Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2324 Level J Science Revision Sheet Final QUESTIONS (1) - 231114 - 095218
Uploaded by
s27685811Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2324 Level J Science Revision Sheet Final QUESTIONS (1) - 231114 - 095218
Uploaded by
s27685811Copyright:
Available Formats
Reference: Level J Cells and Genetics Chapter 1 Section 1
1) A living thing that exhibits characteristics of life is
a) Organism
b) Meadow
c) Mountain
d) Environment
2) Which of the following are essential needs of animals?
a) Place to grow
b) Rocks
c) Nutrients
d) Water
3) For each statement, write growth or development
a) An organism increases in size: …………..
b) An organism changes in appearance over time: …………………….
c) New structures appear in the body of an organism: ………………..
4) List the six characteristics of living things. Grid
a. …………………………………..
b. ………………………………….
c. ………………………………….
d. ………………………………….
e. ………………………………….
f. ………………………………….
5) List the six needs of living things.
a. …………………………………..
b. ………………………………….
c. ………………………………….
d. ………………………………….
e. ………………………………….
f. ………………………………….
6) An organism must control its internal environment because
a) Chemical process take place under certain conditions
b) Nonliving things do not control their internal environment
c) It is unaffected by changes in temperature
d) It cannot reproduce
7) Order the levels of organization from smallest to largest
Organ, cell, organ system, tissue, organism
………………………………………………………………………
8) Compare between unicellular and multicellular organisms.
Date 17/9/23 | Level J | 1
Yeast-seaweed-microscopic-larger organisms-composed of many cells-composed of
one cell- The single cell must carry all basic functions- Cells are organized and
specialized to perform specific functions
Unicellular Multicellular
9) Summarize the three parts of the cell theory.
1. …………………………………………………………….
2. ………………………………………………………………………
3. ………………………………………………………………………
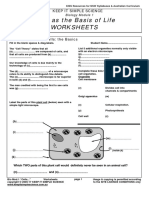
10) What unicellular organisms are shown above?
a) Bacteria
b) Protozoans
c) Fungi
d) Plants
11) What is a stimulus? Grid
…………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………
12) What is a response? Grid
………………………………………………………………………
13) What is homeostasis? Grid
………………………………………………………………………
14) What is a cell? Grid
………………………………………………………………………
15) How does a unicellular organism survive even though it is made up of one cell? Grid
………………………………………………………………………
Date 17/9/23 | Level J | 2
16) What caused early scientists to conclude that all living things are made of cells that
perform all life functions?
………………………………………………………………………
17) Why do growing organisms need to take in raw materials?
………………………………………………………………………
18) What instrument can be used to observe a paramecium?
………………………………………………………………………
19) Name two materials that animals get from the food they eat?
………………………………………………………………………
20) What does a palm tree need to spread out its root and leaves?
………………………………………………………………………
21) What does a palm tree need to do photosynthesis, chemical process, building body
parts and transporting material? List 4 needs
………………………………………………………………………
Reference: Level J Cells and Genetics Chapter 1 Section 2
1. What are the basic compounds found in living things? GRID
………………………………………………………………………
2. Fill in the following table
Elements Importance/Function
Carbohydrates
Lipids
Proteins
Nucleic acid
Water
Date 17/9/23 | Level J | 3
2) Which molecule holds the genetic information for making proteins that a cell needs?
Grid
a) Amino acid
b) DNA
c) RNA
e) Water
3) Small structures in the cytoplasm of a cell are called
a) organs
b) organelles
c) cytoplasm
d) cell membrane
4) Choose the functions of the cell membrane in a cell. Grid
a) building up proteins
b) holding the cell together
c) separating inside of a cell from the outside environment
d) accelerating chemical processes within the cell
e) controlling what enters and leaves the cell.
f) giving the cell its shape
5) Which of the following is true for only bacterial cells?
a. It does not have a nucleus.
b. It does not have organelles with membranes.
c. It has a cell wall.
d. It has genetic material.
e. All life processes take place in the cytoplasm.
6) In each case, tell if the statement describes mitochondria or chloroplasts.
a) Change the energy from sunlight into food: ………………..
b) Change the energy in the food into a form that the cells can use: …………………
c) Present in a green plant cell: …………………………
7) Compare the animal cell to the plant cell by placing check marks
Cell part Plant cell Animal cell
Large central vacuole
Mitochondria
Cell membrane
Cell wall (grid)
Lysosome
Chloroplast (grid)
Date 17/9/23 | Level J | 4
8) Which of the following is not true about the endoplasmic reticulum?
a) It consists of a network of passageways
b) It is the highway system of the cell
c) It breaks down sugars to give a form of energy the cell can use
d) It can have ribosomes attached on its outer surface
9) Which of the following is not true about the Golgi body?
