Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mindmap Ch1. Indian Economy On The Eve of Independence
Uploaded by
Anup DubeyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mindmap Ch1. Indian Economy On The Eve of Independence
Uploaded by
Anup DubeyCopyright:
Available Formats
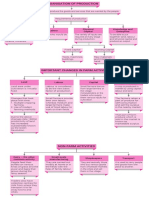
Definition: Farming for personal
consumption, not for trade.\
**Subsistence Farming**\
Characteristics: Small holdings, traditional
methods, low surplus.\
Zamindari: Landlords collect rent from
tenants.\
Ryotwari: Direct settlement between
**Land Tenure Systems**\
government and farmers.\
1. Agricultural Sector\
Mahalwari: Collective settlement with a
group of villages.\
Reasons for Low Productivity: Outdated
farming techniques, lack of capital,
fragmented landholdings.\
Impact of Low Productivity: Food scarcity,
**Low Productivity and Factors**\
dependence on monsoon, low income.\
Other Factors: High land revenue demands,
lack of investment in agriculture.
\
Definition: Decline of traditional industries.\
Causes: Colonial policies, competition from
**Deindustrialization**\
British goods.\
How did the colonial era shape the structure Impact: Unemployment, loss of skills.\
of the Indian economy?\
Causes: Cheap machine-made imports, lack
What were the main challenges faced by the of royal patronage.\
agricultural sector?\ 2. Industrial Sector\ **Decline of Handicrafts Industry**\
Impact on Artisans: Loss of livelihood,
How did the drain of wealth impact India's Questions for Reflection\ migration to agriculture.\
economic development?
Sectors: Cotton and jute mills.\
---
This mind map can be further detailed with **Emergence of Modern Industry**\ Locations: Primarily in Bengal and Bombay.\
specific examples, case studies, and
historical data from the NCERT textbook to Impact: Beginning of modern industry, but
provide a comprehensive understanding of limited scope.
the chapter. \
}
Export: Raw materials like cotton, jute,
indigo.\
**Structure of Trade**\
**Link Between Agriculture and Industry**: Import: Finished goods from Britain.\
Mutual dependency and impact on overall Main Topics\
economy.\
Concept: Transfer of wealth from India to
Britain.\
{
**Trade and Drain of Wealth**: Role of 3. Foreign Trade\ **Drain of Wealth**\
foreign trade in economic exploitation.\ Interconnected Topics\
Methods: High taxes, unequal trade
agreements.\
**Infrastructure and Economic Impact**: Dual
role of infrastructure in development and
colonial exploitation. Dependency on Britain.\
\ **Impact on Indian Economy**\
Depletion of wealth and resources.
\
**Colonial Exploitation**: British policies that Causes: Lack of medical facilities, poor living
**High Birth and Death Rates**\
led to economic stagnation.\ conditions.\
**Economic Stagnation**: No significant 4. Demographic Condition\ **Low Life Expectancy**\ Impact of poverty and disease.\
growth in agriculture or industry.\ Key Concepts\
Rate: Slow growth due to high mortality.
**Social Backwardness**: Poor indicators in **Population Growth**\
\
education, health, and social welfare.
