Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Uploaded by
Utsav DeyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Uploaded by
Utsav DeyCopyright:
Available Formats
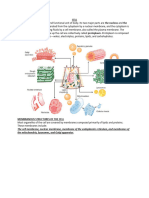
FUNCTION OF ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a complex network of membranous structures
found in eukaryotic cells. The ER is divided into two types: the smooth endoplasmic
reticulum (SER) and the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER). Here are some
functions of SER and RER with points:
1. Functions of Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER):
2. Lipid synthesis: SER is responsible for the synthesis of lipids such as phospholipids,
steroids, and triglycerides. These lipids are used for cell membrane formation and
for energy storage.
3. Detoxification: The SER is involved in the detoxification of drugs and other harmful
substances in liver cells. It does this by modifying these substances to make them
less toxic and more water-soluble, so that they can be eliminated from the body.
4. Calcium storage: The SER also plays a role in calcium storage and release. It
regulates the concentration of calcium ions in the cytosol, which is important for
muscle contraction and other cellular processes.
5. Carbohydrate metabolism: In some cells, the SER is involved in the metabolism of
carbohydrates, such as glycogen
6. Steroid hormone production: SER is involved in the production of steroid hormones,
which are involved in various physiological processes such as growth, development,
and reproduction.
Functions of Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER):
7. Protein synthesis: The RER is studded with ribosomes, which are involved in the
synthesis of proteins that are destined for secretion or incorporation into the
plasma membrane.
8. Protein modification: The RER is also involved in the folding, processing, and
modification of proteins, including the addition of sugars, lipids, and phosphate
groups.
9. Quality control: The RER has a quality control mechanism that ensures that only
properly folded and modified proteins are transported to their final destination.
10. Membrane synthesis: The RER is involved in the synthesis of membrane proteins
and phospholipids.
You might also like
- Human Cell Diagram and Sickle CellDocument11 pagesHuman Cell Diagram and Sickle Cellaryaa2020No ratings yet
- Dep BioDocument4 pagesDep Bioخلدون مهند الحديثيNo ratings yet
- The Cytoplasm: CytosolDocument5 pagesThe Cytoplasm: CytosolHariniNo ratings yet
- Cell PhysiologyDocument45 pagesCell PhysiologyHimani JhaNo ratings yet
- Zoology CHDocument6 pagesZoology CHAtika SadafNo ratings yet
- Exploring The Endoplasmic Reticulum Structure and FunctionDocument2 pagesExploring The Endoplasmic Reticulum Structure and Functionmaury.pd2905No ratings yet
- Endoplasmic Reticulum: Presented by Abhay AryaDocument17 pagesEndoplasmic Reticulum: Presented by Abhay AryaAbhay AryaNo ratings yet
- Endoplasmic ReticulumDocument12 pagesEndoplasmic ReticulumAzka AltafNo ratings yet
- Aphy 101Document2 pagesAphy 101NaliciaNo ratings yet
- Biology - Smooth & Rough EDocument12 pagesBiology - Smooth & Rough ESandhyaPremNo ratings yet
- Cellmol-Group12-Final - PPTX 20231023 073441 0000Document29 pagesCellmol-Group12-Final - PPTX 20231023 073441 0000Noronisa PendalidayNo ratings yet
- Biosynthesis, Modification, and Cell Secretion Track: Endoplasmic Reticulum, Ribosome, and Golgi ComplexDocument5 pagesBiosynthesis, Modification, and Cell Secretion Track: Endoplasmic Reticulum, Ribosome, and Golgi ComplexSri HayuniNo ratings yet
- M4 Check-In Activity 1 - VenusDocument2 pagesM4 Check-In Activity 1 - VenusGrezha Mari VenusNo ratings yet
- Smooth and Granular Endoplasmic Reticulum RibosomesDocument26 pagesSmooth and Granular Endoplasmic Reticulum RibosomesArfiNo ratings yet
- Bm101: Biology For Engineers: Instructor: Yashveer Singh, PHDDocument15 pagesBm101: Biology For Engineers: Instructor: Yashveer Singh, PHDhimanshu singhNo ratings yet
- Lec 2Document12 pagesLec 2HACKER MANNo ratings yet
- Cell HandoutsDocument25 pagesCell Handoutsgameaus00No ratings yet
- Internal Organization: Eukaryotic Cells Have They Performs Specific Functions For The CellDocument12 pagesInternal Organization: Eukaryotic Cells Have They Performs Specific Functions For The CellHACKER MANNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Foundations of BiochemistryDocument36 pagesChapter 1 - Foundations of BiochemistryshireenfNo ratings yet
- Endoplasmic Reticulum and Golgi Apparatus - Organelles That Help Transport and Process Molecules Within The CellDocument1 pageEndoplasmic Reticulum and Golgi Apparatus - Organelles That Help Transport and Process Molecules Within The CellVinícius SouzaNo ratings yet
