSCIENCE DIGESTIONfranzNo ratings yet
- I. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The Letter of The Correct Answer. Write Your Answer On The Space Provided BeforeDocument3 pagesI. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose The Letter of The Correct Answer. Write Your Answer On The Space Provided Beforejam syNo ratings yet
- Digestive System - Free Printable Tests and Worksheets - HelpTeaching PDFDocument1 pageDigestive System - Free Printable Tests and Worksheets - HelpTeaching PDFthiyagarajakannan75% (4)
- Science 8 Q4 Revised Module 1 2Document24 pagesScience 8 Q4 Revised Module 1 2Rai0% (1)
- Science 8 Quarter 4 Week 1 Long QuizDocument2 pagesScience 8 Quarter 4 Week 1 Long Quizjohn rexNo ratings yet
- Digestive System TestDocument5 pagesDigestive System TestShe CeweQq Larazz Mutt'zNo ratings yet
- ollective nouns are words for single things that are made up of more than one personDocument6 pagesollective nouns are words for single things that are made up of more than one personaileen.lastrillaNo ratings yet
- First Periodical Old Ver Test Scie 4Document2 pagesFirst Periodical Old Ver Test Scie 4mary graceNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 6 ReviewerDocument4 pagesSCIENCE 6 ReviewerReshiele FalconNo ratings yet
- I. Encircle The Letter of The Correct Answer.: Science 4Document3 pagesI. Encircle The Letter of The Correct Answer.: Science 4JERIC SAYUMANo ratings yet
- Digestive System QuizDocument1 pageDigestive System QuizTego Shei HarumiNo ratings yet
- Digestive System QuizDocument1 pageDigestive System QuizTego Shei HarumiNo ratings yet
- Summative Test: Science 8 - Module 1Document2 pagesSummative Test: Science 8 - Module 1Clark Bautista100% (2)
- Inbound 6967232979863548400Document3 pagesInbound 6967232979863548400JudieNo ratings yet
- Science and Health: Digestive SystemDocument17 pagesScience and Health: Digestive SystemEDUARDO ACERONo ratings yet
- Act Sheet 1 4th Quarter Science 8Document3 pagesAct Sheet 1 4th Quarter Science 8Joseph Gabriel Genuino CruzNo ratings yet
- Talinong Bulilit Bahay Iskwela: SY 2016-2017 First - Bi Monthly TestDocument7 pagesTalinong Bulilit Bahay Iskwela: SY 2016-2017 First - Bi Monthly TestYael Francisco NarioNo ratings yet
- Name: - Grade/section: - Name: - Grade/sectionDocument2 pagesName: - Grade/section: - Name: - Grade/sectionLiezel E. GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Laboratory: Exercise: Digestive SystemDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Laboratory: Exercise: Digestive SystemLouise Mica LeeNo ratings yet
- 7.5 AbsorptionDocument5 pages7.5 AbsorptionPatrick AbidraNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 Summative Test in MAPEH #2Document2 pagesGrade 6 Summative Test in MAPEH #2Paz Calipes CayagoNo ratings yet
- Quiz #5 Answer KeyDocument1 pageQuiz #5 Answer KeyTego Shei Harumi100% (1)
- Quiz #5 Answer KeyDocument1 pageQuiz #5 Answer KeyTego Shei Harumi100% (1)
- Science 6 - 2nd Quarterly Exam (Grade 6)Document4 pagesScience 6 - 2nd Quarterly Exam (Grade 6)Brian BuiserNo ratings yet
- Digestive System GuideDocument13 pagesDigestive System GuideAnonymous yIlaBBQQ100% (1)
- Animalpractice Test: Identify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDocument16 pagesAnimalpractice Test: Identify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionHuma KhanNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 Summative Test in Science #2Document2 pagesGrade 6 Summative Test in Science #2Paz Calipes CayagoNo ratings yet
- Fourth Periodical Test in Science 8 PDFDocument5 pagesFourth Periodical Test in Science 8 PDFnasser pazaulan12No ratings yet
- Grade 4 Summative 5 THDocument2 pagesGrade 4 Summative 5 THKristine Gallogo0% (1)
- Types of ReactionsDocument22 pagesTypes of ReactionsSalina SalujaNo ratings yet
- Do Now ActivityDocument10 pagesDo Now ActivitySalina SalujaNo ratings yet
