Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Resource and Development
Uploaded by
edumatrac0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views7 pagesThis document provides information from a geography textbook chapter on resources and development in India. It discusses different types of resources based on origin, renewability, ownership, and development status. It also covers topics like sustainable development, Agenda 21, resource planning, conservation, land use patterns, and factors affecting land use. Key points include classifications of biotic and abiotic, renewable and non-renewable, individual, community, national and international resources. It also discusses sustainable development, Agenda 21 signed in 1992, and importance of resource conservation.
Original Description:
Original Title
Resource and development
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides information from a geography textbook chapter on resources and development in India. It discusses different types of resources based on origin, renewability, ownership, and development status. It also covers topics like sustainable development, Agenda 21, resource planning, conservation, land use patterns, and factors affecting land use. Key points include classifications of biotic and abiotic, renewable and non-renewable, individual, community, national and international resources. It also discusses sustainable development, Agenda 21 signed in 1992, and importance of resource conservation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views7 pagesResource and Development
Uploaded by
edumatracThis document provides information from a geography textbook chapter on resources and development in India. It discusses different types of resources based on origin, renewability, ownership, and development status. It also covers topics like sustainable development, Agenda 21, resource planning, conservation, land use patterns, and factors affecting land use. Key points include classifications of biotic and abiotic, renewable and non-renewable, individual, community, national and international resources. It also discusses sustainable development, Agenda 21 signed in 1992, and importance of resource conservation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
A Complete Eng. Medium Boarding School based on C.B.S.E Curriculum from Play Group to Std.
10th
Venue :- West of Dr. Kalyani Singh Clinic, Naya Bazar, Saharsa Contact – 7260925438, 6207772904
Study Material
Class – Ten
Subject –Geography
Chapter - 1
RESOURCES AND DEVELOPMENT
Q:- What is Resource?
Ans:- Anything available in our environment which can be used for satisfying the human needs is called a resource,
provided, it is technologically accessible, economically feasible and culturally acceptable.
Q:- Explain the role of human in resource development.
Ans:-
Human is at the centre of resource development.
Actually all resources become resource only when they are put to use by humans.
It is human who makes natural things usable with help of technology.
Human beings interact with nature with the help of technology and create institutions for their development.
There are regions where natural resources are in abundance but regions not developed for example Africa. But if
human are developed they make the region developed with technology, for example, Japan.
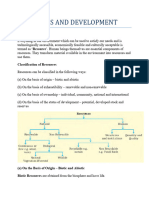
Types of Resources:
Resources can be classified on different bases; into following types:
(i) On the basis of origin – Biotic and Abiotic
(ii) On the basis of exhaustibility – Renewable and Non-renewable
(iii) On the basis of ownership – Individual, community, national and international
(iv) On the basis of status of development – Potential, Developed, Stock and Reserves
Classification of Resources :- On the basis of Origin
(a) Biotic Resources –Resources that we obtain from biosphere and have life are called biotic resources.
For example- trees, animals, insects, etc.
(b) Abiotic Resources: – All non-living things present in our environment are termed as abiotic resources.
For example – earth, air, water, metals, rocks, etc.
Classification of Resources :- On the basis of Exhaustibility:
(a) Renewable Resources: Resources that can be replenished after a short period of time are called Renewable
Resources. For example – agricultural crops, water, forest, wildlife, etc.
(b)Non-renewable Resources: – Resources which takes million years of time to replenish are called non-
renewable resources. For example – fossil fuel.
Classification of Resources - On the Basis of ownership:
(a)Individual – Resources owned by individuals are called Individual Resources. For example – land owned by
farmers, house, etc.
(b)Community – Resources owned by community or society are called Community Owned Resources.
For example – Graveyard, grazing land, ponds, burial grounds, park, etc.
(c) National Resources -Resources lying within the boundary of a nation are called National Resources.
For example – Government land, Roads, canals, railway, etc.
