Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Experiment 5 Calculation
Experiment 5 Calculation
Uploaded by
Gaming UserOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Experiment 5 Calculation
Experiment 5 Calculation
Uploaded by
Gaming UserCopyright:
Available Formats
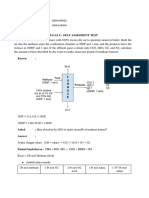
Table 5.
3 Determining the Molar Volume of a Gas
DATA Remarks
Mass of magnesium 0.00789 g Measured
Moles of magnesium Calculated (1)
Initial volume of tube 2 (Vo) 25.00 mL Measured
Final volume of tube 2 (Vf) 16.55 mL Measured
Volume of H2 – H2O vapour-gas
8.45 mL = Vo – Vf
mixture collected
Temperature 23 C = 296 K Measured
Barometric pressure 735 mmHg Measured
Vapor pressure of water at the
measured temperature (refer to 21.0 mmHg From table 5.1
Table 5.1)
Partial pressure of hydrogen gas 714 mmHg Calculated (2)
Volume of H2 at STP 0.00732 L Calculated (3)
Moles of hydrogen gas Calculated (1)
Molar volume of H2 at the
22.5 L/mole Calculated (4)
corrected pressure
Theoretical molar volume of
22.4 L/mole Contant at STP
hydrogen (STP)
% difference 0.446% Calculated (5)
Calculations:
1) Calculate the theoretical number of moles H2 gas produced.
Mg + 2 HCl MgCl2 + H2
According to the balanced reaction, the amount of hydrogen gas produced is equal to the
amount of moles of magnesium in the reaction.
Thus, moles of H2 is also .
2) Calculate the partial pressure of H2 gas. Use Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressure.
Barometric pressure = total pressure (735 mmHg)
Total pressure = PH 2 PH 2O
735 mmHg = PH 2 + 21.0 mmHg
PH 2 = 735 – 21.0 = 714.0 mmHg
3) Use Combined Gas Law to calculate volume of H2 at STP
P1V1 P2V2
Let STP be second conditions (P2, V2, and T2)
T1 T2
At STP, pressure and temperature are constant at 760 mmHg
and 273K, respectively.
P1V1T2 (714.0 mmHg)(0.00845 L)(273 K )
Volume at STP = V2
P2T1 (296 K )(760 mmHg)
= 0.00732 L
4) Calculate the experimentally determined molar volume at STP.
0.00732 L
Molar volume of H2 = = = 22.5 L/mole
3.25 10 4 moles
5) Calculate % difference.
| |
| |
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FjYB8hgkvOU
You might also like
- Calorimetry (Pre-Laboratory Assignment)Document4 pagesCalorimetry (Pre-Laboratory Assignment)Quirino Arzadon IVNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems (Chapter 5) Stoichiometry - KEYDocument3 pagesPractice Problems (Chapter 5) Stoichiometry - KEYGracia ProgellaNo ratings yet
- TUGAS 5 (Revisi Format) - Kelompok 6Document3 pagesTUGAS 5 (Revisi Format) - Kelompok 6Jenny AzzahraNo ratings yet
- Peb Steel Structures Tolerance Table As Per Aisc: Builtup/ Hotroll BeamsDocument2 pagesPeb Steel Structures Tolerance Table As Per Aisc: Builtup/ Hotroll BeamsSamsuNo ratings yet
- Rune CardsDocument170 pagesRune Cardsmimihell75100% (3)
- Carnot CycleDocument9 pagesCarnot CycleVipin TitariyaNo ratings yet
- E B1: M V G Learning Outcomes: Equation 1Document11 pagesE B1: M V G Learning Outcomes: Equation 1Putera AdigunaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 Q Tri Semester Jan 2010Document2 pagesTutorial 2 Q Tri Semester Jan 2010utpNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 Q Tri Semester Jan 2010Document2 pagesTutorial 2 Q Tri Semester Jan 2010utpNo ratings yet
- CHM092 Tutorial Chapter 4ADocument8 pagesCHM092 Tutorial Chapter 4AvNo ratings yet
- 2-Heat Chemistry ProjectDocument6 pages2-Heat Chemistry ProjectMuhammad shehryar wainNo ratings yet
- Gas StoichiometryDocument12 pagesGas StoichiometryAhmed Ali SomosaNo ratings yet
- N (G) - 2Nh (G) : StoichiometryDocument5 pagesN (G) - 2Nh (G) : StoichiometryJaidenNo ratings yet
