Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fisiología. Respiratory System Pathologies
Uploaded by
AndreaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fisiología. Respiratory System Pathologies
Uploaded by
AndreaCopyright:
Available Formats
UNIVERSIDAD AUTÓNOMA DEL ESTADO DE MÉXICO
FACULTAD DE ODONTOLOGÍA
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM PATHOLOGIES
FISIOLOGÍA
ALUMNA: CHÁVEZ ROMERO ANDREA
MATERIA IMPARTIDA POR:
NANCY MILLÁN MORA
ELÍAS NAHUM SALMERÓN VALDES
SEMESTRE: SEGUNDO GRUPO: 04
FECHA: 23 DE MAYO DEL 2023
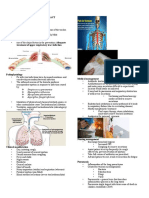
Pathologies of the respiratory system
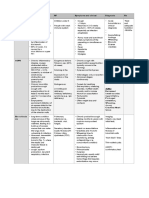
Pathology Definition Causes Symptoms Prevention
• Prolonged exposure of the lungs to
• Frequent coughing or
irritating substances
wheezing.
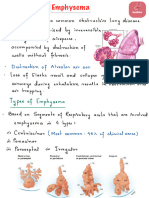
Lung disorder in which progressive • Substances such as nicotine and
• Cough that produces a lot of Emphysema and chronic
damage is generated in the marijuana
mucus. obstructive pulmonary disease
alveoli. The alveoli inflate • High air pollution
Chronic pulmonary • Shortness of breath, especially if cannot be cured, but there are
abnormally, resulting in a • Chemical vapors, fumes and dust
emphysema you are physically active. treatments that can help relieve
permanent enlargement of the existing in certain work environments
• A hissing or grinding sound symptoms and slow the
air spaces, their obstruction, and • Use of coal and firewood in poorly
when you breathe. progression of the disease.
the destruction of their walls. ventilated places
• Sensation of pressure in the
• there is a minimum percentage of
chest.
genetic risk factor
• Blockage of the airway
• Anxiety
• Stress It depends on the cause that
• Bronchospasm • Discomfort when breathing. causes it.
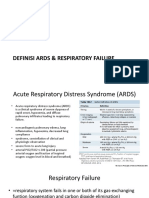
It is respiratory distress or shortness • Hypoxemia • Difficulty breathing.
of breath. Mental anguish occurs For this reason, when faced with
• Fluid between the lungs and the • Inability to get enough air.
Dyspnea associated with the inability to a picture of respiratory distress,
chest wall • Sensation of suffocation,
ventilate sufficiently to meet the an assessment by a specialist is
demand for air. • Pneumonia or infection oppression, suffocation or important to find the cause and
• Inflammation of the lungs after suffocation. apply the appropriate
radiation therapy treatment.
• Low red blood cell count
• A blood clots
• It occurs when not enough oxygen
reaches the brain. It depends on the cause, severity
It's the lack of oxygen. There is • Confusion or altered
• Irregular heart rhythm and health condition of the
depletion of the oxygen-carrying consciousness
• Suffocation person, however, in most cases it
Hypoxia capacity of the blood or • Cyanosis
• Strangulation consists of oxygen administration
envenomation of intracellular • Tachypnea
• Asthma attack through masks or orotracheal
oxidative enzymes. • Tachycardia and diaphoresis
• Poisoning intubation.
• Trauma to the trachea or lungs
It depends on the cause. Mild
It is the collapse of the alveoli; can
• Obstruction of the airways (bronchi or atelectasis may go away without
be localized or generalized. When • Difficulty breathing
bronchioles) due to mucous plugs or treatment. Sometimes
the lung is flexible enough, only a
cancer • Agitated and shallow breathing medications are given to loosen
Atelectasis collapse of the alveoli occurs and
• Pressure on the outside of the lung • Wheezing and thin the mucus. If the
when it occurs in the entire lung it
• Lack of a surfactant secreted by • Cough condition is due to an
is called massive collapse of the
specialized epithelial cells obstruction, surgery or other
lung.
treatments may be required.
