Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ksellybelly - MSK I Arthritis Rheum
Uploaded by
Tricia Kaye IblanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ksellybelly - MSK I Arthritis Rheum
Uploaded by
Tricia Kaye IblanCopyright:
Available Formats
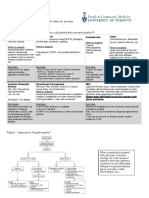
MSK I: Arthritis/Rheum Cheat Sheet
by ksellybelly via cheatography.com/19318/cs/2449/
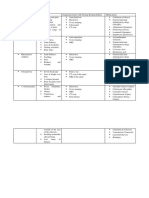
Osteoarthritis Rheumatoid Arthritis (cont) Polymyalgia Rheumatica (PMR)
Definition Lab Studies Definition
Progressive loss of articular cartilage with Elevated ESR + CRP, RF and anti-CCP Syndrome with pain and stiffness in the
reactive changes in the bone, results in pain positive in up to 80% neck/shoulder/pelvic girdles and is
and joint destruction (most common accompanied by constitutional symptoms
Treatment
arthropathy in adults) (fever, fatigue, weight loss, depression)
PT + NSAIDS + DMARDS (MTX,
Clinical Features Etiology
corticosteroids, biologics) and
Decreased ROM, joint crepitus, pain reconstructive surgery for severe cases. Unknown (F>>M)
worsening througout the day
Associated with
Common sites Gout
Temporal arteritis (30% of cases)
DIP joint (Heberden's nodes + PIP joint Definition
Clinical features
(Bouchard's nodes), and
A systemic disease of altered purine
wrist/hip/knee/spine Stiffness, worse after rest and in the
metabolism and subsequent sodium urate
morning. MSK symptoms are bilateral,
Imaging crystal precipitation into synovial fluid
proximal, symmetrical
Asymmetric narrowing or joint spaces, Typical patient
Must r/o...
subchondral sclerosis, cysts, marginal
M>>W (until menopause, then 1:1)
osteophytes Giant Cell Arteritis (scalp tenderness, jaw
Clinical Features of Initial Attack claudication, headache, temporal artery
Treatment
tenderness-->can lead to vision loss)
Metatarsal phalangeal joint of the great toe
Weight reduction, physical actibity,
(podagra) Lab Studies
acetaminophen, NSAIDs, intra-articular
steroids. Total joint replacement in advanced Symptoms around involved joint ESR elevated (>50mm/hr)
cases. Pain, swelling, redness, exquisite Treatment
tenderness
Low-dose corticosteroids (higher doses if
Rheumatoid Arthritis GCA), might need to be on for 2 years
Substance that may form adjacent to the joint,
Definition diagnostic!
Tophi (chalky deposits of uric acid) Sjogren's Syndrome
A chronic autoimmune disease with synovitis
affecting multiple joints and other systemic Lab Studies Definition
extra-articular manifestations. Joint
Joint fluid shows rod-shaped, negatively An autoimmune disease that destroys the
destruction ultimately occurs.
birefringent urate crystals seen. Serum uric salivary and lacrimal glands (exocrine
Typical patient acid level often > 8 mg/dL glands)
F>>M, 40-60yo at onset (juvenile in pts Lifestyle Modifications May be a secondary complication to pre-
<16yo) existing disorders like...
Elevation, dietary modifications (avoid
Clinical Features purines and EtOH) RA, SKE, polymyositis, scleroderma
Morning stiffness, symmetric, Pharmacotherapy Classic Patient
subcutaneous nodules, RF level >95th
NSAIDs (indomethacin), corticosteroid Middle-aged females
percentile, arthritis of hand joints, soft-
injections, colchicine in between attacks
tissue swelling (DIP joints spared) Clinical Features
Extra-articular manifestations Mucus membranes most affected. Parotid
glands might be enlarged.
Osteoporosis, changes in
skin/lungs/kidneys/eyes/liver/bloodstream/hear
t
By ksellybelly Published 12th August, 2014. Sponsored by Readability-Score.com
cheatography.com/ksellybelly/ Last updated 22nd August, 2014. Measure your website readability!
