Professional Documents
Culture Documents
AI
Uploaded by
wagons-wilds-0r0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageai
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentai
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageAI
Uploaded by
wagons-wilds-0rai
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
AI
AI, or artificial intelligence, refers to the simulation of human
intelligence processes by machines, especially computer systems.
These processes include learning (the acquisition of information and
rules for using the information), reasoning (using rules to reach
approximate or definite conclusions), and self-correction. AI can be
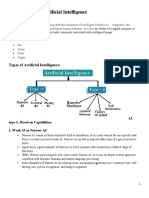
categorized into two types: narrow AI and general AI.
● Narrow AI (Weak AI): This type of AI is designed and
trained for a particular task. It's what we have mostly seen
and used so far. Examples include voice assistants like Siri or
Alexa, recommendation systems like those used by Netflix or
Amazon, and self-driving cars. Narrow AI operates within a
limited context and cannot perform tasks outside of its
programming.
● General AI (Strong AI): This is a theoretical form of AI
that could understand, learn, and apply intelligence to any
problem that a human can. General AI would have the ability
to reason, plan, solve problems, think abstractly, comprehend
complex ideas, learn quickly, and learn from experience.
Currently, we don't have true general AI; it's more of a
concept in science fiction.
AI systems typically rely on large amounts of data and algorithms to
perform tasks. Machine learning is a subset of AI that focuses on
enabling machines to learn from data without being explicitly
programmed. Deep learning, a subset of machine learning, uses
neural networks with many layers to analyze data. These technologies
power many of the recent advancements in AI, such as image and
speech recognition.
AI has numerous applications across various fields, including
healthcare, finance, education, transportation, and entertainment.
While AI offers significant benefits, including increased efficiency and
automation of repetitive tasks, it also raises ethical concerns, such as
job displacement, bias in decision-making, and privacy issues.
Therefore, as AI continues to advance, it's essential to consider its
societal implications and ensure responsible development and
deployment.
You might also like
- What Is Ai?Document1 pageWhat Is Ai?Bever Joan P. ManaloNo ratings yet
- Artificial IntelligenceDocument1 pageArtificial IntelligenceficcsgNo ratings yet
- In Depth Ai DescriptionDocument1 pageIn Depth Ai DescriptionMurtuza AliNo ratings yet
- AiDocument1 pageAiAecha DaliliNo ratings yet
- Resume About AIDocument2 pagesResume About AIDavi Lucas Lima SousaNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)Document6 pagesArtificial Intelligence (AI)tanyatulikaNo ratings yet
- AI InformationDocument1 pageAI Informationbadass.bazoookaNo ratings yet
- Artificial IntelligenceDocument10 pagesArtificial Intelligenceshubh cards bhilwara Wedding cardsNo ratings yet
- Artificial IntelligenceDocument1 pageArtificial IntelligenceUejs AbdullariNo ratings yet
- Artificial IntelligenceDocument2 pagesArtificial IntelligenceDhenn Valmonte SindolNo ratings yet
- Artificial IntelligenceDocument2 pagesArtificial Intelligencennp0wz1lobNo ratings yet
- CH3 NewDocument34 pagesCH3 NewWejdanNo ratings yet
- What Are The Ethics in Artificial Intelligence (AI)Document7 pagesWhat Are The Ethics in Artificial Intelligence (AI)Nezaket Sule ErturkNo ratings yet
- Why Would The Grey Cat Have So Many Fleas in His CoatDocument1 pageWhy Would The Grey Cat Have So Many Fleas in His Coatpokin73091No ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence: Smart AssistantsDocument21 pagesArtificial Intelligence: Smart Assistantsanujapawar1950No ratings yet
- Machine VisionDocument67 pagesMachine VisionRohit AroraNo ratings yet
- AI PresentationDocument14 pagesAI Presentationwwade2454No ratings yet
- Elective 3 Assignment RambleDocument11 pagesElective 3 Assignment Ramblechroma warframeNo ratings yet
- Artificial IntelligenceDocument4 pagesArtificial IntelligenceAnand PokharnaNo ratings yet
- Wepik Demystifying Artificial Intelligence Understanding How It Works 20240416160904tOGrDocument9 pagesWepik Demystifying Artificial Intelligence Understanding How It Works 20240416160904tOGrnicocaprilesNo ratings yet