• Chest pain when breathing or Specific treatment depends on
coughing the type and severity of
It is a pathological process where • Cough that can produce
there is a bacterial invasion of the pneumonia, your age, and your
phlegm general health. Options include
lung parenchyma that causes • Bacteria, viruses and fungi from the
Pneumonia • Fatigue the following:
exudative consolidation of the air we breathe.
viscera. The form it takes depends • Fever, sweating, and chills with
shaking - Antibiotics
on the specific etiologic agent. - Cough medicines
• Nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea
- Fever reducers/analgesics
• Difficulty breathing
• Tobacco smoke • Shortness of breath
• Dust mites • Chest pain or tightness
This usually involves learning to
• Atmospheric pollution • Wheezing on exhalation, which
recognize triggers, taking steps
It is a disease characterized by • Pets is a common sign of asthma in
to avoid them, and monitoring
increased irritability of the children
• Mold your breathing to make sure
Asthma bronchial tree due to paroxysmal • Trouble sleeping caused by
• Smoke from burning wood or grass medications are keeping
narrowing of the bronchial shortness of breath, coughing or
• Sinusitis symptoms under control. In the
airways. wheezing
• Allergies event of an asthma attack, a
• Coughing or wheezing that is quick-relief inhaler may be used.
• Excessive physical exercise made worse by a respiratory
• Medicines virus, such as a cold or flu
It is a blue coloring of the lips, Oxygen therapy is the first
fingers and toes. Blood circulates • Significant cooling of the body • Bluish discoloration of the lips, treatment that is administered,
abnormally, so oxygen-poor • Decreased stroke volume fingers, and toes as in other situations that occur
Cyanosis blood from the right side of the • Local alterations of the arterial system • Dyspnea with low levels of oxygen in the
heart goes directly to the left side, • Vasomotor disturbances • Chest pain blood. Surgery is also an option,
instead of first going through the • Worsening venous return • Tiredness or weakness depending on the type of birth
lungs for more oxygen. defect.
It is a disease caused by the
• Severe cough that lasts 3 weeks
bacterium Mycobacterium Drug treatment, this procedure is
or more
tuberculosis. These bacteria • It is caused by a bacterium called followed especially with people
• Chest pain
Tuberculosis usually attack the lungs, but they Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It who have HIV/AIDS or other
can also attack other parts of the spreads easily in crowded places. • Coughing up blood or sputum factors that increase the risk of
body, such as the kidneys, spine, (phlegm that comes up from the contracting active tuberculosis.
and brain. bottom of the lungs)
1. Tratamiento causal
2. Tratamiento sintomático
(solamente en personas sin
hipoxia):
• Utilizar ansiolíticos o
Hypocapnia is defined as a • Hyperventilation • Alterations of consciousness
depresores del centro
Hypocapnia deficiency of carbon dioxide • Anxiety • Symptoms of cerebral ischemia
respiratorio (benzodiazepinas,
(CO2) in the arterial blood. • Fever • Paresthesia barbitúricos)
• Indicar la respiración en
una bolsa de plástico (para
aumentar el espacio respiratorio
muerto).
• Reddened skin
• Decreased central nervous system • Drowsiness or inability to Limites tu exposición a vapores o
It is a type of respiratory failure. respiratory drive concentrate sustancias químicas si han
Occurs when there is a large
Hypercapnia • Anatomical defects • Mild headache causado hipercapnia
amount of carbon dioxide (CO2)
• Decreased neuromuscular response • Feeling short of breath relacionada con la EPOC.
in the bloodstream.
• Increased dead space within the lung. • Feeling abnormally tired or
exhausted
There are risk factors:
• Loud snoring
• Overweight
Potentially serious sleep disorder • Episodes where breathing stops Recomendar cambios en el estilo
• Deviated nasal septum
in which breathing repeatedly while you sleep de vida, como bajar de peso o
• Very large tonsils
stops and starts again. These • Gasping for breath while dejar de fumar. Podría ser
Apnea • Be of the male sex
interruptions can last from a few sleeping necesario que cambiar la
seconds to minutes and can occur • Family background posición en la que duermes.