(d)International Resources – Resources regulate by International bodies are called International Resources.
For example – Ocean and sea beyond 200 km of the Exclusive Economic Zone and is called open sea or
ocean. No individual country can utilize these resources without the permission of International bodies.
Classification of Resources - On the basis of Status of Development:
(a)Potential Resources: Resources which are found in a particular region, but not yet used properly.
For example – Rajasthan and Gujarat receive plenty of solar energy and have plenty of wind energy, but use
of these resources so far has not been developed properly.
(b)Developed Resources: Resources which are developed and surveyed for utilization and are being used in
present time are known as Developed Resources.
(c) Stock – Resources that are available, but we do not have proper technology to used them are called Stock.
For example – water is made of oxygen and hydrogen, which can be used as fuel, but because of lack of proper
technology these are not being used.
(d)Reserves – Resources which are available and the knowhow to use them is also present but they are yet to be
used are called Reserves.
For example – river water which is not used to generate electricity.
Q. Highlight any three problems associated with the indiscriminate use of resources by the human beings.
Ans:-Indiscriminate use of resources creates following problems :–
(i) Global ecological crises such as global warming.
(ii) It has also led to depletion of the ozone layer.
(iii) It has also caused environmental pollution and land degradation.
The resultant threat to ecology and environment has put the future of our planet in danger.
Q:- What do you mean by sustainable development?
Ans:- Development which takes place without damaging the environment and compromising with needs of future is
called sustainable development.
Q:- Why, where & when the first international earth summit was organised?
Ans:- Keeping the view of justified use of resources and sustainable development, the Earth Summit was organized in
1992 in Rio de Janeiro in which more than 100 state heads agreed with Agenda 21 for the sustainable development and
proper use of resources.
Q:- What is agenda 21?
Ans:- It is the declaration signed by world leaders in 199 at the UNCED which took place in Rio de janerio Brazil.
It is an agenda to combat environmental damage, poverty, disease, etc. through global co-operation on common interests,
mutual needs and shared responsibilities.
Q:- What is resource planning ? Why it us necessary in a country like india ?
Ans:- Resource planning is the widely accepted strategy for the judicious use of resources.
Resource planning becomes more important in a country like India, where resources are not distributed properly.
For example; many states are rich in mineral and deficient in other resources, such as Jharkhand is rich in minerals, but
there is problem of drinking water and other facilities, Arunachal Pradesh has plenty of water but lack of other
development because of lack of resources.
Q:- What does resource planning in india involve ?
Ans:-
(a) Making of inventory of resources after their region-wise identification across the country.
(b) Making of the planning structure with appropriate technology, skill and institutions.
(c) Matching of resource plan with development plan, etc.
Q:- Explain the importance of conservation of resources.
Ans:-Conservation of resources is necessary because of following reasons :
(i) Resources are vital for any developmental activity but irrational consumption and overutilization of
resources may lead to socio-economic and environmental problems.
(ii) To overcome these problems, resource conservation at various level is important.
(iii) If resources are not conserved at this point of time, then our future generations will be left with no
resources at all. So it is very important to think for conservation of resources.
Q:- How land is distributed in India?
Ans:-India comprises of many types of land. These are mountains, plateau, plains and islands.
Mountains –About 30% of land area in India is in the form of mountain.
- Mountain supports the perennial flow of rivers, which carry fertile soils, facilitate irrigation and provide
drinking water.
Plain –About 43% of land area in India is in the form of plains.
- Plains provide facilities for agriculture, building of industries and houses, etc.
Plateau –
- About 27% of land in India is in the form of plateau which provides many types of minerals, fossil fuels and
forest.
Q:- What is the patterns of ushe of Land Resources?
Ans:- Land is utilized for the following purposes:-
1.Forests
2. Land not available for cultivation: There are two types of land which are not used for agriculture purpose.
These are:
(a) Barren and waste land
(b) Lands used for buildings, roads, factories, etc. i.e for non-agriculture purpose.
