Professional Documents
Culture Documents
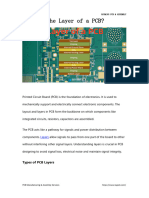
What Is 3 Layer PCB
Uploaded by
jackOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What Is 3 Layer PCB
Uploaded by
jackCopyright:
Available Formats
RAYMING PCB & ASSEMBLY
What is 3 layer PCB?
3 Layer PCB or Three layer PCB Board , Is less in the normally in the
market, most most multilayer plural layer like 4 layer , 6 layer, 32 Layer.
Sometime some electronic device need special layer stack up to get the
performance , and sometime ,just PCB designer want to save cost , not
do 4 layer .
RayMing is 3 layer PCB manufacturer ,Welcome to send your design
to sales@raypcb.com , We will give your quote asap
Request 3 Layer PCB Manufacturing Quote Now
Table of Contents
Introduction
A printed circuit board (PCB) forms the foundation for
building electronic circuits by providing the base for mounting and
PCB Manufacturing & Assembly Services https://www.raypcb.com/
RAYMING PCB & ASSEMBLY
interconnecting components. PCBs with multiple conductive layers enable
increased component density and complex circuit routing. A 3 layer PCB
refers to a board with three copper layers separated by insulating
dielectric substrates.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of 3 layer PCB technology.
We will cover the advantages of 3 layer boards, their construction,
common design techniques, applications, and manufacturing
considerations. With an understanding of their capabilities and limitations,
engineers can effectively utilize 3 layer PCBs in many types of electronic
designs.
Advantages of 3 Layer PCBs
Three layer boards provide the following benefits compared to simpler 2
layer PCBs:
PCB Manufacturing & Assembly Services https://www.raypcb.com/
RAYMING PCB & ASSEMBLY
Added routing flexibility – The extra layer allows more
interconnectivity and circuit optimization. Parts placement and
routing are less constrained.
Improved signal integrity – The middle layer can be a
continuous ground plane. This provides controlled impedance
signal routing on outer layers.
Lower EMI/noise – Enclosing signals between power and ground
layers reduces interference and crosstalk.
Better power distribution – Additional layer allows power-ground
plane pairs for each voltage domain.
Higher component density – Components can be placed on both
sides with vertical interconnects through the middle layer.
Smaller board sizes – Miniaturization by utilizing both sides
for SMT parts placement.
Mixed signal designs – Analog and digital sections can be
segregated across layers.
For these reasons, 3 layer construction provides excellent capability and
cost-benefit for many electronic products.
Construction of 3 Layer PCBs
The fabrication of 3 layer printed circuit boards involves laminating
conductive copper layers separated by insulating dielectric substrates:
PCB Manufacturing & Assembly Services https://www.raypcb.com/
RAYMING PCB & ASSEMBLY
The center substrate is called the core. It provides mechanical
support. The default material for core and prepreg layers is typically
glass reinforced FR-4.
A sheet of copper foil is laminated onto both sides of the core.
These form the top and bottom conductive layers of the PCB.
Photolithographic processing patterns the copper layers into the
required circuit traces, pads, and features.
Plated through holes and buried vias provide vertical
interconnections between the layers.
Soldermask selectively coats the copper layers for protection and
isolation.
This creates a 3 layer board ready for component assembly. The sequence
can be repeated to build multilayer boards.
Typical 3 Layer Stackups
While all 3 layers can be used for routing signals, some standard layer
assignments provide good design starting points:
3 Layer With Ground Plane
Layer 1 – Signals
Layer 2 – Ground plane
Layer 3 – Signals
PCB Manufacturing & Assembly Services https://www.raypcb.com/
RAYMING PCB & ASSEMBLY
This offers a continuous reference ground plane for controlled impedance
routing and shielding.
3 Layer With Split Power Planes
Layer 1 – Signals
Layer 2 – Split power planes (VCC and VDD)
Layer 3 – Signals
Separate power supply domains can be isolated between the split power
planes.
3 Layer With Buried Signal Plane
Layer 1 – Ground
Layer 2 – Signals
Layer 3 – Ground
The buried signal layer fully encompasses routing surrounded by ground
planes.
The stackup can be customized based on signal isolation, thermal
and EMI requirements.
