Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DNA Replication Transcription and Translation TRANSES
Uploaded by
mngnmg80 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views5 pagesThis document discusses several key concepts in DNA replication, transcription, and translation. It defines template DNA, semi-conservative replication, DNA helicase, annealing, single-stranded binding proteins, DNA gyrase, replication forks, replication bubbles, DNA polymerase III, deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates, RNA primers, primase, leading and lagging strands, Okazaki fragments, DNA polymerase I, DNA ligase, and exonuclease. The main steps in DNA replication involve unwinding the DNA double helix, synthesizing new strands using DNA polymerase and RNA primers, and joining DNA fragments.
Original Description:
Original Title
DNA-replication-transcription-and-translation-TRANSES-
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses several key concepts in DNA replication, transcription, and translation. It defines template DNA, semi-conservative replication, DNA helicase, annealing, single-stranded binding proteins, DNA gyrase, replication forks, replication bubbles, DNA polymerase III, deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates, RNA primers, primase, leading and lagging strands, Okazaki fragments, DNA polymerase I, DNA ligase, and exonuclease. The main steps in DNA replication involve unwinding the DNA double helix, synthesizing new strands using DNA polymerase and RNA primers, and joining DNA fragments.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views5 pagesDNA Replication Transcription and Translation TRANSES
Uploaded by
mngnmg8This document discusses several key concepts in DNA replication, transcription, and translation. It defines template DNA, semi-conservative replication, DNA helicase, annealing, single-stranded binding proteins, DNA gyrase, replication forks, replication bubbles, DNA polymerase III, deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates, RNA primers, primase, leading and lagging strands, Okazaki fragments, DNA polymerase I, DNA ligase, and exonuclease. The main steps in DNA replication involve unwinding the DNA double helix, synthesizing new strands using DNA polymerase and RNA primers, and joining DNA fragments.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
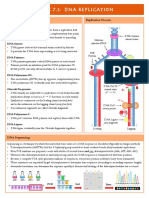
DNA REPLICATION, TRANSCRIPTION AND TRANSLATION
Cell and Molecular Biology
Template
• A single stranded DNA sequence
that acts as the guiding pattern for
producing a complementary DNA
strand.
Semi conservative replication
● Process of replication in which
each DNA molecule is
composed of one parent strand
and one newly synthesized
strand.
DNA Helicase
• The enzyme that
unwinds double helical DNA by
disrupting hydrogen bonds.
Anneal
• The pairing of complementary
strands of DNA through hydrogen
bonding.
Single-stranded binding proteins
• A protein that keeps separate strands
of DNA apart.
DNA gyrase
• The bacterial enzyme that relieves
the tension produced by the unwinding of
DNA during replication.
Replication Fork
• The region where the enzymes
replicating a DNA molecule are
bound to untwisted, single
stranded DNA.
Replication Bubble
• The region where two replication
forks are I close proximity to each
other, producing a bubble in the
replicating DNA.
DNA polymerase III
• The enzyme responsible for
synthesizing complementary strands of
DNA during DNA replication
Deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates
• Molecules composed of a
deoxyribose bonded to three phosphate
groups and a nitrogenous base.
RNA Primer
• A sequence of 10 to 60 RNA bases
that is annealed to a region of single
stranded DNA for the purpose of initiating
DNA replication.
Primase
• The enzyme that builds RNA primers.
Leading strand
• The new strand of DNA that is synthesized
continuously during replication.
Lagging strand
• The new strand of DNA that is synthesized in
short fragments which are later joined together.
Okazaki fragments
Short fragments of DNA that are a result of
synthesis of the lagging strand during
DNAreplication.
DNA polymerase I
• An enzyme that removes RNA
primers and replaces them with the
appropriate deoxyribonucleotides during
DNA replication
DNA ligase
• The enzyme that joins DNA
fragments together by catalyzing the
formation of a bond between the 3'
hydroxyl group and a 5' phosphate group
on the sugar-phosphate backbones.
