Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SAHS HT Management Algorithm Medical Practitioner 2015
Uploaded by
Joana woodsOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SAHS HT Management Algorithm Medical Practitioner 2015
Uploaded by
Joana woodsCopyright:
Available Formats
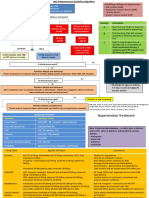
HYPERTENSION MANAGEMENT
Step
1 Assess ALGORITHM Step BP TARGETS
8 • <140/90 mmHg
Major risk factors Step Measure Blood Pressure • <150/90 mmHg if >
according to SAHS guidelines* 80 years
•Levels of systolic and diastolic BP 2
Step
Consider home or 24 hour BP monitoring in patients
•Smoking
with stage 1 hypertension without
•Dyslipidaemia:
TOD/complications/risk factors
ototal cholesterol > 5.1 mmol/L, OR 7
oLDL > 3 mmol/L, OR
oHDL men < 1 and women < 1.2 mmol/L
Step
•Diabetes mellitus
•Men > 55 years
3 Lifestyle changes Routine Management
•Women > 65 years •Weight reduction Step 1:Choose any of the
•Family history of early onset of CVD: •Restrict salt, dietary sugars, and saturated
•Men aged <55 years fat
following:*
•Women aged <65 years •Limit alcohol consumption •Hydrochlorothiazide 12.5 -25 mg daily or
•Waist circumference- abdominal obesity: •Increase fruit and vegetables indapamide 1.25 – 2.5 mg daily
•Men ≥ 94 cm •Increase physical activity •CCB
•Women ≥ 80 cm •Stop all tobacco products •ACE-I or ARB
Step •If 20/10mmHg above goal proceed
Target Organ Damage 4
directly to step 2
Step 2
•LVH: based on ECG 1. Combine any 2 of the above
3 2. Combine all 3 of above
oSokolow-Lyons > 35 mv (S in V1 + R in
V5 or V6) 3. Maximize doses of individual agents
oCornell product > 2440 mm.ms (S in V3 Step 3
+ R in aVL + 6 in females) x QRS •Spironolactone 25mg daily (monitor K+
duration) and avoid if eGFR < 45 mls/min)
oR in aVL > 11 mv •β blocker, blocker, minoxidil, centrally
•LVH on echocardiography acting drug, or hydralazine
•Micro-albuminuria: albumin creatine ratio •Consider furosemide 40mg b.d. in place
- 3-30 mg/mmol of thiazide if eGFR < 45mls/min
•Check adherence, secondary causes,
Complications home or 24 hour BP monitoring for white
coat or pseudoresistance, consider
•Coronary heart disease referral to specialist
•Heart failure
•Chronic kidney disease: * CCBs/diuretics preferred in
oalbuminuria > 30mg/mmol OR eGFR < Blacks/Elderly
60ml/min * 24 hour acting drugs and single pill
Is there a hypertensive
Step
•Stroke or TIA combinations preferred
•Peripheral arterial disease
•Advanced retinopathy: urgency or emergency?
5
ohaemorrhages OR BP > 180/110 mmHg
3 No
oexudates
opapilloedema
with symptoms and/or
accelerated TOD
No
Step Are there compelling
Abbreviations Yes
• LVH = left ventricular hypertrophy
6 indications/contraindications?
• eGFR = estimated glomerular filtration rate (see below)
• TOD = target organ damage Refer for
• TIA = transient ischaemic attack
• ACE-I = angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor hospital
• ARB = angiotensin receptor blocker admission
• CCB = calcium channel blocker
• HF = heart failure
• ISH = isolated systolic hypertension
Routine Tests and Measurements Compelling indications and contraindications
TEST FREQUENCY COMMENT CLASS CONDITIONS CONTRAINDICATIONS
ANTHROPOMETRY FAVOURING THE USE COMPELLING POSSIBLE
Body weight Every visit HF
Height First visit
DIURETICS Elderly Pregnancy
BMI Every visit < 25 for men and women (thiazide; ISH Gout β blockers (especially
Hypertensives of African atenolol)
Waist circumference Men <94 cm; Women <80 cm* thiazide-like)
Every visit origin.
