Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nursing CS Croup
Uploaded by
reuben kadarajaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nursing CS Croup
Uploaded by
reuben kadarajaCopyright:
Available Formats
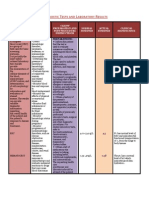
CROUP
Normal Larynx Inflamed Larynx
Trachea Croup is a symptom,
characterized by infection
and inflammation of the upper air-
Vocal chords way (trachea and larynx)
Etiologies Pathophysiology
Viral infection of the laryngeal mucosa
Viral causes Bacterial causes
Imflammation, hyperemia, epithelial necrosis and shredding
• Parainfluenza viruses types 1 • Staphylococcus aureus ⊲ results narrowing of the subglottic region
and 3 (80% of cases) • Streptococcus pyogenes
• Influenza virus A and B Breathe more rapidly and deeper to compensate for the
• Streptococcus pneumoniae
narrowing of the upper airway
• Respiratory syncytial virus • Haemophilus influenzae
(RSV) Turbulent airflow (stridor) through the upper airway, chest
• Moraxella catarrhalis
• Adenovirus wall begins to retract
• Rhinovirus Inefficient asynchronous chest and abdominal movement,
fatigued
Signs & Symptoms Hyproxia and hypercapnia, progress to respiratory failure and
arrest
Typically starts as mild cold
Cough: loud barking Nasal: congestion or
runny nose
Treatment
Corticosteroids (dexamethasone, predni-
Respiratory: difficulty Speech: hoarseness, or sone)
breathing, fast breathing, impaired voice
noisy breathing, short- In serious cases: racemic epinephrine
ness of breath, whee- Time: worse at night nebullizer
zing, or stridor
Acetaminophen and/or Ibuprofen (only > 6
months old)
Also common: agitation, For most children, croup is a
anxiety, phlegm, or sore mild illness that can be mana- Humidified air ― debatable efficacy
throat ged at home
Diagnosis Complications
History of symptoms Secondary bacterial infections
Complications
Physical exam Dehydration
are rare.
Barking cough, hoarseness, inspiratory stridor Respiratory distress
Low-grade fever May need oxygen support, fluids
and racemic epinephrine
Absence of wheezing
www.lecturio.com/nursing WATCH VIDEO
You might also like
- Fundamentals of Nursing ReviewerDocument9 pagesFundamentals of Nursing Reviewerchie9268No ratings yet
- Literature Review On Secondhand SmokeDocument6 pagesLiterature Review On Secondhand Smokeapi-519859495No ratings yet
- Communicable DiseaseDocument5 pagesCommunicable DiseaseVinceNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Nursing CA Sir Archie Alviz 04-09-2022Document3 pagesPediatric Nursing CA Sir Archie Alviz 04-09-2022Jonah MaasinNo ratings yet
- Nursing MnemonicsDocument2 pagesNursing MnemonicsJamie ElizabethNo ratings yet
- Nursing CS TuberculosisDocument1 pageNursing CS TuberculosisJazzmine GuraNo ratings yet
- MS NeuroDocument28 pagesMS NeuroFrechel Ann Landingin PedrozoNo ratings yet
- CC Reinforcement and Mastery Sessions 1Document16 pagesCC Reinforcement and Mastery Sessions 1Anne MorenoNo ratings yet
- Centro Escolar University Nursing Department Malolos City, BulacanDocument5 pagesCentro Escolar University Nursing Department Malolos City, BulacanBee Anne BiñasNo ratings yet
- MS PERI OPushjDocument13 pagesMS PERI OPushjEmeroot RootNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Mock Board RationalizationDocument228 pagesMicrobiology Mock Board RationalizationCla NuvalNo ratings yet
- Final DX ResultsDocument9 pagesFinal DX ResultszysheaiNo ratings yet
- Typhoid Fever: Pathophysiology, Signs, Symptoms and Nursing CareDocument13 pagesTyphoid Fever: Pathophysiology, Signs, Symptoms and Nursing CareCassey CuregNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Immunity Response TransDocument10 pages1.2 Immunity Response TransJoshua SaanNo ratings yet
- Cranial NerveDocument4 pagesCranial NerveBrian OballoNo ratings yet
- Part 1 RenalDocument8 pagesPart 1 RenalKatherine ApostolNo ratings yet
- Review of SystemsDocument4 pagesReview of SystemsKat ArriolaNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics Lecture on Malnutrition Criteria and InterventionsDocument8 pagesPediatrics Lecture on Malnutrition Criteria and InterventionskrishNo ratings yet
- Pedia Drug StudyDocument11 pagesPedia Drug StudyPeetah PanNo ratings yet
- Nurse Licensure Exam CBQs on Renal and Cardiovascular SystemsDocument2 pagesNurse Licensure Exam CBQs on Renal and Cardiovascular SystemsJhannNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument6 pagesUntitledFritz Angelo BullonNo ratings yet