\
Share in Employment: Majority engaged in
agriculture.\
**Predominance of Agriculture**\
Dependency: Economic and social
dependency on agriculture.\
Reasons: Colonial policies, competition with
5. Occupational Structure\ **Decline in Manufacturing**\
British goods.\
Urbanization linked to industrialization, which
**Low Rate of Urbanization**\ was limited.
\
Benefits: Improved communication, trade
facilitation.\
**Development of Railways, Post, and
Telegraph**\
Limitations: Primarily to serve colonial
interests.\
Impact: Hindered internal trade and
6. Infrastructure\ **Neglect of Waterways, Roads**\
connectivity.\
Role in economic exploitation and resource
**Impact on Economy**\ extraction.
\
You might also like
- Crypto Pearls 2021Document34 pagesCrypto Pearls 2021Crypto Atlas100% (4)
- Overview of Brazilian Standardization for StructuresDocument50 pagesOverview of Brazilian Standardization for StructuresaantceNo ratings yet
- The Story of Village Palampur: Flow Chart Economic Ch-1Document1 pageThe Story of Village Palampur: Flow Chart Economic Ch-1GggNo ratings yet
- Mindmap-First ChapterDocument6 pagesMindmap-First ChapterHeer Sirwani100% (1)
- Unit-7 BS-XI RK SinglaDocument34 pagesUnit-7 BS-XI RK SinglaJishnu DuhanNo ratings yet
- 5.ratio Analysis SumsDocument9 pages5.ratio Analysis Sumsvinay kumar nuwalNo ratings yet
- Padhle 11th - Introduction To Accounting - Class 11 AccountancyDocument11 pagesPadhle 11th - Introduction To Accounting - Class 11 AccountancyDHYAN PATELNo ratings yet
- Subhash Dey's IED NOTES For Slow Learners-1Document1 pageSubhash Dey's IED NOTES For Slow Learners-1karanbhattxsNo ratings yet
- 12 Accounts Imp Ch1Document22 pages12 Accounts Imp Ch1Tushar Tyagi100% (1)
- Padhle 11th - 5 MicroeconomicsDocument9 pagesPadhle 11th - 5 MicroeconomicsVikas KumarNo ratings yet
- Journal Entries Questions 123Document3 pagesJournal Entries Questions 123aparajita agarwalNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Industries Padhai Ak Mazza Best Handwritten Notes 2023Document5 pagesManufacturing Industries Padhai Ak Mazza Best Handwritten Notes 2023Mickey xzNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Cyber Ethics WorksheetDocument2 pagesClass 8 Cyber Ethics WorksheetAdwityaNo ratings yet
- Lion On The LooseDocument35 pagesLion On The LoosejenNo ratings yet
- Subhash Dey's IED NOTES For Slow LearnersDocument2 pagesSubhash Dey's IED NOTES For Slow Learnersvy245128No ratings yet
- Class 11 Businessstudy Notes Chapter 5Document18 pagesClass 11 Businessstudy Notes Chapter 5Ayush Singh BaghelNo ratings yet
- XII Accounts Test With SolutionDocument12 pagesXII Accounts Test With SolutionKritika Mahalwal100% (1)
- Maya 2015 in Simple StepsDocument2 pagesMaya 2015 in Simple StepsDreamtech Press100% (1)
- Chapter 7 - TrainingDocument32 pagesChapter 7 - TrainingNhibinhNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Slides - Income Statements - Components and Format of An Income Statement PDFDocument13 pages1.1 Slides - Income Statements - Components and Format of An Income Statement PDFascentcommerceNo ratings yet
- Management Concepts, Functions and ImportanceDocument62 pagesManagement Concepts, Functions and ImportanceBhagya aggarwalNo ratings yet
- K S H I T I J: Kshitij EducationDocument4 pagesK S H I T I J: Kshitij Educationsk23skNo ratings yet
- Understanding Strategic ManagementDocument18 pagesUnderstanding Strategic ManagementbabyNo ratings yet
- Business Economics PPT Chap 1Document18 pagesBusiness Economics PPT Chap 1david sughapriyaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Linear Programming MBADocument25 pagesIntroduction To Linear Programming MBABabasab Patil (Karrisatte)100% (2)
- Mock Paper-2 (With Answer)Document13 pagesMock Paper-2 (With Answer)RNo ratings yet
- Print instructions for odd and even pagesDocument24 pagesPrint instructions for odd and even pagesJyoti Sankar BairagiNo ratings yet
