Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Answer Key
Uploaded by
gurpreeettrendingOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Answer Key
Uploaded by
gurpreeettrendingCopyright:
Available Formats
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN,BHOPAL REGION
HALF YEARLY EXAMINATION, 2022-2023
SUBJECT-BIOLOGY
TIME-3:00 Hrs. MAX.MARKS-70
Answer key
SECTION- A
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
C B B D B B B A
9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
B A C D C A B A
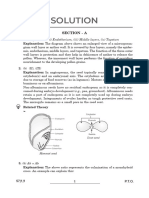
SECTION- B
17 (A)A group of individual organisms with fundamental similarities /A group of
interbreeding organisms/ A group of individual organisms which reproduce and give
birth of fertile offspring = 1M
(B) Systema Naturae =1M
18 Rodophyceae =1M
Floridean Starch =1M
19 Pinnately compound leaf Palmately compound leaf
The leaflets are attached to the common axis, The leaflets are attached at a common
called rachis. point on the leaf stalk.
Examples include neem and Cassia fistula( Examples include silk cotton (Bombax)
also called golden shower plant) and Cannabis.
One correct difference =1M
one example of each =1M
OR
These are made of more than one type of cells and they work together as a unit. =1M
xylem -It is composed of 4 kinds of elements: tracheids, vessels, xylem fibres and xylem
parenchyma.
phloem is composed of sieve tube elements, companion cells, phloem parenchyma &
phloem fibres. = 1M
20 Active and passive transport = 1/2M,
one correct difference = 1M
one correct example of each =1/2M
refer Ch- 08- 8.5.1 ( NCERT Text book)
21 Meiosis =1M,
Germ Cell/ Meiocyte/ Spore mother cell =1M
SECTION- C
22 Ascomycetes = 1M
presence of sac like asci (sing. ascus). =1 M
Yeast(Sacharomyces) , Penicillium,Aspergillus, Claviceps and Neurospora.
( Name of any two members belongs to this class) =1M
Page 1 of 3
refer Ch- 04- 4.2.5 ( NCERT Text book)
23 Phylum- Ascehelminthese / Nematoda = 1/2M
Internal fertilization =1/2M
external development
indirect or direct development with correct examples. =1M
refer Ch- 02- 2.3.2 ( NCERT Text book)
24 In the life cycle of heterosporous ptredophytes . E.g. Selaginella & Salvinia.
- The megaspores & microspores germinate and give rise to female and male
gametophytes, respectively. The female gametophytes are retained on the parent
sporophytes for variable periods. - Within female gametophytes, zygotes develop into
young embryos. This event is a precursor to the seed habit. It is considered as an
important step in evolution of seed habit. =3M
25 International Code for Botanical Nomenclature (ICBN). = 1/2M
1. Biological names are generally in Latin and written in italics. They are Latinised or
derived from Latin irrespective of their origin. = 1/2M
2. The first word in a biological name represents the genus while the second component
denotes the specific epithet. = 1/2M
3. Both the words in a biological name, when handwritten, are separately underlined, or
printed in italics to indicate their Latin origin. = 1/2M
4. The first word denoting the genus starts with a capital letter while the specific epithet
starts with a small letter. = 1/2M
Mangifera indica = 1/2M
26 A= Hypogynous: Here, gynoecium occupies the highest position while other parts are
situated below it. The ovary is superior. Mustard/china rose/ brinjal
B= Perigynous: Here, gynoecium is situated in the centre and other parts are located on
the rim of the thalamus at the same level. Ovary is half inferior.Plum/rose/peach
C= Epigynous: Here, the margin of thalamus grows upward enclosing the ovary
completely and getting fused with it. Other parts arise above the ovary. The ovary is
inferior. Guaua/cucumber/ray florets of sunflower = 1M+1M+1M
27 Nucleotide is a building block of nucleic acids. = 1M
its distinct components are pentose sugar, Nitrogenous base and phosphoric acid/
phosphate. = 2M
28 A= Tonoplast = control the flow of water into and out of the vacuole, =1.5M
B= Cell wall = provide strength and protection against mechanical and osmotic stress
= 1.5M
OR
They function as a catalyst that speeds up the reaction by lowering the activation
energy/ The enzyme accelerates a chemical reaction without changing its equilibrium, so
it is called as a biocatalyst. = 1M
1.They increase the rate of biochemical reactions in an organism.
