Professional Documents
Culture Documents
O-RADS MRI Lexicon Terms Table 2023
O-RADS MRI Lexicon Terms Table 2023
Uploaded by
nguyenthanhhai0974backup02Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
O-RADS MRI Lexicon Terms Table 2023
O-RADS MRI Lexicon Terms Table 2023
Uploaded by
nguyenthanhhai0974backup02Copyright:
Available Formats
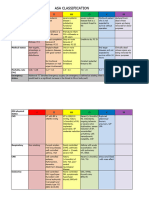
O-RADS™ MR Lexicon Categories, Terms and Definitions
Revised: January 2023
Term Sub-term Definition Comments
Major Categories of Imaging Findings
Physiologic (consistent with normal physiology)
Follicle Simple cyst ≤ 3 cm in premenopausal age group. A follicle is Pre-menopausal
hyperintense on T2WI, hypointense on T1WI and does not women only
enhance on post-contrast T1WI.
Corpus luteum Cyst ≤ 3 cm, with an enhancing crenulated wall on subtracted Pre-menopausal
post-contrast T1WI, +/- blood clot or hemorrhagic contents. women only
Lesion (not physiologic)
Cystic lesion Unilocular cyst Single locule, with or without solid tissue.
Multilocular cyst More than one locule, with or without solid tissue.
Lesion with Solid tissue Conforms to one the following morphologies and enhances:
solid papillary formations, mural nodules, irregular cyst
component wall/septations and solid portion.
Other solid Smooth wall/septation, clot/debris, fat Not considered solid
components, tissue
not considered
solid tissue
Solid lesion Consists of at least 80% solid tissue with <20% of lesion
volume being cystic.
Size
Maximum Largest diameter of the lesion and/or solid component in any
diameter imaging plane.
Shape or contour of solid lesion or solid tissue
Smooth Regular or even margin of a solid lesion or solid tissue.
Irregular Uneven margin of a solid lesion or solid tissue.
Signal Intensity
Homogeneous Uniform appearance of the signal observed in an adnexal
finding.
Heterogeneous Non-uniform or variable appearance of the signal observed in
an adnexal finding.
T2 hypointense Adnexal observation with signal intensity lower or equal to
iliopsoas muscle.
T2 intermediate Adnexal observation with signal intensity higher than iliopsoas
and lower than CSF.
T2 Adnexal observation with signal intensity equal or higher to
hyperintense CSF.
T1 hypointense Adnexal observation with signal intensity that follows simple
fluid.
T1 intermediate Adnexal observation with signal intensity similar or higher to
iliopsoas and lower than fat.
T1 Adnexal observation with signal intensity equal or higher to
hyperintense fat.
ⓒ 2023 American College of Radiology® | All rights reserved
DWI High B- Adnexal lesion with signal similar to urine or cerbral spinal
value Low fluid.
signal
DWI High B- Adnexal lesion with signal clearly higher than urine or CSF.
value High
signal
Lesion Components
Cystic Fluid Descriptors
Simple fluid Fluid content that follows CSF or urine on all sequences:
hyperintense on T2WI and hypointense on T1WI.
Non-simple Hemorrhagic Content can be variable depending on age. Late subacute
fluid fluid hemorrhage is
hyperintense on
T2WI and
hyperintense on
T1WI.
Endometriotic Content is hypointense on T2WI and hyperintense on T1WI.
fluid
Proteinaceous Content is variable in signal on T2WI (and variably
fluid hypointense on T1WI.
Fat or lipid Hyperintense on T2WI and hyperintense on T1WI, and loses If there is
containing fluid signal on fat saturated images. microscopic fat, there
will be signal loss on
out-of-phase images
and there may not be
any signal loss on fat
saturated images.
Additional Fluid-fluid level Appearance where the non-dependent fluid component has a
specific different signal intensity from the dependent fluid component
descriptors for with horizontal delineation.
non-simple
fluid
Shading Cyst fluid that is hypointense on T2WI; the extent of
hypointense T2 signal intensity may be homogeneous,
variable within the cyst or graduated and dependent.