3. Other uncultivated land (excluding fallow land)
(a) Permanent pastures and grazing land,
(b) Land under miscellaneous tree crops groves (not included in net sown area),
(c)Culturable waste land (left uncultivated for more than 5 agricultural years).
4. Fallow lands
(a) Current fallow-(left without cultivation for one or less than one agricultural year),
(b) Other than current fallow-(left uncultivated for the past 1 to 5 agricultural years).
5.Net sown area: Area which is sown at least once in a year is called net sown area.
Q:- Define Gross cropped area.
Ans:- Area sown more than once in an agricultural year plus net sown area is known as gross cropped area.
Q:- Name the factors which determine the pattern of use of land?
Ans.- Pattern of use of land depends upon physical and human factors both:-
Human factors:- Climate, topography, type of soil, etc. are considered as physical factors.
Natural factors:- population density, tradition, technological capability, etc.
Q. Why is it important to raise the land area under forests?
Ans:-
It is very important to raise area under forest because forests are essential for maintenance of the Ecological
balance.
The livelihood of millions of people who live on the fringes of these forests depends upon it.
Forest also provides a number of goods that are required for industry and medicines etc.
Forest also helps in soil conservation and rainfall.
Q:- Why land use data is available for only 93% of the total area of India?
Ans:-India has total 3.28 million square kilometer land used data.
But only 93% of land of total geographical area is available.
This is because land used data has not been collected for the north eastern states except Assam and the land
occupied by Pakistan and China has not been surveyed because of many unavoidable reasons.
Q:- Define land degradation.
Ans:- Land degradation is damage to land that makes it less economically useful & less biologically diverse.
Continuous use of land over a long period of time without taking appropriate measures to conserve and manage it,
has resulted in land degradation.
Overgrazing, mining, deforestation, division of lands in small area because of family feuds, etc. are some of the
major causes of degradation of land.
Q:-Explain any three human activities which are mainly responsible for land degradation in India.
Ans. Continuous use of land over a prolonged period of time without taking necessary steps to conserve and manage
it, has resulted in land degradation.
Human activities responsible for land degradation in India are as follows :
(i) Because of mining in the states of Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Orissa and Madhya Pradesh; lands are left abandoned
without proper treatment after the completion of mining works. This has resulted in the form of deep scars and
traces.
(ii) Along with mining, deforestation in these states has degraded the land very fast.
(iii) In the states of Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana, over irrigation causes water shortage and increase in salinity and
alkalinity due to water logging.
Q:- Suggest some measures to conserve the land resources?
Ans.- Degradation of land can be prevented by taking following measures:
Afforestation
Proper management of grazing.
Stabilisation of sand dunes by plantation of thorny bushes.
Proper management of waste lands. \
By proper irrigation.
By proper harvesting.
Control over mining activities.
Proper management of land after completion of mining work.
Discharge of industrial waste and effluents only after proper treatment.
Plantation of trees along the road sides.
By preventing the deforestation.
Q:- Explain any three steps that can be taken to solve the problem of land degradation?
Ans.
(a)Contour ploughing :Ploughing along the contour lines can decelerate the flow of water down the slopes.
(b)Terrace cultivation :Steps can be cut out on the slopes, making terraces. Terrace cultivation restricts
erosion.
(c)Strip cropping :Large fields can be divided into strips. Strips of grass are left to grow between the crops.
This breaks up the force of the wind reducing its effect.
Q:- Define soil?
Ans:- Soil is the uppermost layer of land composed of rocks particles and humus.
Q:- What are the factors which determine the formation of soil?
Ans.- Soil is formed by the weathering process of the rocks.
Various natural forces, such as temperature, running water, wind, etc. along with many physical and chemical changes are
equally important in the formation of soil formation.
Classification of Soil:-
Soil is categorized in many types on the basis of texture, colour, age, chemical properties, etc.