Page 1 of 4. https://readability-score.com
MSK I: Arthritis/Rheum Cheat Sheet
by ksellybelly via cheatography.com/19318/cs/2449/
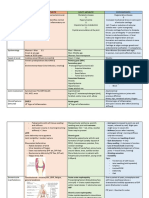
Sjogren's Syndrome (cont) Childhood-onset idiopathic arthritis (cont) Polymyosotis
Characteristic features of primary Sjogren's Polyarticular clinical features Definition
Dry mouth (xerostomia) + dry eyes Resembles adult RA, symmetri, 5+ joints. An inflammatory disease of striated muscle
(seropthalmia or keratoconjunctivitis) Systemic sx: low-grade fever, fatigue, affecting the proximal limbs/neck/pharynx
rheumatoid nodules, anemia. (skin can also be
Lab Studies
affected=dermatomyositis)
Treatment
RF in 70% of cases, ANA in 60%, anti-Ro
Etiology
Abs in 60%, anti-La in 40%. Schirmer's tear PT + NSAIDs
test wetting of <5mm of filter paper in lower Unknown, but strong association with occult
eyelid in 5min = + for decreased secretions malignancy
Psoriatic Arthritis
How to confirm lymphocytic infiltrate and gland Classic patient
Definition
fibrosis
F>>M
An inflammatory arthritis with skin
Lip bx
involvement usually preceding joint disease Clinical Features
Treatment
Clinical features Insidious painless proximal muscle
Mainly symptomatic management, goal of weakness, dysphagia, skin rash (malar or
Symmetric, hands and feet. Affects few
keeping mycosal surfaces moist. Can give heliotrope), polyarthralgias, muscle atrophy
joints. Pitting of nails and onycholysis.
artificial tears and saliva, increased oral fluid
"Sausage-finger" appearance Lab Studies
intake, and lubricants for eyes/vagina.
Pilocarpine may increase saliva flow Lab Studies CPK and aldolase elevated. Muscle bx will
show myopathic inflammatory changes
ESR elevated, hyperuricemia if severe skin
Childhood-onset idiopathic arthritis involvement, "pencil in a cup" deformity on Treatment
x-ray
Definition High-dose steroids, MTX, or azathioprine
Treatment
Characterized by chronic synovitis and
NSAIDs, MTX, reconstructive surgery as Scleroderma (Systemic Sclerosis)
extra-articular manifestations (fever, rash,
weight loss) last resort
Definitions
Typical Patient Characterized by deposition of collagen in
Pseudogout
F>>M, at age 1-3yo (males older 8-12yo) the skin, and also lungs, kidney, heart
Definition stomach. Unknown etiology.
Forms of arthritis
Intra-articular deposition of calcium Classic Patient
Pauciarticular (50%) polyarticular (35%),
pyrophosphate dehydrate (CPPD) in
systemic (15%) F>>M, 30-50yo
peripheral joints
Systemic (JRA) clinical features Clinical Features in general
Acute presentations mimic...
Spiking fevers, myalgias, salmon-pink 95% of patients have skin involvement,
Gout (may be recurrent and abrubt)
maculopapular rashin evening. starts with swelling of fingers and hands,
Hepatosplenomegaly, lymphadenopathy, Clinical features may spread to trunk and face. R
leukocytosis, pericarditis, myocarditis Painful inflammation (when crystals shed Clinical Features: Limited
Pauciarticular clinical features into joint), most common in
Mostly affects skin of face, neck, distal
knees/wrist/elbow
4 or less medium to large joints. Also at risk elbows and knees. Causes pulmonary
for asymptommatic uveitis (can lead to Lab Studies hypertension later in disease.
blindness if +ANA) Rhomboid-shaped CPPD crystals, Clinical Features: Diffuse
negatively birefringement. Will see
Affects the skin plus the heart, lungs, GI
chondrocalcinosis in radiographs (fine, linear
tract, kidneys
calcifications)
Treatment
NSAIDS, colchicine, and intra-articular
steroid injections
By ksellybelly Published 12th August, 2014. Sponsored by Readability-Score.com
cheatography.com/ksellybelly/ Last updated 22nd August, 2014. Measure your website readability!