Solid Component Descriptors
Solid tissue* Papillary Enhancing solid component arising from the inner/outer wall
*Must enhance projection or septation of an adnexal lesion, with a branching
and conform to architecture.
one of these
morphologies Mural nodule Enhancing solid component, measuring >3mm, arising from
the wall or septation of an adnexal lesion, with nodular
appearance.
Irregular Enhancing linear strand that runs from one internal surface of
septation the cyst to the contralateral side demonstrating an uneven
margin.
Irregular wall Enhancing cyst wall demonstrating an uneven margin.
Larger solid Enhancing component of an adnexal lesion that does not fit
portion into the categories of papillary projection, mural nodule, or
irregular septation/wall.
ⓒ 2023 American College of Radiology® | All rights reserved
Other solid Smooth Even contour or margin with no irregularities, mural nodules
components, septations/wall or papillary projections.
not considered
solid tissue Blood clot, non- Solid-appearing material within a cyst that does not enhance.
enhancing debris
and fibrin
strands
Fat Lipid-containing material that does not enhance.
Hair, calcification Other components of a dermoid not considered solid tissue.
and a
Rokitansky
nodule
Enhancement: T1WI post-contrast
Dynamic contrast enhancement with time intensity curves
Low risk curve Enhancement of the solid tissue within the adnexal lesion with
minimal and gradual increase in signal over time with no well-
defined shoulder and no plateau.
Intermediate Enhancement of the solid tissue within the adnexal lesion with
risk curve an initial slope less than the myometrium, moderate increase
in signal intensity with a plateau.
High risk curve Enhancement of the solid tissue within the adnexal lesion with
an initial slope greater than the myometrium, marked increase
in signal intensity with a plateau.
Non-dynamic contrast enhancement at 30-40 seconds post-injection
Less than or Enhancement of the solid tissue within the adnexal lesion is
equal to the hypoenhancing to the outer myometrium at 30-40 seconds
myometrium post-contrast injection.
Greater than Enhancement of the solid tissue within the adnexal lesions is
the equal to or greater than the outer myometrium at 30-40
myometrium seconds post-contrast injection.
General and Extra-Ovarian Findings
Peritoneal fluid Physiologic Small amount of fluid inside the pouch of Douglas or cul-de-
sac or between the uterus and bladder.
Ascites Fluid outside the pouch of Douglas or cul-de-sac or fluid
extending beyond the space between the uterus and bladder.
Fallopian tube Tubular Substantially longer in one dimension than in the two
descriptors perpendicular dimensions.
Endosalpingeal Incomplete septations or short round projections, orthogonal
folds to the length of the tube.
Peritoneal Cyst following contour of adjacent pelvic organs; or normal
inclusion cyst ovary at the edge of/ or surrounded by a cystic mass.
Ovarian Twisted pedicle Swirling appearance of the broad ligament or ovarian pedicle.
torsion
Massive ovarian Enlarged ovary with edematous central stroma.
edema
Ovarian Lack of enhancement of the ovary on T1WI post- contrast.
infarction
Peritoneal Thickening, Uniform thickening, without focal nodularity.
thickening, smooth
nodules
Thickening, Nonuniform thickening or focal areas of nodularity.