- Final Accounts of Sole Proprietorship: Basic ConceptsDocument70 pagesFinal Accounts of Sole Proprietorship: Basic Conceptsmonudeep aggarwalNo ratings yet
- Death of A PartnerDocument14 pagesDeath of A PartnerAkash Justin JathannaNo ratings yet
- The Effectiveness of a Homemade Water FilterDocument7 pagesThe Effectiveness of a Homemade Water FilterNaj Evad HayohayNo ratings yet
- Effective Bank Relationship ManagerDocument8 pagesEffective Bank Relationship ManagerRushil ShahNo ratings yet
- Namma Kalvi 12th Economics Chapter 2 Sura English Medium GuideDocument11 pagesNamma Kalvi 12th Economics Chapter 2 Sura English Medium GuideAakaash C.K.100% (3)
- ProcessDocument16 pagesProcessJoydip DasguptaNo ratings yet
- Xii - BS T - Case StudiesDocument4 pagesXii - BS T - Case StudiesShraddha BansalNo ratings yet
- FREE MEMORY MAPS FOR ECONOMICS CHAPTERSDocument37 pagesFREE MEMORY MAPS FOR ECONOMICS CHAPTERSRonit GuravNo ratings yet
- A Presentation On Cash Book, Pass Book & Bank Reconciliation Statement - Sudarshan Kr. PatelDocument26 pagesA Presentation On Cash Book, Pass Book & Bank Reconciliation Statement - Sudarshan Kr. Patelsh0101100% (1)
- Question Bank Paper: Cost Accounting McqsDocument8 pagesQuestion Bank Paper: Cost Accounting McqsNikhilNo ratings yet
- Mba 1 Sem Management Concept and Organisational Behaviour kmbn101 2022Document2 pagesMba 1 Sem Management Concept and Organisational Behaviour kmbn101 2022Rushda Naaz0% (1)
- Sheet 7 PDFDocument4 pagesSheet 7 PDFIniyan I TNo ratings yet
- Organising Production and Changes in Farm ActivitiesDocument1 pageOrganising Production and Changes in Farm ActivitiesDark DevilNo ratings yet
- Accounting Thoery Notes-1Document39 pagesAccounting Thoery Notes-1JaiNo ratings yet
- HBL Executive Summary ReportDocument19 pagesHBL Executive Summary ReportRana Tahir100% (1)
- Questions Chapter 4 PECDocument18 pagesQuestions Chapter 4 PECJayven BorjaNo ratings yet
- Accounting EquationDocument15 pagesAccounting EquationArkaprava ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- LESSON PLAN-Accounts & StatisticsDocument14 pagesLESSON PLAN-Accounts & StatisticsMaheswari RamasamyNo ratings yet
- B ST XI Subhash Dey All Chapters PPTs Teaching Made EasierDocument1,627 pagesB ST XI Subhash Dey All Chapters PPTs Teaching Made EasierAarush GuptaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Syllabus ST Xaviers Kolkata Eco HonsDocument20 pagesDetailed Syllabus ST Xaviers Kolkata Eco HonsSarbartho MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- DT Question BankDocument193 pagesDT Question BankSangamUpadhayayNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan AccSept 2018Document4 pagesLesson Plan AccSept 2018Anissa E.No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Small Business Chapter QuestionsDocument2 pagesCBSE Class 11 Business Studies Small Business Chapter QuestionsAryan Dev SinghNo ratings yet
- It SiaDocument180 pagesIt Siasupriya guptaNo ratings yet
- Acc030 Exercise Double EntryDocument2 pagesAcc030 Exercise Double EntryAqilahNo ratings yet
- B.ST XI All Chapters PPTs With TestDocument1,399 pagesB.ST XI All Chapters PPTs With TestManmeet Kaur AroraNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper Accountancy 12, Set-3, 2022-23Document10 pagesSample Paper Accountancy 12, Set-3, 2022-23AKKI YTNo ratings yet
- GST Summary Book by CA Yogesh Verma SirDocument90 pagesGST Summary Book by CA Yogesh Verma SirŚańthôsh Ķūmař P100% (1)
- Cidam - OmDocument7 pagesCidam - OmYvette Marie Yaneza NicolasNo ratings yet
- Development Experience 1947-90 and Economic Reforms Since 1991Document18 pagesDevelopment Experience 1947-90 and Economic Reforms Since 1991RafayNo ratings yet
- Agriculture Best Handwritten Notes Padhai Ak Mazza 2024Document7 pagesAgriculture Best Handwritten Notes Padhai Ak Mazza 2024keshavkrishna20007No ratings yet
