Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Edu 105 L2
Uploaded by
Keannu EstoconingOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Edu 105 L2
Uploaded by
Keannu EstoconingCopyright:
Available Formats
Estoconing, Keannu A.
EDU 105 C
BSEd – English II
Learning Task 4: Assessment Scenarios
A 1. A twelve-year old out-of-school youth who stopped during the fourth grade took a
test given by the department of Education to go back to formal schooling. The test
determines the grade or year level appropriate for the learner.
F 2. Every year, a national normed assessment is given to grade 3 pupils in English,
Math and Science.
B 3. The teacher returned a student’s Math worksheet with written comment. The
teacher’s remarks consist of a compliment and a correction. An explanation was
provided concerning what the students did correctly and incorrectly, what was accurate
and inaccurate in the student’s work.
D 4. A Math teacher gives a test towards the end of the unit. He / She will use the test
items as starting point for discussion of conceptual problems revealed by the test.
E 5. An English teacher regularly assesses student’s skills by using probes which are
brief, easily-administered measures. The teacher then graphs changes in the number of
correct words per minute (reading) and compares each student’s growth to the rate of
improvement needed to meet learning goals.
C 6. A technology and Livelihood Education teacher is teaching ICT to his students.
Through oral questioning, he asked several students about the use of the internet in
searching for information and the computer file system. He also provided a short
computer exercise. After confirming what the students know and can do, the teacher
proceeded to the next segment – how to download files from the internet.
Learning Task 5: Interpreting A Concept Map
As a K – 12 teacher, effective assessments in a classroom is a must since as teachers
our main purpose is to improve the student’s learning. To improve the students’ learning
through effective assessment, a concept map about the components of classroom
assessment literacy will be utilized.
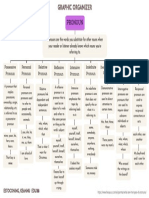
The concept map is a pie graph with eight slice. The first slice is a balanced formation
and summative assessment, which entails a balance of graded and non-graded
activities. The second slice consists of clear targets, which are statements that define
what students should know and be able to perform and are communicated in student-
friendly language. The third slice is test item and task development, followed by the
fourth slice, scoring and guides; these slices deal with creating rubrics and exam
questions. The fifth slice is instructional planning with results, and the sixth slice is
descriptive feedback. These two steps are linked since feedback is required after
tabulating the findings. The seventh slice is self-assessment and goal setting. This is
important because students will be able to understand what they don't know and what
they want to know on their own. The eighth and last slice is tracking resulting and
grading, sometimes known as the school grading system.
With using this concept map, accuracy and effectivity of assessments will be fostered.
Learning Task 6: MEME
Formative assessment’s data are
recorded for the aim of monitoring
students' learning development. These,
however, aren't used as the foundation
for students' grades. That is why failing
a formative assessment activity or
exam does not mean the end of your
high grades.