• Waking up with a dry mouth
more than 30 times per hour. • Advanced age
• Headache in the morning
• Use of alcohol, sedatives or
• Insomnia
tranquilizers
You might also like
- PHARMA 1F Notes RespiratoryDocument9 pagesPHARMA 1F Notes RespiratoryCheryl OrtizNo ratings yet
- The Essential COPD Diet Cookbook:The Complete Nutrition Guide To Shed Excess Fats, Build Muscle And Unleash Your Body Potential With Meal Plan And Nourishing RecipesFrom EverandThe Essential COPD Diet Cookbook:The Complete Nutrition Guide To Shed Excess Fats, Build Muscle And Unleash Your Body Potential With Meal Plan And Nourishing RecipesNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATION Week 11Document49 pagesRESPIRATION Week 11Janelle Alyson De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Snoring, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandSnoring, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Inhalation Injury and Systemic IntoxicationDocument7 pagesInhalation Injury and Systemic IntoxicationDaniel LesmanaNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Dysphonia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Dysphonia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- BBB - Respi&gi ReportsDocument11 pagesBBB - Respi&gi ReportsshesahNo ratings yet
- ... 1 Finals Pulmonary ConditionsDocument9 pages... 1 Finals Pulmonary ConditionsELIZABETH GRACE AMADORNo ratings yet
- Asthma: Symptoms, Treatments, and Medication for Asthma and BronchitisFrom EverandAsthma: Symptoms, Treatments, and Medication for Asthma and BronchitisNo ratings yet
- Concept Map of Copd: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseDocument1 pageConcept Map of Copd: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseWayne Calderon75% (4)
- Pemicu 4 KGD SherDocument91 pagesPemicu 4 KGD SherSheren ReginaNo ratings yet
- Internal Medicine Table SummaryDocument31 pagesInternal Medicine Table SummaryShazaan Nadeem100% (1)
- EmphysemaDocument4 pagesEmphysemaRajuNo ratings yet
- Thoracic and Lung AssessmentDocument37 pagesThoracic and Lung AssessmentJayciel Cabrejas LorNo ratings yet
- Internal Medicine Table PDFDocument31 pagesInternal Medicine Table PDFShazaan NadeemNo ratings yet
- Geron-Ppt - 20231206 131738 0000Document29 pagesGeron-Ppt - 20231206 131738 0000Potato TomatoNo ratings yet
- Trifold Brochure Placeholder 2Document3 pagesTrifold Brochure Placeholder 2api-604097499No ratings yet
- Tachypnea - Use of Accessory Muscles in Breathing - O2: 91% - Nasal FlaringDocument3 pagesTachypnea - Use of Accessory Muscles in Breathing - O2: 91% - Nasal FlaringBenjie DimayacyacNo ratings yet
- Nursing CS CroupDocument1 pageNursing CS Croupreuben kadarajaNo ratings yet
- DDX Paediatrics (HX, PE, Ix)Document27 pagesDDX Paediatrics (HX, PE, Ix)cirlce:twoworldsconnectedNo ratings yet
- Case Study: Acute Exacarbation Chronic Obstructive Aspiration Disease (Aecoad)Document5 pagesCase Study: Acute Exacarbation Chronic Obstructive Aspiration Disease (Aecoad)Muhammad Alif100% (1)
- Basic Concepts in Lung DiseaseDocument38 pagesBasic Concepts in Lung DiseaselecturioNo ratings yet
- ANOLIN, Marc Edriann T. Nursing Care Plan Assessmen T Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesANOLIN, Marc Edriann T. Nursing Care Plan Assessmen T Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationEdrianne Tui100% (2)
- Medsurg Copd Anemia ReviewersDocument21 pagesMedsurg Copd Anemia ReviewersIvy VillalobosNo ratings yet
