Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SankalpBharat Capsule 241
SankalpBharat Capsule 241
Uploaded by
chetandubey938Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SankalpBharat Capsule 241
SankalpBharat Capsule 241
Uploaded by
chetandubey938Copyright:
Available Formats
1
SANKALP BHARAT
Photosynthesis in Higher Plants Worksheet-01
Fill in the blanks
1. In Von Mohl’s experiment ………………. absorbed CO2
2. JoshephPriestely performed a series of experiment that revealed the essential role of in growth of plant……………
3. Ingenhousz by his experiment give importance of …………………….
4. Bubble produce by aquatic plant in bright sunlight prove by Ingenhousz…………………
5. Von sach showed that……………… substance in plant located in special bodies
6. T.W. Engleman worked on …………. algal and use ……………… bacteria to detect site of O2 production
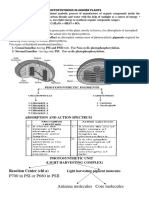
7. First action spectrum was described by …………...which roughly resemble ……………….. chlorophyll
8. On …………….. location PSII present and on ………………. location PS I present in chloroplast
9. Location of photolysis of water is …………………
10. …………..primary acceptor of PS I which can reduce ………………. in cyclic flow of e-
11. PQ is reduced by……………in non-cyclic flow of e- and by in cyclic flow of of e-
12. In light less than 680 nm PQ obtain e- from ……………..
13. FNR is another name for ……………….. enzyme
14. Warburg effect is related with……………
15. Photolysis of water occur when PS II is in state
16. In light Rxn e- of water reduced ……………
17. In dark Rxn e- of water use to reduce…………….
18. No. of e- require to produce 5 O2 molecule…………….
19. Sequence of ETS in non-cyclic flow of e- flow B/w PS II and PS I is ……………
20. Which is hydrogen carrier in ETS B/W PS II and PS I……………….
21. …………and ……………process decrease PH in lumen of Granal thylakoid
22. Process increase PH in stroma and part of light Rxn…………….
23. DCMU block …………….and paraquet block……….
24. No.of photon require to produce 6 O2 molecule……………
25. …………….. e- carrier are part of non-cyclic flow of electron but not cyclic and located b/w PS I and PSII
26. Location O2 production in chloroplast ………….
27. How pH decrease in stromal thylakoid is …………………
28. ………………pigment not have phytol tail but have mg and N
29. ……….. and …………….. pigment are water soluble and present in plastids
30. …………….. is water soluble pigment present in cytoplasm
31. …………. And ………… location in chloroplast and mitochondria develop H+ gradient
32. In ETS B/W PS II and PS I …………….. is hydrogen carrier reduced by…………….
33. Requirement for chemiosmotic hypothesis is ……………………….
34. ……………… and …………….. are sugars in C-3 cycle
35. RuBisco when act oxygenase it form …………….and……………..
36. ……………is first product of C-3 cycle and it is chemically ………..
37. No. of ATP requires for reduction of 12 molecule of PGA…………….
38. No. of PGA form when we fix 2 CO2 in C-3 cycle……………..
2
39. No of ATP require to reduce one PGA ………..
40. ………ATP and ……… NADPH require to produce one Glucose in C-3 cycle
41. Is first produce sugar in C-4 cycle……………
42. In ……………. organelle decarboxylation occurs in photorespiration
43. To produce 10 CO2 in photorespiration no. of RuBP require is…………….
44. ………………and ……………. type of chloroplast present in C-4 plant
45. Phaeophytin present in ………….type of cell in C-4 plant
46. e- from H2O is taken from mesophyll to bundle sheath cell in ………….. form in C-4 cycle