- 06 - 07 - Anatomy of The Chest Wall and BreastDocument16 pages06 - 07 - Anatomy of The Chest Wall and Breastbo gum parkNo ratings yet
- Guiding Environmentally Safe Nursing CareDocument7 pagesGuiding Environmentally Safe Nursing CarepauchanmnlNo ratings yet
- DISTURBANCES IN ABSORPTION AND ELIMINATIONDocument7 pagesDISTURBANCES IN ABSORPTION AND ELIMINATIONHoneylette DarundayNo ratings yet
- Post Test - Neuro - Dr. Arreglo (SC)Document2 pagesPost Test - Neuro - Dr. Arreglo (SC)Kristen FajilanNo ratings yet
- Gastro-Intestinal System Diagnostic TestsDocument11 pagesGastro-Intestinal System Diagnostic TestsFev BanataoNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Nursing GastroDocument3 pagesPediatric Nursing GastronieacatleyaNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Nursing or Child Health NusrsingDocument20 pagesPediatric Nursing or Child Health NusrsingGenynne RagasaNo ratings yet
- CHN Post TestDocument13 pagesCHN Post TestAngel YN Patricio FlorentinoNo ratings yet
- 118 Skills Lab-Week 1-Responses To Altered Ventilatory FunctionsDocument8 pages118 Skills Lab-Week 1-Responses To Altered Ventilatory FunctionsKeisha BartolataNo ratings yet
- Airway Emergencies GuideDocument58 pagesAirway Emergencies GuideKimberlyLaw95No ratings yet
- Assignment #1 - PEDIA (GIT)Document1 pageAssignment #1 - PEDIA (GIT)Kerima Danica Lising GayoNo ratings yet
- MnemonicsDocument10 pagesMnemonicsRichard GarciaNo ratings yet
- ENDO InhouseDocument29 pagesENDO Inhouseniczdelosreyes8No ratings yet
- Pedia-Reviewer CompleteDocument36 pagesPedia-Reviewer CompletePotato BroNo ratings yet
- Growth and Development Growing Complex Phenomenon of A Structure or Whole GrowthDocument69 pagesGrowth and Development Growing Complex Phenomenon of A Structure or Whole GrowthYna RamiroNo ratings yet
- BODY Weight 100%: Balance/Imbalances & TherapyDocument11 pagesBODY Weight 100%: Balance/Imbalances & TherapyVictoria Castillo TamayoNo ratings yet
- NP1 BulletsDocument17 pagesNP1 BulletsJea VesagasNo ratings yet
- Hepatic Disorders: Prepared by Captain: Jumana AL-Momani RN - MSNDocument72 pagesHepatic Disorders: Prepared by Captain: Jumana AL-Momani RN - MSNJanuaryNo ratings yet
- M1 - Urinary DisordersDocument2 pagesM1 - Urinary DisordersjuiceNo ratings yet
- Pentagon CDDocument12 pagesPentagon CDJohnNo ratings yet
- Git HandoutsDocument49 pagesGit HandoutsCharlz Zipagan100% (1)
- Problems with the Power: Dystocia Causes and Nursing ManagementDocument3 pagesProblems with the Power: Dystocia Causes and Nursing ManagementJP Porras Ali100% (1)
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument26 pagesCardiovascular SystemJenny Torreda100% (1)
- STD Treatment GuideDocument2 pagesSTD Treatment GuideapocruNo ratings yet
- CHN1 LEC - DOH Nutritional ProgramDocument3 pagesCHN1 LEC - DOH Nutritional ProgramCassey Anne100% (1)
- Migs (With Summary) +paoDocument6 pagesMigs (With Summary) +paoMigs MedinaNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Nclex Iloilo 4Document27 pagesRESPIRATORY SYSTEM Nclex Iloilo 4Barangay Centro SurNo ratings yet
- Maintaining Potency of EPI VaccinesDocument13 pagesMaintaining Potency of EPI VaccinesMarylle Joy SullanoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Licensure Exam Practice QuestionsDocument11 pagesNursing Licensure Exam Practice QuestionsPaul Lexus Gomez LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Sirs ModsDocument10 pagesSirs ModsRENEROSE TORRESNo ratings yet
- Amoebiasis: An Overview of Its Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument8 pagesAmoebiasis: An Overview of Its Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and TreatmentCheska ت HortelanoNo ratings yet
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Infection and Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS)Document28 pagesHuman Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Infection and Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS)The Living SonneteerNo ratings yet
- Breast and AxillaeDocument13 pagesBreast and AxillaeJemma NocalanNo ratings yet
- NP5 Recalls5Document9 pagesNP5 Recalls5AhrisJeannine EscuadroNo ratings yet
- Philippine Health Advisories, 2012 PDFDocument170 pagesPhilippine Health Advisories, 2012 PDFRyan Michael OducadoNo ratings yet