Exonuclease
An enzyme that cuts out nucleotides at the
end of a DNA strand.
You might also like
- DNA Replication Transcription and Translation TRANSES 1Document5 pagesDNA Replication Transcription and Translation TRANSES 1mngnmg8No ratings yet
- DNA Replication Transcription and Translation TRANSES 1Document5 pagesDNA Replication Transcription and Translation TRANSES 1mngnmg8No ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument6 pagesIlovepdf Mergedmngnmg8No ratings yet
- DNA Replication With Video LinksDocument15 pagesDNA Replication With Video LinksSmilingNo ratings yet
- 2.7 Dna Replication Transcription and Translation 4Document168 pages2.7 Dna Replication Transcription and Translation 4Senam DzakpasuNo ratings yet
- Replication of DNADocument10 pagesReplication of DNA3lyooNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication and RepairDocument11 pagesDNA Replication and RepairCiroanneNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocument9 pagesCentral Dogma of Molecular BiologyHONEY JYL DUCUSINNo ratings yet
- 2 - Dna ReplicationDocument25 pages2 - Dna Replicationwonderwolfblood17No ratings yet
- Bacterial GeneticsDocument38 pagesBacterial Geneticsfatima zafarNo ratings yet
- Semi-Conservative DNA ReplicationDocument12 pagesSemi-Conservative DNA ReplicationDibyakNo ratings yet
- MB Chapter 4 - DNA-Replication-IDocument27 pagesMB Chapter 4 - DNA-Replication-IMustee TeferaNo ratings yet
- Dna Replication and Repair #4Document76 pagesDna Replication and Repair #4Len ArellanoNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument16 pagesDNA ReplicationStephen Moore100% (1)
- FHCG 4 - Nucleic Acids Gene ExpressionDocument58 pagesFHCG 4 - Nucleic Acids Gene ExpressionLeena AkhtarNo ratings yet
- 2.7 DNA Replication, Transcription and TranslationDocument23 pages2.7 DNA Replication, Transcription and TranslationAleksandar KlingNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument47 pagesDNA ReplicationastrogeniusthreeNo ratings yet
- Bio Ninja Unit 7 MergedDocument4 pagesBio Ninja Unit 7 Mergedshwooby shawoobyNo ratings yet
- DNA Strucuture and Replication RNA and Protien SynthesisDocument69 pagesDNA Strucuture and Replication RNA and Protien SynthesisRomelyn Grace BorbeNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument43 pagesDNA ReplicationBilal SajidNo ratings yet
- Dogma Central Biology Pertemuan 4Document18 pagesDogma Central Biology Pertemuan 4Rizky BluesNo ratings yet
- Dna Replication: Elective BiologyDocument7 pagesDna Replication: Elective BiologyMichael KpeliNo ratings yet
- DNA Structure & Replication + RNADocument8 pagesDNA Structure & Replication + RNAClaraNo ratings yet
- Please Switch Off Your MobilesDocument28 pagesPlease Switch Off Your MobilesSadia MushtaqNo ratings yet
- 1.3. Dna Replication1Document44 pages1.3. Dna Replication1sabry tapiaNo ratings yet
- Bic 159: Biochemistry Week 2 Lecture: Dr. Jody Ann JohnsonDocument46 pagesBic 159: Biochemistry Week 2 Lecture: Dr. Jody Ann JohnsonJana-Tae KerrNo ratings yet
- Learning Unit 3 - PART 2 - DNA ReplicationDocument43 pagesLearning Unit 3 - PART 2 - DNA ReplicationSphesihle ThekoNo ratings yet
- Name: Seerat Fatima Department: BS. BIOCHEMISTRY Subject: Cell Biology Roll No: 004 Submitted To: Mudassar Fareed AwanDocument7 pagesName: Seerat Fatima Department: BS. BIOCHEMISTRY Subject: Cell Biology Roll No: 004 Submitted To: Mudassar Fareed AwanMoona MalikNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids Dna & RnaDocument58 pagesNucleic Acids Dna & RnaValeria RosasNo ratings yet