- Endoplasmic ReticulumDocument4 pagesEndoplasmic Reticulumnikki_fuentes_1100% (1)
- 6 - Endoplasmic Reticulum & Protein SynthesisDocument15 pages6 - Endoplasmic Reticulum & Protein Synthesiswhether913No ratings yet
- Structure of Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)Document8 pagesStructure of Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)Ishita KumariNo ratings yet
- Cell OrganellesDocument19 pagesCell Organelleshifzaaijaz366No ratings yet
- VI CytoplasmDocument68 pagesVI CytoplasmELEONORA MĂRGINEANNo ratings yet
- Final Bio VivaDocument49 pagesFinal Bio Vivamanuel ortegaNo ratings yet
- Basic Cell Structure & FunctionDocument27 pagesBasic Cell Structure & FunctionJawaad AsifNo ratings yet
- Endoplasmic ReticulumDocument3 pagesEndoplasmic ReticulumHanumat SinghNo ratings yet
- Mapa Mental. Human Cell Structure and FunctionsDocument2 pagesMapa Mental. Human Cell Structure and FunctionsLiselimrz MrzNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Cell PhysiologyDocument39 pages1.2 Cell PhysiologyChristone “Zuluzulu” ZuluNo ratings yet
- HISTOLOGY Cells OrganellesDocument6 pagesHISTOLOGY Cells OrganellesAhsan KamalNo ratings yet
- Cell and Tissue CharacteristicsDocument12 pagesCell and Tissue Characteristicsgreenflames09100% (1)
- General Medical Biology: Lecture 3: Cell Structure and FunctionDocument23 pagesGeneral Medical Biology: Lecture 3: Cell Structure and FunctionRasan QadrNo ratings yet
- 4, 5 - The Cytoplasm - 2Document58 pages4, 5 - The Cytoplasm - 2Muthana Bani YassenNo ratings yet
- بايو م 2Document7 pagesبايو م 2alidoctor678No ratings yet
- CellsDocument4 pagesCellscalustre2016No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology DR Intesat M.el WahishyDocument30 pagesPathophysiology DR Intesat M.el Wahishyفافي الترهونيNo ratings yet
- Botany Home QuizDocument1 pageBotany Home QuizMarc Augustine BelgaNo ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument21 pagesAnimal CellGuzago, Reina Jane O.No ratings yet
- General Medical Biology: Lecture 3: Cell Structure and FunctionDocument24 pagesGeneral Medical Biology: Lecture 3: Cell Structure and FunctionRasan QadrNo ratings yet
- Cells Structure & FunctionDocument80 pagesCells Structure & Functionderr barrNo ratings yet
- General Biology: First Class Lab 4 & 5 Shahad EmadDocument7 pagesGeneral Biology: First Class Lab 4 & 5 Shahad EmadIraqiNo ratings yet
- Module For Anaphy CellDocument11 pagesModule For Anaphy CellBJ Bernardo IlNo ratings yet
- Cell (Biochemical Aspects) : Dr. Abid AliDocument49 pagesCell (Biochemical Aspects) : Dr. Abid AliShahzad MazharNo ratings yet
- Centro, MF. Module - 5Document9 pagesCentro, MF. Module - 5jessa marie marevilesNo ratings yet
- ORGANELLESDocument3 pagesORGANELLESIya BiancaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document26 pagesChapter 12Macy MarianNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology Standard 1EDocument15 pagesCell Biology Standard 1EveeramaniNo ratings yet
- Plant CellDocument8 pagesPlant CellIrish Nicole PacionNo ratings yet
- Cell BiologyDocument17 pagesCell BiologyVidit DixitNo ratings yet
- Partoza - JB, Concept Article - Endomembranesystem - DocxDocument4 pagesPartoza - JB, Concept Article - Endomembranesystem - DocxJenny PartozaNo ratings yet
- Types Lysosomal EnzymeDocument3 pagesTypes Lysosomal EnzymeDrbee10No ratings yet
- The Endomembran e System: Endoplasmic Reticulum & Golgi ApparatusDocument24 pagesThe Endomembran e System: Endoplasmic Reticulum & Golgi ApparatusTatocatNo ratings yet
- Chemical Characteristic of Endoplasmic HandoutsDocument3 pagesChemical Characteristic of Endoplasmic HandoutsHarley BaseNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure FunctionDocument43 pagesCell Structure Functioneishawajid75No ratings yet
- Zoo Sem2 Endoplasmic ReticulumDocument7 pagesZoo Sem2 Endoplasmic ReticulumAnadi ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Animal Cell: Parts FunctionsDocument32 pagesIntroduction To Animal Cell: Parts FunctionsconfuseciousNo ratings yet
- Cells, Cellular Compartments, Transport Systems, Fluid Movement Between CompartmentsDocument102 pagesCells, Cellular Compartments, Transport Systems, Fluid Movement Between CompartmentsMary Grace MartinNo ratings yet
- Structural Biochemistry/Cell Organelles: Pictorial Representation of Organelles in A Typical Animal CellDocument8 pagesStructural Biochemistry/Cell Organelles: Pictorial Representation of Organelles in A Typical Animal CellPrincess Angie GonzalesNo ratings yet
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)