irregularity
ⓒ 2023 American College of Radiology® | All rights reserved
You might also like
- TransYouth Clinic Presentation To LAUSDDocument40 pagesTransYouth Clinic Presentation To LAUSDDaily Wire Investigations TeamNo ratings yet
- A. Physical (Dillon'S Physical Assessment Tool)Document7 pagesA. Physical (Dillon'S Physical Assessment Tool)Jim RashidNo ratings yet
- O-RADS MR Lexicon Terms Table November 2020Document3 pagesO-RADS MR Lexicon Terms Table November 2020nguyenthanhhai0974backup02No ratings yet
- O-RADS MR Lexicon Terms Table July 2021Document3 pagesO-RADS MR Lexicon Terms Table July 2021nguyenthanhhai0974backup02No ratings yet
- Primbon Mri 2Document25 pagesPrimbon Mri 2maria astrianiNo ratings yet
- Cranio Pha Ryn Gio MaDocument104 pagesCranio Pha Ryn Gio MaBhayu RizallinoorNo ratings yet
- O-RADS MR Risk Stratification System Table September 2020Document2 pagesO-RADS MR Risk Stratification System Table September 2020nguyenthanhhai0974backup02No ratings yet
- Case Cpa LesionDocument52 pagesCase Cpa LesionShahnawazIqubaliNo ratings yet
- Imaging of Cervical Lymphadenopathy in Children and Young AdultsDocument31 pagesImaging of Cervical Lymphadenopathy in Children and Young Adultsdessyana wulandariNo ratings yet
- ASACLASS Renew3Document3 pagesASACLASS Renew3docwepNo ratings yet
- Intradural Extramedullary TumorsDocument10 pagesIntradural Extramedullary TumorsFaizyab Ahmed100% (1)
- GFHP NCP TITO CARSANO WEEK 2 Day 2Document14 pagesGFHP NCP TITO CARSANO WEEK 2 Day 2Hanna CarsanoNo ratings yet
- Shoulder DystociaDocument9 pagesShoulder DystociaSoriao, Lovely Rose V.100% (1)
- L1 Report TemplateDocument2 pagesL1 Report TemplateRasangi Sumudu Clare SuraweeraNo ratings yet
- PIRADS V2-1LexiconDocument9 pagesPIRADS V2-1LexiconMELANITH BRAVONo ratings yet
- Tumors in Central Nervous System: 1) Brain 2) Pituitary 3) PinealDocument43 pagesTumors in Central Nervous System: 1) Brain 2) Pituitary 3) PinealTan Geok EngNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cystic SchwannomaDocument3 pagesSpinal Cystic SchwannomahelenNo ratings yet
- Poliomyel S Guillain Barré Syndrome Trauma C Neuri S Acute Childhood HemiplegiaDocument1 pagePoliomyel S Guillain Barré Syndrome Trauma C Neuri S Acute Childhood HemiplegiaDr-Zulfiqar AliNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Subarachnoid HemorrhagicDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Subarachnoid HemorrhagicAshram Smart0% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Subarachnoid HemorrhagicDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Subarachnoid HemorrhagicAshram Smart100% (1)
- CV Complication SCIDocument28 pagesCV Complication SCIcris weeNo ratings yet
- Pemateri 7 - The Role of Mri in Endometriosis DiagnosticDocument48 pagesPemateri 7 - The Role of Mri in Endometriosis DiagnosticDewi Ayu AstariNo ratings yet
- Pembacaan Jurnal: Deep Vein Thrombosis: A Clinical ReviewDocument22 pagesPembacaan Jurnal: Deep Vein Thrombosis: A Clinical ReviewHadi TryadiNo ratings yet
- IschialgiaDocument13 pagesIschialgiaenha mfNo ratings yet
- 4 Abdominal+ExaminationDocument9 pages4 Abdominal+Examinationمرتضى حسين عبدNo ratings yet
- ARVCDocument6 pagesARVCCatur UtamiNo ratings yet
- CRANIOPHARYNGIOMA (Autosaved)Document42 pagesCRANIOPHARYNGIOMA (Autosaved)ArfaNo ratings yet
- Peritonitis PDFDocument1 pagePeritonitis PDFHoney MacabuhayNo ratings yet
- Open I Tibia Fibula (R) Lacerated Wounded Leg: Our Lady of Fatima UniversityDocument21 pagesOpen I Tibia Fibula (R) Lacerated Wounded Leg: Our Lady of Fatima UniversityPOTENCIANA MAROMANo ratings yet
- Lab 6Document25 pagesLab 6Abdul RaufNo ratings yet
- Wellen SyndromeDocument5 pagesWellen SyndromeMohammed SadoonNo ratings yet
