Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Midterm Lec CHN 2
Uploaded by
jjmaxh20Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Midterm Lec CHN 2
Uploaded by
jjmaxh20Copyright:
Available Formats
COMMUNITY HEALTH NURSING 2 (POPULATION GROUPS AND COMMUNITY AS CLIENTS) MIDTERM
LESSON 1: community, and efficiently and effectively
provide care for members of that in a way
NURSING PROCESS IN THE CARE OF POPULATION that is consistent with the community’s
GROUPS AND COMMUNITY cultural, policy and health resource values.
A multi-sector and multi-disciplinary
collaborative enterprise that uses public
HALLMARK OF COMMUNITY HEALTH NURSING health science, evidence-based strategies, and
other approaches to engage and work with
Population-focused communities, in a culturally appropriate
- “the primary client and recipient of care manner, to optimize the health and quality of
of the nurse is a group of people in the life of all persons who live, work, or are
community”. otherwise active in a defined community or
The nurse works with families, population communities.
/sub-groups.
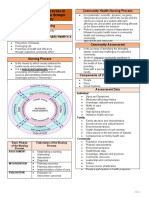
COMMUNITY HEALTH NURSING PROCESS
POPULATION
Community Health Nursing Process
The total of individuals occupying an area or
making up a whole. Is a systematic, scientific, dynamic on-going
Within a population are smaller subgroup interpersonal process in which the nurses
called aggregates–defined by their common and the clients are viewed as a system with
characteristics and concerns, often seen as each affecting one and another and both
population having high-risk for certain health being affected by the factors within the
conditions. behavior.
Children under 5 years old, school-aged An effective tool to help people solve their
children, adolescents, and the elderly. health problems and meet their health and
nursing needs.
Assessment
COMMUNITY Nursing Diagnosis
Planning
A cluster of people with at least one common Implementation
characteristic (geographic, location, Evaluation
occupation, ethnicity, housing condition)
A group of people with a common
I. Assessment of Community Health Needs
characteristic or interest living together in a
larger society.
Health Needs Assessment:
A process of systematically collecting
information to enable the health
POPULATION-BASED CARE: Plans for the Group or practitioner, team, and policy makers
Individual identify, analyze, prioritize and meet
the health needs of an individual,
Approach allows one to assess the health
family or population.
status and health needs of a target
population, implement and evaluate
Community Health needs Assessment:
interventions that are designed to improve
the health of that population, and efficiently A process that describes the state of
and effectively provide care for members of health of local people, enables the
that population in a way that is consistent identification of the major risk factors
with the community’s cultural, policy and and causes of illness and
health resource values. identification of the actions or
interventions needed.
Purposes of Community Health Needs
COMMUNITY-BASED CARE: Plans for the community assessment
Approach allows one to assess the health
status and health needs of a target 1. Will enable the health practitioners,
community, implement and evaluate NGO’s, civic-oriented group, and
policy makers to identify the
interventions that are designed to improve members of the population who need
the health of the people living in the the health care services, and
resources the most, b. Poverty & income
c. Environment
2. To ensure that these resources are d. Social cohesion / social support
used following the rule of equity. e. Destabilizing factors
f. Resources formal & informal
3. Important in health care planning
to identify the priority health needs,
utilize the internal and external
resources of the community and COMPONENTS OF COMMUNITY HEALTH NEEDS
develop community participation and
ASSESSMENT
involvement.
1. Health Status
2. Health Resources
Community Health Nursing Process Assessment tools: 3. Health Action Potential
PRIMARY DATA
Health Needs Assessment
OBSERVATION SURVEY INFORMANT
HEALTH STATUS
INTERVIEW COMMUNITY FORUM Health standing or condition of the
population as indicated by the morbidity,
mortality, and fertility rates (MMF).
1. MORTALITY DATA- describes patterns
SECONDARY DATA
of death in relation to age, gender, and
Registry of vital events cause of death.
Health records 2. MORBIDITY DATA – information is on
Disease registry the types of illness and disability,
Census data their incidence and prevalence.
3. Behavior measures – indicators of
health (like: smoking, or any activity
proven to cause illness.
SOURCES OF ASSESSMENT INFORMATION 4. Quality of life measures – means
assessing physical health, functional
The client
ability, & psychological being.
