Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Difference Between Login Shell and Non Login Shell
Uploaded by
logion78839Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Difference Between Login Shell and Non Login Shell
Uploaded by
logion78839Copyright:
Available Formats
Difference between Login shell and Non login shell
howtolamp.com/articles/difference-between-login-and-non-login-shell
Here we will learn the difference between a Login shell and Non login shell.
The shell program, for example Bash, uses a collection of startup scripts to create an
environment. Each script has a specific use and affects the login environment differently.
Every subsequent script executed can override the values assigned by previous scripts.
1) Login shells
A Login shell is started after a successful login, using /bin/login, by reading the
/etc/passwd file. Login shell is the first process that executes under our user ID when we
log in to a session. The login process tells the shell to behave as a login shell with a
convention: passing argument 0, which is normally the name of the shell executable,
with a “ - ” character prepended. For example, for Bash shell it will be -bash .
When Bash is invoked as a Login shell;
→Login process calls /etc/profile
→/etc/profile calls the scripts in /etc/profile.d/
→Login process calls ~/.bash_profile
→~/.bash_profile calls ~/.bashrc
→~/.bashrc calls /etc/bashrc
Login shells include the following.
• Shells created by explicitly telling to login.
examples: # su - | # su -l | # su --login | # su USERNAME - | # su -l
USERNAME | # su --login USERNAME | # sudo -i
• Shells created at login, including X login.
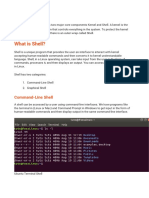
A Login shell can be recognized by the following procedure.
Execute the below command in shell.
# echo $0
If the output is the name of our shell, prepended by a dash, then it is a login shell.
For example -bash, -su etc.
2) Non login shells
A Non login shell is started by a program without a login. In this case, the program just
passes the name of the shell executable. For example, for a Bash shell it will be simply
bash.
When bash is invoked as a Non login shell;
→Non-login process(shell) calls ~/.bashrc
→~/.bashrc calls /etc/bashrc
1/2
→/etc/bashrc calls the scripts in /etc/profile.d/
Non login shells include the following.
• Shells created using the below command syntax.
examples: # su | # su USERNAME
• Graphical terminals
• Executed scripts
• Any other bash instances
A Non login shell can be recognized by the following procedure.
Execute the below command in shell.
# echo $0
If the output is the name of our shell, does not prepend by a dash, then it is a Non login
shell.
For example bash, su etc.
2/2
You might also like
- The Role of Shells in The Linux Environment - Linux Shell Scripting Tutorial - A Beginner's HandbookDocument2 pagesThe Role of Shells in The Linux Environment - Linux Shell Scripting Tutorial - A Beginner's HandbookpiyushNo ratings yet
- Setting PATH To Change at Login or NotDocument4 pagesSetting PATH To Change at Login or NotscherzocrkNo ratings yet
- Bash Main FilesDocument2 pagesBash Main FilesYOUNEXISNo ratings yet
- Unix Shell Programming WorkshopDocument35 pagesUnix Shell Programming WorkshopSachin JainNo ratings yet
- Practical 5Document2 pagesPractical 5Dhruv. Sharma.No ratings yet
- Intro To UNIX Shell Scripting, Writing Pipelines, and Parallelizing TasksDocument13 pagesIntro To UNIX Shell Scripting, Writing Pipelines, and Parallelizing TasksEduardo Luis Escofet BatistaNo ratings yet
- Bash ShellDocument35 pagesBash ShellPalak GandhiNo ratings yet
- What Is Shell ScriptingDocument4 pagesWhat Is Shell ScriptingAziz Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Cis 208 Lecture Notes Introduction To Shell ProgrammingDocument7 pagesCis 208 Lecture Notes Introduction To Shell ProgrammingDeepak DewanganNo ratings yet
- Shell Prompt Shell Types Shell Scripts CommentsDocument7 pagesShell Prompt Shell Types Shell Scripts CommentsManali MahamuniNo ratings yet
- Bash Guide For BeginersDocument11 pagesBash Guide For BeginersJoha KushtiaNo ratings yet