- 03 Molar Volume of A Gas Long ReportDocument5 pages03 Molar Volume of A Gas Long ReportHoomehr TayariyanNo ratings yet
- Chapter3 Mole ConceptDocument10 pagesChapter3 Mole Conceptmatyiman_123No ratings yet
- Solution 8th - Fundamentals of Engineering Thermodynamics (Shapiro) (2) - SplitDocument652 pagesSolution 8th - Fundamentals of Engineering Thermodynamics (Shapiro) (2) - SplitLaura do Prado Goncalves PintoNo ratings yet
- Lee2014 Ie500110v Si 001Document3 pagesLee2014 Ie500110v Si 001Bidesh M KirtaniaNo ratings yet
- As LEVEL CalculationsDocument29 pagesAs LEVEL CalculationsbuseNo ratings yet
- AP Chem 5 WorksheetDocument6 pagesAP Chem 5 WorksheetenesffsNo ratings yet
- Material Balance With Chemical reactions-IIDocument39 pagesMaterial Balance With Chemical reactions-IIThota Venkata Lakshmi Manasa 22120487101No ratings yet
- Exercise 3 Outlet Temperature of A WGS ReactorDocument6 pagesExercise 3 Outlet Temperature of A WGS ReactorMiguelCardonaSalazarNo ratings yet
- Principles of Chemical EquilibriumDocument33 pagesPrinciples of Chemical EquilibriumAgustina ChristianiNo ratings yet
- Ap Stoichiometry Notes 2014Document2 pagesAp Stoichiometry Notes 2014Timothy SeyaramNo ratings yet
- Assignment L01-T6Document7 pagesAssignment L01-T6MawareNo ratings yet
- Heat CalcDocument7 pagesHeat CalcasdfghjkNo ratings yet
- CHEM 1105 Gas EquilibriaDocument5 pagesCHEM 1105 Gas EquilibriaAbu Sufyan ButtNo ratings yet
- 10.6, 10.7 Combined and Avogadro - S Gas LawsDocument17 pages10.6, 10.7 Combined and Avogadro - S Gas LawsolongkodokNo ratings yet
- StoichiometryDocument17 pagesStoichiometryGianna BaldoradoNo ratings yet
- CPC 2018 Make UpDocument3 pagesCPC 2018 Make UpHarshith ShettyNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Moles and VolumesDocument52 pages3.3 Moles and VolumesPratika MNo ratings yet
- Heatcalc: A Natural Gas Heat of Combustion CalculatorDocument7 pagesHeatcalc: A Natural Gas Heat of Combustion CalculatorMuzzamilNo ratings yet
- Chem Bio II Lecture 3 ReviewDocument29 pagesChem Bio II Lecture 3 ReviewKyrby CabalquintoNo ratings yet
- A Carbonate Analysis Molar Volume of Carbon DioxideDocument8 pagesA Carbonate Analysis Molar Volume of Carbon DioxideTest TestNo ratings yet
- Mole Concept and StoichiometryDocument7 pagesMole Concept and StoichiometryRasheethNo ratings yet
- 02 More StoichiometryDocument4 pages02 More StoichiometryfidelityabuNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry Problem/example No.1: Avogadro's Law of Combining VolumesDocument2 pagesStoichiometry Problem/example No.1: Avogadro's Law of Combining Volumesjsn_fNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Practice Problems (Answers)Document4 pagesUnit 5 Practice Problems (Answers)Ka Siang GohNo ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry: Daily Practice ProblemsDocument8 pagesPhysical Chemistry: Daily Practice ProblemsRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter III Combustion ProductsDocument22 pagesChapter III Combustion ProductsKiên GiangNo ratings yet
- 3 Heat CalcDocument7 pages3 Heat CalcNITINNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Notes StoichiometryDocument6 pagesChapter 10 Notes StoichiometryHera RiegoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 StoichiometryDocument45 pagesLecture 3 StoichiometryAndrew LeungNo ratings yet
- Heat DutyDocument7 pagesHeat Dutyingegnere1234No ratings yet
- Chemistry by SD Sir: TARGET-JEE (Main + Advanced)Document2 pagesChemistry by SD Sir: TARGET-JEE (Main + Advanced)Kripal ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Determination of Molar Volume and Universal Gas ConstantDocument4 pagesDetermination of Molar Volume and Universal Gas ConstantChester James PeñarubiaNo ratings yet