India is a vast country which comprises of many types of land.
Thus, many types of soils are found in different regions in India.
1. Alluvial Soil
This is the most widely spread and important soil.
Alluvial soil is found near the river or plains formed by rivers.
In India, alluvial soil is found in the north eastern plain where Ganga, Yamuna, and Brahmaputra flow.
Alluvial soil is deposited by river system. Entire northern plain is made of alluvial soil.
Regions:- Bihar, U.P, Punjab etc.
Alluvial soil is rich in potash, phosphoric acid and lime.
Alluvial soil is good for the growth of sugarcane, paddy, wheat, maize, and pulses.
Alluvial soil is the mixture of various proportions of silt, sand and clay.
Alluvial soils differ in the size of their particles at the area of break of slope.
Q:- What do you mean by Khadar and Bangar?
Ans.-Apart from the size of particles of grains, soils are also classified on the basis of their age.
- The older alluvial soil is known as Bangar and new alluvial soil or Khadar.
- New alluvial soil has more concentration of coarse grains while Old alluvial soil has plenty of fine particles.
2. Black Soil
Because of black colour, this type of soil is called black soil.
It is also known as Regur Soil. Black soil is found in the north west deccan plateau.
It is found in the plateau of Maharashtra, Saurashtra, Malwa, Madhya Pradesh and Chattisgarh and extent along
with the valley of Krishna and Godavari Rivers.
Black soil has high concentration of fine particles and thus can hold moisture for long time.
It contains calcium, potassium, magnesium and lime.
Black soil is suitable for the growth of cotton, but many other crop are grown in the area of black soil.
3. Red and Yellow Soil
The soil looks red due to presence of iron in crystalline or metamorphic rocks.
When the soil look yellow when it occurs in dehydrated form.
Red soil is present in the eastern and southern parts of the Deccan Plateau.
Red soil is also found in Orissa, Chhattisgarh, on the southern part of the Gangetic plains and along the
piedmont zone of the Western Ghats.
4. Laterite Soil
Laterite soil is formed in regions which get high rainfall with high temperature.
This causes leaching of the soil and microorganisms are killed during the process.
Due to this, laterite soil does not contain humus or contains very low amount of humus.
This soil is mainly found in Kerala, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Madhya Pradesh and in hilly areas of Orissa and
Assam.
This soil can be made cultivable with heavy dose of manures.
Tea, coffee, rubber, coconut, cashew nuts etc can be grown.
5. Arid Soil
Arid soil is found in those areas which receive scanty rainfall.
Due to high temperature, evaporation is faster in these regions.
The soil has a high content of salt.
Arid soil can be made cultivable with proper treatment.
Arid soil is present in Rajasthan and Gujarat. Suitable for growing barley, wheat, maize, millets etc
6. Forest Soil
The forest soil is found in hilly areas.
The soil in upper parts is highly acidic because of denudation.
The soil in the lower part is highly fertile.
Suitable for the growth of tea, coffee, spices, etc
Q. What is soil erosion? Write two human activities that lead to soil erosion.
Ans.The denudation of the soil cover and subsequent washing down is described as soil erosion.
Two human factors leading to soil erosion are :
(a) Deforestation :-Due to heavy deforestation, soil erosion is increasing.
(b) Overgrazing :-In many regions people still practise grazing of cattle, goats and sheap. Gradually this
leads to soil erosion.
NCERT EXERCISE SOLUTION
Answer the following questions briefly.
(i) Name three states having black soil and the crop which is mainly grown in it.
Ans:- Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh are some states where black soil is found and cotton is the main
crop grown on black soil.
(ii) What type of soil is found in the river deltas of the eastern coast? Give three main features of this type of soil.
Ans:- Alluvial soil is found in the river deltas of the eastern coast. Alluvial soil is rich in potash, phosphoric acid and
lime. It has a high water retention capacity. It is highly fertile soil.
(iii) What steps can be taken to control soil erosion in the hilly areas?