Request 3 Layer PCB Manufacturing Quote Now
Design Considerations for 3 Layer Boards
PCB Manufacturing & Assembly Services https://www.raypcb.com/
RAYMING PCB & ASSEMBLY
Here are some important design practices when working with 3 layer
PCBs:
Split power planes correctly for digital and analog domains based
on current levels.
Use a large number of via stitches to connect split power planes for
lowest impedance.
Assign critical signals to outer layers adjacent to the ground/power
planes.
Route opposing signal polarities on same layer to minimize
crosstalk.
Use diagonal routing over middle layer to change layers when
needed.
Enable thermal relief stitching for highest current paths.
Maximize copper area on outer layers for best heat dissipation.
Follow adequate design clearances between planes and traces.
PCB Manufacturing & Assembly Services https://www.raypcb.com/
RAYMING PCB & ASSEMBLY
Model power and ground impedances to avoid resonance and
coupling issues.
Simulate signal integrity and radiated emissions to high
frequencies.
Proper 3 layer stackup design and layout techniques result in schematics
which transition smoothly through manufacturing.
Typical Applications of 3 Layer PCBs
Here are some examples of products where 3 layer boards are commonly
used:
Consumer electronics – IoT devices, smart home gadgets, wearable
tech
Vehicles – Auto infotainment panels, GPS display units
Industrial – PLCs, motor controllers, sensors
Instrumentation – Meters, analyzers, handheld testers
Medical – Diagnostic equipment, body-worn monitors
IT – Ethernet switches, modems, routers
Communications – Radio transceivers, video gear
3 layer boards balance cost, complexity and performance for mid-range
applications. The proliferation of digital electronics drives large volumes of
3 layer PCBs today.
PCB Manufacturing & Assembly Services https://www.raypcb.com/
RAYMING PCB & ASSEMBLY
3 Layer PCB Manufacturing Overview
3 layer PCB fabrication in volume involves the following key steps:
Materials – Core substrates, prepreg, copper foils
Imaging – Photoresists, direct laser/mechanical patterning
Lamination – Stacking layers under heat and pressure
Etching – Chemically etching away unwanted copper
Drilling – Machines drilling holes for vias and mounting
Plating – Electroplating copper over hole walls and surfaces
Solder mask – Liquid photoimageable solder resist layers
Silkscreen – Printed reference markings
Testing – Electrical testing, quality inspection
Assembly – SMT component placement and soldering
High-yielding fabrication lines enable cost-effective mass production of 3
layer boards.
Conclusion
With three conductive layers to work with, PCB designers have sufficient
flexibility to route out interconnects and partition domains without undue
complexity. 3 layer boards offer excellent capability per unit cost, enabling
their ubiquity across industrial and consumer electronics. Advances in PCB
materials, fabrication equipment and assembly technologies will continue
PCB Manufacturing & Assembly Services https://www.raypcb.com/
RAYMING PCB & ASSEMBLY
to improve technical features, density and reliability while reducing
manufacturing costs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions about 3 layer PCBs:
What are the typical substrate thicknesses used in 3 layer boards?
Standard cores are commonly 0.8mm, 1.0mm, 1.6mm while prepregs
range from 0.1mm to 0.25mm. Overall thickness is usually between
1.6mm to 2.4mm.
What are the minimum track/spacing dimensions achievable on 3 layer boards?
With processes like direct imaging, trace/space down to 125um (5 mils) is
routinely achievable on outer layers.
What are common 3 layer PCB sizes?
Smaller boards of around 50x50mm to 160x100mm are typical. Large
boards up to 460x360mm area are also manufactured cost-effectively.
What are the limitations of 3 layer boards compared to 4+ layer ones?
Design constraints in routing congestion, inability to isolate multiple
signals, lower component density and lack of flexibility for high pin-count
parts.
PCB Manufacturing & Assembly Services https://www.raypcb.com/
RAYMING PCB & ASSEMBLY
What are common materials available for core and prepreg in 3 layer PCBs?
Standard FR-4, High Tg FR-4, Halogen-free FR-4, Rogers materials for high
frequency, Polyimide for flexibility, Ceramic-filled substrates for thermal
conduction.