- Atificial Intelligence EnglishDocument27 pagesAtificial Intelligence EnglishsammarcoNo ratings yet
- Artificial IntelligenceDocument14 pagesArtificial IntelligencekolarineNo ratings yet
- AI (Artificial Intelligence) : Guide To AI in Customer Service Using Chatbots and NLPDocument16 pagesAI (Artificial Intelligence) : Guide To AI in Customer Service Using Chatbots and NLPdeepak rawatNo ratings yet
- AIDocument19 pagesAImadhanakavimadhanakaviNo ratings yet
- AI UNIT-1 All NotesDocument22 pagesAI UNIT-1 All NotesSimran BargirNo ratings yet
- Emerging Technologies in BusinessDocument35 pagesEmerging Technologies in BusinesshimanshuNo ratings yet
- What Is Artificial IntelligenceDocument14 pagesWhat Is Artificial IntelligenceBeanka PaulNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document13 pagesChapter 3Jiru AlemayehuNo ratings yet
- Conceptsforauto IDocument23 pagesConceptsforauto ImskcegNo ratings yet
- Artificial IntelligenceDocument49 pagesArtificial IntelligenceKristopher France PunioNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Section 5 AIDocument9 pagesModule 2 Section 5 AIElla MontefalcoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computing ApplicationDocument16 pagesIntroduction To Computing ApplicationAhsan frazNo ratings yet
- Talking Points May 22 2021Document17 pagesTalking Points May 22 2021Ka Efren TerciasNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)Document14 pagesArtificial Intelligence (AI)Salaheddine Anamir100% (1)
- Artificial InteligenceDocument7 pagesArtificial InteligenceNitin KashyapNo ratings yet
- What Is Ai TechnologyDocument23 pagesWhat Is Ai TechnologyRyan FabianNo ratings yet
- AI in Action Real-World Applications and ImpactsDocument12 pagesAI in Action Real-World Applications and Impactssaanjh05022011No ratings yet
- What Is Artificial IntelligenceDocument5 pagesWhat Is Artificial IntelligenceVadlamudi DhyanamalikaNo ratings yet
- Computer Science Holiday HomeworkDocument17 pagesComputer Science Holiday HomeworkKevin ShalomNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence Simple ReportDocument2 pagesArtificial Intelligence Simple Reportfefex36608No ratings yet
- AI (Artificial Intelligence) : Expert Systems Speech Recognition Machine VisionDocument9 pagesAI (Artificial Intelligence) : Expert Systems Speech Recognition Machine VisionRasel moreNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3. Introduction To Artificial IntelligenceDocument80 pagesChapter 3. Introduction To Artificial IntelligenceYihune Alemayehu100% (1)
- AI-ML EditedDocument12 pagesAI-ML Editedalum jacob100% (1)
- Artificial IntelligenceDocument12 pagesArtificial IntelligenceOmarNo ratings yet
- Tugas (Writting Essay) - D4 Weekend USBDocument1 pageTugas (Writting Essay) - D4 Weekend USBDendi MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Artificial IntelligenceDocument6 pagesArtificial IntelligenceEesha Mushtaq 1422-FMS/BBAIT/S20No ratings yet
- EdNex Proposal On AI IOT Autonomous Vehicle ARVR Blockchain For Industry 4.0Document47 pagesEdNex Proposal On AI IOT Autonomous Vehicle ARVR Blockchain For Industry 4.0janetNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument3 pagesProjectetash.jain2011No ratings yet
- Assignmet Pre Final Application Dev Emerging TechDocument2 pagesAssignmet Pre Final Application Dev Emerging Techpia espanilloNo ratings yet
- Compte Rendu Partie 1Document19 pagesCompte Rendu Partie 1Soufyane AyanouzNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence (.A.I.) : TopicDocument38 pagesArtificial Intelligence (.A.I.) : TopicSrijan YoutubeNo ratings yet
- Ai PPT 1Document47 pagesAi PPT 1adĪtYa PàtHakNo ratings yet
- What Is Artificial IntelligenceDocument4 pagesWhat Is Artificial IntelligenceroblesangellemaeNo ratings yet
- Edpm SbaDocument16 pagesEdpm SbaROYAL GAMING100% (1)
- Unit 1aimlDocument21 pagesUnit 1aimlworriedaboutcarrierandfutureNo ratings yet
- DsaasdfDocument1 pageDsaasdfashish barwadNo ratings yet
- AIML UNIT I NotesDocument68 pagesAIML UNIT I NotesAbhinavKundraNo ratings yet
- AIChat GPTDocument12 pagesAIChat GPTSajid khanNo ratings yet
- Summary of Mustafa Suleyman's The Coming WaveFrom EverandSummary of Mustafa Suleyman's The Coming WaveRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Master Algorithm: How the Quest for the Ultimate Learning Machine Will Remake Our WorldFrom EverandThe Master Algorithm: How the Quest for the Ultimate Learning Machine Will Remake Our WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (107)