URINE DIPSTICK ROUTINE DIURETICS Renal insufficiency
HF Pregnancy
Protein. First visit (loop)
Blood. Yearly if ABNORMAL DIPSTICK DIURETIC
Glucose normal Any one of the following: HF
Renal failure
Repeat at next Proteinuria ≥ 2+; (anti- Post-myocardial infarction
Hyperkalaemia
Resistant hypertension
visit if Haematuria ≥ 1+. aldosterone)
abnormal on Refer for further investigation Elderly
first visit CCB ISH
URINE ALBUMIN/ Performed on diagnosis of diabetes
LONG ACTING Angina pectoris Tachyarrhythmias
First visit then ONLY Peripheral vascular disease HF
CREATININE RATIO mellitus type 2 or 5 years after the
yearly (dihydropyridine) Carotid atherosclerosis
-Diabetes mellitus only diagnosis type 1
Pregnancy (nifedipine only)
BLOOD TESTS CCB non- Angina pectoris
Creatinine Use eGFR in ml/min/ 1.73m² AV block (grade 2 or
Sodium/Potassium
Yearly if normal dihydropyridine Carotid atherosclerosis Constipation
3)
Uric acid
(except uric acid) (verapamil, Supraventricular
HF
(verapamil)
tachycardia
Fasting glucose Yearly if normal
GTT/HBA1C in patients with impaired diltiazem)
fasting glucose. HF Pregnancy;
Random total Measure fasting lipogram if cholesterol > LV dysfunction Hyperkalaemia;
Yearly if normal 5.1 mmol/L or in high risk groups Post-myocardial infarction Bilateral renal artery
cholesterol
Non-diabetic nephropathy stenosis
Diabetics only ACE-I Type 1 diabetic nephropathy Angioneurotic oedema
HBA1C 6 monthly
Prevention of diabetic (more common in
Yearly in high risk Refer to criteria for LVH, check for microalbuminuria blacks than in
ECG (RESTING)
patients signs of ischaemia Proteinuria Caucasians)
This may include but not limited to Type 2 diabetic nephropathy
ultrasound kidneys, CT scan/angiography Type 2 diabetic with Pregnancy;
and vascular studies, sleep studies or microalbuminuria Hyperkalaemia
SECONDARY CAUSE
Referral endocrine tests as indicated by clinical ARB Proteinuria Bilateral renal artery
or COMPLICATIONS
suspicion LVH stenosis.
ACE-I cough or intolerance
Peripheral vascular
disease
Bradycardia
Asthma
Glucose intolerance
Angina pectoris Chronic obstructive
Suggested referral to specialist level Post-myocardial infarction pulmonary disease
Metabolic syndrome
β-BLOCKER Athletes and
• Severe or resistant hypertension HF (selected only) AV block (grade 2 or
physically active
• Labile hypertension Tachyarrhythmias 3)
patients
Pregnancy (atenolol)
• Secondary causes suspected Non dihydropyridine
CCB’s (verapamil,
• Progressive TOD, complications or multiple
diltiazem)
comorbidities
• Hypertensive urgency or emergency
*Cardiovasc J Afr 2014; 28: 288-94
You might also like
- General Population (No Diabetes or CKD) Diabetes or CKD PresentDocument2 pagesGeneral Population (No Diabetes or CKD) Diabetes or CKD PresentLalu Ranova100% (1)
- Harvard Medical School Guide to Lowering Your CholesterolFrom EverandHarvard Medical School Guide to Lowering Your CholesterolRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (8)
- Hypertension GuidelinesDocument33 pagesHypertension GuidelinesErlinda NRANo ratings yet
- OET Nursing - Official OET Practice Part 2Document46 pagesOET Nursing - Official OET Practice Part 2jonam7102100% (1)
- Unit I (Hypertension) Part 1Document77 pagesUnit I (Hypertension) Part 1RUSSEL JAN ROJASNo ratings yet
- Juan Carlos Vsim Prep 3Document5 pagesJuan Carlos Vsim Prep 3Michelle Pinkhasova100% (3)