Ans:- Terrace farming and shelter belt plantation can be done to prevent soil erosion in hilly areas.
(iv) What are the biotic and abiotic resources? Give some examples.
Ans:-
Biotic Resources – All living organisms in our environment are called biotic resources.
For example, trees, animals, insects, etc.
Abiotic Resources – All non-living things present in our environment are termed as abiotic resources.
For example – earth, air, water, metals, rocks, etc.
3. Long answer type questions.
(i) Explain land use pattern in India and why has the land under forest not increased much since 1960-61?
Ans:-The present land use pattern shows :
(i) Forests – 22.57 percent much below the desired 33 percent as outlined in the National Forest Policy of 1952.
(ii) Land not available for cultivation
(a) Barren and wasteland – 6.29 percent
(b) Land put to non-agricultural uses, e.g., buildings, roads, factories, etc. 7.92 percent of total area
(iii) Other uncultivated land (excluding fallow land)
(a) Permanent pastures and grazing land has decreased to 3.45 percent.
(b) Area under miscellaneous tree crops, groves (not included in net sown area) 1.10 percent
(c)Culturable wasteland (left uncultivated for more than five agricultural years) 4.41 percent
(iv) Fallow lands.
(a) Current fallows (left without cultivation for one or less than one agricultural year) 7.03 percent
(b) Other than current fallow 3.82 percent
(v) Net Sown Area 43.41 percent but the pattern varies greatly from state to state.
Increasing population and subsequent increase in demand for resources is the main reason that forested land has not
increased much during this period.
(ii) How have technical and economic development led to more consumption of resources?
Ans. Technical and economic development involves more utilisation and exploitation of resources for the purpose of
present development.
The history of colonisation reveals that it was primarily the higher level of technological development of the
colonising countries that helped them to exploit resources of other regions and establish their supremacy over the
colonies.
Economic development takes place through more and proper utilisation of available resources for the purpose of
advancement of present generation.
Technical development makes the resources accessible and usable and aids in further exploitation as well as
creation of new resources.
Hence, technical and economic development lead to more and more consumption of resources.
The End
You might also like
- Chapter 1 - Resources and Development: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument17 pagesChapter 1 - Resources and Development: Multiple Choice QuestionsreemNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Ch. 1 Geo.Document9 pagesGrade 10 Ch. 1 Geo.punian344No ratings yet
- Class X: Chapter 1 (Resources and Development)Document10 pagesClass X: Chapter 1 (Resources and Development)Divyansh GargNo ratings yet
- Resources and DevelopmentDocument11 pagesResources and DevelopmentSoniaNo ratings yet
- Geography Les 1 With AnsDocument10 pagesGeography Les 1 With AnsMokshita JainNo ratings yet
- Original 1587566839 Resource and DevelopmentDocument5 pagesOriginal 1587566839 Resource and DevelopmentS KannanNo ratings yet
- 10th Geography 21-22 - RemovedDocument24 pages10th Geography 21-22 - Removedrathermusaib800No ratings yet
- Grade 10 RESOURCESDocument8 pagesGrade 10 RESOURCESAnshika TandonNo ratings yet