47. If DCMU is use in C-4 plant than ATP synthesis occur in ……………. type of cell
48. ……………cell have impervious wall in C-4 plant
49. Below ……………. point light intensity is limiting
50. At high CO2 conc. ……………plant will get more benefit
51. At low light intensity Inc. in CO2 in C-3 is …………...and for C-4 is …………
52. Current environment CO2 conc. Is limiting for …………… not for …………….
53. No. of ATP require to form 1 glucose in C-4 plant……………….
54. Inc. in temp. can affect ……more than…………..
55. Water as limiting factor mainly affect …………….and …………….. in plant
56. In summer afternoon mostly …………….. is limiting factor
57. …………… enzyme is common in C-4 plant and CAM plants
58. In CAM plants vacuole store CO2 in form of …………….
59. ……………and ……………form by OAA in C-4 plant for transport
60. In ………… cell non-cyclic photophosphorylation occur in C-4 plant
3
Answer Key
1. KOH 31. Lumen of thylakoid- chloroplast, Intermembrane
2. Air space in mitochondria
3. Light 32. Plasto Quinone is hydrogen carrier and reduced by
4. Oxygen plastocyanin
5. Green substance 33. Intact membrane, H+ gradient, proton pump, F0-F1
6. Green algae, Cladophora and aerobic particle
7. T.W engleman and absorption spectrum of Chl a 34. RUBP and PGAL
and Chl b 35. It forms PGA and Phosphoglycolate
8. Granal thylakoid- PS II and Stromal lamellae and 36. PGA and it is acid
granal thylakoid –PS I 37. 24 ATP (1 molecule require 2 ATP for reduction)
9. PS II lumen 38. 4PGA (2 PGA when 1 CO2 is fixed)
10. Fes and plasto Quinone in cyclic flow 39. 2 ATP
11. Phaeophytin in non-cyclic and fes in non-cyclic 40. 18 ATP and 12 NADPH
flow 41. PGAL
12. Phaeophytin 42. Mitochondria
13. Ferrodexin NADP reductase 43. 2 RUBP give one CO2 in photorespiration so answer
14. Oxygen is
15. Electron deficient state or oxidized state 44. Granal- mesophyll cell and a granal – bundle sheath
16. NADP into NADPH cell
17. Electron of water in NADPH and it reduce PGA into 45. Mesophyll cell
PGAL 46. Malate
18. Number of electrons for one oxygen molecule is 4, 47. DCMU block PS I and PS II present in Mesophyll
so for 5 oxygen molecules is 20 electrons cell in C-4 plant so Bundle sheath cell is functional
19. Phaeophytin – plastoquinone –cytb6f-plastocyanin and form ATP
20. plasto Quinone 48. Bundle sheath cell
21. Photolysis and transfer of electron from PQ to cyt 49. Saturation point
b6f 50. C-3 plant
22. Transport of proton from stroma to lumen and 51. No effect at low intensity
formation of NADPH in stromal side will decrease 52. Limiting for C-3 not for C-4
proton and increase PH 53. 30
23. DCMU block PSII and Paraquat block PSI 54. Increase in temperature effect more to Dark reaction
24. One oxygen 8 photon so for 6 oxygen molecule 48 than light reaction
photon 55. Rate of transpiration and Surface area
25. Phaeophytin 56. Water
26. Lumen of thylakoid 57. PEPcase
27. By electron flow only 58. Malate
28. Chl c (only 35 carbon) 59. Malate and aspartate
29. Phycoerythin and phycocyanin 60. Bundle sheath cell
30. Anthocyanin
You might also like
- 2016 IM Boards Mayo CLinicDocument901 pages2016 IM Boards Mayo CLinicGladys Paredes100% (5)
- Human Anatomy and Physiology Syllabus. Allan RevisedDocument7 pagesHuman Anatomy and Physiology Syllabus. Allan RevisedAllan IgbuhayNo ratings yet
- Mark Marlatt - Photosynthesis Pogil Track D - 5261224Document11 pagesMark Marlatt - Photosynthesis Pogil Track D - 5261224api-544304176No ratings yet
- WR Pee Ole) / Lot 1 Wan: - / NeuroscienceDocument566 pagesWR Pee Ole) / Lot 1 Wan: - / NeuroscienceItachi UchihaNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of Joints PDFDocument53 pagesStructure and Function of Joints PDFABHAY KUMARNo ratings yet