You might also like
- Section 1.2. Roles of Assessment - 2Document4 pagesSection 1.2. Roles of Assessment - 2Emily BacolodNo ratings yet
- Discussion 2.1 Kemuel BagsitDocument2 pagesDiscussion 2.1 Kemuel BagsitKemuel Bagsit80% (5)
- AL 1.2 - Roles of AssessmentDocument7 pagesAL 1.2 - Roles of AssessmentJessa ParedesNo ratings yet
- Final Evaluation ProjectDocument28 pagesFinal Evaluation ProjectashleyeivinsNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Roles of Assessment 1 1Document9 pagesModule 2 Roles of Assessment 1 1Apple04No ratings yet
- Module 2Document15 pagesModule 2Simply Show100% (3)
- Assessment of Learning 1Document3 pagesAssessment of Learning 1Jerson MadriagaNo ratings yet
- EDAL Concept and Relevance of AssessmentDocument5 pagesEDAL Concept and Relevance of AssessmentChristle EdianonNo ratings yet
- Reporting Test ScoresDocument28 pagesReporting Test Scoresmaheen rasheed100% (2)
- Ed107 Module9Document17 pagesEd107 Module9Veronica FiedacanNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document3 pagesModule 2Merry Jane TagubaNo ratings yet
- Administrative Guidelines StudentsDocument11 pagesAdministrative Guidelines Studentsapi-312554041No ratings yet
- AssessmentDocument4 pagesAssessmentSJC ITR75% (4)
- Module 1 BSEDMATH15Document13 pagesModule 1 BSEDMATH15Abulencia JessamayNo ratings yet
- Observation Sheet #5 Summative AssessmentDocument2 pagesObservation Sheet #5 Summative AssessmentLIAN JENNON RUBLICONo ratings yet
- 2AssessmentDocumentation Mathv Oct2022Document35 pages2AssessmentDocumentation Mathv Oct2022katyaNo ratings yet
- AssessmentDocument11 pagesAssessmentJericho PidoNo ratings yet
- Assesment in Learning ExamDocument3 pagesAssesment in Learning Examdetomasnicoleerika01No ratings yet
- Pre-Assessment or Diagnostic AssessmentDocument12 pagesPre-Assessment or Diagnostic AssessmentM Noaman AkbarNo ratings yet
- Handbook Illinois CollegeDocument115 pagesHandbook Illinois CollegeShaukat Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- AL Chapter 2Document10 pagesAL Chapter 2John Michael Porras HambreNo ratings yet
- 8602.01 DoneDocument38 pages8602.01 DoneTehmina HanifNo ratings yet
- LE12 Instructional Planning and ImplementationDocument5 pagesLE12 Instructional Planning and ImplementationJoana HarvelleNo ratings yet
- Assessment and Evaluation in Mathematics PrelimDocument19 pagesAssessment and Evaluation in Mathematics PrelimLee Yan Ru100% (1)
- Oas Community College: DescriptionDocument7 pagesOas Community College: DescriptionTricia Ann A. SodsodNo ratings yet
- Innovativ QiymetlendirmeDocument25 pagesInnovativ QiymetlendirmeAnonimNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Student Learning PDFDocument27 pagesAssessment of Student Learning PDFSwami Gurunand100% (2)
- 311 AL2 Week 2 Classroom Assessment 1Document8 pages311 AL2 Week 2 Classroom Assessment 1Rellan YbanezNo ratings yet
- Module ActivitiesDocument14 pagesModule ActivitiesPatricia Jane CabangNo ratings yet
- Group 11 (Grading and Student Evaluation-LTA)Document13 pagesGroup 11 (Grading and Student Evaluation-LTA)Annisa Nurul JannahNo ratings yet
- Learning Episode 13 B in Field Study 1Document19 pagesLearning Episode 13 B in Field Study 1payno gelacioNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 ProfEd8Document2 pagesActivity 1 ProfEd8valerosm2No ratings yet
- MODULE 1 - Assessment and EvaluationDocument9 pagesMODULE 1 - Assessment and EvaluationTetche Paña ViceraNo ratings yet
- Sed 3201 Module 1Document12 pagesSed 3201 Module 1JazzyNo ratings yet