Page 2 of 4. https://readability-score.com
MSK I: Arthritis/Rheum Cheat Sheet
by ksellybelly via cheatography.com/19318/cs/2449/
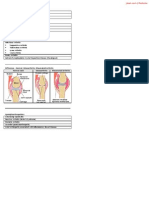
Scleroderma (Systemic Sclerosis) (cont) Septic (Infectious) Arthritis (cont) SLE (Systemic Lupus Erythematous) (cont)
CREST Syndrome (associated with limited Treatment Clinical Features
scleroderma Aggressive IV Abx followed by oral (4+ criteria including high ANA): malar rash,
Calcinosis, Raynaud's, esophageal antibiotics, sometimes arthrotomy and discoid rash, photosensitivity, oral ulcers,
dysfunction, sclerodactyly, telangiectasias arthrocentesis are required. arthritis, serositis, renal dz, ANA,
hematologic/immunologic/neurologic
Initial presentation
Reactive Arthritis (Reiter Syndrome) disorders
Skin changes, polyarthralgias, esophageal
dysfunction What must be ruled out?
Definition
Drug-induced lupus/lupus-like syndrome
Lab Studies A seronegative arthritis that has a tetrad of:
(from INH, hydralazine, quinidine). Usually
urethritis, conjunctivitis, oligoarthritis, and
+ANA in 90% of pts, +anticentromere Ab pt. will have positive antihistone Abs
mucosal ulcers (leading cause of
assoc. w/ limited scleroderma, watch for
nontraumatic monoarthritis) Lab Studies
HTN
Can be seen as a sequele to... Get CBC BUN, Cr, U/A, ESR, serum
Treatment
complement (C3 or C4), anti-Smith
STDs or gastroenteritis
No cure. Treat specific manifestations of antibodies to mark for progression. ANA is
disease (ie PPIs for GERD, ACEis for renal Clinical Features present 99% of the time, but low titers have
dz, aboid triggers, and a low predictive value.
Asymmetric arthritis in large joints below the
immunosuppressives for pulmonary HTN)
waist (knee, ankle), mucocutaneous lesions
Treatment
(balanitis, stomatitis), urethritis,
Septic (Infectious) Arthritis Exercise + sun protection, NSAIDs,
conjunctivitis
Antimalarials (hydroxychloroquine),
Definition Typical patient corticosteroids, MTX
The hematogenous spread of bacteremia M>>F after STDs (1:1 ratio after enteric infx)
infection (osteomyelitis) caused by Polyarteritis Nodosa
Lab Studies
diagnostic or therapeutic procedure
(injection) or infection elsewhere (cellulitis, Up to 80% HLA-B27+, synovial fluid Definition
bursitis) negative culture Small/medium artery inflammation involving
Treatment the skin, kidney, peripheral nerves, muscles,
Classic joint
and gut
Single joint, usually knee (can also be hip, PT + NSAIDs. Abx can reduce chance of
shoulder, ankle) developing disorder, but they don't alleviate Classic patient
sx of the reactive arthritis M>>F, 40-60yo, Hep B pts
Most common pathogen
Etiology
Staph. aureus
SLE (Systemic Lupus Erythematous)
Unknown (concurrent in Hep B pts. 30% of
Pathogen in sexually-active young adults
Definition the time)
Neisseria gonorrhea
An autoimmune disorder characterized by Clinical Features
Clinical Presentation inflammation, plus +ANA, and involvement
Fever, anorexia, weight loss, abdominal
of multiple organs
Acute swelling, fever, joint warmth and pain, peripheral neuropathy, arthralgias,
effusion, tenderness to palpation, increased Classic Patient arthritis, skin lesions. If renal involvement:
pain w/ minimal ROM HTN, edema, oliguria, uremia (if renal
Women of childbearing age, and more in
Lab Studies African-American women involvement.