Related Posts:
1. 28 Layer PCB: An Integrated Multi-Layer PCBs
2. An Introduction to 2 Layer PCB
3. 6 layer PCB Stackup,Thickness and Manufacturing
4. High Quality 20 Layer PCB Manufacturer
https://www.raypcb.com/3-layer-pcb/
PCB Manufacturing & Assembly Services https://www.raypcb.com/
You might also like
- What Is The Inner Layer of A PCBDocument10 pagesWhat Is The Inner Layer of A PCBjackNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1Document46 pagesChapter - 1Vineet KumarNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Guide On Advanced Circuits StackupDocument6 pagesA Comprehensive Guide On Advanced Circuits StackupjackNo ratings yet
- Printed Circuit Ab-1Document38 pagesPrinted Circuit Ab-1pandiarajNo ratings yet
- 6 Layer PCB Stackup, Thickness and ManufacturingDocument15 pages6 Layer PCB Stackup, Thickness and ManufacturingjackNo ratings yet
- Do's and Don'ts For PCB Layer Stack-Up: by - Pragnesh Patel & Ronak ShahDocument9 pagesDo's and Don'ts For PCB Layer Stack-Up: by - Pragnesh Patel & Ronak Shahbasit aliNo ratings yet
- What Is The Layer of A PCBDocument11 pagesWhat Is The Layer of A PCBjackNo ratings yet
- PCB Design Guidelines For EMI EMCDocument7 pagesPCB Design Guidelines For EMI EMCjackNo ratings yet
- PCB InfoDocument19 pagesPCB InfoDarshan Iyer NNo ratings yet
- Layered PCB How Many Types of Layers of PCB Are ThereDocument8 pagesLayered PCB How Many Types of Layers of PCB Are TherejackNo ratings yet
- Printed Circuit BoardDocument16 pagesPrinted Circuit BoardAjayChandrakarNo ratings yet
- MultiSIM - PCB Layout PDFDocument29 pagesMultiSIM - PCB Layout PDFRomeu Corradi JúniorNo ratings yet
- Basic PCB Terminology List You Should KnowDocument13 pagesBasic PCB Terminology List You Should KnowjackNo ratings yet
- RF PCB Design Guidelines You Must KnowDocument13 pagesRF PCB Design Guidelines You Must KnowjackNo ratings yet
- Printed Circuit Board: CharacteristicsDocument23 pagesPrinted Circuit Board: CharacteristicsSai Gautam100% (1)
- UE22EExxx Class1Document58 pagesUE22EExxx Class1Suspicious-Nobody-05No ratings yet
- 12 Layer PCB Manufacturing and Stack Up OptionsDocument12 pages12 Layer PCB Manufacturing and Stack Up OptionsjackNo ratings yet
- Reasons Why PCB Transmission Lines Are ImportantDocument10 pagesReasons Why PCB Transmission Lines Are ImportantjackNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Comparison of Stripline vs. MicrostripDocument10 pagesA Comprehensive Comparison of Stripline vs. MicrostripjackNo ratings yet
- WEEK-3 1. Component Package TypesDocument7 pagesWEEK-3 1. Component Package TypesNAVEENNo ratings yet
- PCB Design For EMCDocument8 pagesPCB Design For EMCSally FangNo ratings yet
- Sibridge Technologies - Design Tip - Do's and Don'Ts For PCB Layer Stack-UpDocument6 pagesSibridge Technologies - Design Tip - Do's and Don'Ts For PCB Layer Stack-Upbhushan86No ratings yet
- PCB Design Presentation: Jakia AfruzDocument33 pagesPCB Design Presentation: Jakia AfruzParth MangukiyaNo ratings yet
- Printed Circuit BoardDocument23 pagesPrinted Circuit Boardahmed100% (2)
- Workshop PCB Desgin 28-10-23 FinalDocument48 pagesWorkshop PCB Desgin 28-10-23 Finalaswinikrn8No ratings yet
- Chapter-1 Wireless Communication - Laser CommunicationDocument56 pagesChapter-1 Wireless Communication - Laser Communicationyash_dk20083706No ratings yet
- How Can A Large PCB Be FabricatedDocument10 pagesHow Can A Large PCB Be FabricatedjackNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing: MaterialsDocument7 pagesManufacturing: MaterialsMaddyNo ratings yet
- Importance of Circuit Card Manufacturing in Electronics IndustryDocument7 pagesImportance of Circuit Card Manufacturing in Electronics IndustryjackNo ratings yet
- PCB Classification - Pattern Class and Drill ClassDocument9 pagesPCB Classification - Pattern Class and Drill ClassjackNo ratings yet
- Micrel PCB Design ConsiderationsDocument0 pagesMicrel PCB Design Considerationstomscribd18No ratings yet
- What Is High Speed PCB DesignDocument13 pagesWhat Is High Speed PCB DesignjackNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Automated Test EquipmentDocument46 pagesProject Report On Automated Test EquipmentGaurav PooniyaNo ratings yet
- PCB Design BasicsDocument18 pagesPCB Design BasicszzhudsxalgmcfeewnwNo ratings yet
- Concepts and Terminology Used in Printed Circuit Boards (PCB)Document9 pagesConcepts and Terminology Used in Printed Circuit Boards (PCB)sonu24meNo ratings yet
- What Is Buried Via PCBDocument10 pagesWhat Is Buried Via PCBjackNo ratings yet
- Stackup Planning AN2011 2Document8 pagesStackup Planning AN2011 2lavaskumarNo ratings yet
- Industrial Training PCBDocument29 pagesIndustrial Training PCBjwndasukhraj100% (2)
- Cem-3 PCBDocument6 pagesCem-3 PCBjimyxtNo ratings yet
- How To Design A PCB For High FrequencyDocument27 pagesHow To Design A PCB For High FrequencyjackNo ratings yet
- What Is The Significance of Home Electronics PCBDocument6 pagesWhat Is The Significance of Home Electronics PCBjackNo ratings yet
- A Closer Look at Analog PCB Design - Comprehensive GuideDocument17 pagesA Closer Look at Analog PCB Design - Comprehensive GuidejackNo ratings yet
- PCB Layout Design Tips - Grounding Considerations - OnElectronTechDocument17 pagesPCB Layout Design Tips - Grounding Considerations - OnElectronTechpapirojedecNo ratings yet
- 3D IC Technology: Pouya Dormiani Christopher LucasDocument37 pages3D IC Technology: Pouya Dormiani Christopher LucasRamakrishnaRao SoogooriNo ratings yet
- How To Order PCB With Components in The Right WayDocument12 pagesHow To Order PCB With Components in The Right WayjackNo ratings yet
- What Is Blind Via PCBDocument10 pagesWhat Is Blind Via PCBjackNo ratings yet
- Printed Circuit Board Manufacturing ProcessDocument2 pagesPrinted Circuit Board Manufacturing ProcessDipesh AggarwalNo ratings yet
- What Are The Components of A Wi-Fi Module and Its PCB PrincipleDocument13 pagesWhat Are The Components of A Wi-Fi Module and Its PCB PrinciplejackNo ratings yet
- PCBDesign Processand Fabrication ChallenDocument14 pagesPCBDesign Processand Fabrication ChallenchioNo ratings yet
- Full Introduction About Antenna Types and PCB MaterialsDocument40 pagesFull Introduction About Antenna Types and PCB MaterialsjackNo ratings yet
- How To Design PCB Trace Spacing and WidthDocument15 pagesHow To Design PCB Trace Spacing and WidthjackNo ratings yet
- How To Design A PCB LayoutDocument13 pagesHow To Design A PCB LayoutjackNo ratings yet
- Presented by Ruby Kumari B.SC (MATHS), B.E (ECE)Document75 pagesPresented by Ruby Kumari B.SC (MATHS), B.E (ECE)AhmedMohabNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Basics of PCBDocument32 pagesLecture 1 Basics of PCBjaltitiNo ratings yet
- 10 Printed Circuit BoardDocument12 pages10 Printed Circuit BoardrameshNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between A Circuit Board and A Bread BoardDocument12 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between A Circuit Board and A Bread BoardjackNo ratings yet
- Basic Thing You Should Know About PCB Assembly ProcessDocument29 pagesBasic Thing You Should Know About PCB Assembly ProcessjackNo ratings yet
- Complete PCB Design Using OrCAD Capture and PCB EditorFrom EverandComplete PCB Design Using OrCAD Capture and PCB EditorRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Why You Should Choose The Shengyi S7439G PCB MaterialDocument5 pagesWhy You Should Choose The Shengyi S7439G PCB MaterialjackNo ratings yet