The family or significant others
5. Use of service information –
Medical records/nurses’ notes
Information gives an account of the
Other members of health team
morbidity status of the community,
Other sources
the hospital admissions and use of
preventive services like immunization
& screening programs.
DATA TO BE COLLECTED 6. Health inequalities – most disease and
illness patterns are closely associated
1. CHARACTERISTICS OF THE POPULATION
to economic circumstances where
a. Geography
there is high rate of death and illness
b. Numbers
among poor sectors of society.
c. Age distribution & gender
d. distribution
e. Ethnicity & religion
f. Population trends HEALTH RESOURCES
g. Language and literacy
Are assets, means, strengths, and skills that
are contributory to the population of health &
2. HEALTH STATUS OF THE POPULATION
well-being that exits within communities to
a. Mortality & morbidity rates
meet the needs of individuals, families or
b. Communicable diseases
social groups.
c. Low birth weights
1. Informal resources – families deliver
d. Breast feeding rates & immunization
the greatest part of all care services in
rates
the community.
e. Health behaviors such as smoking
2. Formal resources- can be provided at
f. Health service use
a variety of levels & by many agencies
including both health services & those
3. LOCAL FACTORS AFFECTING HEALTH
provided by sectors that have an
(strengths and weaknesses)
impact on health.
a. Work & employment
KINDS OF COMMUNITY RESOURCES LESSON 2:
Knowledge & skills in caring
for & promoting health NURSING PROCESS IN THE CARE OF POPULATION
Health careers (family & GROUPS AND COMMUNITY
friends)
Social support networks;
community-based NURSING DIAGNOSIS
organizations
Resources (money, shops, Is the statement of the client’s current health
food, transport) status and concerns which were obtained
The ability to cope in often from the assessment data and can be resolved
very difficult circumstances or minimized through nursing intervention.
(like: supportive
interpersonal relationships) - Clinical judgment about individual, family,
or community responses to actual or
potential health problems/life processes
- Provides the basis for selection of nursing
HEALTH ACTION POTENTIAL
interventions to achieve outcomes for
Action planning is a complex activity and which the nurse is accountable
should be undertaken where the more local
people are involved in action planning
There must be collaboration with other IMPORTANCE OF THE NURSING DIAGNOSIS
groups
1. Nursing Diagnosis allows nurse to develop
individualized plan of care.
2. Nursing diagnosis distinguishes the role of
Stages of Action Planning the nurse from the physician and the medical
Preparation stage diagnosis as the nursing diagnoses focus on
Agreeing to the aims set by the group the human responses and alterations in the
Describing the objectives of the program or project client’s ability to function as an independent
Detailing the activities needed to meet the objectives human being.
Evaluation of the outcomes
Review:
SUMMARY Elements of a Nursing Diagnosis Statement
Assessment is a continuing and dynamic Actual nursing diagnosis
process which must be undertaken to Etiology
validate whether the nursing diagnosis is Defining characteristics
correct, and to find out if the client is on the Wellness
way to achieving the expected outcomes. Actual
Community health needs assessment is the Risk
same process as carrying out a holistic Potential
assessment of an individual or family but
covers a larger population instead of just an
individual or a family. COMMUNITY DIAGNOSIS
The client is the whole community and
involves more people. Is a statement of the health and health-
Community health needs assessment related problems of the community or which
identifies problems and needs and, also have a high risk of developing, and the
assesses the strengths and resources of the possible causes or causative organisms and
community members. the contributory factors.