2. enzymes are made by proteins./ enzymes are PH specific/ temperature specific
( Any four properties ) =2M
SECTION- D
29 1. Leucoplast =1M,
2. Aleuroplasts =1M
3. Amyloplasts = 1M
Page 2 of 3
4. Because it generates energy by light reaction through conversion of light energy in to
chemical energy =1M
OR because plastid has its own genetic material( DNA) also =1M
30 1. When blood always flow in the blood vessels and blood capillaries so that it never
come in contact with tissues =1M
2. Regulate the flow of blood in the heart =1M
3. (d) all of the above 4. arthropods / molluscs =1M
OR its body temperature depends on the surroundings. =1M
SECTION- E
31 (a) Haemocoel =1M
(b) Medusa =1M
(c) Nematocytes =1M
(d) parapodia =1M
(e) malpighian tubules =1M
OR
For five correct differences between chordateds and chordateds non- =5M
refer Ch- 04- table no.4.1 ( NCERT Text book)
32 (a) ) Fate bodies= stores fat there =1M
(b)Testis= produce sperms =1M
(c)kidney= blood filtration =1M
(d)cloaca= is a small, median chamber that is used to pass faecal matter, urine and
sperms to the exterior. =1M
(e) Urinary Bladder= pass urine in to cloaca =1M
OR
A. Name of the fruit= Berry or capsule = ½M
B. Type of inflorescence = Solitary, axillary or cymose = ½M
C. writes its floral formula = refer text book = 2M
D. draw the floral diagram = refer text book = 2M
33 (A) Mitosis is known as growth divisionit is responsible for growth and development in
organisms =1M
(B) Gametic Meiosis = 1M
(C) For any three correct differences =3M
OR
(A) Proteins are the polymers of amino acids = 1M
because they are needed for growth and repair of our body. = 1M
(B) Collagen = 1M
(C) RuBisCO. = 1M
(D) Antibody. = 1M
Page 3 of 3
You might also like
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan Hyderabad Region Marking Scheme Second Pre-Board Examination SESSION-2017-18 Class - Xii Subject - BiologyDocument6 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan Hyderabad Region Marking Scheme Second Pre-Board Examination SESSION-2017-18 Class - Xii Subject - Biologyhimanshu kumarNo ratings yet
- KENDRIYAVIDYALAYA SANGATHAN BIOLOGY ANSWER KEYDocument5 pagesKENDRIYAVIDYALAYA SANGATHAN BIOLOGY ANSWER KEYYash BhagatNo ratings yet
- Biology 2019 Answer SheetDocument17 pagesBiology 2019 Answer SheetTechno PointNo ratings yet
- Sample Question Paper Class XII (2017-18) Class: Xii Biology (044) Marking Scheme Time: 3hours MM:70Document6 pagesSample Question Paper Class XII (2017-18) Class: Xii Biology (044) Marking Scheme Time: 3hours MM:70Nitin MhatreNo ratings yet
- Hsslive Xi Biology Dec 2023 Key DR SunilDocument6 pagesHsslive Xi Biology Dec 2023 Key DR Sunilkgadarsh0No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Biology 2019 Question Paper Solution Set 4Document14 pagesCBSE Class 12 Biology 2019 Question Paper Solution Set 4PavanNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Biology 2019 Question Paper Solution Set 1Document15 pagesCBSE Class 12 Biology 2019 Question Paper Solution Set 1Shaanika Justin13No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Biology Question Paper Solution 2015Document16 pagesCBSE Class 12 Biology Question Paper Solution 2015Shubh MishraNo ratings yet
- Sample Question Paper II Class XII (2016-17) BiologyDocument7 pagesSample Question Paper II Class XII (2016-17) BiologyAwaish KhanNo ratings yet
- High Yield Test #1 (Level 1) - NEW NCERTDocument23 pagesHigh Yield Test #1 (Level 1) - NEW NCERTArshia PatniNo ratings yet