- Summative AssessmentDocument15 pagesSummative AssessmentHoneylyn Vee SabatinNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Prof Ed 8Document15 pagesUnit 3 Prof Ed 8ardee753No ratings yet
- MATH 139 Week-4-6Document13 pagesMATH 139 Week-4-6marjoralyn.esganaNo ratings yet
- The Outcomes Assessment Phases in The Instructional CycleDocument4 pagesThe Outcomes Assessment Phases in The Instructional Cyclemarvin cayabyabNo ratings yet
- UNIT2 Performance Assessment-Lesson1Document10 pagesUNIT2 Performance Assessment-Lesson1Hizzel De CastroNo ratings yet
- Geoffrey Crisp 2011 - Teacher's Handbook On E-AssessmentDocument24 pagesGeoffrey Crisp 2011 - Teacher's Handbook On E-Assessmentluiz carvalho100% (1)
- Examples of Formative and Summative AssessmentsDocument10 pagesExamples of Formative and Summative AssessmentsJers Batan100% (1)
- Fs 5 Episode 8Document3 pagesFs 5 Episode 8Sharina Mae EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Reflection 2 1 2Document4 pagesLesson 2 - Reflection 2 1 2Mikken Casing0% (1)
- RenenjayOctaviano Module2 ActivityDocument6 pagesRenenjayOctaviano Module2 ActivityGrizzel DomingoNo ratings yet
- Diaz Sc21 Assessment Scenarios 1Document2 pagesDiaz Sc21 Assessment Scenarios 1John Rafael Obera DiazNo ratings yet
- 8602 Assignment AnswerDocument16 pages8602 Assignment Answernaveed shakeelNo ratings yet
- Critical EssayDocument5 pagesCritical EssayFrance Xavier Solite VillagonzaloNo ratings yet
- PROFED8 FrommodulesDocument5 pagesPROFED8 FrommodulesBren GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Refresh Session Grades 9-12 Feb 2013Document44 pagesRefresh Session Grades 9-12 Feb 2013api-202232251No ratings yet
- EAD 533 - Clinical Field Experience C - Assessment Analysis FeedbackDocument4 pagesEAD 533 - Clinical Field Experience C - Assessment Analysis Feedbackshirley moligaNo ratings yet
- Educ 10. Unit 4-5Document6 pagesEduc 10. Unit 4-5Junard AsentistaNo ratings yet
- 0697 Assignmnt No-01Document21 pages0697 Assignmnt No-01Muhammad Ibrahim HamdardNo ratings yet
- Internet Resources For AssessmentDocument17 pagesInternet Resources For AssessmentMeoLuoi13No ratings yet
- Chappuis Assessment Chap 1Document16 pagesChappuis Assessment Chap 1SethycNo ratings yet
- Ed107 Module7Document10 pagesEd107 Module7Veronica FiedacanNo ratings yet
- Week 7 Lets Think-Role PlayDocument2 pagesWeek 7 Lets Think-Role Playapi-732797125No ratings yet
- Ethical Grading Tips: Ctl/Gradingtips - 3 - 2017/ Sagmiller/OregonstateuniversityDocument2 pagesEthical Grading Tips: Ctl/Gradingtips - 3 - 2017/ Sagmiller/OregonstateuniversitySamiNo ratings yet
- Deped Order No. 8Document17 pagesDeped Order No. 8May Ann Sevilla Emradura100% (2)
- Assessment PrecyDocument52 pagesAssessment PrecyCristina MontenegroNo ratings yet
- Audio MediaDocument2 pagesAudio MediaKeannu EstoconingNo ratings yet
- Learning StylesDocument3 pagesLearning StylesKeannu EstoconingNo ratings yet
- EDU178C Final Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesEDU178C Final Lesson PlanKeannu EstoconingNo ratings yet
- PronounDocument1 pagePronounKeannu EstoconingNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan G8Document8 pagesLesson Plan G8Keannu EstoconingNo ratings yet
- Semi Detail Lesson Plan English PPADocument3 pagesSemi Detail Lesson Plan English PPAKeannu EstoconingNo ratings yet
- Template For Reflective Journal 1Document7 pagesTemplate For Reflective Journal 1Keannu EstoconingNo ratings yet
- 200-301 CCNA Old and New CCNA ComparisonDocument5 pages200-301 CCNA Old and New CCNA ComparisonmihirmmbNo ratings yet