It is the end-result of data collection and
analysis
TYPES OF COMMUNITY DIAGNOSIS
STEPS IN CONDUCTING COMMUNITY DIAGNOSIS 3. MODIFIABILITY OF THE PROBLEM –the
probability of success in reducing, controlling
1. Determine the objective or eradicating the problem through
2. Define the study population interventions
3. Determine the data to be gathered 4. PREVENTIVE POTENTIAL –the nature &
4. Collect the data magnitude of future problems that can be
5. Develop the instrument minimized, controlled, or totally prevented if
6. Actual data gathering intervention is done.
7. Data collation 5. SOCIAL CONCERN –the community’s
8. Data presentation perception & evaluation of the problem in
9. Data analysis & interpretation terms of seriousness & urgency of attention
10. Problem identification needed.
11. Health status –mortality, morbidity, fertility
12. Health resources-money, manpower,
material, institution
13. Health related –environment, culture, HEALTH PROBLEM PRIORITIZATION
economic, political
14. Prioritization of HEALTH PROBLEMS
PRIORITIZING HEALTH PROBLEMS
Which one needs the most attention or is most
critical
The most urgent or immediate needs of the
client/clients
HEALTH PROBLEM PRIORITIZATION CRITERIA
Priorities can either becritical
physical or psychological in SCORE
nature
Which one needs the most attention or is most
critical
PROBLEM IDENTIFICATION
A. HEALTH STATUS PROBLEM –described in EXAMPLE: COMMUNITY DIAGNOSIS STATEMENT
terms of increased/ decreased morbidity,
mortality, fertility or reduced capability for Deficient Knowledge associated with
wellness. community health can be caused by
B. HEALTH RESOURCES PROBLEM-described in inadequate knowledge of resources, access to
terms of lack of or absence of manpower, the healthcare system and programs, and an
money, materials or institutions necessary to understanding of individual and community
solve health problems. health risks.
C. HEALTH-RELATED PROBLEMS –described in
terms of existence of social, economic, Nursing Diagnosis: Deficient Knowledge
environmental & political factors that
Related to:
aggravate the illnessinducing situations in
the community. Inadequate knowledge of community
support and resources
Inadequate access to healthcare
PRIORITY SETTING professionals
Lack of financial and social resources
1. NATURE OF THE CONDITION/PROBLEM Program budget, outcome information, or
PRESENTED evaluation plan deficiencies
a) health status Inability of existing programs to address
b) health resources health concerns
c) health-related
2. MAGNITUDE OF THE PROBLEM-the severity Nursing Diagnosis: Deficient Knowledge
of the problem which can be measured in
As evidenced by:
terms of the proportion of the population
affected by the problem Community members’ verbalization of
confusion/concern
Community members’ noncompliance with EXAMPLE: COMMUNITY DIAGNOSIS STATEMENT
the health program
Community members’ inquiries about a Ineffective community coping can be caused
certain topic by unsatisfactory community efforts to adapt
Community members’ misconceptions and solve problems in a way that satisfies
Community members’ exacerbation of health community desires or needs.
symptoms
Nursing Diagnosis: Ineffective Community Coping
Health program’s inability to address the
health concern Related to:
Preventable hospital readmissions
Increased incidence of physiological or Insufficient resources for problem-solving
psychological conditions Inadequate community resources
(emergency services, transportation)
Lack of social support services
DEFICIENT KNOWLEDGE ASSESSMENT
1. Assess healthcare providers’ knowledge and Nursing Diagnosis: Ineffective Community Coping
practices related to the community’s health.
As evidenced by:
Having the same knowledge and Community members’ expression of lack of
using the same knowledge makes it support or excessive stress
easier for those working in the Higher rates of illness
community to recognize one another High rates of crime, abuse, unemployment,
and communicate ideas more and poverty
effectively.
Community members’ expression of
powerlessness or hopelessness
2. Assess the community’s existing and potential
health problems.
By identifying particular issues,
population-based treatments can INEFFECTIVE COMMUNITY COPING ASSESSMENT
focus on the existing problem that 1. Assess the community’s needs.
may be solved by primary prevention
A needs assessment is essential to
and proactive intervention.
identify the gaps preventing it from
achieving its targeted objectives.
3. Assess the community’s resources.
Knowing what resources are 2. Assess disaster plans and response to
currently accessible and how the emergencies.
community accesses them helps to
Evaluate the policies of local and
identify potential gaps. Resources
regional efforts in the face of
may not be meeting the needs of the
epidemics, threats, terrorist attacks,
community or the community may
and natural catastrophes to assess
not be aware they exist
preparedness.
4. Note the community members’ complaints/
3. Identify the availability, accessibility, and
concerns.
usage of community resources.
Taking note of the members’
Even when resources are accessible,
concerns presents a realistic image of
they are not always utilized properly
issue areas through feedback from
or to their full potential. Evaluate
those who are affected most.
programs and resources available,
referral processes, and follow-up
measures.
4. Identify unmet community expectations.
Establishing shortcomings is the first
step in overcoming gaps.
Communication is crucial to
understanding the perspective of the
community.