- New Senior Secondary Mastering Biology (Second Edition) Book 2 SolutionsDocument3 pagesNew Senior Secondary Mastering Biology (Second Edition) Book 2 SolutionsHarry LeungNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 BiologyWorksheetsDocument36 pagesCBSE Class 12 BiologyWorksheetsHarshitNo ratings yet
- Xii Biology SQP 2018 19Document11 pagesXii Biology SQP 2018 19KOMAL NAVARIYANo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - The Cell As The Basic Unit of LifeDocument5 pagesChapter 2 - The Cell As The Basic Unit of LifeGrace LeungNo ratings yet
- 2pu - Midterm-2022 Scheme of EvaluationDocument10 pages2pu - Midterm-2022 Scheme of EvaluationhosamaneramaswamyNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Biology Question Paper Solutions Set 57-1-1Document12 pagesCBSE Class 12 Biology Question Paper Solutions Set 57-1-1AvinashhNo ratings yet
- Suggested Answers To Exercise and Reading To Learn: CH 11 Cell Cycle and DivisionDocument15 pagesSuggested Answers To Exercise and Reading To Learn: CH 11 Cell Cycle and DivisionCharmine HolmesNo ratings yet
- F4 BIO2 Year End 2022 AnswersDocument9 pagesF4 BIO2 Year End 2022 AnswersArsyad DanishNo ratings yet
- Biology Sample PapersDocument5 pagesBiology Sample PapersAnsuman PadhiNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Principles of InheritanceDocument59 pagesUnit 1 Principles of InheritanceAshley Nicole V. SangoyoNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Biology 2019 Question Paper Solution Set 2Document14 pagesCBSE Class 12 Biology 2019 Question Paper Solution Set 2Yuvraj MehtaNo ratings yet
- 2009 (Dib Et Al.) Isolation of Bacteria From Remote High Altitude Andean Lakes Able To Grow in The Presence of AntibioticsDocument11 pages2009 (Dib Et Al.) Isolation of Bacteria From Remote High Altitude Andean Lakes Able To Grow in The Presence of AntibioticsDaniel AlonsoNo ratings yet
- Senior School Certificate Examination COMPARTMENT (2015) Marking Scheme - Biology (Theory) Expected Answers/Value Points General InstructionsDocument8 pagesSenior School Certificate Examination COMPARTMENT (2015) Marking Scheme - Biology (Theory) Expected Answers/Value Points General InstructionsRishiraj PatidarNo ratings yet
- Set B Skema Jawapan Soalan No. 1: Peperiksaan Percubaan SPM 2018 4551/2 Biologi Kertas 2 Ogos 2018Document16 pagesSet B Skema Jawapan Soalan No. 1: Peperiksaan Percubaan SPM 2018 4551/2 Biologi Kertas 2 Ogos 2018Sue SuhailaNo ratings yet
- BIO100 LE2ReviewerDocument2 pagesBIO100 LE2ReviewerMariel De Leon GinesNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Biology Question Paper Solution 2010 Set 1Document8 pagesCBSE Class 12 Biology Question Paper Solution 2010 Set 1Bhavya PatelNo ratings yet
- Handout ScienceTechnologySociety JimenezJasonDocument6 pagesHandout ScienceTechnologySociety JimenezJasonNico John Bauzon CapuaNo ratings yet
- 1) What Is Water Potential?Document4 pages1) What Is Water Potential?Tsheyang LhazomNo ratings yet
- Suggested Answers To Exercise and Reading To LearnDocument24 pagesSuggested Answers To Exercise and Reading To Learnsafas agsaNo ratings yet
- SMK Dpha Gapor Biology STPM: Trial Exam P3 2017 Section ADocument6 pagesSMK Dpha Gapor Biology STPM: Trial Exam P3 2017 Section AViola Voon Li WeiNo ratings yet
- Biology Theory Marking Guide DistrictDocument5 pagesBiology Theory Marking Guide Districtitangishaka alphonseNo ratings yet
- Expression and Localization of Laminin-5 Subunits in The Mouse IncisorDocument7 pagesExpression and Localization of Laminin-5 Subunits in The Mouse Incisornovi putri ayuNo ratings yet