- Acute Scrotal Pain or SwellingDocument6 pagesAcute Scrotal Pain or SwellingAnna N WachidahNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation in Geriatric Ward "Cancer of The Larynx"Document130 pagesCase Presentation in Geriatric Ward "Cancer of The Larynx"Christina GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation of Prostate CA and BPHDocument81 pagesCase Presentation of Prostate CA and BPHJon Gab Paquit100% (8)
- 2 Examination of SwellingDocument43 pages2 Examination of SwellingSneha ThiagarajanNo ratings yet
- February 2016 Paediatric Musculoskeletal MRI DR Saira HaqueDocument4 pagesFebruary 2016 Paediatric Musculoskeletal MRI DR Saira HaqueindiatradeteoNo ratings yet
- BiopsiesDocument13 pagesBiopsiesSubbu ManiNo ratings yet
- NCP NeuroDocument20 pagesNCP NeuroNica Gaborne Navarro100% (3)
- EpiscleritisDocument2 pagesEpiscleritisDasNo ratings yet
- 11 TM AngiomiolipomaDocument9 pages11 TM AngiomiolipomaDonaldo ReleyNo ratings yet
- Appendicitis: Anetha Jodhan Ravindra SinghDocument34 pagesAppendicitis: Anetha Jodhan Ravindra SinghMarlon GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Physical Assessment: System/ Method of Assessment Normal Findings Actual Findings InterpretationDocument8 pagesPhysical Assessment: System/ Method of Assessment Normal Findings Actual Findings Interpretationハリコ ノビNo ratings yet
- Spontaneous AbortionDocument29 pagesSpontaneous Abortionد.أيمن بسام صالح الصواحيNo ratings yet
- Mri Report Flair - DanelaDocument11 pagesMri Report Flair - DanelaDanela D AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Physical Assessment: No Area of Increased Vascularity and Ecchymosis No Area of Increased Vascularity and EcchymosisDocument8 pagesPhysical Assessment: No Area of Increased Vascularity and Ecchymosis No Area of Increased Vascularity and EcchymosisPantaleon PacisNo ratings yet
- Neonatology High Yield 3Document1 pageNeonatology High Yield 3Nirubhana ArunthavasothyNo ratings yet
- Surgery Revalida Review PDFDocument11 pagesSurgery Revalida Review PDFMara Medina - BorleoNo ratings yet
- Bladder Tumors: Normal AnatomyDocument11 pagesBladder Tumors: Normal AnatomyPankaj DubeyNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Uterine BleedingDocument55 pagesAbnormal Uterine BleedingRiskyWulandariNo ratings yet
- Lymphoma NewDocument36 pagesLymphoma Newmedo2002alfadaliNo ratings yet
- S.NO. Name of Procedure Indications Contraindications Articles Required Special Considerations and Precautions 1. Non-Stress Test MaternalDocument4 pagesS.NO. Name of Procedure Indications Contraindications Articles Required Special Considerations and Precautions 1. Non-Stress Test Maternaljyoti ranaNo ratings yet
- Thoracic Lymph Node Enlargement in Usual.7Document5 pagesThoracic Lymph Node Enlargement in Usual.7Andiie ResminNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 15-Nov-2022Document13 pagesAdobe Scan 15-Nov-2022Oscar Golden pupNo ratings yet
- A. Physical (Dillon'S Physical Assessment Tool)Document7 pagesA. Physical (Dillon'S Physical Assessment Tool)Jim RashidNo ratings yet
- Hypoxic-Ischaemic Encephalopathy (HIE) : Maternity and Neonatal Clinical GuidelineDocument27 pagesHypoxic-Ischaemic Encephalopathy (HIE) : Maternity and Neonatal Clinical GuidelineGordon InformationNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation and Discussion: Internal Medicine DepartmentDocument8 pagesCase Presentation and Discussion: Internal Medicine DepartmentCalingalan Hussin CaluangNo ratings yet
- Haemorrage During Late PregnencyDocument38 pagesHaemorrage During Late PregnencysuthaNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Myocardial InfarctionDocument20 pagesCase Study On Myocardial InfarctionrumasadraunaNo ratings yet
