Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Physics:0 PDF
Uploaded by
aosdfaosduOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Physics:0 PDF
Uploaded by
aosdfaosduCopyright:
Available Formats
Physics Notes
All Formulas
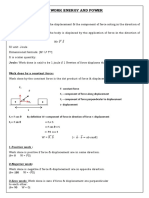
F=ma
V2=u2+2as
S=ut+1/2at2
V=u+at
A=(v-u)/t
S=1/2(u+v)t
Ug=mgh
Ek=mas
KE=1/2 mv2
T=mg+ma
Energy Efficiency= useful energy out/total energy in
Work=Fs = mgh = 1/2 mv2
Power= Work/time
Momentum=mv
Impulse=Ft=mat=m[(v-u)/t]t
(m1) (v1) +(m2) (v1) =(m1) (v2) +(m2) (v2)
ΣEk before = ΣEk after
Kinematics
Velocity
The relative velocity is the difference between the velocity of the object relative to the ground and the
velocity of the observer relative to the ground.
Displacement over time graph shows velocity (y’)
Velocity over time graph shows acceleration (y’’)
Vectors
All vectors may be described as the sum of their horizontal and vertical component vectors.
A vector can be resolved into two independent, perpendicular components: Vx = V cos θ, and Vy = V sin θ
Two vectors are added by placing the tail of the second vector at the head of the first vector. The sum of the
vectors is represented by a resultant vector, which is drawn from the tail of the first vector to the head of
the last vector.
In vector subtraction, the resultant of A − B = A + (−B) where (−B) has the same magnitude as B but is
directed in the opposite direction.
Dynamics
Forces
Contact forces- is exerted by an object that is in physical contact with another object
Non-contact forces- can be exerted by an object that is not touching the thing that it is influencing.
Gravity
The force of gravity is a force of attraction that exists between any pair of objects that have mass
Mass remains the same wherever because it is a measure of the amount of matter in an object or substance
Normal Reaction Force
The sum of these upward forces must be just enough to balance the pull of gravity downwards.
Each one of these upward forces, or support forces, is called a normal reaction force.
You might also like
- Physics Finals Reviewer FinalDocument15 pagesPhysics Finals Reviewer FinalMark Justin NiloNo ratings yet
- Physics Topic 2 Study GuideDocument7 pagesPhysics Topic 2 Study GuideSai 0235No ratings yet
- Work, Energy and Power Class 11 Physics - NotesDocument17 pagesWork, Energy and Power Class 11 Physics - NotesStudy ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Physics Finals NotesDocument4 pagesPhysics Finals Notesramalingam1299No ratings yet
- Unit 2Document6 pagesUnit 2Mihailo MilicNo ratings yet
- Basic Engineering Sciences Reviewer - CompleteDocument87 pagesBasic Engineering Sciences Reviewer - Completeyomz719No ratings yet
- Physics Formulas and ConceptsDocument23 pagesPhysics Formulas and Conceptschand7790No ratings yet
- Statics - PresentationDocument164 pagesStatics - PresentationKorpy KorpyNo ratings yet
- Physics Formulas and ConceptsDocument23 pagesPhysics Formulas and ConceptsShivam TiwariNo ratings yet
- Ring KasanDocument11 pagesRing Kasandini_25No ratings yet
- Phy Lab 06 Theory Part-1Document3 pagesPhy Lab 06 Theory Part-1shamaiem shabbirNo ratings yet
- AP Physics Test ReviewDocument21 pagesAP Physics Test ReviewAnish KalappaNo ratings yet
- ETU Engineering Mechanics I 1 To 8Document184 pagesETU Engineering Mechanics I 1 To 8AidanNo ratings yet
- TFU3013 General Physics I: RevisionDocument82 pagesTFU3013 General Physics I: Revisionerdayu86No ratings yet
- MCAT Prep Physics Equation SheetDocument3 pagesMCAT Prep Physics Equation SheetChris_Barber0971% (7)
- Physics Equation Sheet: MG F MG FDocument4 pagesPhysics Equation Sheet: MG F MG FFayzan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics DynamicsChapter14Document8 pagesEngineering Mechanics DynamicsChapter14Eenz EduNo ratings yet
- Basic Engineering Sciences Reviewer - Complete PDFDocument87 pagesBasic Engineering Sciences Reviewer - Complete PDFashier dave calulotNo ratings yet
- MCAT Physics Formula SheetDocument3 pagesMCAT Physics Formula Sheetemma_reese100% (2)
- Chapter 5 Two Dimensional KinematicsDocument16 pagesChapter 5 Two Dimensional KinematicsMac MagsinoNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument8 pagesPhysicsDarius AdibaNo ratings yet
