Professional Documents
Culture Documents
? ?? Nomenclature Organizer Template
Uploaded by
8145560 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pagesIonic and covalent compounds differ in their bonding and naming conventions:
- Ionic compounds involve the transfer of electrons between metals and nonmetals, and are named by writing the metal followed by the nonmetal with "ide". Covalent bonds involve sharing of electrons between elements.
- Binary ionic compounds contain two elements, while multivalent ionic compounds contain a polyatomic ion and metal. Polyatomic covalent compounds name the ions or molecules as a whole.
- Ionic compounds are named by writing the metal followed by the nonmetal with "ide". Covalent compounds follow specific naming rules based on the number of atoms present.
Original Description:
Science nomenclature assignment and notes
Original Title
_ ?️??️ Nomenclature Organizer Template
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentIonic and covalent compounds differ in their bonding and naming conventions:
- Ionic compounds involve the transfer of electrons between metals and nonmetals, and are named by writing the metal followed by the nonmetal with "ide". Covalent bonds involve sharing of electrons between elements.
- Binary ionic compounds contain two elements, while multivalent ionic compounds contain a polyatomic ion and metal. Polyatomic covalent compounds name the ions or molecules as a whole.
- Ionic compounds are named by writing the metal followed by the nonmetal with "ide". Covalent compounds follow specific naming rules based on the number of atoms present.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pages? ?? Nomenclature Organizer Template
Uploaded by
814556Ionic and covalent compounds differ in their bonding and naming conventions:
- Ionic compounds involve the transfer of electrons between metals and nonmetals, and are named by writing the metal followed by the nonmetal with "ide". Covalent bonds involve sharing of electrons between elements.
- Binary ionic compounds contain two elements, while multivalent ionic compounds contain a polyatomic ion and metal. Polyatomic covalent compounds name the ions or molecules as a whole.
- Ionic compounds are named by writing the metal followed by the nonmetal with "ide". Covalent compounds follow specific naming rules based on the number of atoms present.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
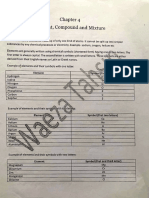
Ionic Compounds Covalent Compounds
Criteria Binary Multivalent Polyatomic Regular Covalent Diatomic
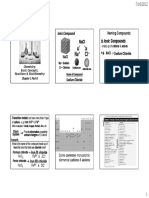
Mgs = Magnesium Sulfide FeBr2 = Iron (II) Bromide Ca3 (PO4) 2 = Calcium Phosphate NF3 = Nitrogen Trifluride HCl = Hydrogen Chloride
Elements
Ionic Bond Ionic Bond Ionic Bond Covalent Bond
Type of Bond Covalent Bond
First name the Metal (Iron) as it is. And then
name the non metal which is (Bromine)
replacing the ne with de. The Iron has a 2 plus
charge so we need to write the 2 plus charge in
roman number form between Iron and Bromine
First name the Metal (Magnesium) Write the metal as it is and write the Polyatomic First figure out the prefix for each of the element Write the positive ion first then write the
as it is. And then name the non as it is. you have. Second write the prefix before the element negative ion and put an Ide at the end.
metal which is (sulfur) replacing the = Iron (II) Bromide name. Finally add an ide at the end of the second
ur with ide. element.
Naming Rule
Example: Example: Example: Example: Exampl
Iron has 2 plus charge.So we add roman
Leave the Magnesium as it is and number 2 in between Iron and Bromide. Ca3(PO4) 2 NF3 HCl
replace the (sulfur) with sulfide. = Nitrogen Trifluride = Hydrogen Chloride
FeBr2 Ca 3 - Calcium
= Magnesium sulfide = Iron (II) Bromide Since N has at least 1 atom it stays the same and Since Hydrogen is the first we keep it the
PO 4 - Phosphate since F has at least 3 atoms it becomes Trifluride. same. Chlorine is the second element so
we put an ide at the end.
= Ca3(PO4) 2 - Calcium Phosphate So NF3 = Nitrogen Trifluride
HCl = Hydrogen Chloride
Formulas Lewis Structure Lewis Structure
Lewis Structure Lewis Structure
(Zero Sum Rule,
Lewis Structures OR
Criss-Cross Method)
Example: Example: Example: Example: Example:
1.