- ChatGPT Side Hustles 2024 - Unlock the Digital Goldmine and Get AI Working for You Fast with More Than 85 Side Hustle Ideas to Boost Passive Income, Create New Cash Flow, and Get Ahead of the CurveFrom EverandChatGPT Side Hustles 2024 - Unlock the Digital Goldmine and Get AI Working for You Fast with More Than 85 Side Hustle Ideas to Boost Passive Income, Create New Cash Flow, and Get Ahead of the CurveNo ratings yet
- Generative AI: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewFrom EverandGenerative AI: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Working with AI: Real Stories of Human-Machine Collaboration (Management on the Cutting Edge)From EverandWorking with AI: Real Stories of Human-Machine Collaboration (Management on the Cutting Edge)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- HBR's 10 Must Reads on AI, Analytics, and the New Machine AgeFrom EverandHBR's 10 Must Reads on AI, Analytics, and the New Machine AgeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (69)
- Scary Smart: The Future of Artificial Intelligence and How You Can Save Our WorldFrom EverandScary Smart: The Future of Artificial Intelligence and How You Can Save Our WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (55)
- The AI Advantage: How to Put the Artificial Intelligence Revolution to WorkFrom EverandThe AI Advantage: How to Put the Artificial Intelligence Revolution to WorkRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (7)
- Artificial Intelligence & Generative AI for Beginners: The Complete GuideFrom EverandArtificial Intelligence & Generative AI for Beginners: The Complete GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Artificial Intelligence: An Executive Guide to Make AI Work for Your BusinessFrom EverandArtificial Intelligence: An Executive Guide to Make AI Work for Your BusinessNo ratings yet
- System Design Interview: 300 Questions And Answers: Prepare And PassFrom EverandSystem Design Interview: 300 Questions And Answers: Prepare And PassNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewFrom EverandArtificial Intelligence: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (104)
- T-Minus AI: Humanity's Countdown to Artificial Intelligence and the New Pursuit of Global PowerFrom EverandT-Minus AI: Humanity's Countdown to Artificial Intelligence and the New Pursuit of Global PowerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- The Roadmap to AI Mastery: A Guide to Building and Scaling ProjectsFrom EverandThe Roadmap to AI Mastery: A Guide to Building and Scaling ProjectsNo ratings yet
- Your AI Survival Guide: Scraped Knees, Bruised Elbows, and Lessons Learned from Real-World AI DeploymentsFrom EverandYour AI Survival Guide: Scraped Knees, Bruised Elbows, and Lessons Learned from Real-World AI DeploymentsNo ratings yet
- Mastering Large Language Models: Advanced techniques, applications, cutting-edge methods, and top LLMs (English Edition)From EverandMastering Large Language Models: Advanced techniques, applications, cutting-edge methods, and top LLMs (English Edition)No ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence: A Guide for Thinking HumansFrom EverandArtificial Intelligence: A Guide for Thinking HumansRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (30)
- MidJourney Magnified: Crafting Visual Magic – The Novice to Pro PlaybookFrom EverandMidJourney Magnified: Crafting Visual Magic – The Novice to Pro PlaybookNo ratings yet
- Our Final Invention: Artificial Intelligence and the End of the Human EraFrom EverandOur Final Invention: Artificial Intelligence and the End of the Human EraRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (82)
- Four Battlegrounds: Power in the Age of Artificial IntelligenceFrom EverandFour Battlegrounds: Power in the Age of Artificial IntelligenceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- ChatGPT 4 $10,000 per Month #1 Beginners Guide to Make Money Online Generated by Artificial IntelligenceFrom EverandChatGPT 4 $10,000 per Month #1 Beginners Guide to Make Money Online Generated by Artificial IntelligenceNo ratings yet
- THE FUSION ENERGY EQUATIONS: Unlocking Q40 with AI, Quantum Computing, and the New Energy EconomyFrom EverandTHE FUSION ENERGY EQUATIONS: Unlocking Q40 with AI, Quantum Computing, and the New Energy EconomyNo ratings yet