Collect/aspirate synovial fluid, many will also Lab Studies
have a positive blood culture. Vessel bx or angiography to diagnose
(might also see ANCA, elevated ESR and
CRP)
By ksellybelly Published 12th August, 2014. Sponsored by Readability-Score.com
cheatography.com/ksellybelly/ Last updated 22nd August, 2014. Measure your website readability!
Page 3 of 4. https://readability-score.com
MSK I: Arthritis/Rheum Cheat Sheet
by ksellybelly via cheatography.com/19318/cs/2449/
Polyarteritis Nodosa (cont)
Treatment
High-dose corticosteroids, cytotoxic drugs, immunotherapy.
Might need to also treat for Hep B. Treat HTN if present
Fibromyalgia Syndrome
Definition
A central pain disorder; cause and pathogenesis are poorly
understood
Can occur concurrently with...
RA, SLE, Sjogren's
Clinicla Features
Nonarticular MSK aches, fatigue, sleep disturbance,
multiple tender points on exam, anxiety, depression,
headaches, irritable bowel syndrome, dysmenorrhea,
paresthesias
Lab Studies
Diagnosis of exclusion, must r/o hormonal and vitamin
disturbances. Sometimes abnormalities of T-cell subsets
Treatment
SSRIs, SSNRIs, RCAs. Lyrica is only FDA-approved drug to
specifically treat fibromyalgia. Aerobic exercise, stress
reduction, and sleep assistance are helpful.
By ksellybelly Published 12th August, 2014. Sponsored by Readability-Score.com
cheatography.com/ksellybelly/ Last updated 22nd August, 2014. Measure your website readability!
Page 4 of 4. https://readability-score.com
You might also like
- Kelainan Muskuloskeletal Akibat Penyakit Autoimun & MetabolikDocument75 pagesKelainan Muskuloskeletal Akibat Penyakit Autoimun & MetabolikWita sarumpaetNo ratings yet
- Week 29 Outpatients (L28.6) Gout Epidemiology AetiologyDocument3 pagesWeek 29 Outpatients (L28.6) Gout Epidemiology Aetiologydragtoss2No ratings yet
- Arthritis 2Document22 pagesArthritis 2bellayuandaNo ratings yet
- Ms DisorderDocument2 pagesMs DisorderIan Michael EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Joint Disorders: Robbins Basic Pathology by Kumar, Abbas, Aster, 9 Edition, W. B. Saunders 2012Document19 pagesJoint Disorders: Robbins Basic Pathology by Kumar, Abbas, Aster, 9 Edition, W. B. Saunders 2012lailatul husnaNo ratings yet
- Simposium Papdi 3-Hari 1-5. Ws 1 - Dr. Lita-Untuk Share-2. Dr. LitaDocument46 pagesSimposium Papdi 3-Hari 1-5. Ws 1 - Dr. Lita-Untuk Share-2. Dr. LitaRangga Alam VaneoNo ratings yet
- Section of Rheumatology, Internal Medicine Department Faculty of Medicine GMU / Dr. Sardjito General HospitalDocument47 pagesSection of Rheumatology, Internal Medicine Department Faculty of Medicine GMU / Dr. Sardjito General HospitalYane Aulia YasminNo ratings yet
- Ellieacook OsteoarthritisDocument1 pageEllieacook OsteoarthritisMonica PavelNo ratings yet
- Amputation - DR EKADocument41 pagesAmputation - DR EKADiah agungNo ratings yet
- Rheuma (Gout, CPD, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Osteoarthritis)Document2 pagesRheuma (Gout, CPD, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Osteoarthritis)Jezreel Yanah De LeonNo ratings yet
- Chapter38 Assessment and Management of Patients With Rheumatic DisordersDocument38 pagesChapter38 Assessment and Management of Patients With Rheumatic Disordersjericho dinglasanNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Approach To Musculoskeletal PainDocument32 pagesDiagnostic Approach To Musculoskeletal PainTri P BukerNo ratings yet