You might also like
- Chemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandChemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Chemical Register List 2021 (25.05.2021)Document9 pagesChemical Register List 2021 (25.05.2021)Osh 0717100% (2)
- Notes in ChemistryDocument3 pagesNotes in ChemistryAriane Andrea HerreraNo ratings yet
- Mass BalancesDocument40 pagesMass Balancesnazar9515100% (2)
- Stoichiometry and The Mole Concept NotesDocument26 pagesStoichiometry and The Mole Concept Noteshafizhapni93% (30)
- Naming CompoundsDocument84 pagesNaming CompoundsangelaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2.4 - 2.7Document63 pagesLesson 2.4 - 2.7Tristan PereyNo ratings yet
- 03 - Element of Value Worksheets and Visual Art Mini-LessonsDocument11 pages03 - Element of Value Worksheets and Visual Art Mini-Lessons814556No ratings yet
- Naming of Chemical CompoundsDocument44 pagesNaming of Chemical Compoundsteresita a. ibatan100% (1)
- Symble, Formula & ValencyDocument16 pagesSymble, Formula & Valencykawsar2250% (4)
- Chemical Formulas KeynoteDocument34 pagesChemical Formulas Keynotewperry42No ratings yet
- Api 570 PDFDocument2 pagesApi 570 PDFK U Masood Ahmad100% (1)
- Fire Resistance UL 1709Document2 pagesFire Resistance UL 1709ednavilod100% (3)
- Odour Filtration Range From BioactionDocument24 pagesOdour Filtration Range From BioactionLarry Botham100% (1)
- Element and CompoundsDocument14 pagesElement and CompoundsKehekeshan RizwanNo ratings yet
- DefoamerDocument8 pagesDefoamerdtgpandNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet: 1. Identification of The Substance/Preparation and The Company/UndertakingDocument7 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet: 1. Identification of The Substance/Preparation and The Company/UndertakingHarinta Dwi Septiana100% (1)
- Naming CompoundsDocument3 pagesNaming CompoundsGab CaparosoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry WordDocument26 pagesChemistry Wordyuuu32716No ratings yet
- Chemical Formulas and Nomenclature of CoDocument10 pagesChemical Formulas and Nomenclature of CoAbdullah Sabry AzzamNo ratings yet
- Q1 W6 Naming 2Document44 pagesQ1 W6 Naming 2lululumururuNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 - Notes Nomenclature DLB Key Pages 1-7Document9 pagesUnit 5 - Notes Nomenclature DLB Key Pages 1-7Alea PrillyNo ratings yet
- Chem CCH Elements, Compounds, MixturesDocument4 pagesChem CCH Elements, Compounds, MixturesSami SumonNo ratings yet
- Rules For Naming Ionic Compounds: C. Examples: Nacl Sodium ChlorideDocument3 pagesRules For Naming Ionic Compounds: C. Examples: Nacl Sodium ChloridePaui Parado EranNo ratings yet
- PCM Chapter 01 Part BDocument7 pagesPCM Chapter 01 Part BAlif AzmirNo ratings yet
- 6 NP UQq TRX 8 B 2 Js ZC 2 NQTDocument7 pages6 NP UQq TRX 8 B 2 Js ZC 2 NQTOm KarmakarNo ratings yet
- Ionic Bonds: Atoms Give Up or Gain E: Unit 5: Bonding and Inorganic NomenclatureDocument6 pagesIonic Bonds: Atoms Give Up or Gain E: Unit 5: Bonding and Inorganic NomenclatureGrace FafelNo ratings yet
- Language of ChemistryDocument12 pagesLanguage of ChemistryVenkatNo ratings yet
- Molecules and Ions, Chemical Formulas, and Naming CompoundsDocument3 pagesMolecules and Ions, Chemical Formulas, and Naming Compoundsmain.marygrace.crisostomoNo ratings yet
- Chemical Formula and NomenclatureDocument8 pagesChemical Formula and NomenclatureElaiza Angelene NacarioNo ratings yet
- Note On Atoms, Molecules, Valency and RadicalsDocument3 pagesNote On Atoms, Molecules, Valency and RadicalsRadiant BrothersNo ratings yet
- The-Language-of-Chemistry (8 Files Merged)Document50 pagesThe-Language-of-Chemistry (8 Files Merged)salmanazli24No ratings yet
- Gen Chem PDFDocument34 pagesGen Chem PDFPaul VillasencioNo ratings yet