- CBSE Notes Class 10 Social Science Geography Chapter 1 Resources and DevelopmentDocument11 pagesCBSE Notes Class 10 Social Science Geography Chapter 1 Resources and DevelopmentEKLABAY SONINo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Resources and Development: CBSE Notes Class 10 Social Science GeographyDocument38 pagesChapter 1 - Resources and Development: CBSE Notes Class 10 Social Science GeographyscedhuNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Geo. CH 1 - Resource and Development NotesDocument13 pagesClass 10 Geo. CH 1 - Resource and Development Notessadhna yadav100% (2)
- GeoDocument28 pagesGeoSakshi GoelNo ratings yet
- Resources & DevelopmentDocument10 pagesResources & Developmentdhdahanuwala100% (1)
- Untitled Document 1 3Document7 pagesUntitled Document 1 3Himesh kushwahaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Social Science Revision Notes Geography Chapter-1 Resources and DevelopmentDocument5 pagesCBSE Class 10 Social Science Revision Notes Geography Chapter-1 Resources and DevelopmentAadi GautamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Geography Resources and DevelopmentDocument27 pagesChapter 1 Geography Resources and DevelopmentKapil LavaniaNo ratings yet
- CH-1 Resources and DevelopmentDocument7 pagesCH-1 Resources and DevelopmentBaby QueenNo ratings yet
- Geography Notes by S.KDocument8 pagesGeography Notes by S.KTech GURUNo ratings yet
- Grade - 10 Geo - Resource and DevelopmentDocument8 pagesGrade - 10 Geo - Resource and DevelopmentLatika MarwahaNo ratings yet
- Geography VS, S, L AqDocument27 pagesGeography VS, S, L AqJamunamary JamunamaryNo ratings yet
- Define Resources? Mention Its Features?Document19 pagesDefine Resources? Mention Its Features?Sampa AcharjeeNo ratings yet
- Resources and DevelopmentDocument10 pagesResources and DevelopmentswitchangryNo ratings yet
- Amity International School, Sector 46, Gurgaon Class 10 Chapter 1: Resources and Development (Minimum Learning Programme) Resources AreDocument11 pagesAmity International School, Sector 46, Gurgaon Class 10 Chapter 1: Resources and Development (Minimum Learning Programme) Resources AreRam KapoorNo ratings yet
- 10geo-Chap1-Resources and DevelopmentDocument7 pages10geo-Chap1-Resources and DevelopmentYukti KoliNo ratings yet
- Classification of ResourcesDocument11 pagesClassification of ResourcesbasilNo ratings yet
- Resources and DevelopmentDocument11 pagesResources and Developmentpujal dabasNo ratings yet
- Geo-10 2Document107 pagesGeo-10 2SonalikaNo ratings yet
- Geo - Resources and Development PDFDocument14 pagesGeo - Resources and Development PDFJatin SinglaNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Geo X NotesDocument15 pagesCH 1 Geo X NoteskniFe VisualzNo ratings yet
- GeographyDocument30 pagesGeographyA:-Piyush ShirsekarNo ratings yet
- Geography Class 10Document56 pagesGeography Class 10niwanshi1No ratings yet
- Class X - Resources and DevelopmentDocument8 pagesClass X - Resources and DevelopmentAryavir SardanaNo ratings yet
- Geography X 2020 Madhu PDFDocument35 pagesGeography X 2020 Madhu PDFShivani MadhusoodananNo ratings yet
- Classification of Resources: Notes Class 10 Chapter 1 - Resources and Development GeographyDocument18 pagesClassification of Resources: Notes Class 10 Chapter 1 - Resources and Development GeographyMANISH JOSHINo ratings yet
- Resources and Devolopment NotesDocument20 pagesResources and Devolopment NotesDanyaNo ratings yet
- Resources and Development WSDocument8 pagesResources and Development WSabhigna.ravikumarNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Social Sciences Geography: Chapter 1 Notes Resources and Development 1. ResourcesDocument8 pagesClass 10 Social Sciences Geography: Chapter 1 Notes Resources and Development 1. ResourcesSandhya SinghNo ratings yet