- 7.chest and Lower Respiratory Tract DisordersDocument8 pages7.chest and Lower Respiratory Tract Disorders2BGrp3Plaza, Anna MaeNo ratings yet
- Q3 HEALTH 8 WK1 LESSON 1 Disease Prevention and Control CommunicableDocument35 pagesQ3 HEALTH 8 WK1 LESSON 1 Disease Prevention and Control CommunicableJaeda EuclidNo ratings yet
- Iv. Pathophysiology 1. Schematic Diagram Book Based Pathophysiology: Precipitating/Modifiable Factors Non Modifiable / Predisposing FactorsDocument2 pagesIv. Pathophysiology 1. Schematic Diagram Book Based Pathophysiology: Precipitating/Modifiable Factors Non Modifiable / Predisposing Factorsikemas67% (6)
- Respiratory Pathology 2Document28 pagesRespiratory Pathology 2AZALEA SANIANONo ratings yet
- Chronic CoughDocument6 pagesChronic CoughironNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Bronchial AsthmaDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Bronchial Asthmaderic93% (60)
- NCP FinalDocument5 pagesNCP FinalYoongiNo ratings yet
- NCM103 - 2016 - Lecture2 - Response To Altered Respiratory FunctionDocument128 pagesNCM103 - 2016 - Lecture2 - Response To Altered Respiratory FunctionrimeoznekNo ratings yet
- Oxygenation Respiration: Hypoxia Is A Condition in Which The Body or A Region ofDocument3 pagesOxygenation Respiration: Hypoxia Is A Condition in Which The Body or A Region ofMarissa AsimNo ratings yet
- NCP PDFDocument8 pagesNCP PDFThee AzirahNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Medicine Dental 2018Document28 pagesRespiratory Medicine Dental 2018David McMahonNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlansDocument7 pagesNursing Care PlansJayson Sumampong100% (1)
- Respirations 1Document42 pagesRespirations 1api-3697326No ratings yet
- CD 1Document5 pagesCD 1Iriah Mara100% (1)
- PEDIA-Bronchitis, Bronchiectasis, Aspiration Pneumonia, Abscess (Dr. Tampus)Document4 pagesPEDIA-Bronchitis, Bronchiectasis, Aspiration Pneumonia, Abscess (Dr. Tampus)Monique BorresNo ratings yet
- Lower Respiratory Tract InfectionsDocument14 pagesLower Respiratory Tract InfectionsEric EpahNo ratings yet
- Week 5-14 Notes 3Document8 pagesWeek 5-14 Notes 3navkkirangillNo ratings yet
- (Ofi) Respiratory SystemDocument12 pages(Ofi) Respiratory SystemPimpamNo ratings yet
- NCM 109Document18 pagesNCM 109Grace Jane HannaNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Case PresentationDocument1 pagePneumonia Case PresentationFrancine kimberlyNo ratings yet
- 6.4 Gas ExchangeDocument1 page6.4 Gas ExchangeAndreaNo ratings yet
- Chronic CoughDocument6 pagesChronic CoughironNo ratings yet
- NCP Hyperthermia IBPDocument4 pagesNCP Hyperthermia IBPJohn Patrick CuencoNo ratings yet
- Emphysem A: Presentation Made By: Ison, Von Jose V. Regancia, NoricelDocument12 pagesEmphysem A: Presentation Made By: Ison, Von Jose V. Regancia, NoricelVon Jose IsonNo ratings yet
- 2.health AssessmentDocument7 pages2.health Assessment2BGrp3Plaza, Anna MaeNo ratings yet
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)Document16 pagesChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)Kimberly Abella CabreraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)deric95% (41)
- Vartes Io-A2 Final VersionDocument94 pagesVartes Io-A2 Final VersionAlex CastelNo ratings yet
- Forensic PracticalDocument59 pagesForensic PracticalDhiraj PantNo ratings yet
- NSTP 1 Module 4 Drug Education Objectives: The Comprehensive Dangerous Drugs Act of 2002Document5 pagesNSTP 1 Module 4 Drug Education Objectives: The Comprehensive Dangerous Drugs Act of 2002Juliet ArdalesNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument340 pagesUntitledAlistair KohNo ratings yet
