Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DNA Replication Transcription and Translation TRANSES 1
DNA Replication Transcription and Translation TRANSES 1
Uploaded by
mngnmg80 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views5 pagesThe document defines key terms related to DNA replication:
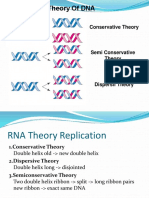
- DNA replication is semi-conservative, with each new DNA molecule composed of one original parent strand and one newly synthesized strand.
- DNA helicase unwinds the double helix by breaking the hydrogen bonds between bases, while single-stranded binding proteins keep the strands apart.
- RNA primers, DNA polymerase, and deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates are involved in building the new DNA strands along the templates.
Original Description:
Original Title
DNA-replication-transcription-and-translation-TRANSES-1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document defines key terms related to DNA replication:
- DNA replication is semi-conservative, with each new DNA molecule composed of one original parent strand and one newly synthesized strand.
- DNA helicase unwinds the double helix by breaking the hydrogen bonds between bases, while single-stranded binding proteins keep the strands apart.
- RNA primers, DNA polymerase, and deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates are involved in building the new DNA strands along the templates.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views5 pagesDNA Replication Transcription and Translation TRANSES 1
DNA Replication Transcription and Translation TRANSES 1
Uploaded by
mngnmg8The document defines key terms related to DNA replication:
- DNA replication is semi-conservative, with each new DNA molecule composed of one original parent strand and one newly synthesized strand.
- DNA helicase unwinds the double helix by breaking the hydrogen bonds between bases, while single-stranded binding proteins keep the strands apart.
- RNA primers, DNA polymerase, and deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates are involved in building the new DNA strands along the templates.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
Template
• A single stranded DNA sequence that
acts as the guiding pattern for
producing a complementary DNA
strand.
Semi conservative replication
• Process of replication in which each
DNA molecule is composed of one
parent strand and one newly
synthesized strand.
DNA Helicase
• The enzyme that unwinds double
helical DNA by disrupting hydrogen
bonds.
Anneal
• The pairing of complementary strands
of DNA through hydrogen bonding.
-stranded binding proteins
• A protein that keeps separate strands of
DNA apart.
DNA gyrase
• The bacterial enzyme that relieves the tension
produced by the unwinding of DNA during
replication.
Replication Fork
• The region where the enzymes
replicating a DNA molecule are bound
to untwisted, single stranded DNA.
Replication Bubble
• The region where two replication forks
are I close proximity to each other,
producing a bubble in the replicating
DNA.
DNA polymerase III
• The enzyme responsible for synthesizing
complementary strands of DNA during DNA
replication
Deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates
• Molecules composed of a deoxyribose bonded
to three phosphate groups and a nitrogenous
base.
RNA Primer
• A sequence of 10 to 60 RNA bases that is
annealed to a region of single stranded DNA for
the purpose of initiating DNA replication.
Primase
• The enzyme that builds RNA primers.
Leading strand
• The new strand of DNA that is synthesized
continuously during replication.
Lagging strand
• The new strand of DNA that is synthesized in
short fragments which are later joined together.
Okazaki fragments
Short fragments of DNA that are a result of
synthesis of the lagging strand during
DNAreplication.
DNA polymerase I
• An enzyme that removes RNA primers and
replaces them with the appropriate
deoxyribonucleotides during DNA replication
DNA ligase
• The enzyme that joins DNA fragments
together by catalyzing the formation of a bond
between the 3' hydroxyl group and a 5'
phosphate group on the sugar-phosphate
backbones.
Exonuclease
An enzyme that cuts out nucleotides at the end
of a DNA strand.
1. What does it mean when DNA replication is
referred to as semi-conservative?
• DNA replication is referred to as semi-
conservative because when the parent strand
unzips and acts as a template for the newly
replicated DNA, each new daughter strand
produced contains one new DNA strand and
half of the parent strand.