- The Business Model CanvasDocument1 pageThe Business Model Canvastonyclinton156No ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document10 pagesChapter 6saanviNo ratings yet
- Agriculture Shobhit NirwanDocument11 pagesAgriculture Shobhit NirwanTarun JainNo ratings yet
- Sectors of Indian Economy Shobhit NirwanDocument36 pagesSectors of Indian Economy Shobhit NirwanHONEYGAIN100% (2)
- Pemerintah Kabupaten Penajam Paser Utara Dinas Ketahanan PanganDocument3 pagesPemerintah Kabupaten Penajam Paser Utara Dinas Ketahanan PanganMustofiNo ratings yet
- Tema 3 Strategia de Internationalizare A Companiei Wizz Air: Duval Alexandru, Grupa 948 ADocument3 pagesTema 3 Strategia de Internationalizare A Companiei Wizz Air: Duval Alexandru, Grupa 948 AAlexandruNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Mini Riset Kel 6 FinalDocument10 pagesJurnal Mini Riset Kel 6 FinalKusnadi 0817No ratings yet
- Body 1:: Petrol and Oil 1980: Greatest + 2 Times More Than Coal and Natural Gas: in 1980Document4 pagesBody 1:: Petrol and Oil 1980: Greatest + 2 Times More Than Coal and Natural Gas: in 1980Tuấn Hiệp NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Solution CA Inter TaxationDocument17 pagesSolution CA Inter TaxationBhola Shankar PrasadNo ratings yet
- X1 Manchester Factsheet 04062020Document10 pagesX1 Manchester Factsheet 04062020mr meNo ratings yet
- Rise of Germany and Japan As Economic PowersDocument19 pagesRise of Germany and Japan As Economic PowersMaheen AliNo ratings yet
- Capacity PlanningDocument17 pagesCapacity PlanningfuriousTaherNo ratings yet
- Halaf UbaidDocument33 pagesHalaf UbaidSeth BullockNo ratings yet
- Summary Cocopeat Final 1Document18 pagesSummary Cocopeat Final 1jimmydwinantoNo ratings yet
- BHP Billiton Industry AnalysisDocument6 pagesBHP Billiton Industry AnalysisRahul Singh DeoNo ratings yet
- Shareholders' Equity (Part 2) : Name: Date: Professor: Section: Score: QuizDocument3 pagesShareholders' Equity (Part 2) : Name: Date: Professor: Section: Score: QuizAriesJaved Godinez100% (1)
- (DISS 3) MARXISM Students'Document1 page(DISS 3) MARXISM Students'AndreiNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Gems and Jewelry IndustryDocument61 pagesProject Report On Gems and Jewelry IndustrylakshitaNo ratings yet
- Covid 19 Assessment Economic Impact Construction Sector PDFDocument28 pagesCovid 19 Assessment Economic Impact Construction Sector PDFAKSHAYNo ratings yet
- 2 Why Do Nation TradeDocument4 pages2 Why Do Nation TradeAfrina JannatNo ratings yet
- EDS 111 Week 6 Entrepreneurship and Its Environment 2Document30 pagesEDS 111 Week 6 Entrepreneurship and Its Environment 2NitestreamNo ratings yet
- 5 Cambridge Version of Quantity Theory of MOneyDocument2 pages5 Cambridge Version of Quantity Theory of MOneyChenkual ThazualaNo ratings yet
- International BusinessDocument14 pagesInternational BusinessTareq IslamNo ratings yet
- Report11 12Document24 pagesReport11 12mangeoNo ratings yet
- Business Studies - Business Studies Form 3 - Question PaperDocument10 pagesBusiness Studies - Business Studies Form 3 - Question PapershiklemeNo ratings yet
- Impact of Covid-19Document59 pagesImpact of Covid-19Md Mostafijur RahmanNo ratings yet
- APGENCO - Andhra Pradesh Power Generation Corporation LimitedDocument2 pagesAPGENCO - Andhra Pradesh Power Generation Corporation LimitedMALLIKARJUNA RAO100% (1)
- How to Start Trading Crypto Signals in 7 StepsDocument8 pagesHow to Start Trading Crypto Signals in 7 Stepsaditya suranaNo ratings yet
- MA 3103 Market ApproachDocument7 pagesMA 3103 Market ApproachJacinta Fatima ChingNo ratings yet
- Documentos de EmbarqueDocument10 pagesDocumentos de EmbarqueLisseth MendozaNo ratings yet
- PSAF 2019 Pilot Solution Set 2Document17 pagesPSAF 2019 Pilot Solution Set 2divaamy4No ratings yet