Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cells
Uploaded by
findpeace3130 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
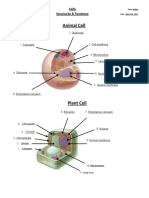
2 views1 pageAnimal cells lack a cell wall, vacuole, and chloroplasts that plant cells contain. Animal cells tend to be rounder while plant cells are more often rectangular, hexagonal, or square in shape. The key differences between animal and plant cells are that animal cells do not have a cell wall, vacuole, or chloroplasts, and tend to be rounder, whereas plant cells have these structures and are more often rectangular, hexagonal or square in shape.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAnimal cells lack a cell wall, vacuole, and chloroplasts that plant cells contain. Animal cells tend to be rounder while plant cells are more often rectangular, hexagonal, or square in shape. The key differences between animal and plant cells are that animal cells do not have a cell wall, vacuole, or chloroplasts, and tend to be rounder, whereas plant cells have these structures and are more often rectangular, hexagonal or square in shape.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageCells
Uploaded by
findpeace313Animal cells lack a cell wall, vacuole, and chloroplasts that plant cells contain. Animal cells tend to be rounder while plant cells are more often rectangular, hexagonal, or square in shape. The key differences between animal and plant cells are that animal cells do not have a cell wall, vacuole, or chloroplasts, and tend to be rounder, whereas plant cells have these structures and are more often rectangular, hexagonal or square in shape.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Differences between animal and plant cells
Animal cells have no cell wall, vacuole or chloroplasts.
Year 7 Knowledge Organiser - Cells They tend to be rounder and plant cells are more
rectangular, hexagonal or square.
Key words: Cell structure
Cell – The unit of a living organism;
contains parts to carry out life
processes.
Unicellular: Living things made up of
one cell.
Multicellular: Living things made up of
many types of cell.
Tissue: Group of cells of one type.
Organ: Group of different tissues
working together to carry out a job.
Cell membrane: Surrounds the cell and Microscope parts Specialised cells
controls movement of substances in
and out. Many cells have adaptations to their
Nucleus: Contains genetic material function. For example sperm cells
(DNA) which controls the cell’s have tails to swim and many
activities. mitochondria to release energy.
Vacuole: Area in a cell that contains
liquid; used by plants to keep the cell
rigid and store substances.
Cell wall: Strengthens the cell. In plant
cells it is made of cellulose.
Chloroplast: Part of a plant cell that
absorbs light for photosynthesis Websites that might be useful: Cells divide by a process called
Cytoplasm: Jelly-like substance where https://www.bbc.com/bitesize/articles mitosis, which produces two
most chemical processes happen. /zr69dxs identical cells from one parent cell.
Mitochondrion (plural mitochondria): Extension ideas to research: Yeast cell
sausage shaped organelle where • What do bacterial cells look like? dividing:
energy is released • Who were the first people to see
cells and when was this?
You might also like
- DR. WZCA SEC 1 SCIENCE Revision Notes For Chapter 6Document14 pagesDR. WZCA SEC 1 SCIENCE Revision Notes For Chapter 6Cole- Min Khant KyawNo ratings yet
- Class: 8 Science Chapter - 8 Cell - Structure and FunctionsDocument10 pagesClass: 8 Science Chapter - 8 Cell - Structure and FunctionsAmiteshwar SinghNo ratings yet
- Notes Cells (Slides by Slidesgo)Document38 pagesNotes Cells (Slides by Slidesgo)salinaNo ratings yet
- Cells Unit Powerpoint 2Document110 pagesCells Unit Powerpoint 2.....No ratings yet
- Introduction To Cells (1.1) :: The Cell TheoryDocument65 pagesIntroduction To Cells (1.1) :: The Cell Theoryelvira sta.mariaNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Chapter 8 Cbse Class 8 Science NotesDocument8 pagesChapter 8 Cbse Class 8 Science Notesdeepti jainNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2.1. The CellDocument7 pagesLesson 2.1. The CellGemma CabañasNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Revision NotesDocument4 pagesClass 8 Science Chapter 8 Revision NotesneilNo ratings yet
- Acfrogahwtgjhymcdbhqd9juy0ihb5dgzqyobwgygm44pyrxkeh Dixuo Odyslryl Jpqgjhd4udt63zm6ot2mgudp GWKKKDFLLJD 4nxfp5i Pvcee 9pyuxltmliuwhn9qmanxfhy82jt1l4Document8 pagesAcfrogahwtgjhymcdbhqd9juy0ihb5dgzqyobwgygm44pyrxkeh Dixuo Odyslryl Jpqgjhd4udt63zm6ot2mgudp GWKKKDFLLJD 4nxfp5i Pvcee 9pyuxltmliuwhn9qmanxfhy82jt1l4s20003No ratings yet
- 2 - Cell+WSDocument3 pages2 - Cell+WSRohan SoniNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant CellDocument41 pagesAnimal and Plant CellSabrina LavegaNo ratings yet
- Cells and Cell StructureDocument3 pagesCells and Cell Structureapi-238197463No ratings yet
- 4-5-Prokaryotic Cells and MembranesDocument38 pages4-5-Prokaryotic Cells and MembranesaarnavskrishnaNo ratings yet