- Naming Ionic Compounds: A. Identify Three Elements That Form Only One CationDocument6 pagesNaming Ionic Compounds: A. Identify Three Elements That Form Only One Cationandrew fortneyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes PT 3 4Document53 pagesChemistry Notes PT 3 4Eunice Kyla MapisaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Nomenclature: Experiment #3Document27 pagesChemical Nomenclature: Experiment #3Ayi PunsalanNo ratings yet
- 3224 Topper 21 110 1 2 392 1102 Basics of Chemistry Up201508251715 14405031Document9 pages3224 Topper 21 110 1 2 392 1102 Basics of Chemistry Up201508251715 14405031Naresh world SinghNo ratings yet
- Complete NomenclatureDocument10 pagesComplete NomenclaturezainalexanderaliNo ratings yet
- Cha 7Document13 pagesCha 7Tun Lin AungNo ratings yet
- The Living World 2Document50 pagesThe Living World 2Technical Section- Sr.DEE/G/ASNNo ratings yet
- 5.8 Ionic CompoundsDocument4 pages5.8 Ionic Compoundsmichael.delaney8541100% (2)
- Valency and Formulae-HandoutDocument3 pagesValency and Formulae-HandoutABHAVYA RAJNo ratings yet
- Naming Compounds UpdateDocument34 pagesNaming Compounds UpdatedigreeleeNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 7 Science The Language of Chemistry Exam Notes: IntroductionDocument8 pagesCBSE Class 7 Science The Language of Chemistry Exam Notes: Introductionanika varshneyNo ratings yet
- 3b Ionic CompoundsDocument35 pages3b Ionic Compoundsapi-369690183No ratings yet
- 6 - Multivalent & Polyatomic - Naming & Chemical FormulasDocument16 pages6 - Multivalent & Polyatomic - Naming & Chemical Formulasruihan0123wNo ratings yet
- A. Naming Binary Ionic CompoundsDocument3 pagesA. Naming Binary Ionic CompoundsEmikah TaylorNo ratings yet
- 05 Handout 4Document3 pages05 Handout 4Jamaica GuevarraNo ratings yet
- How To Count Atoms InstructionsDocument7 pagesHow To Count Atoms InstructionskenelhfnbekabqegotNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry IIDocument10 pagesGeneral Chemistry IIAravindan NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Naming CompoundsDocument58 pagesNaming CompoundsMELODY VERGARANo ratings yet
- Recognizing and Naming Binary Ionic CompoundDocument30 pagesRecognizing and Naming Binary Ionic CompoundJoressaNo ratings yet
- Ionic Compounds 4.1Document16 pagesIonic Compounds 4.1Ailin ZhangNo ratings yet
- LECTURE Naming CompoundsDocument63 pagesLECTURE Naming CompoundsCheri BulahanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Coordination CompoundDocument36 pagesChapter 5 Coordination Compoundammar zakariaNo ratings yet
- Binary Ionic CompoundDocument15 pagesBinary Ionic CompoundKaren BasistaNo ratings yet
- Notes Chapter 3-StoichiometryDocument31 pagesNotes Chapter 3-StoichiometryHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- Reactivity Series Worksheet QuDocument8 pagesReactivity Series Worksheet Quقاتل مستأجرNo ratings yet
- NamingDocument8 pagesNamingMADAYAG, RUTH L.No ratings yet
- G9 Science Q2-Week 2 - Types of CompoundsDocument79 pagesG9 Science Q2-Week 2 - Types of CompoundsKarina GentonNo ratings yet
- ENITV21D-Naming Compounds Summary2Document5 pagesENITV21D-Naming Compounds Summary2Sean PimentelNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature Is The Systematic Naming of Chemical CompoundsDocument7 pagesNomenclature Is The Systematic Naming of Chemical CompoundsjanekatherineNo ratings yet
- Recognizing and Naming Binary Ionic CompoundDocument30 pagesRecognizing and Naming Binary Ionic CompoundNeal RobinNo ratings yet
- Writing Chemical FormulaDocument19 pagesWriting Chemical FormulaDelano Pete100% (1)
