0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views36 pagesES209 Module 2 - Probability
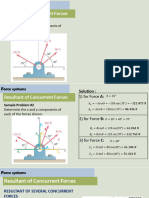
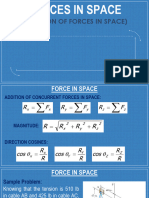
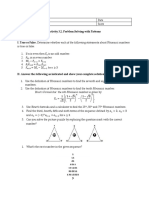
1. The document introduces probability and key concepts like sample space, events, simple and compound events.
2. It explains how to calculate probability as the number of favorable outcomes divided by the total number of possible outcomes.
3. The document covers probability rules and operations with events like union, intersection, complement, and dependent and independent events.
Uploaded by
Mianira MigoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views36 pagesES209 Module 2 - Probability
1. The document introduces probability and key concepts like sample space, events, simple and compound events.
2. It explains how to calculate probability as the number of favorable outcomes divided by the total number of possible outcomes.
3. The document covers probability rules and operations with events like union, intersection, complement, and dependent and independent events.
Uploaded by
Mianira MigoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd