Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bash Main Files
Uploaded by
YOUNEXISCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bash Main Files
Uploaded by
YOUNEXISCopyright:
Available Formats
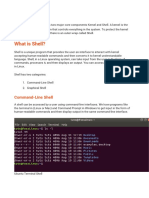
Main point about bash
BASH Files
/etc/profile : It is a system-wide initialization file which is executed when using login shells.
/etc/bash.bashrc : It is system-wide BASH startup file. Runs when we start BASH for the the
first time in our system after turning it on.
/etc/bash.logout : It is system-wide BASH cleanup file. Runs at the time of closing BASH for
cleaning the processes of BASH.
~/.bash_profile : It is user-based BASH initialization file.
~/.bashrc : It is a pre-interactive shell startup file that runs every time we run BASH.
~/.bash_logout : It is cleanup file for every shell we have opened.
BASH Startup Scripts and their execution order
Login Shells
Login shells are those, which gets started when we login into a system. Login shells are used to setup
an environment for our system. When environment setup is complete, the control is passed to Non-
Login shell.
A login shell perform the following on startup,
1. On starting, a login shell calls /etc/profile, which runs first every time we login to our system.
2. On succesful execution, the following files are called, *~/.bash_profile, ~/.bash_login &
~/.profile whose roles are described above.
3. The file ~/.bash_profile on running calls ~/.bashrc which in turn further calls /etc/bashrc.
Each of them perform different level of initialization as explained.
Non-Login Shells
Non-Login shells are those, which are started after we have completed the login procedure for a
system.
As the environment for the system is setup by the Login shell itself, so the non-login shell perform the
following on startup,
1. It calls ~/.bashrc which calls /etc/bash.bashrc which in turn calls /etc/profile.d
The functionality for all the files is proveded above in the section mentioning different
BASH files.
BASH Logout Script
When Login Shell exits, BASH exectes the file ~/.bash_logout that logs out the user and calls the
/etc/bash.logout for further clearing the whole system.
Debugging a BASH Script
To debug a shell script, we can use the command
bash -x SCRIPT
Now, both the input as well as output will be visible.
To debug a shell script every time we run it, we can also modify the shebang line and suppy the
debugging option there only. The modified shebang is,
#!/bin/bash -x
We can also specify the debugging mode after the shebang line using,
#!/bin/bash
set -x
Converting BASH Scripts to Binary
BASH Scripts can be converted to binaries to hide the functionality of the shell script and prevent users
from accessing it to change or modify its source code.
For conversion of a BASH Script to binary, gcc & shc must be installed on our device.
shc : shc is a command line utility and is a BASH compiler. It is used for the functionality of hiding the
source code & to remove the dependencies to the file by merging them all into a single file.
To convert the BASH script to binary,
shc -f FILE
You might also like
- Configuration of a Simple Samba File Server, Quota and Schedule BackupFrom EverandConfiguration of a Simple Samba File Server, Quota and Schedule BackupNo ratings yet
- Linux Shell Initialization and RoleDocument2 pagesLinux Shell Initialization and RolepiyushNo ratings yet
- Bash Startup ScriptsDocument2 pagesBash Startup Scriptslogion78839No ratings yet
- Bash Startup Files: Invoked As An Interactive Login Shell, or With ' - Login'Document2 pagesBash Startup Files: Invoked As An Interactive Login Shell, or With ' - Login'marco rossiNo ratings yet
- Bash Guide For BeginersDocument11 pagesBash Guide For BeginersJoha KushtiaNo ratings yet
- What Is Shell ScriptingDocument4 pagesWhat Is Shell ScriptingAziz Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Foss Unit 3Document32 pagesFoss Unit 3vigneshwarane257No ratings yet
- Bash ShellDocument35 pagesBash ShellPalak GandhiNo ratings yet
- Setting PATH To Change at Login or NotDocument4 pagesSetting PATH To Change at Login or NotscherzocrkNo ratings yet
- BashDocument112 pagesBashDarkoNo ratings yet
- Booting Up and Shutting Down A Primer For Troubleshooting: BootloadersDocument7 pagesBooting Up and Shutting Down A Primer For Troubleshooting: BootloadersFEI WANNo ratings yet
- Cis 208 Lecture Notes Introduction To Shell ProgrammingDocument7 pagesCis 208 Lecture Notes Introduction To Shell ProgrammingDeepak DewanganNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Login Shell and Non Login ShellDocument2 pagesDifference Between Login Shell and Non Login Shelllogion78839No ratings yet
- BashDocument81 pagesBashceciNo ratings yet
- BASHDocument6 pagesBASHdeniseNo ratings yet
- System-Wide Configuration Files: /etc/rc3.d/s )Document2 pagesSystem-Wide Configuration Files: /etc/rc3.d/s )marco rossiNo ratings yet
- Linux Bash Beginners - Guide 4Document2 pagesLinux Bash Beginners - Guide 4marco rossiNo ratings yet
- Introduction Bash Shell ScriptingDocument7 pagesIntroduction Bash Shell ScriptingDanielColoradoGaviriaNo ratings yet
- Shells, Shell Scripting, and The UNIX File SystemDocument19 pagesShells, Shell Scripting, and The UNIX File SystemUtsav BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Installing PowerShell On macOSDocument6 pagesInstalling PowerShell On macOSAnonymous enr3NGjNo ratings yet
- Bash ManualDocument98 pagesBash ManualcrazydmanNo ratings yet
- Unix ShellsDocument19 pagesUnix ShellsPoornima EgNo ratings yet
- Bash PDFDocument77 pagesBash PDFSxiretiNo ratings yet
- Shell offerings guideDocument2 pagesShell offerings guideShantanu AgnihotriNo ratings yet
- The PATH Environment VariableDocument1 pageThe PATH Environment VariableRoshan JangirNo ratings yet
- Linux Day 3 - Bash Shell ScriptingDocument7 pagesLinux Day 3 - Bash Shell Scriptingichbin1199No ratings yet
- Introduction To BASHDocument14 pagesIntroduction To BASHPrasanth YgNo ratings yet
- Update BashrcDocument1 pageUpdate BashrcSaurabh SahuNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument7 pagesDocumentAndrew XNo ratings yet
- BashDocument8 pagesBashSmriti KakkarNo ratings yet
- Executing The Script: Syntax Highlighting in VimDocument3 pagesExecuting The Script: Syntax Highlighting in Vimmarco rossiNo ratings yet
- Linux Runlevels StartupScriptsDocument31 pagesLinux Runlevels StartupScriptsTrurlScribdNo ratings yet
- GCC Lab ManualDocument61 pagesGCC Lab ManualMadhu BalaNo ratings yet
- Project 4: Access Control: Date Assigned: Date DueDocument7 pagesProject 4: Access Control: Date Assigned: Date DuejXNo ratings yet
- Unix - Environment: (Amrood) $TEST "Unix Programming" (Amrood) $echo $TEST Unix ProgrammingDocument5 pagesUnix - Environment: (Amrood) $TEST "Unix Programming" (Amrood) $echo $TEST Unix ProgrammingSuman ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Windows - Flask API AutomationDocument3 pagesWindows - Flask API AutomationbrianNo ratings yet
- Lab 7 - Bash ScriptDocument10 pagesLab 7 - Bash ScriptNourhan TarekNo ratings yet
- Shells, Shell Scripting, and The UNIX File SystemDocument19 pagesShells, Shell Scripting, and The UNIX File SystemDevaNo ratings yet
- Bash ShellDocument3 pagesBash Shell2N3055No ratings yet
- Introduction to Unix Shell Scripting with csh/tcshDocument35 pagesIntroduction to Unix Shell Scripting with csh/tcshSachin JainNo ratings yet
- Unix - What Is Shells?: Shell PromptDocument3 pagesUnix - What Is Shells?: Shell Promptseenuvasan1985No ratings yet
- Midterm 3-4Document17 pagesMidterm 3-4Trang Lò ThịNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 Installing Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server: 1. Basic Shell SkillsDocument7 pagesCHAPTER 1 Installing Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server: 1. Basic Shell SkillsKhan Ahsan MasroorNo ratings yet
- Unix LabDocument54 pagesUnix LabMuhammad Zuhair KhanNo ratings yet
- Configuring SFTP Access in SASDocument15 pagesConfiguring SFTP Access in SASdanobikwelu_scribdNo ratings yet
- Shibboleth IDP Setup LinuxDocument17 pagesShibboleth IDP Setup LinuxSaless SenNo ratings yet
- DAY-4Document73 pagesDAY-4poorvaja.rNo ratings yet
- CyberAces Module3-Bash 1 IntroReviewDocument19 pagesCyberAces Module3-Bash 1 IntroReviewPedro FreitasNo ratings yet
- Upgrade SSH Di Centos7Document3 pagesUpgrade SSH Di Centos7bbwsupportNo ratings yet
- 7.1 Backup Script Project - BriefDocument2 pages7.1 Backup Script Project - Briefa49663487No ratings yet
- Useful Linux Commands Guide for BeginnersDocument33 pagesUseful Linux Commands Guide for Beginnerspaino81No ratings yet
- Install CadenceDocument4 pagesInstall Cadencenguyenbinh12xNo ratings yet
- Configure Shell VariablesDocument18 pagesConfigure Shell VariablesKiran AnimestarNo ratings yet
- CIT 383 / Lab 4: DescriptionDocument10 pagesCIT 383 / Lab 4: DescriptionMichael DavisNo ratings yet
- Shebang (Unix)Document8 pagesShebang (Unix)diaslongosNo ratings yet
- Science - BSC Information Technology - Semester 5 - 2022 - November - Linux System Administration CbcsDocument37 pagesScience - BSC Information Technology - Semester 5 - 2022 - November - Linux System Administration Cbcskoolhacker393No ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document14 pagesAssignment 2Muhammad Adil NaeemNo ratings yet
- Bash Startup Files Linux/Unix Files Stty Todd KelleyDocument31 pagesBash Startup Files Linux/Unix Files Stty Todd Kelleydarwinvargas2011No ratings yet
- Linux Commands 3Document52 pagesLinux Commands 3Rakesh RakeeNo ratings yet
- USING COMMAND LINE AND MANAGING SOFTWAREDocument35 pagesUSING COMMAND LINE AND MANAGING SOFTWAREAdeefa AnsariNo ratings yet
- API MCQ Set1Document25 pagesAPI MCQ Set1Praneet kumarNo ratings yet
- TASS User Guide 2.0 PDFDocument46 pagesTASS User Guide 2.0 PDFBezakulu Minwouyelet67% (6)
- Mzpack 3 User Guide (En)Document60 pagesMzpack 3 User Guide (En)Ravi Varakala100% (1)
- Ansible Hands-OnDocument35 pagesAnsible Hands-Onarm_max78No ratings yet
- Pochana Srikar Reddy Resume 1Document1 pagePochana Srikar Reddy Resume 1SrikarNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence - What It Means For The Built EnvironmentDocument28 pagesArtificial Intelligence - What It Means For The Built Environmentmathew.kolkataNo ratings yet
- 10 It Samplepaper 07Document10 pages10 It Samplepaper 07Rohan SenapathiNo ratings yet
- QM3G Programming ManualDocument114 pagesQM3G Programming ManualBorunte BulgariaNo ratings yet
- Postman - Guru99Document40 pagesPostman - Guru99gayu89No ratings yet
- Jainam Bhavsar: Career ObjectiveDocument1 pageJainam Bhavsar: Career ObjectivejenniferNo ratings yet
- FYP Project Report For PlagiarismDocument47 pagesFYP Project Report For PlagiarismTouseef SattiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document4 pagesAssignment 3Simoli ModiNo ratings yet
- Ug427: Efr32Xg21 2.4 GHZ 20 DBM Wireless Starter Kit User'S GuideDocument34 pagesUg427: Efr32Xg21 2.4 GHZ 20 DBM Wireless Starter Kit User'S Guideazazello 43No ratings yet