- AbstractDocument10 pagesAbstractprecillaugartehalagoNo ratings yet
- br1 2Document16 pagesbr1 2disha_gupta_16No ratings yet
- Monitoring Tool For Quarterly TestDocument3 pagesMonitoring Tool For Quarterly TestAnna Dominique Daen100% (2)
- BiophysicsDocument16 pagesBiophysicsNurarief AffendyNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 English Language and Literature Sample Paper 2011Document27 pagesCBSE Class 10 English Language and Literature Sample Paper 2011sbarathiNo ratings yet
- 2019 Speciman Paper 1Document12 pages2019 Speciman Paper 1Anitha NathenNo ratings yet
- UTPRAS Guidelines Legal Basis:: o o o oDocument5 pagesUTPRAS Guidelines Legal Basis:: o o o oHilario Domingo ChicanoNo ratings yet
- An Investigation Into The Impact of COVID-19 On Private Schools in Gwagwalada Area Council of FCT, NigeriaDocument10 pagesAn Investigation Into The Impact of COVID-19 On Private Schools in Gwagwalada Area Council of FCT, NigeriaresearchparksNo ratings yet
- Compare and Contrast Essay 012Document4 pagesCompare and Contrast Essay 012api-293952433No ratings yet
- Drops On A PennyDocument5 pagesDrops On A Pennyapi-329168688100% (1)
- Root Cause AnalysisDocument5 pagesRoot Cause AnalysisNishabharatNo ratings yet
- For Admission To Polytechnics of West Bengal For The Academic Session 2019-20 Through JEXPO-2019Document1 pageFor Admission To Polytechnics of West Bengal For The Academic Session 2019-20 Through JEXPO-2019Anirban DebnathNo ratings yet
- Research ProposalsDocument4 pagesResearch ProposalsNuwan UdawattaNo ratings yet
- CPE Student's.handbook 2013Document36 pagesCPE Student's.handbook 2013David Hayes100% (1)
- Emmanuel Serrano Pre-Test (Chapter 5, 6, 7, 8) IiiDocument8 pagesEmmanuel Serrano Pre-Test (Chapter 5, 6, 7, 8) Iiiemmanuel80% (15)
- Diploma Iii Sem SchemeDocument1 pageDiploma Iii Sem Schemeii year ceNo ratings yet
- MHT CET A-Complete-Guide PDFDocument32 pagesMHT CET A-Complete-Guide PDFAnshita JainNo ratings yet
- Qualitative PPT Characteristics of Qualitative ResearchDocument24 pagesQualitative PPT Characteristics of Qualitative ResearchAhmed Yousufzai0% (1)
- Equipment Centrifugal Compressor Major Inspect FinalDocument2 pagesEquipment Centrifugal Compressor Major Inspect FinalMohammed AbdallaNo ratings yet
- 02 Olympiads PhysicsDocument4 pages02 Olympiads PhysicsHarsh Tiwari33% (6)
- Https Niva - Vidyanikethan.edu Examination ExaminationApplicationAcknowledgement - Aspx PDFDocument2 pagesHttps Niva - Vidyanikethan.edu Examination ExaminationApplicationAcknowledgement - Aspx PDFKotte lokeshNo ratings yet
- NLD CBR Evaluation and AssessmentDocument101 pagesNLD CBR Evaluation and AssessmentrodrigocorreaaranedaNo ratings yet
- NP3. Nursing Board Exam November 2008 Answer KeyDocument12 pagesNP3. Nursing Board Exam November 2008 Answer KeyAlyssa Mier Dacua Patalinjug100% (1)
- CW 2073R - Newly AmmendedDocument3 pagesCW 2073R - Newly AmmendedPuteri AdlinaNo ratings yet
- Research Title Handouts + VariablesDocument3 pagesResearch Title Handouts + VariablesAngelixa JavierNo ratings yet
- Kenny IepDocument5 pagesKenny Iepapi-252428564No ratings yet
- No Research No Right To SpeakDocument52 pagesNo Research No Right To SpeakTungstar De Martinez100% (1)
- Syllabus NWU - ACA - 010: FIELD STUDY 5 (Learning Assessment Strategies)Document14 pagesSyllabus NWU - ACA - 010: FIELD STUDY 5 (Learning Assessment Strategies)Mark GanitanoNo ratings yet
- Research Methodology PH.D Entrance Test Paper 2017 Ganpat University PDFDocument11 pagesResearch Methodology PH.D Entrance Test Paper 2017 Ganpat University PDFDeepakNo ratings yet