Professional Documents
Culture Documents
M4 PPT For Students 2
M4 PPT For Students 2
Uploaded by
Franchesca Lheanne Real Morales0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views25 pagesThe document summarizes key aspects of the Earth's structure and plate tectonics. It describes the mantle, asthenosphere, magma, convection currents, and core that make up Earth's layers. Plate tectonics is driven by convection currents in the asthenosphere that cause the lithospheric plates to float and slowly move over time.
Original Description:
Kyfgjk
Original Title
M4-PPT-FOR-STUDENTS-2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes key aspects of the Earth's structure and plate tectonics. It describes the mantle, asthenosphere, magma, convection currents, and core that make up Earth's layers. Plate tectonics is driven by convection currents in the asthenosphere that cause the lithospheric plates to float and slowly move over time.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views25 pagesM4 PPT For Students 2
M4 PPT For Students 2
Uploaded by
Franchesca Lheanne Real MoralesThe document summarizes key aspects of the Earth's structure and plate tectonics. It describes the mantle, asthenosphere, magma, convection currents, and core that make up Earth's layers. Plate tectonics is driven by convection currents in the asthenosphere that cause the lithospheric plates to float and slowly move over time.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 25
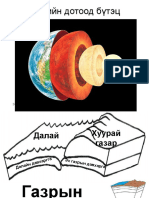
Mantle
A layer beneath where the less
dense hot molten material rises,
and sinks
Asthenosphere
A soft, weak, and plastic-like
layer, the upper part of the
mantle where the lithospheric
plates float and move
Magma
Hot molten rocks
formed beneath the
Earth’s surface
Convection Current
Facilitates the
movement of the
lithospheric plates
Core
The innermost layer of
the earth, which
generates heat to the
mantle
The Earth’s lithosphere; crust
and the upper mantle- is broken
up into several pieces called
PLATES that move slowly.
- a heat transfer process
that involves the movement
of energy from one place to
another
- fluid, gas particles, or
molten rock.
- due to the differences
in the densities and
the temperature
- hot fluid tends to rise
as it expands,
whereas cold fluid
tends to sink
a. The decomposition of radioactive elements causes heat in
the interior part of the Earth.
b. Heat slowly rises to the mantle and creates a convection
current.
c. Lithospheric plates move in the asthenosphere due to the
rising and sinking of materials.
d. Heat moves to the core.
e. The process repeats as a cycle.
You might also like
- Science 10 Quarter 1 Lesson 8Document2 pagesScience 10 Quarter 1 Lesson 8ViaNo ratings yet
- Science 10Document1 pageScience 10Glaidylle Jade PagasNo ratings yet
- Earth's MechanismDocument26 pagesEarth's MechanismMARITES DURANGONo ratings yet
- Earths MechanismDocument20 pagesEarths MechanismMarieFranz ChuaNo ratings yet
- EARTHS-MECHANISM PPTDocument15 pagesEARTHS-MECHANISM PPTLourdes Largado100% (1)
- Forces Causing Plate MotionDocument16 pagesForces Causing Plate MotionMark Niño JavierNo ratings yet
- Q1-W6-Convection and The MantleDocument47 pagesQ1-W6-Convection and The MantleLea Camille PacleNo ratings yet
- (Template) As WEEK 5&6Document3 pages(Template) As WEEK 5&6Jaemee Agnes BoadoNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics Plate Tectonics: Crust Mantle Plate Boundaries Thrust Faults Oceanic Spreading Ridges Transform FaultsDocument3 pagesPlate Tectonics Plate Tectonics: Crust Mantle Plate Boundaries Thrust Faults Oceanic Spreading Ridges Transform FaultsFaye Andrea FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Lebs ScienceDocument9 pagesLebs ScienceVince Casison Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- Qim 7Document7 pagesQim 7Mae JeminaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Endogenic ProcessDocument3 pagesLesson 2 Endogenic ProcessSelene HmpNo ratings yet
- THE COMPOSITION AND STRUCTURE OF EARTH - HECHOdocxDocument9 pagesTHE COMPOSITION AND STRUCTURE OF EARTH - HECHOdocxCarmen Rosa Castelo CortezNo ratings yet
- Q1M2 120703Document4 pagesQ1M2 120703katekyleonozaNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-09-19 at 10.37.39 PMDocument23 pagesScreenshot 2023-09-19 at 10.37.39 PMKeara Allene ArriesgadoNo ratings yet
- Earth Structure and Rock CycleDocument31 pagesEarth Structure and Rock CycleJulius Magaru RaquelNo ratings yet
- Es 2ND Week2Document16 pagesEs 2ND Week2kiyohachiroNo ratings yet