- ROIK-MIB2 v200311Document31 pagesROIK-MIB2 v200311Dario GuerraNo ratings yet
- OM Manuals TemplateDocument9 pagesOM Manuals TemplatejanempatricioNo ratings yet
- IT Project SampleDocument21 pagesIT Project SampleMarlo AristorenasNo ratings yet
- Bank Management System ProjectDocument33 pagesBank Management System ProjectPrateek DubeyNo ratings yet
- Softcopy Aerial Triangulation: Laboratory ManualDocument74 pagesSoftcopy Aerial Triangulation: Laboratory ManualShuaibu Abubakar sulaimanNo ratings yet
- Hannah Mohammed ResumeDocument2 pagesHannah Mohammed Resumeapi-283484526No ratings yet
- Developer-Days - NSO-CDM MigrationDocument25 pagesDeveloper-Days - NSO-CDM MigrationAla JebnounNo ratings yet
- Capstone Assignment 3.2 - Deployment DiagramDocument1 pageCapstone Assignment 3.2 - Deployment DiagramweweyNo ratings yet
- Animated Powerpoint Infographics With Morph TrfansitionDocument10 pagesAnimated Powerpoint Infographics With Morph TrfansitionMuhammad FauziNo ratings yet
- Sample For Problem Statement 1 Unilever 1-2-1706548549121Document9 pagesSample For Problem Statement 1 Unilever 1-2-1706548549121surajsahu225No ratings yet
- RSLinx Gateway InternetDocument4 pagesRSLinx Gateway Internetdiegos109No ratings yet
- Use Case DiagramDocument26 pagesUse Case DiagramHamid AliNo ratings yet
- F 22 Raptor Depron PDFDocument2 pagesF 22 Raptor Depron PDFAaronNo ratings yet
- Google HTML - CSS Style GuideDocument17 pagesGoogle HTML - CSS Style GuideMiguel OstosNo ratings yet
- AD218x - Flash MEMDocument67 pagesAD218x - Flash MEMJaime Andres Aranguren CardonaNo ratings yet
- Technical Information: Micro-PercussionDocument2 pagesTechnical Information: Micro-PercussionOrivaldo PenaNo ratings yet
- Modder'S Guide: To The ModhubDocument15 pagesModder'S Guide: To The ModhubAleixoNo ratings yet
- Azure DevOps Engineer: Exam AZ-400: Azure DevOps Engineer: Exam AZ-400 Designing and Implementing Microsoft DevOps SolutionsFrom EverandAzure DevOps Engineer: Exam AZ-400: Azure DevOps Engineer: Exam AZ-400 Designing and Implementing Microsoft DevOps SolutionsNo ratings yet
- Kali Linux - An Ethical Hacker's Cookbook - Second Edition: Practical recipes that combine strategies, attacks, and tools for advanced penetration testing, 2nd EditionFrom EverandKali Linux - An Ethical Hacker's Cookbook - Second Edition: Practical recipes that combine strategies, attacks, and tools for advanced penetration testing, 2nd EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Hackers & Painters: Big Ideas from the Computer AgeFrom EverandHackers & Painters: Big Ideas from the Computer AgeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- Linux for Beginners: Linux Command Line, Linux Programming and Linux Operating SystemFrom EverandLinux for Beginners: Linux Command Line, Linux Programming and Linux Operating SystemRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Linux: The Ultimate Beginner's Guide to Learn Linux Operating System, Command Line and Linux Programming Step by StepFrom EverandLinux: The Ultimate Beginner's Guide to Learn Linux Operating System, Command Line and Linux Programming Step by StepRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (9)
- Windows 11 Manual For Seniors: A Beginners Guide to Navigate Your Computer with Step-by-Step InstructionsFrom EverandWindows 11 Manual For Seniors: A Beginners Guide to Navigate Your Computer with Step-by-Step InstructionsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Java Professional Interview Guide: Learn About Java Interview Questions and Practise Answering About Concurrency, JDBC, Exception Handling, Spring, and HibernateFrom EverandJava Professional Interview Guide: Learn About Java Interview Questions and Practise Answering About Concurrency, JDBC, Exception Handling, Spring, and HibernateNo ratings yet