- PC Question Paper Nov 2021Document4 pagesPC Question Paper Nov 2021venkatesan sivaramuNo ratings yet
- CPP Assignment 1Document2 pagesCPP Assignment 1AmandaEdwinNo ratings yet
- Exercise 3 - Outlet Temperature of A WGS ReactorDocument6 pagesExercise 3 - Outlet Temperature of A WGS ReactorAlejandro BarreraNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips Cdo Ib Chemistry SL Unit 2 Review 2cdo Ib Chemistry SL Unit 2 Review 23Document11 pagesDokumen - Tips Cdo Ib Chemistry SL Unit 2 Review 2cdo Ib Chemistry SL Unit 2 Review 23Ibnu PratamaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Class Xi 2013 14 PDFDocument149 pagesChemistry Class Xi 2013 14 PDFaman singhNo ratings yet
- Worksheet-1 StoichiometryDocument11 pagesWorksheet-1 StoichiometryDOMS XNo ratings yet
- Chap3lect 2020Document62 pagesChap3lect 2020Anonymous wt2BA7uNo ratings yet
- Test 2 (Total 60 Marks) Name: Wong Yau Hsiung Student IDDocument7 pagesTest 2 (Total 60 Marks) Name: Wong Yau Hsiung Student IDJames WongNo ratings yet
- TakeHomeQuiz2.CalcI&II Compre.2ndsem1718Document2 pagesTakeHomeQuiz2.CalcI&II Compre.2ndsem1718Dianne Aicie ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Tugas 5 - Self Assesment Test: KnownDocument3 pagesTugas 5 - Self Assesment Test: KnownJenny AzzahraNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 Material-GasesDocument33 pagesExam 1 Material-GasesMaxiene Andrei GuintoNo ratings yet
- 2.2. Chemical ReactionsDocument4 pages2.2. Chemical Reactionsasfass sfasfasfasNo ratings yet
- Task 3 and 4Document8 pagesTask 3 and 4tlsandiaaaNo ratings yet
- Using Chemical Equations in Mole CalculationsDocument6 pagesUsing Chemical Equations in Mole CalculationsAlex noslenNo ratings yet
- A. Data: PpendixDocument2 pagesA. Data: PpendixMc Jason LaureteNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Moles, Molar Volume & Gas LawsDocument14 pages1.2 Moles, Molar Volume & Gas LawsShyamal DlrNo ratings yet
- Soal Heat BalanceDocument5 pagesSoal Heat BalanceRfc KusyadiNo ratings yet
- Temperature Measurement PDFDocument136 pagesTemperature Measurement PDFGaming User100% (2)
- Online Experiment 2 Temperature Sensors: Procedure: 1. Create An Account In: 2. Create This CircuitDocument4 pagesOnline Experiment 2 Temperature Sensors: Procedure: 1. Create An Account In: 2. Create This CircuitGaming UserNo ratings yet
- Other Industrial Measuring Devices PDFDocument102 pagesOther Industrial Measuring Devices PDFGaming UserNo ratings yet
- Flow Measurement PDFDocument77 pagesFlow Measurement PDFGaming UserNo ratings yet
- Activity 1Document2 pagesActivity 1Gaming UserNo ratings yet
- Listening ExerciseDocument6 pagesListening ExerciseGaming UserNo ratings yet
- Level Measurement PDFDocument97 pagesLevel Measurement PDFGaming UserNo ratings yet
- Code of Mechanical Engineering Ethics in The PhilippinesDocument39 pagesCode of Mechanical Engineering Ethics in The PhilippinesGaming User0% (1)
- Pattern of Paragraph Development ReviewDocument8 pagesPattern of Paragraph Development ReviewGaming UserNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 9 - Making InferencesDocument17 pagesChapter - 9 - Making InferencesGaming User100% (1)
- Chapter - 5 - Identifying Implied Main IdeasDocument22 pagesChapter - 5 - Identifying Implied Main IdeasGaming UserNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 6 - Recognizing Patterns of OrganizationDocument81 pagesChapter - 6 - Recognizing Patterns of OrganizationGaming UserNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 4 - Finding The Main IdeaDocument36 pagesChapter - 4 - Finding The Main IdeaGaming UserNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3 - Developing Your VocabularyDocument6 pagesChapter - 3 - Developing Your VocabularyGaming UserNo ratings yet