- MCAT Sample Questions Template 1Document42 pagesMCAT Sample Questions Template 1gendut_novri0% (1)
- Problem Set - Enzymes From LehningerDocument11 pagesProblem Set - Enzymes From LehningervioletbrownNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10. Photosynthesis AnswersDocument3 pagesChapter 10. Photosynthesis Answerskarlitarmz100% (2)
- Cellular Respiration PogilDocument7 pagesCellular Respiration PogilEmmaNo ratings yet
- FCM Lec 18 Family Life CycleDocument4 pagesFCM Lec 18 Family Life Cycleabstabs100% (2)
- AP Biology Test Cheat Sheet (Photosynthesis)Document22 pagesAP Biology Test Cheat Sheet (Photosynthesis)Mr. IntelNo ratings yet
- Ester Formation and Hydrolysis and Related ReactionsFrom EverandEster Formation and Hydrolysis and Related ReactionsNo ratings yet
- Function of PhotosynthesisDocument58 pagesFunction of PhotosynthesisJulian ChristopherNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 21 PhotosynthesisDocument12 pagesCHAPTER 21 Photosynthesis楊畯凱No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Short ConceptsDocument51 pagesPhotosynthesis Short Conceptsauguste noe100% (2)
- Traction: Dr.K.Arvind Natarajan 1 Year MS OrthoDocument30 pagesTraction: Dr.K.Arvind Natarajan 1 Year MS OrthoKarthick50% (2)
- Genetic Disorders PDFDocument38 pagesGenetic Disorders PDFEllen Mae PrincipeNo ratings yet
- STPM Biology Past Year QuestionDocument8 pagesSTPM Biology Past Year QuestionMc Donalds Ohl Ohlsen100% (2)
- Chapter 10 Multiple Choice Practice: CO H O O PDocument7 pagesChapter 10 Multiple Choice Practice: CO H O O PShaira CogollodoNo ratings yet
- François Ascher, Metapolis, Ou L'avenir Des VillesDocument1 pageFrançois Ascher, Metapolis, Ou L'avenir Des VillesJoren SteensNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis in Higher Plants: Class: 11 Sub: Biology Chapter - 13Document7 pagesPhotosynthesis in Higher Plants: Class: 11 Sub: Biology Chapter - 13kuldeep kumarNo ratings yet
- Biology - XI - Photosynthesis in Higher Plants - MCQs 3Document26 pagesBiology - XI - Photosynthesis in Higher Plants - MCQs 3SDO BSNL NALAGARHNo ratings yet
- Chapter-13: Photosynthesis in Higher PlantsDocument8 pagesChapter-13: Photosynthesis in Higher PlantssujushNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument14 pagesPhotosynthesisArpan MondalNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis 90 QuestionsDocument92 pagesPhotosynthesis 90 QuestionsNITISH KUMARNo ratings yet
- 2 Semester Final Exam (2009A.Y.) Grade 11 Subject: Biology Time: 1:10 Mark: 40%Document5 pages2 Semester Final Exam (2009A.Y.) Grade 11 Subject: Biology Time: 1:10 Mark: 40%Nahom GarefoNo ratings yet
- 3119Document6 pages3119leenaburiuliNo ratings yet
- Chapter-4 Photosynthesis in Higher Plants: Very Short Answers QuestionsDocument10 pagesChapter-4 Photosynthesis in Higher Plants: Very Short Answers QuestionsPraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis in Higher PlantsDocument6 pagesPhotosynthesis in Higher PlantskhushiNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis in Higher PlantsDocument13 pagesPhotosynthesis in Higher PlantsAjay JamwalNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Learning Activity Worksheets (LAW) General Biology 1 Grade 12Document4 pagesDepartment of Education: Learning Activity Worksheets (LAW) General Biology 1 Grade 12Maria Bettina DizonNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Exploration Guide - Cell Metabolism #3Document6 pagesAP Biology Exploration Guide - Cell Metabolism #3Gunnar OlsonNo ratings yet