- Geo ch-1 Class 10Document9 pagesGeo ch-1 Class 10nayshajain63No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 GeographyDocument6 pagesChapter 1 GeographyTapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Geography 1 Class X Assignment (2020-21)Document6 pagesGeography 1 Class X Assignment (2020-21)Binode SarkarNo ratings yet
- Resource DevelopmentDocument11 pagesResource DevelopmentSimrah RehanNo ratings yet
- Resources and DevelopmentDocument32 pagesResources and DevelopmentSwastiNo ratings yet
- Resources and DevelopmentDocument44 pagesResources and Developmentvidhaan guptaNo ratings yet
- Resource and DevelopmentDocument26 pagesResource and DevelopmentthinkiitNo ratings yet
- Geography Class XDocument46 pagesGeography Class Xbhupenderrana78% (32)
- Bhatnagar International School Paschim Vihar Class 10 - GeographyDocument13 pagesBhatnagar International School Paschim Vihar Class 10 - Geographykanica bathlaNo ratings yet
- Geography Session 1Document13 pagesGeography Session 1kanica bathlaNo ratings yet
- Resources and Development: by Adarsh - NJDocument27 pagesResources and Development: by Adarsh - NJAnkur ChopraNo ratings yet
- Class 10th Geography by Towseef SirDocument27 pagesClass 10th Geography by Towseef Sirdr3altafNo ratings yet
- Resources & Development Notes GRADE 10Document12 pagesResources & Development Notes GRADE 10Zara FarooquiNo ratings yet
- Resource and Development NotesDocument5 pagesResource and Development NotesatharvasapreytNo ratings yet
- Study Material: Short Notes, Chapter1, Gwegraphy Class X: Compiled by Mrs Nigar Akhtar PGT AMU City School AligarhDocument14 pagesStudy Material: Short Notes, Chapter1, Gwegraphy Class X: Compiled by Mrs Nigar Akhtar PGT AMU City School Aligarhmonika khetanNo ratings yet
- Resources and Development NotesDocument10 pagesResources and Development NotesKushan MittalNo ratings yet
- Study Material Question Bank and Answer Key Geography: Chapter-1: Resource and DevelopmentDocument14 pagesStudy Material Question Bank and Answer Key Geography: Chapter-1: Resource and DevelopmentsaanviNo ratings yet
- Resources and Development NotesDocument27 pagesResources and Development NotesbhaviknsrNo ratings yet
- Grade X Geography Chapter 1 Resources and DevelopmentDocument5 pagesGrade X Geography Chapter 1 Resources and DevelopmentMohammed OwaisNo ratings yet
- SST CH 1 Geography ResourcesDocument2 pagesSST CH 1 Geography ResourcesA GUPTANo ratings yet
- Soils as a Key Component of the Critical Zone 1: Functions and ServicesFrom EverandSoils as a Key Component of the Critical Zone 1: Functions and ServicesJacques BerthelinNo ratings yet
- Land Use and Spatial Planning: Enabling Sustainable Management of Land ResourcesFrom EverandLand Use and Spatial Planning: Enabling Sustainable Management of Land ResourcesNo ratings yet
- Our Country, The Planet: Forging A Partnership For SurvivalFrom EverandOur Country, The Planet: Forging A Partnership For SurvivalNo ratings yet
- Vikram Sarabhai Library: New Arrivals (Books)Document10 pagesVikram Sarabhai Library: New Arrivals (Books)ds ram sktNo ratings yet
- A La Juventud Filipina or To The Filipino YouthDocument2 pagesA La Juventud Filipina or To The Filipino YouthClyde PeraltaNo ratings yet
- ERP ProposalDocument10 pagesERP Proposalajmal_2kNo ratings yet
- Financial Documents Learner NotesDocument21 pagesFinancial Documents Learner NotesYolanda WillsonNo ratings yet
- CVD EmailSecurityUsingCiscoESADesignGuide AUG14Document36 pagesCVD EmailSecurityUsingCiscoESADesignGuide AUG14zxkiwiNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Introduction To Cost ConceptsDocument51 pagesModule 2 - Introduction To Cost Conceptskaizen4apexNo ratings yet