- Unix - What Is Shells?: Shell PromptDocument3 pagesUnix - What Is Shells?: Shell Promptseenuvasan1985No ratings yet
- TCSH Scripting MCSR BasicDocument35 pagesTCSH Scripting MCSR Basicsatya28No ratings yet
- Shell Scripting: A Linux Foundation Training PublicationDocument5 pagesShell Scripting: A Linux Foundation Training Publicationdimoni_etNo ratings yet
- Local Security Shell ScriptingDocument5 pagesLocal Security Shell Scriptingdimoni_etNo ratings yet
- U4 - The UNIX Shell Offerings - 39 - 23-11-20 1Document2 pagesU4 - The UNIX Shell Offerings - 39 - 23-11-20 1Shantanu AgnihotriNo ratings yet
- Shell Programming Module2 Part2Document120 pagesShell Programming Module2 Part2HIMANK MISHRANo ratings yet
- Bash Scripting - MDDocument5 pagesBash Scripting - MDAlaa BaraziNo ratings yet
- Shell ScriptDocument4 pagesShell ScriptAnnie MastiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document14 pagesAssignment 2Muhammad Adil NaeemNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document14 pagesAssignment 1Birhaneselasie AbebeNo ratings yet
- Week 9 Lecture NotesDocument44 pagesWeek 9 Lecture NotesJunior EkenNo ratings yet
- Linux Shell ProgrammingDocument143 pagesLinux Shell ProgrammingSangline ThomasNo ratings yet
- Summer 2021 Lab 5Document21 pagesSummer 2021 Lab 5mannNo ratings yet
- Shell Scriptingfor Beginners Howto Write Bash Scriptsin LinuxDocument27 pagesShell Scriptingfor Beginners Howto Write Bash Scriptsin LinuxKyla PinedaNo ratings yet
- Unit-5 Shell ScriptingDocument40 pagesUnit-5 Shell ScriptingLinda BrownNo ratings yet
- Executing The Script: Syntax Highlighting in VimDocument3 pagesExecuting The Script: Syntax Highlighting in Vimmarco rossiNo ratings yet
- Bash Startup Files: Invoked As An Interactive Login Shell, or With ' - Login'Document2 pagesBash Startup Files: Invoked As An Interactive Login Shell, or With ' - Login'marco rossiNo ratings yet
- Unix Personal NotesDocument7 pagesUnix Personal NotesChakraborthy CharkaborthyNo ratings yet
- Exp Shell Scrit Interview Q & ADocument25 pagesExp Shell Scrit Interview Q & AChalama ReddyNo ratings yet
- Lab 7 - Bash ScriptDocument10 pagesLab 7 - Bash ScriptNourhan TarekNo ratings yet
- Shell Script ProgrammingDocument14 pagesShell Script ProgrammingSumanta KarNo ratings yet
- Bash Startup ScriptsDocument2 pagesBash Startup Scriptslogion78839No ratings yet
- 30 Bash Script Examples - Linux HintDocument22 pages30 Bash Script Examples - Linux Hintarun0076@gmail.com100% (2)
- Unix ShellsDocument19 pagesUnix ShellsPoornima EgNo ratings yet
- Scripting Languages M2Document29 pagesScripting Languages M2vibaviattigalaNo ratings yet
- Foss Unit 3Document32 pagesFoss Unit 3vigneshwarane257No ratings yet
- Shell Scripts and Grep CommandDocument14 pagesShell Scripts and Grep CommandpmmanickNo ratings yet
- Bash Scripting Tutorial - LinuxConfigDocument23 pagesBash Scripting Tutorial - LinuxConfigpeter hardyNo ratings yet
- Shell Scripting For SysAd The BasicsDocument7 pagesShell Scripting For SysAd The BasicsErwinMacaraigNo ratings yet
- Unit+3 LinuxDocument91 pagesUnit+3 LinuxyawenNo ratings yet
- CyberAces Module3-Bash 5 PracticalUsesDocument16 pagesCyberAces Module3-Bash 5 PracticalUsesPedro FreitasNo ratings yet
- Shells and Shell ScriptsDocument6 pagesShells and Shell ScriptseshwardwNo ratings yet
- System-Wide Configuration Files: /etc/rc3.d/s )Document2 pagesSystem-Wide Configuration Files: /etc/rc3.d/s )marco rossiNo ratings yet
- Linux Restricted Shell Bypass GuideDocument10 pagesLinux Restricted Shell Bypass GuideanargratosNo ratings yet
- Section 6Document8 pagesSection 6pspc139No ratings yet
- MahrukhBatool LabManual OS LABDocument108 pagesMahrukhBatool LabManual OS LABMahrukh batoolNo ratings yet
- School of Computer Applications Babu Banarasi Das University Lucknow-UPDocument12 pagesSchool of Computer Applications Babu Banarasi Das University Lucknow-UPRumana BegumNo ratings yet
- Lab 1Document5 pagesLab 1MeerShahrukhNo ratings yet
- Shells, Shell Scripting, and The UNIX File SystemDocument19 pagesShells, Shell Scripting, and The UNIX File SystemUtsav BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- 30 Bash Script ExamplesDocument23 pages30 Bash Script ExamplesPhoenix Liebe JeffNo ratings yet