- Biosci 3Document15 pagesBiosci 3MARJORYNo ratings yet
- Biology - XI - Photosynthesis in Higher Plants - MCQs 1Document105 pagesBiology - XI - Photosynthesis in Higher Plants - MCQs 1SDO BSNL NALAGARHNo ratings yet
- Presentation G3. Lec 4. The Cell 2Document23 pagesPresentation G3. Lec 4. The Cell 2Nguyễn Phan Tuấn AnhNo ratings yet
- Light Dependent RXNDocument10 pagesLight Dependent RXNChristoPher TorioNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 11 ch11 Class 11Document4 pagesWorksheet 11 ch11 Class 11akilapaul17682No ratings yet
- 11 Biology Notes Ch13 Photosymthesis in Higher PlantsDocument6 pages11 Biology Notes Ch13 Photosymthesis in Higher PlantsAAYUSH KUMARNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 13 - Photosynthesis in Higher Plants Important Questions 2022-23Document13 pagesCBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 13 - Photosynthesis in Higher Plants Important Questions 2022-23tytytfbfvhbvb dhbvNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis (KEY)Document6 pagesPhotosynthesis (KEY)kylevNo ratings yet
- Respiration 5.2.1Document11 pagesRespiration 5.2.1bexNo ratings yet
- Biology CH 13 TestDocument1 pageBiology CH 13 TestVishal MalikNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisCrackpot TestDocument1 pagePhotosynthesisCrackpot TestnatalieNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology Imp Ch13 2Document4 pages11 Biology Imp Ch13 2Kiran KrutanjaliNo ratings yet
- APBioCh10ReadingGuide10 11Document2 pagesAPBioCh10ReadingGuide10 11Sergio LivingroomsNo ratings yet
- Prochlorophytes), Also Generates Oxygen. The: Photosynthesis Occurs On Thylakoid MembranesDocument6 pagesProchlorophytes), Also Generates Oxygen. The: Photosynthesis Occurs On Thylakoid MembranesPearl Jean FrueldaNo ratings yet
- Efficiency of ATP ProductionDocument10 pagesEfficiency of ATP ProductionMichael NyaongoNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument44 pagesPhotosynthesisBruce MendezNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Light Reaction, Dark Reaction (Calvin Cycle) and c3 Plant, c4 Plant, and Cam PlantDocument6 pagesPhotosynthesis Light Reaction, Dark Reaction (Calvin Cycle) and c3 Plant, c4 Plant, and Cam Plantwahyunipbiologi100% (1)
- Respiration in Hingher PlantsDocument6 pagesRespiration in Hingher PlantsTrillionare HackNo ratings yet
- Cuestionario Fisiotecnia en InglésDocument4 pagesCuestionario Fisiotecnia en InglésMokr Guerrero EsperanzaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis: Capturing EnergyDocument26 pagesPhotosynthesis: Capturing EnergyJustineMarieClarisaCruzNo ratings yet
- Biology Practice PhotosynthesisDocument7 pagesBiology Practice Photosynthesisbrowhocares121212No ratings yet
- Biology-Photosynthsis WorksheetDocument3 pagesBiology-Photosynthsis WorksheetAbhipshaNo ratings yet
- Ch05 Answerkey Hoefnagels EssDocument7 pagesCh05 Answerkey Hoefnagels EssCry The WolffNo ratings yet
- Target Test PariDocument23 pagesTarget Test PariAditya ChawlaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis in Higher PlantsDocument17 pagesPhotosynthesis in Higher Plantsyahake5036No ratings yet
- Wa0009Document9 pagesWa0009law fullNo ratings yet
- General Biology Quarter 2 - Week 7 Name: Rona Mae N. Betita Grade and Section: STEM-12 Vygotsky Intext Questions 11.1Document4 pagesGeneral Biology Quarter 2 - Week 7 Name: Rona Mae N. Betita Grade and Section: STEM-12 Vygotsky Intext Questions 11.1Rona Mae BetitaNo ratings yet