- Basic PLC Ladder ProgrammingDocument2 pagesBasic PLC Ladder ProgrammingGaming UserNo ratings yet
- W1 Mechanical EngineeringDocument3 pagesW1 Mechanical EngineeringGaming UserNo ratings yet
- CAGI Files Combined PDFDocument681 pagesCAGI Files Combined PDFGaming UserNo ratings yet
- Circuit DiagramsDocument144 pagesCircuit Diagramsangel alvarezNo ratings yet
- Fluorescent Ballast Troubleshooting Guide ADVANCE 1Document11 pagesFluorescent Ballast Troubleshooting Guide ADVANCE 1franklynNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 281: Leonard EvansDocument716 pagesMathematics 281: Leonard EvansJoeNo ratings yet
- 17ae73 As&c Module-2 ClassDocument47 pages17ae73 As&c Module-2 ClassSanjana ShivaprakashNo ratings yet
- Electrohydrodynamic Jet Printing Thesis Univ of ILL 2013 Sarah - MannenDocument101 pagesElectrohydrodynamic Jet Printing Thesis Univ of ILL 2013 Sarah - ManneninzanerNo ratings yet
- Ap Calculus Ab Cram Sheet: Abcramsheet - NBDocument5 pagesAp Calculus Ab Cram Sheet: Abcramsheet - NBticoninxNo ratings yet
- Time-Resolved Photoluminescence and PhotovoltaicsDocument6 pagesTime-Resolved Photoluminescence and PhotovoltaicsRovshen AtajanovNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1 Month 1Document96 pagesGeneral Physics 1 Month 1Benice GarciaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Techniques NEET Study Materials Download PDFDocument10 pagesOrganic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Techniques NEET Study Materials Download PDFbrovinsbrovinNo ratings yet
- Eye Optical SystemDocument28 pagesEye Optical SystemUshana JamilNo ratings yet
- Single Phase Capacitor SizingDocument34 pagesSingle Phase Capacitor SizingVer Bautista60% (5)
- Describing Motion Score: - /30: BPK PENABUR - Physics 8 GradeDocument2 pagesDescribing Motion Score: - /30: BPK PENABUR - Physics 8 GradeMaridjan WiwahaNo ratings yet
- Haz Id Poster1Document1 pageHaz Id Poster1AmeenudeenNo ratings yet
- Test2thursday1803 2015Document1 pageTest2thursday1803 2015eidalinNo ratings yet
- 5991-2171EN (Measuring Dielectric Properties)Document7 pages5991-2171EN (Measuring Dielectric Properties)ranaehsan7964No ratings yet
- HW6 20220367 신동민Document9 pagesHW6 20220367 신동민sdongmin488No ratings yet
- Lesson 7.1 Presentation With AnswersDocument21 pagesLesson 7.1 Presentation With Answersmalobaid6No ratings yet
- Fluidic-Based Instruments For Space Biology Research in CubeSatsDocument9 pagesFluidic-Based Instruments For Space Biology Research in CubeSatsnoeliaquispecondoriNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Physics - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument15 pagesUnit 1 - Physics - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inMayank SharmaNo ratings yet
- RCD Module 11 Length Development Elefante OchoaDocument28 pagesRCD Module 11 Length Development Elefante OchoaJemson VictorioNo ratings yet
- NDA NA English GeneralDocument396 pagesNDA NA English Generalvipin100% (1)
- Hannes Koerber Sandwich Composites ENDocument20 pagesHannes Koerber Sandwich Composites ENGhassan Al-RasheedNo ratings yet
- CE 210 Assignment 1Document2 pagesCE 210 Assignment 1shadrick soleNo ratings yet
- CE Board Nov 2020 Strength of Materials Set 1Document2 pagesCE Board Nov 2020 Strength of Materials Set 1Eugenio Genesis AbadNo ratings yet
- Lay BudhebhaparDocument1 pageLay BudhebhaparHarak DhamiNo ratings yet
- Confusion of Mass and WeightDocument3 pagesConfusion of Mass and WeightKarizamae MijaresNo ratings yet
- Week 6-8Document3 pagesWeek 6-8Christian John Paul LijayanNo ratings yet