You might also like
- DNA ReplicationDocument16 pagesDNA ReplicationStephen Moore100% (1)
- 2019 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic DNA ReplicationDocument32 pages2019 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic DNA ReplicationALEXANDRA MARIE BUNQUINNo ratings yet
- Dna ReplicationDocument26 pagesDna ReplicationJerric Cristobal100% (3)
- Functional Food and Health PDFDocument530 pagesFunctional Food and Health PDFkiranbnysNo ratings yet
- GROUP1-DNA Replication in ProkaryotesDocument24 pagesGROUP1-DNA Replication in ProkaryotesAlbert Jade Pontimayor Legaria100% (1)
- 6.2 DNA Replication Full NoteDocument44 pages6.2 DNA Replication Full NotejiaenNo ratings yet
- 7th Cytogenetics Lecture 20121 1Document37 pages7th Cytogenetics Lecture 20121 1RC SILVESTRENo ratings yet
- All DNADocument69 pagesAll DNAkeerthiNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication in ProkaryotesDocument24 pagesDNA Replication in ProkaryotesAlbert Jade Pontimayor Legaria100% (1)
- Prokaryotic Dna ReplicationDocument53 pagesProkaryotic Dna ReplicationRININo ratings yet
- 10 Biosynthesis of Nucleic AcidsDocument26 pages10 Biosynthesis of Nucleic AcidsDayne Ocampo-Soliman100% (1)
- 2.7 DNA Replication, Transcription and TranslationDocument23 pages2.7 DNA Replication, Transcription and TranslationAleksandar KlingNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument28 pagesDNA ReplicationAsim Bin Arshad 58-FBAS/BSBIO/S19100% (1)
- Dna Replication and Repair #4Document76 pagesDna Replication and Repair #4Len ArellanoNo ratings yet
- NEET - Biology - Cell Structure and FunctionDocument38 pagesNEET - Biology - Cell Structure and Functionknlsinha67% (3)
- DNA Replication Transcription and Translation TRANSES 1Document5 pagesDNA Replication Transcription and Translation TRANSES 1mngnmg8No ratings yet
- DNA Replication Transcription and Translation TRANSESDocument5 pagesDNA Replication Transcription and Translation TRANSESmngnmg8No ratings yet
- DNA Replication With Video LinksDocument15 pagesDNA Replication With Video LinksSmilingNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument6 pagesIlovepdf Mergedmngnmg8No ratings yet
- Submitted By: Fatima Parvez 13/117Document24 pagesSubmitted By: Fatima Parvez 13/117Eng CirroNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument24 pagesDNA ReplicationAkhtar MuneerNo ratings yet
- Learning Unit 3 - PART 2 - DNA ReplicationDocument43 pagesLearning Unit 3 - PART 2 - DNA ReplicationSphesihle ThekoNo ratings yet
- 2.7 Dna Replication Transcription and Translation 4Document168 pages2.7 Dna Replication Transcription and Translation 4Senam DzakpasuNo ratings yet
- Semi-Conservative DNA ReplicationDocument12 pagesSemi-Conservative DNA ReplicationDibyakNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3-Enzyme For DNA Manipulation in Recombinant DNADocument42 pagesLecture 3-Enzyme For DNA Manipulation in Recombinant DNANurfarahain ZolkeflyNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication and RepairDocument11 pagesDNA Replication and RepairCiroanneNo ratings yet
- DNA and Protein SynthesisDocument33 pagesDNA and Protein Synthesismenaga ilangkovanNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids Dna & RnaDocument58 pagesNucleic Acids Dna & RnaValeria RosasNo ratings yet
- 2 - Dna ReplicationDocument25 pages2 - Dna Replicationwonderwolfblood17No ratings yet
- Chapter 1.2 DNA Replication (Autosaved)Document36 pagesChapter 1.2 DNA Replication (Autosaved)abdullaNo ratings yet
- Bacterial GeneticsDocument38 pagesBacterial Geneticsfatima zafarNo ratings yet
- MB Chapter 4 - DNA-Replication-IDocument27 pagesMB Chapter 4 - DNA-Replication-IMustee TeferaNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplDocument40 pagesDNA ReplnunutsehaynuNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument47 pagesDNA ReplicationastrogeniusthreeNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 11Document42 pagesBiology Chapter 11sanaassaf19No ratings yet
- DNA and Gene ExpressionDocument31 pagesDNA and Gene Expressionmenaga ilangkovanNo ratings yet
- Molecular BiologyDocument34 pagesMolecular BiologyMega XtericsNo ratings yet
- DNA Structure & Replication + RNADocument8 pagesDNA Structure & Replication + RNAClaraNo ratings yet
- DNA Strucuture and Replication RNA and Protien SynthesisDocument69 pagesDNA Strucuture and Replication RNA and Protien SynthesisRomelyn Grace BorbeNo ratings yet
- Replication of DNADocument2 pagesReplication of DNAzibnehuqNo ratings yet
- Replication of DNADocument10 pagesReplication of DNA3lyooNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument16 pagesDNA Replicationwmdpr4x64fNo ratings yet
- The Flow of Genetic InformationDocument34 pagesThe Flow of Genetic InformationOdaiNo ratings yet
- 1.3. Dna Replication1Document44 pages1.3. Dna Replication1sabry tapiaNo ratings yet
- 6.4 - DNA Replication and Repair (Text RefDocument2 pages6.4 - DNA Replication and Repair (Text RefReeNo ratings yet