- Malayang Kapisanan NG Manggagawa Sa Associated Anglo American Tobacco Corp. (MAKAMANGGAGAWA) v. Associated Anglo American Tobacco Corp., G.R. No. 156613, 18 February 2008Document3 pagesMalayang Kapisanan NG Manggagawa Sa Associated Anglo American Tobacco Corp. (MAKAMANGGAGAWA) v. Associated Anglo American Tobacco Corp., G.R. No. 156613, 18 February 2008Daniela Sandra AgootNo ratings yet
- Food Safety and Quality ReferEnce Guide - BIORADDocument52 pagesFood Safety and Quality ReferEnce Guide - BIORADAhsanal KasasiahNo ratings yet
- RJC COP December 2019Document36 pagesRJC COP December 2019Vikram TNo ratings yet
- Mrugala Fabrice - Celtic GodsDocument13 pagesMrugala Fabrice - Celtic GodsElithemessieNo ratings yet
- AccreditationDocument6 pagesAccreditationmyra delos santosNo ratings yet
- Client/shipper Visit (New Shipper & Twice A Year For Regular Client) (Commercial Team)Document2 pagesClient/shipper Visit (New Shipper & Twice A Year For Regular Client) (Commercial Team)PT. Estupedo Agri MakmurNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 Study of Philippine ValuesDocument15 pagesLesson 7 Study of Philippine ValuesAlma Yumul BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Arezzo Place Pasig - Metro Manila Condo Thru PAG-IBIG Pasig City Philippines - 10772477Document14 pagesArezzo Place Pasig - Metro Manila Condo Thru PAG-IBIG Pasig City Philippines - 10772477ganguly147147No ratings yet
- Chapter Two: Cost of Capital & Capital Structure TheoriesDocument17 pagesChapter Two: Cost of Capital & Capital Structure TheoriesBaharu AbebeNo ratings yet
- Boletin 163Document92 pagesBoletin 163jhonatanNo ratings yet
- SAP Community Network Forums - Physical Inventory WM ..Document2 pagesSAP Community Network Forums - Physical Inventory WM ..Kosaraju SandeepNo ratings yet
- Title II - NLRC (Powers)Document17 pagesTitle II - NLRC (Powers)Mary Ann TumbagaNo ratings yet
- Snyder Contracts Fall 2009Document58 pagesSnyder Contracts Fall 2009fvillarroel6No ratings yet
- Difference Between Withholding Taxes and Extended TaxesDocument2 pagesDifference Between Withholding Taxes and Extended Taxesrohit12345aNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan - Teaching English in Elem - Grades - Gabat Clara ADocument8 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan - Teaching English in Elem - Grades - Gabat Clara AClara GabatNo ratings yet
- HDFC Life IR22 040622Document492 pagesHDFC Life IR22 040622Javed KhanNo ratings yet
- 上海证券交易所股票上市规则(英文版)Document145 pages上海证券交易所股票上市规则(英文版)monicakuoNo ratings yet
- Balao vs. Ermita - Ermita vs. BalaoDocument2 pagesBalao vs. Ermita - Ermita vs. BalaoKim OngNo ratings yet
- Administrative Order No. 42: Inter AliaDocument3 pagesAdministrative Order No. 42: Inter AliaBenica Atud VentilacionNo ratings yet
- Battle Companies 2016 1 PDFDocument117 pagesBattle Companies 2016 1 PDFMarcus BallNo ratings yet
- AB Bank - 2022Document131 pagesAB Bank - 2022Mostafa Noman DeepNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Global Marketing Plus 2014 Mymarketinglab With Pearson Etext Package 8 e Warren J Keegan Mark C Green Full DownloadDocument24 pagesSolution Manual For Global Marketing Plus 2014 Mymarketinglab With Pearson Etext Package 8 e Warren J Keegan Mark C Green Full Downloadcarlyterrysnycxdekbz100% (42)
- Organic Chemistry 3rd Edition Klein Solutions ManualDocument25 pagesOrganic Chemistry 3rd Edition Klein Solutions ManualRobertBoydeona98% (49)
- Practice Test 9 - 1Document9 pagesPractice Test 9 - 1Phuong DaoNo ratings yet