- Why Is The Home Energy Monitor ImportantDocument7 pagesWhy Is The Home Energy Monitor ImportantjackNo ratings yet
- Why 3D Print PCBs Matter in Today's Electronics ProductionDocument4 pagesWhy 3D Print PCBs Matter in Today's Electronics ProductionjackNo ratings yet
- Why Non Recurring Engineering Cost (NRE Charge) Is Important For Your PCBDocument4 pagesWhy Non Recurring Engineering Cost (NRE Charge) Is Important For Your PCBjackNo ratings yet
- Why OEM Circuit Boards Are Ideal For Use in Several ApplicationsDocument6 pagesWhy OEM Circuit Boards Are Ideal For Use in Several ApplicationsjackNo ratings yet
- Why Is The Panasonic R-F705S Useful For Mobile and Automotive ProductsDocument4 pagesWhy Is The Panasonic R-F705S Useful For Mobile and Automotive ProductsjackNo ratings yet
- Xilinx XAZU2EG-1SBVA484I Fpga ApplicationDocument5 pagesXilinx XAZU2EG-1SBVA484I Fpga ApplicationjackNo ratings yet
- Why The Arlon 49N PCB Material Is Useful in High Temperature or High Performance ApplicationsDocument4 pagesWhy The Arlon 49N PCB Material Is Useful in High Temperature or High Performance ApplicationsjackNo ratings yet
- Why A PCB Ground Plane Is Crucial For PCB FunctioningDocument3 pagesWhy A PCB Ground Plane Is Crucial For PCB FunctioningjackNo ratings yet
- What Is The Significance of Home Electronics PCBDocument6 pagesWhat Is The Significance of Home Electronics PCBjackNo ratings yet
- Where To Buy Rogers RT Duroid 5880 LaminateDocument5 pagesWhere To Buy Rogers RT Duroid 5880 LaminatejackNo ratings yet
- What Is Xilinx Spartan-7 Its Datasheet and Reference DesignsDocument20 pagesWhat Is Xilinx Spartan-7 Its Datasheet and Reference DesignsjackNo ratings yet
- Who Are The Leading Electrical Coil ManufacturersDocument5 pagesWho Are The Leading Electrical Coil ManufacturersjackNo ratings yet
- Where Does The QuickLogic Eclipse FPGA Architecture Family Play A RoleDocument11 pagesWhere Does The QuickLogic Eclipse FPGA Architecture Family Play A RolejackNo ratings yet
- What Is Xilinx Virtex-5 FPGADocument8 pagesWhat Is Xilinx Virtex-5 FPGAjackNo ratings yet
- What Is The Significance of ENIG Plating ThicknessDocument4 pagesWhat Is The Significance of ENIG Plating ThicknessjackNo ratings yet
- What Is Xilinx Kintex UltraScale UltraScale+Document8 pagesWhat Is Xilinx Kintex UltraScale UltraScale+jackNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between Clean Flux and No Clean Flux Off PCBDocument13 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between Clean Flux and No Clean Flux Off PCBjackNo ratings yet
- What Is SMT Soldering Process Step by StepDocument12 pagesWhat Is SMT Soldering Process Step by StepjackNo ratings yet
- What Is Through Hole PCB AssemblyDocument12 pagesWhat Is Through Hole PCB AssemblyjackNo ratings yet
- What Is Thermal Consideration in PCB DesignDocument6 pagesWhat Is Thermal Consideration in PCB DesignjackNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between ARM and FPGA ProcessorsDocument9 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between ARM and FPGA ProcessorsjackNo ratings yet
- What Is The Significance of IOT in AgricultureDocument8 pagesWhat Is The Significance of IOT in AgriculturejackNo ratings yet
- What Is Taconic TSM-DS3b PCBDocument7 pagesWhat Is Taconic TSM-DS3b PCBjackNo ratings yet
- What Is Taconic TSM-DS3b PCBDocument7 pagesWhat Is Taconic TSM-DS3b PCBjackNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between FFC Connector and FPC ConnectorDocument14 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between FFC Connector and FPC ConnectorjackNo ratings yet
- What Is The Melting Point of SolderDocument4 pagesWhat Is The Melting Point of SolderjackNo ratings yet
- What Is The Purpose and Applications of A PCB MotherboardDocument4 pagesWhat Is The Purpose and Applications of A PCB MotherboardjackNo ratings yet