- AL Biology 1989 Paper 1 MarkingDocument12 pagesAL Biology 1989 Paper 1 Markingapi-3860987No ratings yet
- The Water Lily Genome and The Early Evolution of Flowering PlantsDocument10 pagesThe Water Lily Genome and The Early Evolution of Flowering PlantsJohanna AriasNo ratings yet
- Biology 36Document10 pagesBiology 36Suhas SnNo ratings yet
- Answer Scheme Bio Paper 2 PPT f4 2017Document7 pagesAnswer Scheme Bio Paper 2 PPT f4 2017Norfaezah RomliNo ratings yet
- Revision F4 C8 Dynamic EcosystemDocument35 pagesRevision F4 C8 Dynamic EcosystemMuhammad NaquibNo ratings yet
- Suggested Answers To Exercise and Reading To Learn: CH 11 Cell Cycle and DivisionDocument4 pagesSuggested Answers To Exercise and Reading To Learn: CH 11 Cell Cycle and DivisionyaNo ratings yet
- Pollen grain structure and reproduction in flowering plantsDocument36 pagesPollen grain structure and reproduction in flowering plantsIHB BHARTINo ratings yet
- Plants: An Introduction to Structure, Function and Water TransportDocument7 pagesPlants: An Introduction to Structure, Function and Water TransportE 3No ratings yet
- Cellular Structure and Function of ParameciumDocument8 pagesCellular Structure and Function of ParameciumRaphael Joshua De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Browne 1998Document14 pagesBrowne 1998harisankarhsNo ratings yet
- Maximum Marks: 100Document14 pagesMaximum Marks: 100Anshit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Plant Systematics: Michael G. SimpsonDocument76 pagesFundamentals of Plant Systematics: Michael G. SimpsonDimo PratannaNo ratings yet
- Class: XII Biology-044 Marking Scheme-2018-19 MM: 70 Time: 3 HoursDocument8 pagesClass: XII Biology-044 Marking Scheme-2018-19 MM: 70 Time: 3 HoursSushant BagulNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 MSDocument7 pagesTopic 2 MSmohamed.salim2509No ratings yet
- First Year Model Exam 2021. Answer KeyDocument4 pagesFirst Year Model Exam 2021. Answer KeyKHADER bhaiNo ratings yet
- Cap. 01 - Amphibian Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument12 pagesCap. 01 - Amphibian Anatomy and PhysiologyNailson JúniorNo ratings yet
- Jeuel Bensi - ACTIVITYDocument2 pagesJeuel Bensi - ACTIVITYJeuel BensiNo ratings yet
- 2015 - P81-Salvia UrmiensisDocument6 pages2015 - P81-Salvia Urmiensismehdiamohamadi67No ratings yet
- Science 7 Quarter 2 Week 6 Living Things and Their EnvironmentDocument8 pagesScience 7 Quarter 2 Week 6 Living Things and Their EnvironmentAveCorpuz BioCornerNo ratings yet
- Class XII Biology 23-24 Pre-Board AnsDocument16 pagesClass XII Biology 23-24 Pre-Board AnsAyushman DharNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Biology 2016 Question Paper Solution Set 1Document10 pagesCBSE Class 12 Biology 2016 Question Paper Solution Set 1Kaja abdul MajeedNo ratings yet
- YangDocument13 pagesYangAJMRNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Science Sample Paper SolutionsDocument6 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science Sample Paper SolutionsNithin AnilNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences P2 Nov 2020 EngDocument17 pagesLife Sciences P2 Nov 2020 EngbabelekhathiniNo ratings yet
- 9201 92011 International Gcse Biology Mark Scheme v2Document13 pages9201 92011 International Gcse Biology Mark Scheme v2laurelxu33No ratings yet
- Atlas of Pyrenulaceae and Trypetheliaceae - Volume 1: Lichenized AscomycotaFrom EverandAtlas of Pyrenulaceae and Trypetheliaceae - Volume 1: Lichenized AscomycotaNo ratings yet
