Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Is Ai?
Uploaded by
Bever Joan P. ManaloOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What Is Ai?
Uploaded by
Bever Joan P. ManaloCopyright:
Available Formats
WHAT IS AI?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines that are
programmed to think and learn like humans. The goal of AI is to develop systems that can perform tasks
that typically require human intelligence, such as visual perception, speech recognition, decision-
making, and language translation.
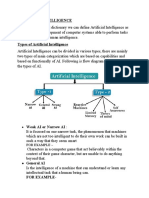
There are two main types of AI:
Narrow or Weak AI: This type of AI is designed and trained for a particular task. It can excel in
that specific task, but it lacks the ability to generalize its learning to other domains. Examples of
narrow AI include virtual personal assistants (like Siri or Alexa), image recognition software, and
recommendation algorithms.
General or Strong AI: This refers to a type of AI that possesses the ability to understand, learn,
and apply knowledge across different domains, much like a human. General AI is still largely
theoretical and does not yet exist. Achieving general AI would involve creating machines with
cognitive abilities comparable to human beings.
AI applications can be categorized into three broad types:
Reactive Machines: These systems are designed to perform specific tasks based on predefined
rules. They don't have the ability to learn from experience or adapt to new situations.
Limited Memory: This type of AI can learn from historical data to make better decisions. Self-
driving cars, for example, use limited memory systems to process data from sensors and learn
from past experiences on the road.
Theory of Mind (ToM): This is a more advanced form of AI that involves understanding human
emotions, beliefs, intentions, and other mental states. Developing AI with a full theory of mind is
a complex challenge and is currently more of a long-term goal.
AI technologies include machine learning, natural language processing, computer vision, and robotics,
among others. Machine learning, a subset of AI, involves the use of algorithms that allow systems to
learn from data and improve their performance over time without being explicitly programmed.
It's important to note that while AI has made significant advancements, it is not without ethical and
societal considerations. Issues such as bias in algorithms, privacy concerns, and the impact on
employment are some of the topics that researchers, policymakers, and society at large are actively
addressing.
You might also like
- Module 2 'Machine Learning-AI'Document19 pagesModule 2 'Machine Learning-AI'DE CASTRO, Xyra Kate D.No ratings yet
- Artificial IntelligenceDocument6 pagesArtificial IntelligenceEesha Mushtaq 1422-FMS/BBAIT/S20No ratings yet
- AI-ML EditedDocument12 pagesAI-ML Editedalum jacob100% (1)
- Introduction To Artificial Intelligence 2021 NSDocument43 pagesIntroduction To Artificial Intelligence 2021 NSFitriana Zahirah TNo ratings yet
- Role of AIDocument27 pagesRole of AIofficer rawat100% (1)
- Artificial IntelligenceDocument49 pagesArtificial IntelligenceKristopher France PunioNo ratings yet
- Auto ML Adnan MasoodDocument270 pagesAuto ML Adnan Masoodsayantan royNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence Report MS WordDocument11 pagesArtificial Intelligence Report MS Wordlucifer75% (4)
- AIDocument1 pageAIwagons-wilds-0rNo ratings yet
- In Depth Ai DescriptionDocument1 pageIn Depth Ai DescriptionMurtuza AliNo ratings yet
- Artificial IntelligenceDocument1 pageArtificial IntelligenceficcsgNo ratings yet
- Artificial IntelligenceDocument10 pagesArtificial Intelligenceshubh cards bhilwara Wedding cardsNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)Document6 pagesArtificial Intelligence (AI)tanyatulikaNo ratings yet
- Artificial IntelligenceDocument2 pagesArtificial IntelligenceDhenn Valmonte SindolNo ratings yet
- Elective 3 Assignment RambleDocument11 pagesElective 3 Assignment Ramblechroma warframeNo ratings yet