- Oral Diagnosis Chapter 2 MidtermsDocument5 pagesOral Diagnosis Chapter 2 Midtermsabsjob1No ratings yet
- E Vascular (Blue Keyword Pyq)Document3 pagesE Vascular (Blue Keyword Pyq)Irsyad SiddeeqNo ratings yet
- Problem Process Common Location Pattern of Spread Onset Progression and Duration Associated SymptomsDocument2 pagesProblem Process Common Location Pattern of Spread Onset Progression and Duration Associated SymptomsMarc Armand Balubal MaruzzoNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic RheumatologyDocument9 pagesOrthopedic RheumatologyAngelinaNo ratings yet
- Approach To Case of ArthritisDocument53 pagesApproach To Case of ArthritisdrsarathmenonNo ratings yet
- MSK Ncm106lecDocument50 pagesMSK Ncm106lecJASTINE JOY PEREZNo ratings yet
- OsteoarthritisDocument2 pagesOsteoarthritisapi-518311936No ratings yet
- Inflammatory Rheumatic Disorders: Christopher Edwards, Louis SolomonDocument20 pagesInflammatory Rheumatic Disorders: Christopher Edwards, Louis SolomonHary Wahyu SoemaliNo ratings yet
- Nyari's Consultation Visit 4Document39 pagesNyari's Consultation Visit 4nrmadegaNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Rheumatoid and OsteoarthritisDocument4 pagesComparison of Rheumatoid and OsteoarthritisWaseem Khan AfridiNo ratings yet
- 1 3-ArthritisDocument9 pages1 3-ArthritisRohit kumar Saravana kumarNo ratings yet
- Medicine Cheat SheetsDocument16 pagesMedicine Cheat SheetsRisa Muthmainah100% (1)
- T Score - 1Document8 pagesT Score - 1muhammadridhwanNo ratings yet
- Complications of FractureDocument3 pagesComplications of FractureGerardLumNo ratings yet
- RaDocument40 pagesRaMuhammad MakkiNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug Studyunkown userNo ratings yet
- ArthritisDocument7 pagesArthritisGerardLum100% (1)
- Ortho NotesDocument283 pagesOrtho NotesGaushinee VallimanalanNo ratings yet
- Ra SlideshowDocument16 pagesRa Slideshowapi-582804360No ratings yet
- Metabolic Trauma Inflamation: Malposition/ Anatomical AbnormalitiesDocument1 pageMetabolic Trauma Inflamation: Malposition/ Anatomical AbnormalitiesrinNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Trauma Inflamation: Malposition/ Anatomical AbnormalitiesDocument1 pageMetabolic Trauma Inflamation: Malposition/ Anatomical AbnormalitiesnadeNo ratings yet
- P3 Ortho RebyuwerDocument13 pagesP3 Ortho Rebyuwerlorelyn corpuzNo ratings yet
- Bones and JointsDocument39 pagesBones and JointsnomankidwaiNo ratings yet
- Riwayat Pendidikan: Lahir Di: Bali 16 September 1960Document34 pagesRiwayat Pendidikan: Lahir Di: Bali 16 September 1960Riris SutrisnoNo ratings yet
- Diplopia - Eye Disorders - MSD Manual Professional Edition-TableDocument3 pagesDiplopia - Eye Disorders - MSD Manual Professional Edition-TableApostolos T.No ratings yet
- Joint Pain One PagerDocument3 pagesJoint Pain One PagermustafaNo ratings yet
- ArthritisDocument2 pagesArthritisBest of pinoyNo ratings yet
- ORTHOPEDICSDocument8 pagesORTHOPEDICSjsreyes.402No ratings yet
- Lumbar SpineDocument4 pagesLumbar SpineCherrie MaeNo ratings yet
- Conversion From Mmol, Arthritis DifferentiationDocument7 pagesConversion From Mmol, Arthritis DifferentiationRobz ApacionadoNo ratings yet