- 6.2 DNA Replication Full NoteDocument44 pages6.2 DNA Replication Full NotejiaenNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument24 pagesDNA ReplicationAkhtar MuneerNo ratings yet
- Submitted By: Fatima Parvez 13/117Document24 pagesSubmitted By: Fatima Parvez 13/117Eng CirroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1.2 DNA Replication (Autosaved)Document36 pagesChapter 1.2 DNA Replication (Autosaved)abdullaNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument28 pagesDNA ReplicationAsim Bin Arshad 58-FBAS/BSBIO/S19100% (1)
- Biology Chapter 11Document42 pagesBiology Chapter 11sanaassaf19No ratings yet
- Unit 8 Biosynthesis of Nucleic Acids - ReplicationDocument12 pagesUnit 8 Biosynthesis of Nucleic Acids - ReplicationMing mingNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument48 pagesDNA ReplicationAamir MumtazNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma: - Replication - Transcription - TranslationDocument15 pagesCentral Dogma: - Replication - Transcription - TranslationCristina RocheNo ratings yet
- Genes Are Dna and Encode Rnas and PolypeptidesDocument66 pagesGenes Are Dna and Encode Rnas and Polypeptidesshaurya singhNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument26 pagesDNA ReplicationZainab AshroffNo ratings yet
- H.-Nucleic AcidsDocument69 pagesH.-Nucleic AcidsBrianna Pauline BantugNo ratings yet
- 5 - DNA Replication, Transcription and TranslationDocument85 pages5 - DNA Replication, Transcription and TranslationJustina VillageNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3-Enzyme For DNA Manipulation in Recombinant DNADocument42 pagesLecture 3-Enzyme For DNA Manipulation in Recombinant DNANurfarahain ZolkeflyNo ratings yet
- 2.7 7.1DNAReplicationDocument33 pages2.7 7.1DNAReplicationKhin (Darin) Hnin PhyuNo ratings yet
- ObjectivesDocument36 pagesObjectivesMARIAN SABENECIONo ratings yet
- 10 Biosynthesis of Nucleic AcidsDocument26 pages10 Biosynthesis of Nucleic AcidsDayne Ocampo-Soliman100% (1)
- DNA and Protein SynthesisDocument33 pagesDNA and Protein Synthesismenaga ilangkovanNo ratings yet
- Molecular Mechanism of ReplicationDocument23 pagesMolecular Mechanism of ReplicationIarrNo ratings yet
- Module 5aDocument28 pagesModule 5aMing YanNo ratings yet
- Dna Code of LifeDocument9 pagesDna Code of Lifendlovusenamile401No ratings yet
- DNA Replication: THINK: Why Does DNA Need To Replicate?Document33 pagesDNA Replication: THINK: Why Does DNA Need To Replicate?AkshiNo ratings yet
- Recombinant DNA Technology: Presented To: Sir Ashfaq Presented By: Nasira Bashir Roll Number: 01Document31 pagesRecombinant DNA Technology: Presented To: Sir Ashfaq Presented By: Nasira Bashir Roll Number: 01Rabiya KianiNo ratings yet
- 6.2: Dna ReplicationDocument43 pages6.2: Dna Replicationa200812No ratings yet
- BCH 401 Note 1 - KWASUDocument35 pagesBCH 401 Note 1 - KWASUidriscognitoleadsNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument25 pagesDNA ReplicationPhilani KheswaNo ratings yet
- Structure of DNA and RNADocument42 pagesStructure of DNA and RNAAldrin LupasNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument19 pagesDNA ReplicationLouis HilarioNo ratings yet