- Balancing Equations Cornell Doodle Notes Powerpoint PresentationDocument22 pagesBalancing Equations Cornell Doodle Notes Powerpoint PresentationSalina Saluja0% (1)
- The Atom: Cornell Doodle NotesDocument22 pagesThe Atom: Cornell Doodle NotesSalina SalujaNo ratings yet
- 04 MixturesDocument21 pages04 MixturesSalina SalujaNo ratings yet
- Luftwaffe Night Fighter Control MethodsDocument17 pagesLuftwaffe Night Fighter Control MethodsKIRU SILVIU100% (3)
- GX7000 New CatalogeDocument20 pagesGX7000 New CatalogeyohanesNo ratings yet
- Rev Quiz All PDFDocument46 pagesRev Quiz All PDFNota Belz82% (17)
- Jeanine Meyer - Origami As A General Education Math CourDocument4 pagesJeanine Meyer - Origami As A General Education Math CourscheeleNo ratings yet
- Fluosilic Acid MsdsDocument5 pagesFluosilic Acid MsdsVuglaShemmanNo ratings yet
- Upper Gastro Intestinal BleedingDocument13 pagesUpper Gastro Intestinal BleedingmuniningmicanNo ratings yet
- SR-21 SniperDocument6 pagesSR-21 SniperBaba HeadquaterNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mathematics For Gate Chapter1Document1 pageEngineering Mathematics For Gate Chapter1Sai VeerendraNo ratings yet
- Is 1726 1991Document17 pagesIs 1726 1991RaykochiNo ratings yet
- Ch.2 Case and Duct SystemDocument11 pagesCh.2 Case and Duct Systemcpt.ghostNo ratings yet
- Table Napkin Folding TechniquesDocument6 pagesTable Napkin Folding TechniquesMiguel BaricuatroNo ratings yet
- Steven Churchill, Jack Reynolds (Eds.) - Jean-Paul Sartre - Key Concepts-Routledge (2014)Document257 pagesSteven Churchill, Jack Reynolds (Eds.) - Jean-Paul Sartre - Key Concepts-Routledge (2014)Leonardo Grana100% (3)
- Industrial Training IntroductionDocument1 pageIndustrial Training Introductionsgurjar07No ratings yet
- Applications of Sine and Cosine Functions PDFDocument1 pageApplications of Sine and Cosine Functions PDFShane RajapakshaNo ratings yet
- Definitions for Agricultural FinancingDocument15 pagesDefinitions for Agricultural FinancingShahid MehmoodNo ratings yet
- De-Escalation of Critical Care and Prevention of Iatrogenicity Through PICU Liberation Rounding Process and A Daily Rounding ChecklistDocument1 pageDe-Escalation of Critical Care and Prevention of Iatrogenicity Through PICU Liberation Rounding Process and A Daily Rounding ChecklistdarlingcarvajalduqueNo ratings yet
- Modern Chicken Types & BreedsDocument14 pagesModern Chicken Types & BreedsMelody DacanayNo ratings yet
- MRCP EthicsDocument33 pagesMRCP EthicstaherNo ratings yet
- 2) Inequality GraphsDocument14 pages2) Inequality Graphsmanobilli30No ratings yet
- Chiller Maintenance Service 2015Document29 pagesChiller Maintenance Service 2015Huong Ban MaiNo ratings yet
- Philosophy, Logic, & Rhetoric SyllabusDocument3 pagesPhilosophy, Logic, & Rhetoric SyllabusBrynja KnappNo ratings yet
- BINALAY VS ManaloDocument3 pagesBINALAY VS ManaloAnonymous 7BpT9OWPNo ratings yet
- The Macadamia Industry in MalawiDocument77 pagesThe Macadamia Industry in Malawiwarlord_ckNo ratings yet
- India's Power Industry History and FutureDocument11 pagesIndia's Power Industry History and FutureMinesh Chand MeenaNo ratings yet
- Decline of Controversy and the Catholic ChurchDocument3 pagesDecline of Controversy and the Catholic ChurchEugenio PalandriNo ratings yet
- "Fragile" - StingDocument4 pages"Fragile" - StingFabián ReinosoNo ratings yet
- Methyl methacrylate allergy case study in dentistry studentDocument3 pagesMethyl methacrylate allergy case study in dentistry studentDaniela CapitanuNo ratings yet
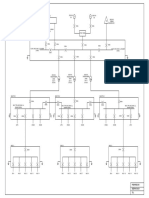
- Conceptual SLDDocument1 pageConceptual SLDakhilNo ratings yet
- Fmea PC ProcessDocument2 pagesFmea PC Processsudeep_singh1No ratings yet
- NAS810 Protection of Fluid Lines & EquipDocument1 pageNAS810 Protection of Fluid Lines & EquipfdhgjklNo ratings yet