You might also like
- Midterm Lec CHN 2Document10 pagesMidterm Lec CHN 2jjmaxh20No ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing Lecture Module 4Document10 pagesCommunity Health Nursing Lecture Module 4Meryville JacildoNo ratings yet
- 2 NCM113 LecDocument9 pages2 NCM113 LecAdrian SantiagoNo ratings yet
- CHN II Prelim Coverage Compilation 1Document13 pagesCHN II Prelim Coverage Compilation 1SVPSNo ratings yet
- 1.Chn Introduction and FamilyDocument7 pages1.Chn Introduction and FamilyLuzie Mae SuanNo ratings yet
- CHN Lecture - 2Document13 pagesCHN Lecture - 2HANNAH LEAL RENDAJE SHARIFFNo ratings yet
- CPH LecDocument46 pagesCPH LectuamicaiiiNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts and Principles of Community Health NursingDocument9 pagesBasic Concepts and Principles of Community Health NursingElgen B. AgravanteNo ratings yet
- CHN II Prelim Coverage Compilation 1Document12 pagesCHN II Prelim Coverage Compilation 1SVPSNo ratings yet
- CHN - Nursing ConceptsDocument5 pagesCHN - Nursing ConceptsJessa Mae BarquillaNo ratings yet
- 2 Nursing-Process-in-the-care-of-the-Community - FGBDocument41 pages2 Nursing-Process-in-the-care-of-the-Community - FGBKim Bok JooNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing Review NotesDocument12 pagesCommunity Health Nursing Review NotesISICLE GTNo ratings yet
- CPH Lab Week 1-6Document8 pagesCPH Lab Week 1-6tuamicaiiiNo ratings yet
- CPH ReviewerDocument12 pagesCPH ReviewerRicanie CadornaNo ratings yet
- CHN OutlineDocument29 pagesCHN OutlineMeryville JacildoNo ratings yet
- CPH Lec ReviewrDocument24 pagesCPH Lec ReviewrCresma Santa Rayjane DesamparoNo ratings yet
- CHN Topic1-NEWDocument9 pagesCHN Topic1-NEWsecondacvalo123No ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document11 pagesLesson 2John Dave V. VillarmenteNo ratings yet
- Principles of CHN New UpdatedDocument4 pagesPrinciples of CHN New Updatediheart musicNo ratings yet
- CHN IiDocument33 pagesCHN IiAila Hinlog100% (1)
- The Nursing Process in The Care of The CommunityDocument3 pagesThe Nursing Process in The Care of The CommunityHanz Medina Manganar100% (1)
- CLARITO - Comparative Analysis Between Public Health Nursing and Community Health NursingDocument3 pagesCLARITO - Comparative Analysis Between Public Health Nursing and Community Health NursingQuincy ClaritoNo ratings yet
- CPH Week 1Document6 pagesCPH Week 1Jabez MatigaNo ratings yet
- NCM 222 CHN Lesson 1Document5 pagesNCM 222 CHN Lesson 1Krishane JustaleroNo ratings yet
- NCM 113 - CHN ConceptDocument5 pagesNCM 113 - CHN ConceptLorelyn FabrigarasNo ratings yet
- The Community - Chn2 1Document56 pagesThe Community - Chn2 1Andree GalloNo ratings yet
- 01 Public Health PrelimsDocument2 pages01 Public Health PrelimsRay Alfonso SabioNo ratings yet
- CHN Reviewer PrelimDocument19 pagesCHN Reviewer PrelimCher Ann RuilesNo ratings yet
- NCM 113 - Lec Reviewer PrelimDocument9 pagesNCM 113 - Lec Reviewer PrelimKylle AlimosaNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 - OVERVIEW of COMMUNITY HEALTH NURSING Flashcards - QuizletDocument24 pagesMODULE 1 - OVERVIEW of COMMUNITY HEALTH NURSING Flashcards - QuizletmarieNo ratings yet
- Community Health NursingDocument8 pagesCommunity Health NursingMae CalicaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 CHN ConceptsDocument10 pagesUnit 1 CHN ConceptsJacqueline S. PunoNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing 1 NCM 104Document4 pagesCommunity Health Nursing 1 NCM 104Sheila May Teope Santos100% (1)