- Unix LabDocument54 pagesUnix LabMuhammad Zuhair KhanNo ratings yet
- BashDocument81 pagesBashceciNo ratings yet
- Executing Shell Commands With PythonDocument12 pagesExecuting Shell Commands With PythonHbsodndkNo ratings yet
- Linux Unit IiiDocument33 pagesLinux Unit IiiAbhishek DhakaNo ratings yet
- Basic Shell ScriptingDocument67 pagesBasic Shell ScriptingRais ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BASHDocument14 pagesIntroduction To BASHPrasanth YgNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document52 pagesChapter 3Leo KingNo ratings yet
- BourneshellDocument71 pagesBourneshellumamaheshbattaNo ratings yet
- Dfsort: ICETOOL Mini-User Guide: Dfsort/Mvs Web SiteDocument58 pagesDfsort: ICETOOL Mini-User Guide: Dfsort/Mvs Web Sitesathish38No ratings yet
- Tibco Iprocess Tips and Troble ShootingDocument8 pagesTibco Iprocess Tips and Troble Shootingsurya43No ratings yet
- Loading Talent Data Using HCM Data LoaderDocument38 pagesLoading Talent Data Using HCM Data LoaderMohammed Kh DerballaNo ratings yet
- Integer Value Name Symbolic Constant File Stream: Unistd.h Stdio.hDocument4 pagesInteger Value Name Symbolic Constant File Stream: Unistd.h Stdio.hliuylNo ratings yet
- Dbms 1Document28 pagesDbms 1Srinu ArnuriNo ratings yet
- Flow Chart SymbolsDocument7 pagesFlow Chart SymbolsAbhishekNo ratings yet
- MA60002 Data Structure and Algorithms (Bhakt)Document2 pagesMA60002 Data Structure and Algorithms (Bhakt)Gaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- D1 L3 Bin Packing AlgorithmDocument14 pagesD1 L3 Bin Packing AlgorithmAlexandru DanielNo ratings yet
- 4 - Chapter 2 - Relational Model of Data - P3Document41 pages4 - Chapter 2 - Relational Model of Data - P3Tran Van Ngoc (K16HL)No ratings yet
- Data Visualisation With Matplotlib - by June Tao Ching - Sep, 2020 - Towards Data ScienceDocument7 pagesData Visualisation With Matplotlib - by June Tao Ching - Sep, 2020 - Towards Data Sciencelalooprasad15No ratings yet
- MD070 OECOGS Generate Cost of Goods Sold AccountDocument24 pagesMD070 OECOGS Generate Cost of Goods Sold AccountMario NesterovicNo ratings yet
- Restricting Characteristics - BI Suite - Business Explorer - SAP LibraryDocument4 pagesRestricting Characteristics - BI Suite - Business Explorer - SAP LibrarysudhNo ratings yet
- 8051 InstructionsDocument44 pages8051 InstructionsSoumya Ranjan PandaNo ratings yet
- Lab # 05 Implementation of SQL Wildcards & OperatorsDocument11 pagesLab # 05 Implementation of SQL Wildcards & OperatorsMehak FatimaNo ratings yet
- 6e02ba PDFDocument108 pages6e02ba PDFanon_204018250No ratings yet
- Ruby Deep DiveDocument262 pagesRuby Deep DiveJaviera Francisca Tapia Bobadilla100% (2)
- Oracle APPS Interview Question AnswersDocument60 pagesOracle APPS Interview Question Answersparvathi12No ratings yet
- Odesk Test HTML 5 Answers For 2014Document6 pagesOdesk Test HTML 5 Answers For 2014ShalabhNo ratings yet
- TAM2 - Operators and Control Structures PDFDocument8 pagesTAM2 - Operators and Control Structures PDFKimCanillasVincereNo ratings yet
- Arduino ProgrammingDocument3 pagesArduino ProgrammingDinesh Sharma100% (1)
- Interview QuestionsDocument13 pagesInterview QuestionsHariprasad Reddy GNo ratings yet
- MSBTE Class Test I - MCQ NewDocument2 pagesMSBTE Class Test I - MCQ NewPrathamesh PatilNo ratings yet
- Asyncio Event in PythonDocument7 pagesAsyncio Event in PythonLeonNo ratings yet
- CalculatorDocument6 pagesCalculatorapi-3765961100% (1)
- Mainframe QuestionnaireDocument34 pagesMainframe QuestionnairebhaskarbhomiaNo ratings yet
- Java Project Report - Your Project NameDocument24 pagesJava Project Report - Your Project NameKUMAR GAURAVNo ratings yet
- DBMS One Mark Questions-NewDocument60 pagesDBMS One Mark Questions-Newlucky75% (8)
- Totalview: Author: Blaise Barney, Lawrence Livermore National LaboratoryDocument33 pagesTotalview: Author: Blaise Barney, Lawrence Livermore National LaboratoryPedro Elias Romero NietoNo ratings yet
- Asm51 TutorialDocument5 pagesAsm51 TutorialdoanvanhienNo ratings yet
- DFA - Problems With SolutionsDocument28 pagesDFA - Problems With SolutionsLahari TummalapalliNo ratings yet