- Steps of DNA ReplicationDocument13 pagesSteps of DNA ReplicationShakila mumtazNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleDocument13 pagesDNA Replication: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleTaufik AhmadNo ratings yet
- Bic 159: Biochemistry Week 2 Lecture: Dr. Jody Ann JohnsonDocument46 pagesBic 159: Biochemistry Week 2 Lecture: Dr. Jody Ann JohnsonJana-Tae KerrNo ratings yet
- 6.2: Dna ReplicationDocument43 pages6.2: Dna Replicationa200812No ratings yet
- BCH 401 Note 1 - KWASUDocument35 pagesBCH 401 Note 1 - KWASUidriscognitoleadsNo ratings yet
- Dna Replication: Elective BiologyDocument7 pagesDna Replication: Elective BiologyMichael KpeliNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication1.Document9 pagesDNA Replication1.9jyqwjpp6sNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument43 pagesDNA ReplicationBilal SajidNo ratings yet
- 3 5 2 Heredity and Inheritance (DNA Replication)Document32 pages3 5 2 Heredity and Inheritance (DNA Replication)6ix9ine SoulNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument26 pagesDNA ReplicationZainab AshroffNo ratings yet
- Please Switch Off Your MobilesDocument28 pagesPlease Switch Off Your MobilesSadia MushtaqNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Dna ReplicationDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Dna ReplicationAlexa ChaviraNo ratings yet
- Pleno SintesisDocument19 pagesPleno SintesisDevinNo ratings yet
- Bridgeamplificationpart1 141217163328 Conversion Gate02 PDFDocument9 pagesBridgeamplificationpart1 141217163328 Conversion Gate02 PDFJohnNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument47 pagesDNA ReplicationYSOBELLATHERESE BILOLONo ratings yet
- CharterDocument1 pageCharterhmz_andi74No ratings yet
- Language and MindDocument19 pagesLanguage and MinddavidrojasvNo ratings yet
- I Semester: M.Tech Full Time Scheme (New)Document53 pagesI Semester: M.Tech Full Time Scheme (New)jayanthbumaiyyaNo ratings yet
- Animal Biotechnology - The Advantages & Disadvantages of Animal BiotechnologyDocument13 pagesAnimal Biotechnology - The Advantages & Disadvantages of Animal Biotechnologysabatini89100% (3)
- Nesters Microbiology A Human Perspective 8th Edition Anderson Solutions ManualDocument2 pagesNesters Microbiology A Human Perspective 8th Edition Anderson Solutions Manualcoactiongaleaiyan100% (23)
- Review of Wonderful Life (Gould)Document3 pagesReview of Wonderful Life (Gould)luminitalupuliasaNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument8 pagesLab ReportLatoya JonesNo ratings yet
- Family (Biology) - WikipediaDocument12 pagesFamily (Biology) - WikipediaBashiir NuurNo ratings yet
- MCQ Immunology BasicDocument71 pagesMCQ Immunology BasicMatthew HallNo ratings yet
- 7762075-Dreger and WielgusDocument15 pages7762075-Dreger and WielgusAlma KunicNo ratings yet
- Phytochemical and Antimicrobial Screening of Alugbati (Basella Rubra Linn.) Leaves and Stems Extracts Against Pathogenic MicrooganismsDocument1 pagePhytochemical and Antimicrobial Screening of Alugbati (Basella Rubra Linn.) Leaves and Stems Extracts Against Pathogenic MicrooganismsJowanna Burce88% (8)
- Fundamentals of Anatomy and Physiology: Course Description and ObjectivesDocument3 pagesFundamentals of Anatomy and Physiology: Course Description and Objectivesvamsi karna100% (1)
- Gcse Marking Scheme: Science - Biology SUMMER 2012Document31 pagesGcse Marking Scheme: Science - Biology SUMMER 2012sureshthevanNo ratings yet
- Mammalian Transient Receptor Potential (TRP) Cation Channels II PDFDocument569 pagesMammalian Transient Receptor Potential (TRP) Cation Channels II PDFAndrei TatomirNo ratings yet
- Est 1Document9 pagesEst 1Shriyog Jambekar100% (1)
- Bio 107 Lab Report 2 (Methods, Results, and Discussion)Document7 pagesBio 107 Lab Report 2 (Methods, Results, and Discussion)Ousman JammehNo ratings yet
- BCM Amino AcidDocument3 pagesBCM Amino Acidtomato pasteNo ratings yet
- Inside: BloodDocument3 pagesInside: Bloodayu_cicuuNo ratings yet
- Niche OverlapDocument14 pagesNiche OverlapMuhammad Fayzal100% (1)
- Centella Asiatica - A Review of Its Medicinal Uses and Pharmacological EffectsDocument8 pagesCentella Asiatica - A Review of Its Medicinal Uses and Pharmacological Effectsjiva_shakti0No ratings yet
- 10 Science Notes 09 Heredity and Evolution 1Document16 pages10 Science Notes 09 Heredity and Evolution 1harshit gargNo ratings yet
- Cell City IntroductionDocument2 pagesCell City IntroductionJanin CodillaNo ratings yet
- Bone Cancer ThesisDocument7 pagesBone Cancer Thesisafkojbvmz100% (2)
- Biology Memory MapDocument40 pagesBiology Memory MapadditpleasNo ratings yet
- E ColiDocument25 pagesE ColiVer Garcera TalosigNo ratings yet
- Anti-Melanoma Effect of Ruthenium (II) - Diphosphine Complexes Containing Naphthoquinone LigandDocument9 pagesAnti-Melanoma Effect of Ruthenium (II) - Diphosphine Complexes Containing Naphthoquinone LigandRodrigo Maximiliano RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Lab 5 Plant UitmDocument8 pagesLab 5 Plant UitmSarah AfiqahNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Self - Final Module 1Document25 pagesUnderstanding The Self - Final Module 1Rona Jane SanchezNo ratings yet