- CHN Semi Final TransesDocument6 pagesCHN Semi Final TransesCAÑADA, JOHANNELYN M.No ratings yet
- CHN-213-Prelim-2020 StudentDocument33 pagesCHN-213-Prelim-2020 StudentSVPSNo ratings yet
- ALL SUBJECTS PRELIM TO MIDTERM HANDOUTS CompressedDocument117 pagesALL SUBJECTS PRELIM TO MIDTERM HANDOUTS CompressedRose Anne AbivaNo ratings yet
- NSG 101 Community Health NursingDocument7 pagesNSG 101 Community Health NursingAl-mathar L. TingkahanNo ratings yet
- CPH Lec - Week 1Document9 pagesCPH Lec - Week 1tuamicaiiiNo ratings yet
- CHN Reviewer Final Na ToDocument27 pagesCHN Reviewer Final Na ToDESSA GALOSONo ratings yet
- A Text Book of Community Health Diagnosis (PDFDrive)Document110 pagesA Text Book of Community Health Diagnosis (PDFDrive)Felix FwsNo ratings yet
- Concepts, Principles and Theories in Community Health NursingDocument13 pagesConcepts, Principles and Theories in Community Health NursingKristine KimNo ratings yet
- Updated - CONCEPT OF COMMUNITY EMPOWERMENT - DF - 2020-2021Document40 pagesUpdated - CONCEPT OF COMMUNITY EMPOWERMENT - DF - 2020-2021Ahmad HabibNo ratings yet
- CHN Week 1: Definition of Community Health Nursing Principles of Community Health NursingDocument22 pagesCHN Week 1: Definition of Community Health Nursing Principles of Community Health NursingYoko Mae YanoNo ratings yet
- NCM 113 Mod1Document6 pagesNCM 113 Mod1Samantha BolanteNo ratings yet
- COMMUNIT Y HEALTH NURSING 2 Reviewer (Week 1-4)Document7 pagesCOMMUNIT Y HEALTH NURSING 2 Reviewer (Week 1-4)Angelica Marie MacaslingNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing ReviewerDocument18 pagesCommunity Health Nursing ReviewerNicole Sherry M. CHEENo ratings yet
- CHN II - ReviewerDocument34 pagesCHN II - ReviewerKarina Blanca Sanico AdranedaNo ratings yet
- CHN 2 LectureDocument44 pagesCHN 2 Lectureandrea.maungca.mnlNo ratings yet
- CHN 1Document10 pagesCHN 1keiemorayaNo ratings yet
- Famorca Et Al. 2013. Nursing Care of The CommunityDocument126 pagesFamorca Et Al. 2013. Nursing Care of The CommunityShyne HazyNo ratings yet
- Community & Public Health: Course TittleDocument11 pagesCommunity & Public Health: Course TittleAesthetics MinNo ratings yet
- Foundation 1.1Document3 pagesFoundation 1.1ANDRIANNE FAGUTAONo ratings yet
- Primary Health CareDocument2 pagesPrimary Health CareAmethystNo ratings yet
- FINALSDocument15 pagesFINALSmayangernszNo ratings yet
- COMMUNITY HEALTH NURSING PDF FileDocument16 pagesCOMMUNITY HEALTH NURSING PDF FileJenniea Lyl SolatorioNo ratings yet
- Community Health NursingDocument76 pagesCommunity Health Nursingmary navalNo ratings yet
- CHN-213-Prelim-2020 StudentDocument33 pagesCHN-213-Prelim-2020 StudentSVPSNo ratings yet
- CHN in House Module 1Document7 pagesCHN in House Module 1Catherine AteradoNo ratings yet
- CHN 1Document12 pagesCHN 1Karl Gabriel BonifacioNo ratings yet
- NCP - Acute Pain Stomach CancerDocument2 pagesNCP - Acute Pain Stomach CancerJohn Michael TaylanNo ratings yet
- Necrotising Ulcerative Gingivitis: A Literature Review: James Dufty / Nikolaos Gkranias / Nikos DonosDocument10 pagesNecrotising Ulcerative Gingivitis: A Literature Review: James Dufty / Nikolaos Gkranias / Nikos DonosmayaNo ratings yet
- Big Data Security and Privacy in Healthcare: A Review Big Data Security and Privacy in Healthcare: A ReviewDocument8 pagesBig Data Security and Privacy in Healthcare: A Review Big Data Security and Privacy in Healthcare: A ReviewDalene EvangelioNo ratings yet