- CHP 5 PhotosynthesisDocument43 pagesCHP 5 PhotosynthesisSIMBA The Lion KingNo ratings yet
- 5 FotosintesiDocument29 pages5 FotosintesiSerena DamianNo ratings yet
- Biology Unit 5 Review QuestionsDocument9 pagesBiology Unit 5 Review QuestionsMoa ArmyNo ratings yet
- Photo SystemsDocument8 pagesPhoto SystemsTinna Devi ArmasamyNo ratings yet
- Botany - (K) Photosynthesis - KeyDocument2 pagesBotany - (K) Photosynthesis - Keykmonishasai7No ratings yet
- Botany 4Document4 pagesBotany 4Vibushitha KabardineshwarNo ratings yet
- MY Bio 12 Photosynthesis AssignmentDocument6 pagesMY Bio 12 Photosynthesis AssignmentGSemenkovaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Bioenergetics (Part 2)Document19 pagesChapter 4 - Bioenergetics (Part 2)Nasir KhanNo ratings yet
- Q2 STEM General Biology 1 Week 2Document4 pagesQ2 STEM General Biology 1 Week 2MarkElijah ObelNo ratings yet
- Progress in Phytochemistry: Volume 6From EverandProgress in Phytochemistry: Volume 6L. ReinholdNo ratings yet
- Advertisement For The Post of Group A, B & C at AIIMS, New DelhiDocument17 pagesAdvertisement For The Post of Group A, B & C at AIIMS, New DelhiAvinash SharmaNo ratings yet
- G8 Biology Lesson 2 Heredity Inheritance and Variation of TraitsDocument2 pagesG8 Biology Lesson 2 Heredity Inheritance and Variation of TraitsCindy CrahayNo ratings yet
- Bio Tools BookletDocument5 pagesBio Tools BookletTanvi GargNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2021-08-31 at 21.05.45Document1 pageScreenshot 2021-08-31 at 21.05.45Claudio ErasmusNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 SummaryDocument5 pagesChapter 13 SummaryCharlotteNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts - IntroductionDocument18 pagesBasic Concepts - IntroductionDj ArofNo ratings yet
- Process Modeling and Simulation For Chemical Engineers, Theory and Practice (2017)Document52 pagesProcess Modeling and Simulation For Chemical Engineers, Theory and Practice (2017)marmaduke32No ratings yet
- 1.2 Unifying Themes of BiologyDocument20 pages1.2 Unifying Themes of BiologyJofel CañadaNo ratings yet
- Darwin Digital Library of Evolution Alphabetical Listing of WorksDocument211 pagesDarwin Digital Library of Evolution Alphabetical Listing of WorksEduardo Martín PérezNo ratings yet
- Lec 5 - Cryopreservation - Freezing Cells - v2Document24 pagesLec 5 - Cryopreservation - Freezing Cells - v2Sama Al HayekNo ratings yet
- A Genetic Algorithm Approach To Solve The Shortest Path Problem For Road MapsDocument4 pagesA Genetic Algorithm Approach To Solve The Shortest Path Problem For Road MapswendersoncsdepNo ratings yet
- Download textbook Ganongs Review Of Medical Physiology Kim E Barrett ebook all chapter pdfDocument53 pagesDownload textbook Ganongs Review Of Medical Physiology Kim E Barrett ebook all chapter pdfmichael.penland389100% (8)
- Biocatalysis and Agricultural BiotechnologyDocument13 pagesBiocatalysis and Agricultural BiotechnologyDANIELA GELVEZNo ratings yet
- 253 2022 Article 12270Document12 pages253 2022 Article 12270Novia khasanahNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles JigsawDocument10 pagesCell Organelles JigsawSusan VictoriaNo ratings yet
- Biomaterials PDFDocument19 pagesBiomaterials PDFdjurdjicAANo ratings yet
- Lumiskin V2 Techn EngDocument45 pagesLumiskin V2 Techn EngGabriel FloresNo ratings yet
- Matter, Life and GenerationDocument111 pagesMatter, Life and GenerationmarcelloluchiniNo ratings yet
- I Can't Believe It!Document1 pageI Can't Believe It!Jonathan PrietoNo ratings yet
- MSDS Servvo SV-36Document6 pagesMSDS Servvo SV-36Ricky SeptianNo ratings yet