- 2019 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic DNA ReplicationDocument32 pages2019 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic DNA ReplicationALEXANDRA MARIE BUNQUINNo ratings yet
- Agro Tech Foods LTDDocument17 pagesAgro Tech Foods LTDAlmas KhanNo ratings yet
- Router Board Performance TestsDocument2 pagesRouter Board Performance TestsedkaviNo ratings yet
- Micron Serial NOR Flash Memory: 3V, Multiple I/O, 4KB Sector Erase N25Q256A FeaturesDocument92 pagesMicron Serial NOR Flash Memory: 3V, Multiple I/O, 4KB Sector Erase N25Q256A FeaturesAENo ratings yet
- Medicinal Chemistry/ CHEM 458/658 Chapter 8-Receptors and MessengersDocument41 pagesMedicinal Chemistry/ CHEM 458/658 Chapter 8-Receptors and MessengersMehak SarfrazNo ratings yet
- Computer ArchitectureDocument46 pagesComputer Architecturejaime_parada3097100% (2)
- Netflix Annual Report 2010Document76 pagesNetflix Annual Report 2010Arman AliNo ratings yet
- Honeymoon in Vegas Word FileDocument3 pagesHoneymoon in Vegas Word FileElenaNo ratings yet
- WP Seagull Open Source Tool For IMS TestingDocument7 pagesWP Seagull Open Source Tool For IMS Testingsourchhabs25No ratings yet
- Migloo's Day Info SheetDocument4 pagesMigloo's Day Info SheetCandlewick PressNo ratings yet
- Data Mining With Apriori AlgorithmDocument12 pagesData Mining With Apriori AlgorithmMAYANK JAINNo ratings yet
- GMN RodamientosDocument51 pagesGMN RodamientosJayNo ratings yet
- InvoiceDocument1 pageInvoiceKidambi SureshNo ratings yet
- Alma Matter SpeechDocument1 pageAlma Matter Speechlariza gallegoNo ratings yet
- ADM-FR-003 Student Directory FormDocument2 pagesADM-FR-003 Student Directory FormRahayuNo ratings yet
- WestIntroToSSB PDFDocument100 pagesWestIntroToSSB PDFnaval_05No ratings yet
- IHRM Midterm ASHUVANI 201903040007Document9 pagesIHRM Midterm ASHUVANI 201903040007ashu vaniNo ratings yet
- Flexure Hinge Mechanisms Modeled by Nonlinear Euler-Bernoulli-BeamsDocument2 pagesFlexure Hinge Mechanisms Modeled by Nonlinear Euler-Bernoulli-BeamsMobile SunNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Philippine MusicDocument11 pagesContemporary Philippine MusicmattyuuNo ratings yet
- RK3066 Mid PDFDocument17 pagesRK3066 Mid PDFSharon MurphyNo ratings yet
- Ocular Trauma - BantaDocument211 pagesOcular Trauma - BantaLuisa Fernanda Arboleda100% (1)
- Angles - of - Elevation - and - Depression Lesson STEMDocument18 pagesAngles - of - Elevation - and - Depression Lesson STEMmheojhun0% (1)
- TV ExplorerDocument2 pagesTV Explorerdan r.No ratings yet
- Awareness On Stock MarketDocument11 pagesAwareness On Stock MarketBharath ReddyNo ratings yet
- G5 Series User ManualDocument22 pagesG5 Series User ManualDaniel MekonnenNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering Construction Manager in ST Louis MO Resume Mark JensenDocument3 pagesCivil Engineering Construction Manager in ST Louis MO Resume Mark JensenMark JensenNo ratings yet
- MAT Foundation DesignDocument35 pagesMAT Foundation DesignHim Yilay100% (2)
- Zencrack Installation and ExecutionDocument48 pagesZencrack Installation and ExecutionJu waNo ratings yet
- Alburg-Caldwell Manor 1784-1826 Draft by Fay YoungDocument3 pagesAlburg-Caldwell Manor 1784-1826 Draft by Fay YoungNancy Cunningham100% (1)
- Install Sensor Lsi Fl061Document14 pagesInstall Sensor Lsi Fl061AlterSon Grafi KalayNo ratings yet