- Applied Chem Week 1-3Document32 pagesApplied Chem Week 1-3Zenly AlleraNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Hydrides: The Commonwealth and International Library: Chemistry DivisionFrom EverandInorganic Hydrides: The Commonwealth and International Library: Chemistry DivisionNo ratings yet
- Bismi NOC Job Classification ResearchDocument6 pagesBismi NOC Job Classification Research814556No ratings yet
- Bismi's Lighthouse Biology Cells and Tissues AssignmentDocument3 pagesBismi's Lighthouse Biology Cells and Tissues Assignment814556No ratings yet
- Gle OrganizerDocument4 pagesGle Organizer814556No ratings yet
- ? ?? Copy of Grade 10 The VeldtDocument2 pages? ?? Copy of Grade 10 The Veldt814556No ratings yet
- ? ?? Copy of Skiba Grade 10 Art Week 4 Line and Shape Mini ProjectDocument9 pages? ?? Copy of Skiba Grade 10 Art Week 4 Line and Shape Mini Project814556No ratings yet
- Totalenergiescorbionpla Brochure A4spread DigitalDocument6 pagesTotalenergiescorbionpla Brochure A4spread DigitalSiddharthBhasneyNo ratings yet
- Cofmow ItpDocument7 pagesCofmow ItpAjay HazarikaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Water and Solution: 5.1 Physical Characteristics of WaterDocument15 pagesChapter 5 Water and Solution: 5.1 Physical Characteristics of WaterAlan WongNo ratings yet
- Complexometric and Precipitation TitrationsDocument10 pagesComplexometric and Precipitation Titrationskhanny96100% (1)
- Cored Wires: Cement IndustryDocument2 pagesCored Wires: Cement Industrymunal23No ratings yet
- A Comparative Study of Sodium Hydrogen Titanate Nanotubes 2017 Journal of CDocument10 pagesA Comparative Study of Sodium Hydrogen Titanate Nanotubes 2017 Journal of CDes RiliNo ratings yet
- Slurry W Alls: Design, Construction, and Quality Contro/: Ichard - SoDocument4 pagesSlurry W Alls: Design, Construction, and Quality Contro/: Ichard - SoAyman SobhyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document20 pagesChapter 3Chin Fout LengNo ratings yet
- Operator'S Manual Px15P-Xxx-Xxx-Axxx: 1-1/2" Diaphragm PumpDocument12 pagesOperator'S Manual Px15P-Xxx-Xxx-Axxx: 1-1/2" Diaphragm PumpNashrullah AhmadNo ratings yet
- Chem 121-1Document45 pagesChem 121-1Zechariah NggitaNo ratings yet
- Cap 2Document33 pagesCap 2Ricardo Rincon VegaNo ratings yet
- Mucell: Proven Lightweighting Technology For Automotive ApplicationsDocument8 pagesMucell: Proven Lightweighting Technology For Automotive ApplicationsRidha FaturachmiNo ratings yet
- 2011, Ippolito, Drinking Water Treatment Residuals A Review of RecDocument13 pages2011, Ippolito, Drinking Water Treatment Residuals A Review of RecAfranio Neves JrNo ratings yet
- Building Envelope Compliance Form 2013Document9 pagesBuilding Envelope Compliance Form 2013JWNo ratings yet
- Concrete Slender Wall DesignDocument9 pagesConcrete Slender Wall Designamokhta100% (1)
- Inspection N Test PlanDocument20 pagesInspection N Test PlanMohd Kamal TajudinNo ratings yet
- FMPRV 41Document36 pagesFMPRV 41vsumedhaNo ratings yet
- Abrasive Flow MachiningDocument28 pagesAbrasive Flow MachiningsnvijayanNo ratings yet
- Laminar and Turbulent FlowDocument5 pagesLaminar and Turbulent FlowVian gardashNo ratings yet
- Ethylene ExperimentDocument3 pagesEthylene ExperimentLexzyrie Sybelle S. TolarbaNo ratings yet
- TDS - Epolam 2015 US Rev-04Document3 pagesTDS - Epolam 2015 US Rev-04McFlyNo ratings yet
- Microchannel Heat Exchanger As EvaporatorDocument11 pagesMicrochannel Heat Exchanger As EvaporatorAbhilash TilakNo ratings yet
- 3SE51620CH121AN5 Datasheet enDocument4 pages3SE51620CH121AN5 Datasheet enrayggzz_88482611No ratings yet
- Eat339 - Engineering Dynamics and Thermofluids SESSIONAL EXAMINATION 2015 - 2016 (Paper 2)Document7 pagesEat339 - Engineering Dynamics and Thermofluids SESSIONAL EXAMINATION 2015 - 2016 (Paper 2)أحمد صلاح الدين0% (1)