- The Linux Command Line Beginner's GuideFrom EverandThe Linux Command Line Beginner's GuideRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (23)
- Python Programming Illustrated For Beginners & Intermediates“Learn By Doing” Approach-Step By Step Ultimate Guide To Mastering Python: The Future Is Here!From EverandPython Programming Illustrated For Beginners & Intermediates“Learn By Doing” Approach-Step By Step Ultimate Guide To Mastering Python: The Future Is Here!Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- The Ultimate Kali Linux Book - Second Edition: Perform advanced penetration testing using Nmap, Metasploit, Aircrack-ng, and EmpireFrom EverandThe Ultimate Kali Linux Book - Second Edition: Perform advanced penetration testing using Nmap, Metasploit, Aircrack-ng, and EmpireNo ratings yet
- COBOL Basic Training Using VSAM, IMS and DB2From EverandCOBOL Basic Training Using VSAM, IMS and DB2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Kali Linux Intrusion and Exploitation CookbookFrom EverandKali Linux Intrusion and Exploitation CookbookRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Powershell: The ultimate beginner's guide to Powershell, making you a master at Windows Powershell command line fast!From EverandPowershell: The ultimate beginner's guide to Powershell, making you a master at Windows Powershell command line fast!Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Mac Terminal Reference and Scripting PrimerFrom EverandThe Mac Terminal Reference and Scripting PrimerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Excel : The Ultimate Comprehensive Step-By-Step Guide to the Basics of Excel Programming: 1From EverandExcel : The Ultimate Comprehensive Step-By-Step Guide to the Basics of Excel Programming: 1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Hacking with Kali Linux: A Step by Step Guide to Learn the Basics of Linux Penetration. What A Beginner Needs to Know About Wireless Networks Hacking and Systems Security. Tools Explanation IncludedFrom EverandHacking with Kali Linux: A Step by Step Guide to Learn the Basics of Linux Penetration. What A Beginner Needs to Know About Wireless Networks Hacking and Systems Security. Tools Explanation IncludedNo ratings yet
- Make Your PC Stable and Fast: What Microsoft Forgot to Tell YouFrom EverandMake Your PC Stable and Fast: What Microsoft Forgot to Tell YouRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- CompTIA Linux+/LPIC-1: Training and Exam Preparation Guide (Exam Codes: LX0-103/101-400 and LX0-104/102-400)From EverandCompTIA Linux+/LPIC-1: Training and Exam Preparation Guide (Exam Codes: LX0-103/101-400 and LX0-104/102-400)No ratings yet
- HACKING: Social Engineering Attacks, Techniques & PreventionFrom EverandHACKING: Social Engineering Attacks, Techniques & PreventionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Ubuntu Linux Toolbox: 1000+ Commands for Power UsersFrom EverandUbuntu Linux Toolbox: 1000+ Commands for Power UsersRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Kali Linux for Beginners: A Step-by-Step Guide to Learn the Basics of Hacking and Security TestingFrom EverandKali Linux for Beginners: A Step-by-Step Guide to Learn the Basics of Hacking and Security TestingNo ratings yet
- Ubuntu 22.04 Essentials: A Guide to Ubuntu 22.04 Desktop and Server EditionsFrom EverandUbuntu 22.04 Essentials: A Guide to Ubuntu 22.04 Desktop and Server EditionsNo ratings yet