- Physics Formulas: Mechanics: Newton's Law of MotionDocument12 pagesPhysics Formulas: Mechanics: Newton's Law of Motionatyalo11No ratings yet
- PHYSICS (Principles)Document45 pagesPHYSICS (Principles)Year Yveneil Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Uniformly Accelerated Motion in Vertical DimentaionDocument11 pagesUniformly Accelerated Motion in Vertical DimentaionEricka Pallon CamayudoNo ratings yet
- Work Energy and PowerDocument11 pagesWork Energy and PowerKunal RaikarNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Physics Study Guide / Notes For Final Exam SPH3U1Document23 pagesGrade 11 Physics Study Guide / Notes For Final Exam SPH3U1Niki79% (14)
- Grade 11 Physics Study Guide Notes For Final Exam SPH3U1Document23 pagesGrade 11 Physics Study Guide Notes For Final Exam SPH3U1Kamil GhoshNo ratings yet
- Math Investigatory ProjectDocument9 pagesMath Investigatory ProjectKavinn100% (1)
- Physics 11 SummaryDocument8 pagesPhysics 11 SummaryJ100% (5)
- Strain Energy Methods: 2.1 WorkDocument7 pagesStrain Energy Methods: 2.1 WorkvsanthanamNo ratings yet
- Scalars and VectorsDocument11 pagesScalars and VectorsEFRAIM CAMBENo ratings yet
- Physics Week 7Document5 pagesPhysics Week 7EDUARDO lll NADATENo ratings yet
- Cape Unit I RevisionDocument56 pagesCape Unit I Revisionsarcasticb15No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 2010Document15 pagesChapter 2 2010Agnes YaoYaoNo ratings yet
- Numerical SDocument82 pagesNumerical Smuhammad adilNo ratings yet
- ALEVEL PHYSICS AQA Unit 2 Mechanics Materials and Waves NOTESDocument37 pagesALEVEL PHYSICS AQA Unit 2 Mechanics Materials and Waves NOTESJames ChongNo ratings yet
- Mechanics: 2.1 - Motion Distance and DisplacementDocument17 pagesMechanics: 2.1 - Motion Distance and DisplacementMido YoussefNo ratings yet
- Displacement:: R R T R VDocument76 pagesDisplacement:: R R T R Vg3om3No ratings yet
- Case Study Questions Class 11 Physics - Work, Energy and PowerDocument7 pagesCase Study Questions Class 11 Physics - Work, Energy and PowerRavinder KumarNo ratings yet
- Notes For Dynamics:: Ideal BodiesDocument29 pagesNotes For Dynamics:: Ideal BodiesJohn FerrarNo ratings yet
- IB Physics DefinitionsDocument12 pagesIB Physics DefinitionsDoda BubbsNo ratings yet
- Newton'S Law of Motion: ForceDocument2 pagesNewton'S Law of Motion: ForceJohanna AlumbroNo ratings yet
- MECH2210 Lecture NotesDocument39 pagesMECH2210 Lecture NotesKeith WellsNo ratings yet
- Work, Energy and Power: Art Intgrated ActivityDocument27 pagesWork, Energy and Power: Art Intgrated ActivitylakeishaNo ratings yet
- Physics ReviewerDocument6 pagesPhysics ReviewerHeart Del MundoNo ratings yet
- Physics Key Terms and Meaning-Semester-1Document6 pagesPhysics Key Terms and Meaning-Semester-1techzealNo ratings yet
- 186 Ri FoundSolMech 99Document53 pages186 Ri FoundSolMech 99Chandra ClarkNo ratings yet
- Impulse - MomentumDocument15 pagesImpulse - MomentumVijay Mohan SettiNo ratings yet
- Concept of Force and Newton's Laws of MotionDocument27 pagesConcept of Force and Newton's Laws of MotionManuel LarreaNo ratings yet
- Physics Review SheetDocument18 pagesPhysics Review SheetRayhan Ahmed100% (1)
- Definitions and Questions Paper 1Document47 pagesDefinitions and Questions Paper 1ThabeloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Work and EnergyDocument9 pagesChapter 6 Work and Energybmz00000No ratings yet
- 1 StressDocument36 pages1 StressWAKHIDATUN NISANo ratings yet
- Full Free Motion of Celestial Bodies Around a Central Mass - Why Do They Mostly Orbit in the Equatorial Plane?From EverandFull Free Motion of Celestial Bodies Around a Central Mass - Why Do They Mostly Orbit in the Equatorial Plane?No ratings yet
- f1s WF 2023 TechregsDocument57 pagesf1s WF 2023 TechregsaosdfaosduNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes - Preliminary 2021 4Document35 pagesChemistry Notes - Preliminary 2021 4Sejal SinhaNo ratings yet
- Courses Science Chemistry 532e69c4d20dcDocument38 pagesCourses Science Chemistry 532e69c4d20dcaosdfaosduNo ratings yet
- Courses Techsci It 1254965515 2009 Information Technology NotesDocument14 pagesCourses Techsci It 1254965515 2009 Information Technology NotesaosdfaosduNo ratings yet