- Case Reviews in Ophthalmology Expert Consult - OnlDocument2 pagesCase Reviews in Ophthalmology Expert Consult - Onldr. mostakNo ratings yet
- Medical Reimbursement PDFDocument3 pagesMedical Reimbursement PDFOrlando WilliamsNo ratings yet
- PROGRAM - DETAILAT Conferinta Bioinginerie 2015 PDFDocument41 pagesPROGRAM - DETAILAT Conferinta Bioinginerie 2015 PDFAlina RogojanuNo ratings yet
- 2022 IMG Assessment PolicyDocument25 pages2022 IMG Assessment PolicyshakkiryousufNo ratings yet
- Tooth Implant Supported Prosthesis: A Literature ReviewDocument8 pagesTooth Implant Supported Prosthesis: A Literature ReviewTung Thanh NguyenNo ratings yet
- EVALUATION 1.1 THE ROLE OF NURSES IN THE OPERATING ROOM Unscramble SentencesDocument3 pagesEVALUATION 1.1 THE ROLE OF NURSES IN THE OPERATING ROOM Unscramble SentencesRonald Alfredo Gordillo PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Process RecordingsDocument4 pagesProcess RecordingsJayakrishnan P KripNo ratings yet
- Assess Appropriateness For Clinical Condition. Heart Rate Typically 50/min If BradyarrhythmiaDocument1 pageAssess Appropriateness For Clinical Condition. Heart Rate Typically 50/min If BradyarrhythmiaatikaNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective AirwayDocument4 pagesNCP Ineffective AirwayMark Ronhel Gallardo PerenalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Occupational TherapyDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Occupational TherapyDevy CaruzNo ratings yet
- B.SC., - N - GuidelinesDocument5 pagesB.SC., - N - Guidelinesசெங்கை மஜீத் இராவுத்தர்No ratings yet
- Revised Norms For Sanctioned Strength in ESIC HospitalsDocument2 pagesRevised Norms For Sanctioned Strength in ESIC Hospitalssksonu722No ratings yet
- This Study Resource WasDocument2 pagesThis Study Resource Waswriter topNo ratings yet
- Mapeh 6 Health PPT q4 - MedicinesDocument17 pagesMapeh 6 Health PPT q4 - MedicinesMaureen VillacobaNo ratings yet
- Case ConceptualizationDocument18 pagesCase ConceptualizationKrishno RaeNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Health 1ST QuarterDocument32 pagesGrade 10 Health 1ST QuarterKristela Mae ColomaNo ratings yet
- Global Health Care Outlook1525Document47 pagesGlobal Health Care Outlook1525arifmukhtarNo ratings yet
- Treatment Algorithm For Multiple Sclerosis Disease-Modifying TherapiesDocument25 pagesTreatment Algorithm For Multiple Sclerosis Disease-Modifying TherapiesjaysonNo ratings yet
- Retrospective Analysis of The Relationship Between Infantile Seborrheic Dermatitis and Atopic DermatitisDocument6 pagesRetrospective Analysis of The Relationship Between Infantile Seborrheic Dermatitis and Atopic DermatitisIkmal ShahromNo ratings yet
- For Nurses Managers and Executives. St. Louis, Missouri: SaundersDocument4 pagesFor Nurses Managers and Executives. St. Louis, Missouri: SaundersMaria KordasNo ratings yet
- PeriodontistDocument4 pagesPeriodontistapi-79293215No ratings yet
- Joric M. Magusara, RN: Teacher / InstructorDocument5 pagesJoric M. Magusara, RN: Teacher / InstructorJoric MagusaraNo ratings yet
- CPT Modifier NewDocument10 pagesCPT Modifier NewSeenuvasanLeeManiNo ratings yet
- Oet Speakingr PDFDocument133 pagesOet Speakingr PDFAlphonsa Thomas100% (1)
- Ashraf Report FinalDocument19 pagesAshraf Report Finalmuhammad syahmiNo ratings yet
- Vero DoxDocument61 pagesVero DoxMWANGINo ratings yet
- Processing Prescription OrdersDocument33 pagesProcessing Prescription OrdersEv3rgreenNo ratings yet