- Conditions of The Lumbar SpineDocument4 pagesConditions of The Lumbar SpineCherrie MaeNo ratings yet
- حل اسئلة العملي-1Document91 pagesحل اسئلة العملي-1حسام الوجيهNo ratings yet
- Chir 3Document6 pagesChir 3George MogaNo ratings yet
- Temporo Mandibular Joint Disorder Oral SurgeryDocument59 pagesTemporo Mandibular Joint Disorder Oral SurgeryFourthMolar.comNo ratings yet
- OSTEOARTHRITISDocument4 pagesOSTEOARTHRITISKhiara Yapha AlfarNo ratings yet
- Clinical Therapeutics: Eva Fe R. Columna M D - 3 BDocument16 pagesClinical Therapeutics: Eva Fe R. Columna M D - 3 BMichelle Vera GabunNo ratings yet
- Ra Concept Map CompletionDocument18 pagesRa Concept Map Completionapi-308471999No ratings yet
- Imaging Approach To Inflammatory ArthritisDocument94 pagesImaging Approach To Inflammatory ArthritisYashan SharmaNo ratings yet
- C1 Recuperare in PR Ian2017Document49 pagesC1 Recuperare in PR Ian2017Mihaela Costea100% (1)
- PREVIOUS NEET TOPICS 2018-2021 - Dr. Vishnu SomakumarDocument1 pagePREVIOUS NEET TOPICS 2018-2021 - Dr. Vishnu SomakumarAvi KhannaNo ratings yet
- Algodystrophy (AD) : Prof. Hazem Abdel Azeem (MD)Document179 pagesAlgodystrophy (AD) : Prof. Hazem Abdel Azeem (MD)tarikeopsNo ratings yet
- KetorolacDocument1 pageKetorolacunkown userNo ratings yet
- Rheumatology MANTAP - NoRestrictionDocument29 pagesRheumatology MANTAP - NoRestrictionpanduNo ratings yet
- Rheumatoid Arthritis OsteoarthritisDocument33 pagesRheumatoid Arthritis OsteoarthritisTri Hastuti HendrayaniNo ratings yet
- Thoracic Outlet SyndromeDocument11 pagesThoracic Outlet SyndromeTan Zhen XinNo ratings yet
- Psych Meds 2Document2 pagesPsych Meds 2Cole SchaferNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Antipsychotic Agents Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesPharmacology of Antipsychotic Agents Cheat SheetCrystal MarloweNo ratings yet
- Lizzie Heisler - Hypertension MedsDocument2 pagesLizzie Heisler - Hypertension MedsTricia Kaye IblanNo ratings yet
- Thuốc tđ trên hệ andrenergicDocument3 pagesThuốc tđ trên hệ andrenergicThư PhạmNo ratings yet
- Carmilaa - Introduction To PharmacologyDocument2 pagesCarmilaa - Introduction To PharmacologyTricia Kaye IblanNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Antipsychotic Agents Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesPharmacology of Antipsychotic Agents Cheat SheetCrystal MarloweNo ratings yet
- X0xheather - Principles of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy PDFDocument3 pagesX0xheather - Principles of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy PDFAbdul RaufNo ratings yet
- Reuben - Drug Classes and Actions NsaidsDocument2 pagesReuben - Drug Classes and Actions NsaidsTricia Kaye IblanNo ratings yet
- UWI St. Augustine Student Wireless Network - Instruction / Setup GuideDocument2 pagesUWI St. Augustine Student Wireless Network - Instruction / Setup GuideBrendan B. MastayNo ratings yet
- STO Trade Qualifier Application GuideDocument15 pagesSTO Trade Qualifier Application Guidechrisandersen1111No ratings yet
- 2021 Community ReportDocument28 pages2021 Community Reportapi-309161587No ratings yet
- Practical Auditing by Empleo 2022 Chapter 4 Receivables Related RevenuesDocument55 pagesPractical Auditing by Empleo 2022 Chapter 4 Receivables Related RevenuesDarence IndayaNo ratings yet