- 6 Alterations On Tissue Perfusion Poleno Serrano TajalaDocument18 pages6 Alterations On Tissue Perfusion Poleno Serrano TajalaSophia A. GoNo ratings yet
- Bronchiolitis 44Document7 pagesBronchiolitis 44Fati NurNo ratings yet
- 4.1 PEDIA-Pneumonia, Tuberculosis, Interstitial Lung Diseases (Dr. Bermejo)Document6 pages4.1 PEDIA-Pneumonia, Tuberculosis, Interstitial Lung Diseases (Dr. Bermejo)Monique BorresNo ratings yet
- Approach To CoughDocument5 pagesApproach To CoughZulaikha HattaNo ratings yet
- Fevo 08 602190Document10 pagesFevo 08 602190Sohan kunduNo ratings yet
- Malaysia Employers FaderationDocument12 pagesMalaysia Employers FaderationHa HoNo ratings yet
- Tilapia Lake Virus Disease Strategy Manual: NFIM/C1220 (En)Document62 pagesTilapia Lake Virus Disease Strategy Manual: NFIM/C1220 (En)Angel DerrickNo ratings yet
- Zhuhai Lituo Biotechnology Co., LTD: Leading Technology For Healthy LifeDocument32 pagesZhuhai Lituo Biotechnology Co., LTD: Leading Technology For Healthy LifeFrancisca RamliNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument7 pagesMultiple Choice QuestionsDr-Sanjay SinghaniaNo ratings yet
- Uber CEO EmailDocument5 pagesUber CEO EmailKhristopher J. BrooksNo ratings yet
- Potential and Limitation of Biocontrol Methods Against Vibriosis: A ReviewDocument44 pagesPotential and Limitation of Biocontrol Methods Against Vibriosis: A ReviewAlvaro Parra BóccoliNo ratings yet
- Hospital Discharge Patient Leaflet - Editable - V3Document2 pagesHospital Discharge Patient Leaflet - Editable - V3el esNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: BIOLOGY 9700/22Document16 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: BIOLOGY 9700/22Milinda De SilvaNo ratings yet
- FOURTH MEETING RickyDocument3 pagesFOURTH MEETING RickyQhie'yPhie ArdiansyahNo ratings yet
- NORTH SYDNEY GIRLS HIGH SCHOOL 2021 PRACTICE HSC EXAMINATION BIOLOGYDocument58 pagesNORTH SYDNEY GIRLS HIGH SCHOOL 2021 PRACTICE HSC EXAMINATION BIOLOGYHewadNo ratings yet
- DiseaseSpreadSE - GizmoDocument5 pagesDiseaseSpreadSE - GizmoSTU-Xavier GarrettNo ratings yet
- Post Test On Needle Stick InjuryDocument4 pagesPost Test On Needle Stick InjurysunitapuniaNo ratings yet
- Case Report: Yafanita Izzati Nurina, Usman HadiDocument8 pagesCase Report: Yafanita Izzati Nurina, Usman HadiZuraidaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6Document9 pagesLesson 6nida intongNo ratings yet
- Module 9: Lymphatic System & Immunity: InnateDocument5 pagesModule 9: Lymphatic System & Immunity: InnatejunquelalaNo ratings yet
- 3-1 - Ida ParwatiDocument34 pages3-1 - Ida ParwatiFaisal NurlanNo ratings yet
- Role of PCR Testing in Monitoring Asymptomatic COVID-19 CarriersDocument5 pagesRole of PCR Testing in Monitoring Asymptomatic COVID-19 CarriersBiogxincNo ratings yet
- Seroprevalence of Newcastle Disease Virus Infection and Detection of Paramyxovirus On Duck at Farmland and Poultry Market in BaliDocument9 pagesSeroprevalence of Newcastle Disease Virus Infection and Detection of Paramyxovirus On Duck at Farmland and Poultry Market in BaliResha MustikaNo ratings yet
- Ch. 23 Infectious DiseasesDocument40 pagesCh. 23 Infectious Diseases吴昊No ratings yet
- SSTi Diabetic PETRI 2019Document36 pagesSSTi Diabetic PETRI 2019intermoska soloNo ratings yet
- PODS Health Global Catalogue - May 2022Document439 pagesPODS Health Global Catalogue - May 2022Malc BergeNo ratings yet
- CRISPRCas Correction of Muscular DystrophiesDocument9 pagesCRISPRCas Correction of Muscular DystrophiesRooh UllahNo ratings yet
- Uxz PDFDocument16 pagesUxz PDFSaifur RahmanNo ratings yet
- SOP Hostel (February)Document5 pagesSOP Hostel (February)jc9322No ratings yet
- DCM Micr B IntroductionDocument58 pagesDCM Micr B Introductioncyber secNo ratings yet
- IMMUNOTECH™ - A Immunomodulator in Poultry by ABTL EnzymesDocument4 pagesIMMUNOTECH™ - A Immunomodulator in Poultry by ABTL EnzymesabtlenzymesNo ratings yet
- Atmosphere Mini Vs Sharp PDFDocument12 pagesAtmosphere Mini Vs Sharp PDFParthiban BalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- VOL 27 NO 110 Antigua Distillery Adds Hand Sanitiser; Nurses Mark Int'l DayDocument24 pagesVOL 27 NO 110 Antigua Distillery Adds Hand Sanitiser; Nurses Mark Int'l DayA GrosvenorNo ratings yet
- HT - Delhi 13 April 2020 PDFDocument16 pagesHT - Delhi 13 April 2020 PDFRakesh GujralNo ratings yet