- Pembahasan Semester 4-5 Maret 2022Document21 pagesPembahasan Semester 4-5 Maret 2022Angger SatriaNo ratings yet
- ProP Ophthalmic Examination Made EasyDocument5 pagesProP Ophthalmic Examination Made EasyRosario AyalaNo ratings yet
- Biology (Ethiopian Students' Textbook)Document280 pagesBiology (Ethiopian Students' Textbook)Gadisa100% (1)
- Speaking Sample Test 3 - Veterinary ScienceDocument1 pageSpeaking Sample Test 3 - Veterinary ScienceMehdi YarmohammadiNo ratings yet
- The IRM India - Lessons Learned From The COVID-19 PandemicDocument38 pagesThe IRM India - Lessons Learned From The COVID-19 PandemicIRM IndiaNo ratings yet
- Admission, Criteria - Adult Intensive Care Unit.Document5 pagesAdmission, Criteria - Adult Intensive Care Unit.EsamNo ratings yet
- File 146 - Stupid-UsmleDocument14 pagesFile 146 - Stupid-UsmlePrarthana100% (4)
- SFH MCQ 2Document5 pagesSFH MCQ 2Shamanth MNo ratings yet
- Pericystectomy With HemicolectomyDocument19 pagesPericystectomy With HemicolectomyValarmathiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Definition Lecture NotesDocument4 pagesLecture 6 Definition Lecture NotesOanaNo ratings yet
- Animal Diversity 7Th Edition Hickman Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument30 pagesAnimal Diversity 7Th Edition Hickman Test Bank Full Chapter PDFarthur.brown523100% (16)
- Seidman 2014Document17 pagesSeidman 2014Anonymous G6zDTD2yNo ratings yet
- Diare Akut: Adhesi Invasi Sitotoksin EnterotoksinDocument4 pagesDiare Akut: Adhesi Invasi Sitotoksin EnterotoksinVeronica Yosita AnandaNo ratings yet
- BDI (Becks' Depression Inventory) Assessment For Children: Children'S Depression Self-Rating Scale: InstructionsDocument4 pagesBDI (Becks' Depression Inventory) Assessment For Children: Children'S Depression Self-Rating Scale: InstructionsHimaniNo ratings yet
- DR, Zainal Safri, SPPD, SPJP / Dr. Amran Lubis SPJP (K) : Penyakit Pembuluh Darah Arteri, Vena Dan LimfeDocument41 pagesDR, Zainal Safri, SPPD, SPJP / Dr. Amran Lubis SPJP (K) : Penyakit Pembuluh Darah Arteri, Vena Dan Limfeろりたんいあ黒ヴぃNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPJonna Mae TurquezaNo ratings yet
- Inflammatory DermatologyDocument64 pagesInflammatory DermatologyDragonNo ratings yet
- Jane Eyre 3Document10 pagesJane Eyre 3Vincent SottoNo ratings yet
- Psychological Disorder (Schizophrenia)Document31 pagesPsychological Disorder (Schizophrenia)Farah Bashir0% (1)
- NLE2Document10 pagesNLE2giansulakisosuNo ratings yet
- 2ENGLISH10 - Q1 - Module 2 - Week2 - Determine The Effect of Textual Aids On Understanding A Text - v4BDocument25 pages2ENGLISH10 - Q1 - Module 2 - Week2 - Determine The Effect of Textual Aids On Understanding A Text - v4Bcodm PlayerNo ratings yet
- Feature Writing About Covid-19 - MortelDocument2 pagesFeature Writing About Covid-19 - MortelAna Carmela MortelNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of HormonDocument16 pagesBiochemistry of HormonMuhamad SdeqNo ratings yet
- Nipah Virus PDFDocument2 pagesNipah Virus PDFRakesh SahuNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Republic v. CA & Molina and Tan-Andal v. AndalDocument2 pagesComparison of Republic v. CA & Molina and Tan-Andal v. AndalArah Obias CopeNo ratings yet
- Cymbopogon Citratus DcstapfDocument91 pagesCymbopogon Citratus DcstapfKeyla Rodríguez SanmartínNo ratings yet