- AiDocument1 pageAiAecha DaliliNo ratings yet
- Resume About AIDocument2 pagesResume About AIDavi Lucas Lima SousaNo ratings yet
- CH3 NewDocument34 pagesCH3 NewWejdanNo ratings yet
- AI InformationDocument1 pageAI Informationbadass.bazoookaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Section 5 AIDocument9 pagesModule 2 Section 5 AIElla MontefalcoNo ratings yet
- Tugas (Writting Essay) - D4 Weekend USBDocument1 pageTugas (Writting Essay) - D4 Weekend USBDendi MaulanaNo ratings yet
- What Is Artificial IntelligenceDocument5 pagesWhat Is Artificial IntelligenceVadlamudi DhyanamalikaNo ratings yet
- Artificial IntelligenceDocument1 pageArtificial IntelligenceUejs AbdullariNo ratings yet
- What Is Artificial IntelligenceDocument4 pagesWhat Is Artificial IntelligenceroblesangellemaeNo ratings yet
- AI (Artificial Intelligence) : Expert Systems Speech Recognition Machine VisionDocument9 pagesAI (Artificial Intelligence) : Expert Systems Speech Recognition Machine VisionRasel moreNo ratings yet
- Artificial IntelligenceDocument14 pagesArtificial IntelligencekolarineNo ratings yet
- Artificial IntelligenceDocument2 pagesArtificial Intelligencennp0wz1lobNo ratings yet
- AI PresentationDocument14 pagesAI Presentationwwade2454No ratings yet
- Artificial IntelligenceDocument11 pagesArtificial IntelligenceRould Christian Ganzon AlertaNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence and It's TypesDocument2 pagesArtificial Intelligence and It's Typeslimtlesleg8988No ratings yet
- CC 13 Unit 1Document12 pagesCC 13 Unit 1Priyaranjan SorenNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence.Document2 pagesArtificial Intelligence.Hamzah Hussein HNo ratings yet
- Chapter ThreeDocument15 pagesChapter ThreeTade GaromaNo ratings yet
- Conceptsforauto IDocument23 pagesConceptsforauto ImskcegNo ratings yet
- Unit 1-Notes - AI - Docx - 0Document15 pagesUnit 1-Notes - AI - Docx - 0Måyāñk GãürNo ratings yet
- Unit 1aimlDocument21 pagesUnit 1aimlworriedaboutcarrierandfutureNo ratings yet
- AIML UNIT I NotesDocument68 pagesAIML UNIT I NotesAbhinavKundraNo ratings yet
- OFTW#2 - Emerging Technologies Artificial Intelligence (AI)Document8 pagesOFTW#2 - Emerging Technologies Artificial Intelligence (AI)depapcatNo ratings yet
- OFTW#2 - Emerging Technologies Artificial Intelligence (AI)Document8 pagesOFTW#2 - Emerging Technologies Artificial Intelligence (AI)depapcatNo ratings yet
- Machine VisionDocument67 pagesMachine VisionRohit AroraNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 AI QP Pattern and Unit 1 - Into To AIDocument64 pagesGrade 9 AI QP Pattern and Unit 1 - Into To AIharrshanrmt20No ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document13 pagesChapter 3Jiru AlemayehuNo ratings yet
- AI (Artificial Intelligence) : Guide To AI in Customer Service Using Chatbots and NLPDocument16 pagesAI (Artificial Intelligence) : Guide To AI in Customer Service Using Chatbots and NLPdeepak rawatNo ratings yet
- BB BiDocument4 pagesBB BirayanmaazsiddigNo ratings yet
- What Is Artificial IntelligenceDocument4 pagesWhat Is Artificial IntelligenceFyreal MyoNo ratings yet
- 5 - AI and Machine Learning EthicsDocument8 pages5 - AI and Machine Learning EthicsBatuhan OrkunNo ratings yet
- Computer Science Holiday HomeworkDocument17 pagesComputer Science Holiday HomeworkKevin ShalomNo ratings yet
- EdNex Proposal On AI IOT Autonomous Vehicle ARVR Blockchain For Industry 4.0Document47 pagesEdNex Proposal On AI IOT Autonomous Vehicle ARVR Blockchain For Industry 4.0janetNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Artificial IntelligenceDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Artificial IntelligenceHarshNo ratings yet
- AI UNIT-1 All NotesDocument22 pagesAI UNIT-1 All NotesSimran BargirNo ratings yet
- Compte Rendu Partie 1Document19 pagesCompte Rendu Partie 1Soufyane AyanouzNo ratings yet
- What Is Ai TechnologyDocument23 pagesWhat Is Ai TechnologyRyan FabianNo ratings yet
- What Is Artificial IntelligenceDocument14 pagesWhat Is Artificial IntelligenceBeanka PaulNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence and The LawDocument32 pagesArtificial Intelligence and The LawBarr A. A KolawoleNo ratings yet