- Grade 4-6 2024 PresentationDocument31 pagesGrade 4-6 2024 PresentationJoana woodsNo ratings yet
- Non-Pharmacological Treatment of HypertensionDocument25 pagesNon-Pharmacological Treatment of Hypertensionastrid abrahams0% (2)
- Reverse Type 2 Diabetes: How to Control and Prevent Diabetes NaturallyFrom EverandReverse Type 2 Diabetes: How to Control and Prevent Diabetes NaturallyNo ratings yet
- Europea GuiaDocument12 pagesEuropea GuiaSindy VergaraNo ratings yet
- Hypertension Guidelines PDFDocument10 pagesHypertension Guidelines PDFARAVINDANo ratings yet
- Diabetes Kit HCP PocketDocument2 pagesDiabetes Kit HCP PocketjoepinoxNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument28 pagesHypertensionSanthoshi Sadhanaa SankarNo ratings yet
- Medication Hypertension OlaDocument13 pagesMedication Hypertension OlaNoor AliNo ratings yet
- West Bengal - Hypertension ProtocolDocument1 pageWest Bengal - Hypertension ProtocolDebanjan BasakNo ratings yet
- 2014 JNC 8 HypertensionDocument3 pages2014 JNC 8 HypertensionFernandez-De Ala NicaNo ratings yet
- Hypertension Pocket Guide: Classification of Blood Pressure Levels For People 18 and OlderDocument2 pagesHypertension Pocket Guide: Classification of Blood Pressure Levels For People 18 and OlderMuhammad Mubeen Iqbal PuriNo ratings yet
- JNC 7 (Klasifikasi Hipertensi) PDFDocument2 pagesJNC 7 (Klasifikasi Hipertensi) PDFAbdur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Hypertension, Definition, Classification and Initial ManagementDocument24 pagesHypertension, Definition, Classification and Initial ManagementSissiNo ratings yet
- 02 Jones DouglasDocument27 pages02 Jones DouglasKarthik SNo ratings yet
- Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in AdultsDocument30 pagesPrevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in AdultsShazi AliNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument8 pagesHypertensioncookie.rajabNo ratings yet
- What Is High Blood Pressure?: HeartDocument2 pagesWhat Is High Blood Pressure?: Heartمحمود محمدNo ratings yet
- L12 HypertensionDocument9 pagesL12 HypertensionEslam Ibrahiem IbrahiemNo ratings yet
- Im Cluster 2 Master Table UpdatedDocument246 pagesIm Cluster 2 Master Table UpdatedRea Dominique CabanillaNo ratings yet
- Hypretension ProtocolDocument11 pagesHypretension ProtocolVarun ArunagiriNo ratings yet
- The Seventh Report of The Joint National Committee On Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure (JNC 7)Document33 pagesThe Seventh Report of The Joint National Committee On Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure (JNC 7)billi lisanuddinNo ratings yet
- Arterial HypertensionDocument11 pagesArterial HypertensionMelissa MuñozNo ratings yet
- Management of Newly Diagnosed Hypertension PDFDocument19 pagesManagement of Newly Diagnosed Hypertension PDFLubeeha HaselNo ratings yet
- L1 IM Hypertension (Aug2122)Document7 pagesL1 IM Hypertension (Aug2122)Maria Carmela CastilloNo ratings yet
- HipertensiDocument2 pagesHipertensiTeti AndriNo ratings yet
- DR Philip Swales - GIM 22 MayDocument34 pagesDR Philip Swales - GIM 22 MaySathvika BNo ratings yet
- HTN Clinical Practice Guidelines (ISH, 2020) : Medscape May 29, 2020Document1 pageHTN Clinical Practice Guidelines (ISH, 2020) : Medscape May 29, 2020RithNo ratings yet
- 2017 DCP 1. Telmisartan Untuk KasusDocument26 pages2017 DCP 1. Telmisartan Untuk KasusOcto IndradjajaNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For DiabetesDocument43 pagesGuidelines For Diabeteskashiftdr100% (1)