- What Is Signal Integrity A Comprehensive OverviewDocument9 pagesWhat Is Signal Integrity A Comprehensive OverviewjackNo ratings yet
- What Is Signal Integrity A Comprehensive OverviewDocument9 pagesWhat Is Signal Integrity A Comprehensive OverviewjackNo ratings yet
- TD 3.6 L4 TCD 3.6 L4: Operation ManualDocument72 pagesTD 3.6 L4 TCD 3.6 L4: Operation ManualMajd50% (2)
- GMD 15 3161 2022Document22 pagesGMD 15 3161 2022Matija LozicNo ratings yet
- Verilog Code For Traffic Light Control Using FSMDocument7 pagesVerilog Code For Traffic Light Control Using FSMEr Pradip PatelNo ratings yet
- Jungle Safari Booking Management System: Mini Project ReportDocument19 pagesJungle Safari Booking Management System: Mini Project ReportNIRAV SHAH100% (1)
- Stanley Diamond Toward A Marxist AnthropologyDocument504 pagesStanley Diamond Toward A Marxist AnthropologyZachNo ratings yet
- 6 - Designing Manufacturing Processes - Hill - Product ProfilingDocument20 pages6 - Designing Manufacturing Processes - Hill - Product ProfilingLalit S KathpaliaNo ratings yet
- Growth of Luxury Market & Products in IndiaDocument60 pagesGrowth of Luxury Market & Products in IndiaMohammed Yunus100% (2)
- Gardner Gary ResumeDocument1 pageGardner Gary ResumeGary GardnerNo ratings yet
- قدرة تحمل التربةDocument3 pagesقدرة تحمل التربةjaleelNo ratings yet
- Progress Test 3Document7 pagesProgress Test 3Mỹ Dung PntNo ratings yet
- Human Behavior in OrganizationDocument85 pagesHuman Behavior in OrganizationNeric Ico Magleo100% (1)
- 10 Professional Tax Software Must-Haves White PaperDocument2 pages10 Professional Tax Software Must-Haves White PaperRakesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Dissertation Bowden PDFDocument98 pagesDissertation Bowden PDFmostafaNo ratings yet
- Pro & Contra Hydropower: AdvantagesDocument16 pagesPro & Contra Hydropower: AdvantagesbarukomkssNo ratings yet
- Managing Digital Transformations - 1Document105 pagesManaging Digital Transformations - 1RamyaNo ratings yet
- Ergonomics InvestmentDocument4 pagesErgonomics InvestmentLiliana Alejandra Rodriguez ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Game Theory TwoDocument9 pagesChapter 6 Game Theory TwoMextli BarritaNo ratings yet
- 5c X-Tend FG Filter InstallationDocument1 page5c X-Tend FG Filter Installationfmk342112100% (1)
- Computer Systems Servicing NC II CGDocument238 pagesComputer Systems Servicing NC II CGRickyJeciel100% (2)
- Beverage Companies in PakistanDocument3 pagesBeverage Companies in PakistanZeeshan JavedNo ratings yet
- Dialux BRP391 40W DM CT Cabinet SystemDocument20 pagesDialux BRP391 40W DM CT Cabinet SystemRahmat mulyanaNo ratings yet
- Con Law Koppelman HugeDocument203 pagesCon Law Koppelman HugemrstudynowNo ratings yet
- SWP-10 Loading & Unloading Using Lorry & Mobile Crane DaimanDocument2 pagesSWP-10 Loading & Unloading Using Lorry & Mobile Crane DaimanHassan AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Carbon Fiber 395GPA Structural Ansys ReportDocument13 pagesCarbon Fiber 395GPA Structural Ansys ReportKrish KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 02 Running EnergyPlusDocument29 pagesLecture 02 Running EnergyPlusJoanne SiaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1technoDocument3 pagesAssignment 1technonadiyaxxNo ratings yet
- Datasheet Solis 3.6K 2G US 1phase 20170613Document2 pagesDatasheet Solis 3.6K 2G US 1phase 20170613Jimmy F HernandezNo ratings yet
- FDD SRM & NDGDocument3 pagesFDD SRM & NDGEnd EndNo ratings yet
- Flight Eticket - PdfaaaDocument3 pagesFlight Eticket - PdfaaaIgnacio Gonzalez PastranoNo ratings yet
- Brand Trust, Customer SatisfacDocument21 pagesBrand Trust, Customer SatisfacJar JarNo ratings yet