- Artificial IntelligenceDocument4 pagesArtificial IntelligenceAnand PokharnaNo ratings yet
- 2-AI IntroductionDocument10 pages2-AI Introductionlookup.itsNo ratings yet
- Artificial IntelligenceDocument2 pagesArtificial Intelligencecelt instituteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document14 pagesChapter 3Eyasu demsewNo ratings yet
- Artificial IntelligenceDocument10 pagesArtificial IntelligenceRo TechnologiesNo ratings yet
- Why Would The Grey Cat Have So Many Fleas in His CoatDocument1 pageWhy Would The Grey Cat Have So Many Fleas in His Coatpokin73091No ratings yet
- Object Detection and Tracking Using Opencv in Python: March 2020Document43 pagesObject Detection and Tracking Using Opencv in Python: March 2020Rohit Krishnan MNo ratings yet
- Research Paper - Human Face DetectionDocument8 pagesResearch Paper - Human Face DetectionPremchand LukramNo ratings yet
- Real-Time Detection of Colored Objects in Multiple Camera Streams With Off-the-Shelf Hardware ComponentsDocument10 pagesReal-Time Detection of Colored Objects in Multiple Camera Streams With Off-the-Shelf Hardware ComponentsUsman AsadNo ratings yet
- Ai SpeechDocument17 pagesAi SpeechJishnu RajendranNo ratings yet
- Computer Vision & Image ProcessingDocument34 pagesComputer Vision & Image ProcessingkcchtphdNo ratings yet
- Leaf Recognition': Pes UniversityDocument27 pagesLeaf Recognition': Pes UniversityLavanya SureshNo ratings yet
- Hello, World: Artificial Intelligence and Its Use in The Public SectorDocument185 pagesHello, World: Artificial Intelligence and Its Use in The Public SectorHPot PotTechNo ratings yet
- Computer Vision Is A Field of Artificial IntelligenceDocument2 pagesComputer Vision Is A Field of Artificial IntelligencefigureabcNo ratings yet
- Digital Image Processing Lecture 1: IntroductionDocument28 pagesDigital Image Processing Lecture 1: IntroductionUzair AhmadNo ratings yet
- Adobe PhotoshopDocument4 pagesAdobe PhotoshopPj SalayonNo ratings yet
- Blob Detection PDFDocument6 pagesBlob Detection PDFVinod TheteNo ratings yet
- Research Proposal AKh PPTXDocument15 pagesResearch Proposal AKh PPTXLEKHAN GAVINo ratings yet
- 2104 00680 PDFDocument10 pages2104 00680 PDFmarko CavdarNo ratings yet
- Digital Image Processing: Ming-Sui (Amy) Lee Mar. 8, 2007Document43 pagesDigital Image Processing: Ming-Sui (Amy) Lee Mar. 8, 2007faqihinsaniinthecatNo ratings yet
- Cengage Book ListDocument54 pagesCengage Book ListVijayalakshmi Suresh100% (1)
- Leapfrog Geo File TypesDocument6 pagesLeapfrog Geo File TypesMarcos Vinícius MoraesNo ratings yet
- Pantech - AI, ML & Image Processing Projects Using MATLAB and OpenCV - 2021 - 22Document6 pagesPantech - AI, ML & Image Processing Projects Using MATLAB and OpenCV - 2021 - 22SHINUMMNo ratings yet
- Slide 11 DiagimgDocument39 pagesSlide 11 Diagimghayumbe08No ratings yet
- Raja Rocky - Assignment - UpesDocument11 pagesRaja Rocky - Assignment - Upesraja rockyNo ratings yet
- Koteswar Rao Jerripothula CVDocument4 pagesKoteswar Rao Jerripothula CVkotes RJNo ratings yet
- Prash - ROBOTIC VISIONDocument38 pagesPrash - ROBOTIC VISIONpreethu02100% (1)
- Haar WaveletDocument56 pagesHaar Waveletcristi_badNo ratings yet
- 30 June 2020 - Stereophotogrammetry by Dr. Poonam S. TiwariDocument36 pages30 June 2020 - Stereophotogrammetry by Dr. Poonam S. TiwariLiamNo ratings yet
- Digital Imaging & Adobe Photoshop CS3Document15 pagesDigital Imaging & Adobe Photoshop CS3KatNo ratings yet
- Proposal For The Computer VisionDocument5 pagesProposal For The Computer Visionph KithsiriNo ratings yet
- PDF To Image Converter v2 HOW TO USEDocument3 pagesPDF To Image Converter v2 HOW TO USEfairfaxcyclesNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument2 pagesSyllabusPriyanka TakalkarNo ratings yet
- Siddhartha Engineering College (Autonomous) Department of Information TechnologyDocument47 pagesSiddhartha Engineering College (Autonomous) Department of Information Technologytamilbharathi94No ratings yet