- 9.3 Main Processes of EarthDocument18 pages9.3 Main Processes of EarthEmily Ti Er ChiNo ratings yet
- The Heat EngineDocument2 pagesThe Heat Engineapi-237645705No ratings yet
- Q2 M2 Presentation MWFDocument34 pagesQ2 M2 Presentation MWFEspinosa , Lance G.No ratings yet
- Pointers To Review ElsDocument15 pagesPointers To Review ElsAnico MartinNo ratings yet
- Answe Earth ScienceDocument3 pagesAnswe Earth ScienceStanley Rey CaramoanNo ratings yet
- 6 Earths Mechanisms Mantle ConvectionDocument22 pages6 Earths Mechanisms Mantle ConvectionSile LuNo ratings yet
- Earths InteriorDocument64 pagesEarths InteriorBuuye ChNo ratings yet
- Endogenic ProcessDocument47 pagesEndogenic Processnicole balangNo ratings yet
- Layers of The EarthDocument26 pagesLayers of The EarthLoo DrBrad100% (1)
- Module 2: Earth's Internal Heat SourcesDocument4 pagesModule 2: Earth's Internal Heat SourcesMiczkie AjocNo ratings yet
- Earths Interior HeatDocument30 pagesEarths Interior HeatK-Ann AcostaNo ratings yet
- Sources of Earth's Internal HeatDocument23 pagesSources of Earth's Internal HeatGabrielle EllisNo ratings yet
- Endogenic Processes: Earth and Life Science Engr. Mai SasaDocument23 pagesEndogenic Processes: Earth and Life Science Engr. Mai SasaMai SasaNo ratings yet
- What Are: How Are They Interconnected?Document40 pagesWhat Are: How Are They Interconnected?hihsNo ratings yet
- Escie GarDocument13 pagesEscie Garandreweinstein0206No ratings yet
- Q1 W1 Lesson 5 and 6Document13 pagesQ1 W1 Lesson 5 and 6Teacher BearNo ratings yet
- Earths Internat HeatDocument63 pagesEarths Internat HeatRyan CortezNo ratings yet
- The Anatomy of A Tectonic PlateDocument2 pagesThe Anatomy of A Tectonic PlateIan Vincent CadisalNo ratings yet
- It Is The Kingfisher?Document69 pagesIt Is The Kingfisher?Jocelyn LoreñanaNo ratings yet
- Earth Science: Journey The EarthDocument5 pagesEarth Science: Journey The EarthElyka Marie LambarteNo ratings yet
- Magmatism & Earth's Internal HeatDocument5 pagesMagmatism & Earth's Internal HeatLorraine ReyesNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 11 WEEK 6c - Endogenic ProcessDocument57 pagesSCIENCE 11 WEEK 6c - Endogenic ProcessChristine CayosaNo ratings yet
- The Earths Internal HeatDocument13 pagesThe Earths Internal HeatCisca Noda RafusonNo ratings yet
- Name: Cesar John Catuburan Grade/ Section: Stem CDocument8 pagesName: Cesar John Catuburan Grade/ Section: Stem CMakapikon NagudNo ratings yet
- The Earth's Internal HeatDocument15 pagesThe Earth's Internal HeatApril Mae ArcayaNo ratings yet
- Causes of Plate MovementsDocument17 pagesCauses of Plate MovementsMacoy Cortez PalomaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2.1 Magma FormationDocument23 pagesLesson 2.1 Magma FormationRexTheKingNo ratings yet
- EARTH AND LIFE SCIENCE Module 3 Lesson 6-7Document10 pagesEARTH AND LIFE SCIENCE Module 3 Lesson 6-7christianaries.lapuzNo ratings yet
- Science10 q1 Mod4 Earth S Mechanism FINAL08082020Document20 pagesScience10 q1 Mod4 Earth S Mechanism FINAL08082020이지우100% (3)
- Geology For Kids - Pictionary | Geology Encyclopedia Of Terms | Children's Rock & Mineral BooksFrom EverandGeology For Kids - Pictionary | Geology Encyclopedia Of Terms | Children's Rock & Mineral BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- l3 Earth's Internal HeatDocument75 pagesl3 Earth's Internal HeatLearni J. EscoteNo ratings yet
- CONVECTIONGOWITHTHEFLOWDocument17 pagesCONVECTIONGOWITHTHEFLOWMarivon Mejilla-DaveNo ratings yet
- Endogenic ProcessesDocument26 pagesEndogenic ProcessesSherie Mae Querubin LozadaNo ratings yet
- Module 6-8 - EARTH AND LIFE SCIENCEDocument9 pagesModule 6-8 - EARTH AND LIFE SCIENCEKristine AlcordoNo ratings yet
- Module 6 Earth and Life ScienceDocument33 pagesModule 6 Earth and Life ScienceKim LiaNo ratings yet
- Mantle Convection: Plate Tectonic TheoryDocument3 pagesMantle Convection: Plate Tectonic TheoryRuby Jean LagunayNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6. Earth's Internal HeatDocument3 pagesLesson 6. Earth's Internal Heatrevelachtion02No ratings yet
- Formation of MagmaDocument2 pagesFormation of MagmaBJ Bernardo IlNo ratings yet
- Earth's Internal HeatDocument7 pagesEarth's Internal HeatRalph EgeNo ratings yet
- Earth Internal Heat SourceDocument21 pagesEarth Internal Heat SourceRickyNo ratings yet
- JC Excellente Christian Academy Inc.: Earth Science Week 7Document7 pagesJC Excellente Christian Academy Inc.: Earth Science Week 7Ji PaoNo ratings yet
- Review Sheet Periodical ExaminationDocument4 pagesReview Sheet Periodical ExaminationRhaven Gonzales100% (1)