- Searchinger Et Al Nature 2018Document4 pagesSearchinger Et Al Nature 2018Bjart HoltsmarkNo ratings yet
- Ebook PDF Contracts in Context From Transaction To Litigation Aspen Casebook PDFDocument40 pagesEbook PDF Contracts in Context From Transaction To Litigation Aspen Casebook PDFflorence.padilla424100% (35)
- Atty. SungaDocument22 pagesAtty. SungaKris MercadoNo ratings yet
- Psscoc For Design Build 2020Document78 pagesPsscoc For Design Build 2020王佳乐No ratings yet
- Recount Text1Document14 pagesRecount Text1Ika Yuniati WinataNo ratings yet
- Ingles TripticoDocument2 pagesIngles Triptico'YanetCruzRamosNo ratings yet
- Book 1Document30 pagesBook 1uday sonawaneNo ratings yet
- Ball Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesBall Lesson Planapi-350245383No ratings yet
- Outcomes of Democracy: How Do We Assess Democracy?Document7 pagesOutcomes of Democracy: How Do We Assess Democracy?Ankita MondalNo ratings yet
- First Conditional Advice Interactive WorksheetDocument2 pagesFirst Conditional Advice Interactive WorksheetMurilo BaldanNo ratings yet
- Rizal Module 2 Concept of A HeroDocument11 pagesRizal Module 2 Concept of A HeropinkgirljojiNo ratings yet
- Nestle Philippines, Inc., v. PuedanDocument1 pageNestle Philippines, Inc., v. PuedanJoycee ArmilloNo ratings yet
- Site Induction PresentationDocument17 pagesSite Induction PresentationalisyalalaNo ratings yet
- Aggarwal A. - Go Web Development Cookbook - 2018Document458 pagesAggarwal A. - Go Web Development Cookbook - 2018Calvin Benhardi100% (1)
- FPSC - Inspector - Custom - Intelligence - Officer - PDF Filename - UTF-8''FPSC Inspector Custom Intelligence OfficerDocument405 pagesFPSC - Inspector - Custom - Intelligence - Officer - PDF Filename - UTF-8''FPSC Inspector Custom Intelligence Officerasimafzal100% (1)
- Courtney Loper-ResumeDocument2 pagesCourtney Loper-Resumeapi-354618234No ratings yet
- Hindi Cinema 3rd Sem Notes PDF (2) - 1 PDFDocument37 pagesHindi Cinema 3rd Sem Notes PDF (2) - 1 PDFLateef ah malik100% (1)
- Unit 2 - Chapter 2Document20 pagesUnit 2 - Chapter 2Dennise Kate CabiedesNo ratings yet
- Assessment Items: Fifth Grade Tri 2a - Ava Farley: A Good Reason To Look Up Do What You LoveDocument7 pagesAssessment Items: Fifth Grade Tri 2a - Ava Farley: A Good Reason To Look Up Do What You Loveapi-348637033No ratings yet
- Ch05 P24 Build A ModelDocument5 pagesCh05 P24 Build A ModelKatarína HúlekováNo ratings yet
- My Day: Reading Materials I CourseDocument7 pagesMy Day: Reading Materials I CourseZeynab BagirovaNo ratings yet
- Special Power of Attorney 2017-Michael John Dj. OpidoDocument2 pagesSpecial Power of Attorney 2017-Michael John Dj. OpidoJhoanne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Oracle® Inventory: Consigned Inventory From Supplier Process Guide Release 12.1Document76 pagesOracle® Inventory: Consigned Inventory From Supplier Process Guide Release 12.1Guillermo ToddNo ratings yet
- A Conceptualization of Vehicle Platoons and Platoon OperationsDocument19 pagesA Conceptualization of Vehicle Platoons and Platoon OperationsWatthanasak JeamwatthanachaiNo ratings yet
- Carbon Trading-The Future Money Venture For IndiaDocument11 pagesCarbon Trading-The Future Money Venture For IndiaijsretNo ratings yet
- Novena To ST JudeDocument2 pagesNovena To ST JudeBeatrice Mae ChuaNo ratings yet