- Structure of CellsDocument14 pagesStructure of CellsTimothy JonesNo ratings yet
- Cell Theory ModifiedDocument33 pagesCell Theory ModifiedNazish Altaf100% (1)
- Beed1 - Rejano, Mary Grace M.Document6 pagesBeed1 - Rejano, Mary Grace M.GraceNo ratings yet
- Cells: by - NatalieDocument24 pagesCells: by - NatalieNatalie JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 1 Lesson 1.1 Cell Structure and ClassificationDocument47 pagesGen Bio 1 Lesson 1.1 Cell Structure and ClassificationZander Ezekiell FernandezNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant Cell Staining PracticalDocument3 pagesAnimal and Plant Cell Staining PracticalSeerat FatimaNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes Class - 8 Science Chapter 8 - Cell - Structure and FunctionsDocument5 pagesRevision Notes Class - 8 Science Chapter 8 - Cell - Structure and FunctionsArpit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal CellDocument23 pagesPlant and Animal CellAnnisa Aulia100% (1)
- Structure of CellsDocument14 pagesStructure of CellsTimothy JonesNo ratings yet
- Cell Theory1Document62 pagesCell Theory1Micoper ApolinarioNo ratings yet
- 1st Ch. CellsDocument27 pages1st Ch. CellsAdnan Khan100% (1)
- Biology Notes PDFDocument63 pagesBiology Notes PDFInari KarppinenNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument24 pagesThe CellCaren AdongoNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 1 18-19 Cells Reference PPT1Document68 pagesGen Bio 1 18-19 Cells Reference PPT1Ciena GaddiNo ratings yet
- Cells 22-23Document7 pagesCells 22-23hiNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument34 pagesThe Celljaco_ansaldiNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Cell Theory: Topic 2: CellsDocument11 pages2.1 Cell Theory: Topic 2: CellsMorgan LockeNo ratings yet
- Cell Definition, Types, & Functions BritannicaDocument10 pagesCell Definition, Types, & Functions BritannicaKolade YousuffNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure-Group #4Document17 pagesCell Structure-Group #4Andrea MorochoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Living OrganismsDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Living OrganismsSabita SinghNo ratings yet
- Biology Note About CellsDocument17 pagesBiology Note About CellsEK TubeNo ratings yet
- 10 CMH Human and Social Biology: CellsDocument28 pages10 CMH Human and Social Biology: CellsScience,Physical Education And Sports VideosNo ratings yet
- PRPLLLDocument19 pagesPRPLLLPraveen KolaganiNo ratings yet
- The Cell: Eukaryotic Cells and Prokaryotic CellsDocument13 pagesThe Cell: Eukaryotic Cells and Prokaryotic CellsDiane CastroNo ratings yet
- General BiologyDocument14 pagesGeneral BiologybonNo ratings yet
- Cells - Structure and Function: Important Events in The Discovery of CellsDocument24 pagesCells - Structure and Function: Important Events in The Discovery of CellsJaspher Joshua CallangaNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts & Functions PRSNTTN 20Document136 pagesCell Parts & Functions PRSNTTN 20Scar ShadowNo ratings yet
- CELL CYCLE MODULE Dec 18Document34 pagesCELL CYCLE MODULE Dec 18arnel AguelNo ratings yet
- What Is A MicroscopeDocument6 pagesWhat Is A MicroscopeMcj TeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document44 pagesChapter 3Altaf Hussain KhanNo ratings yet
- CELL in Biology-AnnottedDocument6 pagesCELL in Biology-AnnottedSaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- Earth Life Science Module 5Document15 pagesEarth Life Science Module 5Rosalyn Pagatpatan BarolaNo ratings yet
- Notes 1Document5 pagesNotes 1plat7wbNo ratings yet
- Unit Cell. Organization of The Human Body: Organ SystemDocument12 pagesUnit Cell. Organization of The Human Body: Organ SystemD IngaNo ratings yet
- 2cytology 70 27Document4 pages2cytology 70 27rajani jidagamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: "The Fundamental Unit of Life"Document7 pagesChapter 5: "The Fundamental Unit of Life"Zeel ChauhanNo ratings yet
- 1SS - Cells, Tissues, Organs and Systems - Notes B2Document7 pages1SS - Cells, Tissues, Organs and Systems - Notes B2Gavin Ng100% (1)
- Notes of Cell ChapterDocument15 pagesNotes of Cell ChapterSudha SinghNo ratings yet
- The CellsDocument4 pagesThe CellsSlaheddineNo ratings yet
- 1.1cell ConceptDocument10 pages1.1cell ConceptMokariya SanjayNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Cell Structure and Function - NotesDocument8 pagesUnit 2 - Cell Structure and Function - Notesronel.jnmsNo ratings yet
- S4en Biology Chapter 1Document59 pagesS4en Biology Chapter 1MeharNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology What Is A Cell? What Are The Essential Characteristics of Cells?Document11 pagesCell Biology What Is A Cell? What Are The Essential Characteristics of Cells?Renel Esteves RestauroNo ratings yet
- Key Notes For Chapter-The Fundamental Unit of Life, Are: CellDocument14 pagesKey Notes For Chapter-The Fundamental Unit of Life, Are: CellShweta ShuklaNo ratings yet
- BioDocument3 pagesBioJoelle SwaisNo ratings yet