- AP Environmental Science Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date ReviewFrom EverandAP Environmental Science Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date ReviewNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument6 pagesBiologySuraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Transport in PlantsDocument3 pagesChapter 8 - Transport in PlantsLeann LeeNo ratings yet
- Class 11th Complete BotanyDocument52 pagesClass 11th Complete Botanymohammedibnu456No ratings yet
- Bacterial Leaf Spot and Tipburn GuideDocument4 pagesBacterial Leaf Spot and Tipburn GuideAlvin WatinNo ratings yet
- The Origin of Epiphytic CactiDocument126 pagesThe Origin of Epiphytic Cactikengelking8No ratings yet
- ID Komposisi Kimia Dan Keawetan Alami 20 JeDocument11 pagesID Komposisi Kimia Dan Keawetan Alami 20 JeMeikaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Plant Growth and DevelopmentDocument13 pagesModule 1 Plant Growth and DevelopmentJamie VillaceranNo ratings yet
- INVESTIGATORY Project - Dispersal of Seeds 1 (Final)Document27 pagesINVESTIGATORY Project - Dispersal of Seeds 1 (Final)Uma100% (3)
- Edexcel iGCSE Biology Plant ReproductionDocument2 pagesEdexcel iGCSE Biology Plant ReproductionNeo MafukidzeNo ratings yet
- Mughal GardensDocument46 pagesMughal GardensparvinmalickNo ratings yet
- Toxic and Non-Toxic Plant List - Cats - ASPCADocument81 pagesToxic and Non-Toxic Plant List - Cats - ASPCAÁlvaro GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Science 7 w5Document5 pagesScience 7 w5fitz zamoraNo ratings yet
- Stomata ExperimentDocument15 pagesStomata Experimentumict100% (1)
- Heterokont Chloroplast EvolutionDocument22 pagesHeterokont Chloroplast EvolutionsenorgustoNo ratings yet
- College B Otan Y: (NimohDocument1,209 pagesCollege B Otan Y: (NimohFATIMA HASANNo ratings yet
- Coffee EstablishmentDocument23 pagesCoffee EstablishmentAMERUDIN DIMALANASNo ratings yet
- Real Estate Finance 9Th Edition Wiedemer Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument25 pagesReal Estate Finance 9Th Edition Wiedemer Test Bank Full Chapter PDFMichaelHughesafdmb100% (7)
- Botany Laboratory ManualDocument22 pagesBotany Laboratory ManualKEVIN REY GUIRITANNo ratings yet
- Lemerenhons Agriculture Pride - Errol GonzalesDocument3 pagesLemerenhons Agriculture Pride - Errol Gonzalesroger lacuartaNo ratings yet
- Materi 3 - Budidaya RL (Bibit-Panen)Document60 pagesMateri 3 - Budidaya RL (Bibit-Panen)NurhasanahNo ratings yet
- List of PhilesDocument5 pagesList of Phileskatts4u100% (1)
- Poisonous weeds threaten livestockDocument6 pagesPoisonous weeds threaten livestockCla SaguilNo ratings yet
- Flowering Handout1Document8 pagesFlowering Handout1homoriNo ratings yet
- Karakterisasi Meristem Ujung Tajuk Planlet Dendrobium (Orchidaceae) Setelah Penambahan Zat Pengatur Tumbuh BA (Benzyl Adenin)Document6 pagesKarakterisasi Meristem Ujung Tajuk Planlet Dendrobium (Orchidaceae) Setelah Penambahan Zat Pengatur Tumbuh BA (Benzyl Adenin)YusnaaNo ratings yet
- SREO BiologyDocument8 pagesSREO BiologySaktheeswaran VNo ratings yet
- No-Foam Wreaths: Get Ready For A Blooming Beautiful ChristmasDocument76 pagesNo-Foam Wreaths: Get Ready For A Blooming Beautiful ChristmasTaniNo ratings yet
- Bio101 Important Short NotesDocument23 pagesBio101 Important Short Notesasma zahidNo ratings yet
- EEB XVIII PerumalDocument7 pagesEEB XVIII PerumalDr. Prasad B. O.No ratings yet
- PteridophytesDocument4 pagesPteridophytesprathitaprilNo ratings yet
- Viviana Stevenson - Sweet Potato Lab Final ReportDocument2 pagesViviana Stevenson - Sweet Potato Lab Final Reportapi-535565679No ratings yet