- Hypertension Final PDFDocument48 pagesHypertension Final PDFakshayshinde24995No ratings yet
- 112 Obes Ty Los: Anatomy: Embryology of The GutDocument5 pages112 Obes Ty Los: Anatomy: Embryology of The GutjassbhanguNo ratings yet
- Liang - Exercise and HypertensionDocument19 pagesLiang - Exercise and HypertensionsenthilNo ratings yet
- Hypertension Bootcamp Re-EchoDocument41 pagesHypertension Bootcamp Re-EchoAngeline Zamoras-ToledoNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument39 pagesHypertensionMa. Jewon LAGGUINo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument8 pagesHypertensionchandra9000No ratings yet
- Treatment of Hypertension: Jai Radhakrishnan, M.D. Division of NephrologyDocument34 pagesTreatment of Hypertension: Jai Radhakrishnan, M.D. Division of NephrologyAndika HNo ratings yet
- HIP MalesDocument3 pagesHIP MalesMaddy HuckelNo ratings yet
- Management of Newly Diagnosed HypertensionDocument19 pagesManagement of Newly Diagnosed HypertensionLubeeha HaselNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument33 pagesHypertensionKelvinTMaikanaNo ratings yet
- Hypertension: Silent KillerDocument28 pagesHypertension: Silent KilleribratiNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument44 pagesHypertensionasadcabdi613No ratings yet
- JNC ViiiDocument45 pagesJNC ViiiNurul F AzzahraNo ratings yet
- Hypertension: Blood Pressure Classification in ChildrenDocument4 pagesHypertension: Blood Pressure Classification in ChildrenNdra NuelNo ratings yet
- Cvs BP Monitor 271245 Wrong UmDocument31 pagesCvs BP Monitor 271245 Wrong UmDarlaNo ratings yet
- Hypertension EvidenceDocument43 pagesHypertension EvidenceDesfa RizaNo ratings yet
- JNC8 HTNGuidelines Book BookletDocument2 pagesJNC8 HTNGuidelines Book BookletDestya SNNo ratings yet
- Hypertension GuidelinesDocument33 pagesHypertension GuidelinesTika wahyuNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument25 pagesHypertensionsameersidana18No ratings yet
- CPT Group 5 Section DDocument83 pagesCPT Group 5 Section DLinus WerkeNo ratings yet
- Dr. Hasyim Kasim, HipertensiDocument50 pagesDr. Hasyim Kasim, HipertensiImaji Corp MakassarNo ratings yet
- HTN and RamadanDocument37 pagesHTN and Ramadanابو عبد الرحمنNo ratings yet
- Healthy Lifestyle:: - No Magic Bullet - Not New - Requires AttentionDocument28 pagesHealthy Lifestyle:: - No Magic Bullet - Not New - Requires AttentionBiswa1983No ratings yet
- Ketogenic Diet "Yes & No" Guide For BeginnersFrom EverandKetogenic Diet "Yes & No" Guide For BeginnersRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- WebsysDocument2 pagesWebsysJoana woodsNo ratings yet
- WHO PREP CAB GuidelinesDocument40 pagesWHO PREP CAB GuidelinesJoana woodsNo ratings yet
- User Guide On The Prevention and Treatment of Hypertension in Adults at PHC Level 2021Document70 pagesUser Guide On The Prevention and Treatment of Hypertension in Adults at PHC Level 2021Joana woodsNo ratings yet
- CH19 2 Biology WsDocument5 pagesCH19 2 Biology Ws陳詩淇No ratings yet
- Principles of Management of DKADocument4 pagesPrinciples of Management of DKAHassen Kavi IsseNo ratings yet
- Learner's Activity Sheet: MAPEH Physical Education (Quarter I - Week 1)Document4 pagesLearner's Activity Sheet: MAPEH Physical Education (Quarter I - Week 1)She Ena Man UelNo ratings yet