- Copes Et Al. 2016aDocument12 pagesCopes Et Al. 2016aManuel MesaNo ratings yet
- 7Document5 pages7Amjad SaudNo ratings yet
- Ms Sabiha ReportDocument4 pagesMs Sabiha Reportzafir alamNo ratings yet
- Uog 21933Document10 pagesUog 21933Kenny AraujoNo ratings yet
- How To Balance Your HormonesDocument4 pagesHow To Balance Your Hormonesjb100% (1)
- FCL6 - Midterm Issues in Human SocietyDocument19 pagesFCL6 - Midterm Issues in Human SocietyJamaeca A EdraNo ratings yet
- Lec01 - Assessing Male and Female GenitaliaDocument13 pagesLec01 - Assessing Male and Female GenitaliaIRISH MANIAGONo ratings yet
- 2.1 Assessment of Normal Pregnant MotherDocument41 pages2.1 Assessment of Normal Pregnant Mother11 - JEMELYN LOTERTENo ratings yet
- Asking-Filling in Medical ReportDocument5 pagesAsking-Filling in Medical ReportMiss Hanay VinnyNo ratings yet
- Managing Urinary Tract Problem: FOCUS On The FollowingDocument11 pagesManaging Urinary Tract Problem: FOCUS On The FollowingLovely DaroleNo ratings yet
- Thesis Topics in GynecologyDocument5 pagesThesis Topics in Gynecologyxdkankjbf100% (2)
- PolicyPrint DoDocument8 pagesPolicyPrint DoJabeen JuwaleyNo ratings yet
- Postpartum Psychosis: Clinical Considerations: Marlene Freeman, M.DDocument9 pagesPostpartum Psychosis: Clinical Considerations: Marlene Freeman, M.DKreshnik IdrizajNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0266613821002722 MainDocument10 pages1 s2.0 S0266613821002722 MainlinaNo ratings yet
- 3555 Ais - Database.model - file.LampiranLain Soal UTS Bahasa Inggris 1 S.Kep Semetser 2-1Document4 pages3555 Ais - Database.model - file.LampiranLain Soal UTS Bahasa Inggris 1 S.Kep Semetser 2-1Dyah AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 - Normal Changes During PregnancyDocument4 pagesTopic 5 - Normal Changes During PregnancyREANNE MAE ABRERANo ratings yet
- Pathologic Jaundice: A Case Analysis OnDocument22 pagesPathologic Jaundice: A Case Analysis Onfrozen loombandsNo ratings yet
- Impact of Applying Different Physical Activity GuidelinesDocument9 pagesImpact of Applying Different Physical Activity GuidelinesnirchennNo ratings yet
- Pro-Oxidants and Antioxidants in Retinopathy of PrematurityDocument6 pagesPro-Oxidants and Antioxidants in Retinopathy of PrematurityNejraNo ratings yet
- Module 6: THE Sexual SelfDocument34 pagesModule 6: THE Sexual SelfEsther Joy HugoNo ratings yet
- PIYUSH BIO 01amniocentesis-Cbsebiology4uDocument15 pagesPIYUSH BIO 01amniocentesis-Cbsebiology4uNikhil ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Jharkhand ReportDocument133 pagesJharkhand ReportNutan TiggaNo ratings yet
- Individual and Family Application Checklist (Uae) : How To ApplyDocument9 pagesIndividual and Family Application Checklist (Uae) : How To ApplyJacob PriyadharshanNo ratings yet
- Jaundice 20 PDFDocument54 pagesJaundice 20 PDFHaziq KamardinNo ratings yet
- 13 15 DRDocument16 pages13 15 DRMarie Ashley CasiaNo ratings yet
- END-IAP Exam Question Paper - March-JulyDocument3 pagesEND-IAP Exam Question Paper - March-JulyLinus JohannesNo ratings yet
- New English SBA 1Document10 pagesNew English SBA 1Chrisena CampbellNo ratings yet
- Virgin The Untouched History (Blank, Hanne)Document300 pagesVirgin The Untouched History (Blank, Hanne)Paula Sofía GNo ratings yet
- Adu Con CHN 1 Family Health Assessment FormDocument18 pagesAdu Con CHN 1 Family Health Assessment FormShene Claire VigillaNo ratings yet
- Weeks 12-16 Learning ObjectivesDocument14 pagesWeeks 12-16 Learning ObjectivesAmber DavisNo ratings yet
- Levonorgestrel Emergency Contraception: (Plan B or Generic Equivalent)Document2 pagesLevonorgestrel Emergency Contraception: (Plan B or Generic Equivalent)AdityaWijayaNo ratings yet