- Elisa Dal Canto 2019Document8 pagesElisa Dal Canto 2019Nikola Dragicka DragicevicNo ratings yet
- Civil Rights and ADA Disability Complaint Walmart MCSODocument27 pagesCivil Rights and ADA Disability Complaint Walmart MCSONeil GillespieNo ratings yet
- Injection Experts: BD - Your DiabetesDocument7 pagesInjection Experts: BD - Your Diabetesspeed maanNo ratings yet
- 2020 01 22 PDFDocument3 pages2020 01 22 PDFMirza RehmanNo ratings yet
- Diabetes InsipidusDocument3 pagesDiabetes InsipidusSu Ging SamNo ratings yet
- Prevention: Can Prediabetes, Type 2 Diabetes and Gestational Diabetes Be Prevented?Document9 pagesPrevention: Can Prediabetes, Type 2 Diabetes and Gestational Diabetes Be Prevented?BethChay LacsonNo ratings yet
- Case Study PresentationDocument35 pagesCase Study PresentationblairNo ratings yet
- AQ FamilyMedicine 06Document12 pagesAQ FamilyMedicine 06Eduardo OrtizNo ratings yet
- PH Protein Glucose Ketones Blood Bilirubin Urobilinogen Nitrite Leukocyte Esterase Specific GravityDocument20 pagesPH Protein Glucose Ketones Blood Bilirubin Urobilinogen Nitrite Leukocyte Esterase Specific GravityChrissa Mae Tumaliuan CatindoyNo ratings yet
- English A June 2003Document6 pagesEnglish A June 2003LilyNo ratings yet
- Karanja SeedDocument2 pagesKaranja Seedrockingtwo07100% (1)
- Serum Oxidative Stress Markers Are Not Associated With Renal and Common Carotid Arteries Arteriosclerotic Vascular Changes in Patients With GoutDocument7 pagesSerum Oxidative Stress Markers Are Not Associated With Renal and Common Carotid Arteries Arteriosclerotic Vascular Changes in Patients With GoutTeodorNo ratings yet
- Review of Literature On Diabetes Mellitus in IndiaDocument6 pagesReview of Literature On Diabetes Mellitus in Indiaafmztsqbdnusia100% (1)
- Glimepiride-Metformin Vs Glimepiride-SitagliptinDocument6 pagesGlimepiride-Metformin Vs Glimepiride-SitagliptinHendri YantoNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1Document5 pagesQuiz 1P PpNo ratings yet
- Diabetes: Statistics Symptoms Causes Diagnosis PreventionDocument67 pagesDiabetes: Statistics Symptoms Causes Diagnosis PreventionShanthi_KVNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study of Change of Hba1C With Voglibose and Teneligliptin On Ongoing Metformin MonotherapyDocument6 pagesComparative Study of Change of Hba1C With Voglibose and Teneligliptin On Ongoing Metformin MonotherapyUttam BasakNo ratings yet
- Synopsis PallaviDocument31 pagesSynopsis PallaviSanjeet DuhanNo ratings yet
- Columnar Insulin Dosing Chart : (1 ML 1 Unit)Document1 pageColumnar Insulin Dosing Chart : (1 ML 1 Unit)Philippe KinnaerNo ratings yet
- 33 Insulin Sliding Scale OrdersDocument1 page33 Insulin Sliding Scale OrdersseifNo ratings yet
- LADA (Latent Autoimmune Disease of The Adult)Document11 pagesLADA (Latent Autoimmune Disease of The Adult)Patrick CommettantNo ratings yet
- CKD Case StudyDocument3 pagesCKD Case StudyKhizra AmjadNo ratings yet
- NHS FPX 6004 Assessment 1 Dashboard Metrics EvaluationDocument8 pagesNHS FPX 6004 Assessment 1 Dashboard Metrics Evaluationzadem5266No ratings yet
- 23.Keto-Asidosis DiabetikDocument30 pages23.Keto-Asidosis DiabetikmutiaNo ratings yet
- Diabetes in Pregnancy: Multiple Choice Questions For Vol. 25, No. 1 - Obgyn KeyDocument1 pageDiabetes in Pregnancy: Multiple Choice Questions For Vol. 25, No. 1 - Obgyn Keyabdelrazag T GhadbanNo ratings yet