a) It resembles a stack of flat pancakes and vesicles
b) It is the cell’s power plant
c) It receives materials from the endoplasmic reticulum
d) It sorts materials to where they are needed in the cell
10) Fill in the table to show how a cell wall an cell membrane compare. Write Yes or
No
Function Cell membrane Cell wall
Surrounds a cell
Protects a cell
Allows only certain materials to pass through
Is thin and flexible
Is thick and rigid
Present in animals
Present in plants
11) Proteins that speed up chemical processes in an organism Grid
a) enzymes
b) water
c) carbohydrates
d) nucleic acid
e) RNA
12) A nucleic acid involved in making proteins Grid
a) DNA
b) water
c) MNA
d) TNA
e) RNA
13) What is the function of the nucleus in a cell? Grid
………………………………………………………………………
14)What is the main function of the ribosomes in a cell? Grid
………………………………………………………………………
15) Where are chloroplasts found? Grid
………………………………………………………………………
Date 17/9/23 | Level J | 5
16) Where does most of the cell activities take place
a) in the ribosome
b) in the mitochondria
c) in the cytoplasm
d) in the nucleus
17) fill in the table for carbohydrates and lipids
Cholesterol - starch - stored as fat - provide energy
Carbohydrates Lipids
18) which of the following is false about DNA
a) it holds the genetic information
b) can be found in the cytoplasm
c) it builds protein on ribosomes
19) compare and contrast animal cell and bacterial cell use the word in the box
Ribosome- chromosomes-cell membrane- DNA is suspended in cytoplasm -
DNA is inside nucleus- mitochondrion
Animal cell Bacterial cell Both Animal
and bacterial
cell
Date 17/9/23 | Level J | 6
22) Which of the following captures energy from sunlight and uses it to make food
23) List the functions of water
…………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………
24) List 2 functions of the central vacuole
…………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………
25) What happens to partially processed lipids and proteins that leave the ER?
…………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………
Reference: Level J Cells and Genetics Chapter 1 Section 3
1. Fill in the table
Cell Structure Adaptation
Nerve cells
Plant leaf cells
Date 17/9/23 | Level J | 7
Smooth muscle cells
Red blood cells
Sperm cells
Plant roots
2. List the levels of cell organization from the most complex to the simplest level.
grid
………………………………………………………………………
3. Give examples of each of the following
Plant tissue Animal tissue
Plant organ Animal organ
Date 17/9/23 | Level J | 8
Plant organ system Animal organ system
4. Arrange the following with the correct cellular organizational level within an
organism.
…. Eye
…. Nervous system
…. Nervous tissue
… Nerve cell
Reference: Level J Cells and Genetics Chapter 2 Section 1
1. Why is a cell membrane considered as “selectively permeable”? Grid
……………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………….
2. Describe Osmosis
……………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………….
3. In which direction will water move?
…………………………………………………………
Date 17/9/23 | Level J | 9
4. What happens to a red blood cell placed in pure water? Explain.
……………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………….
5. What happens to a red blood cell placed in 20% salt solution? Explain.
……………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………….
6. What happens to a plant cell placed in pure water? Explain.
……………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………….
7. How do transport proteins help plants?
……………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………….
8. Which of the following requires energy?
A. Diffusion
B. Osmosis
C. Endocytosis
D. Exocytosis.
9. Which process is shown by the following figure?.............................
10. Which process is shown by the following figure? …………………..
Date 17/9/23 | Level J | 10
11. A cell needs to take in large protein molecule. How will this molecule enter
the cell? Order the steps below.
….. A pocket forms inside the cell.
….. Part of the cell membrane wraps itself around the particle
….. A vesicle forms
….. The pocket containing the particle pinches off into the cell.
….. Energy is used during the process.
12. Compare passive and active transport, by choosing the correct feature(s).
Feature Passive Active transport
transport
1. Requires energy grid Yes / No Yes / No
2. Does not require energy Yes / No Yes / No
grid
3. Moves material from the region of Yes / No Yes / No
higher to a region of lower
concentration
4. Moves material from the region of Yes / No Yes / No
lower to the region of higher
concentration
5. Diffusion and osmosis are Yes / No Yes / No
examples of it.
13. What allow materials to diffuse in and out easily in the cell?
……………………………………………………………………
14. How are the following transported?
a. Proteins secreted by the cells of the stomach ……………………….
b. White blood cells engulfing bacteria ………………………..
c. Secretion of salts by marine fish ……………………..
d. Absorption of salts by the roots of plants ………………
15. An animal cell is placed in distilled water (pure water without solute)
a- what is the name of the process by which water molecules move across the cell
membrane?.............................
b- In which direction do the water molecules move across the cell membrane?
…………………………………………….
Date 17/9/23 | Level J | 11
16. In order to keep its shape and function, a cell must be in an environment in which there
is
A. a higher number of solute molecules than the cytoplasm.
B. a lower number of solute molecules than the cytoplasm.
C. a higher number of water molecules than the cytoplasm.
D. a lower number of water molecules than the cytoplasm.
E. the same number of water and solute molecules as the cytoplasm.
17. Which of the following are reasons why a cell must be small?
A. to get the needed materials as fast as required
B. to get rid of waste fast enough
C. to prevent water molecules from entering the cell
D. to fit inside the body tissues
E. to allow the growth of other cells
18. Plants take in minerals from the soil by
A. transport proteins (active transport)
B. endocytosis
C. osmosis
D. diffusion
E. exocytosis
19. Which of the following statements is true for passive transport?
a. Small molecules such as glucose and amino acid can pass freely through the
membrane
b. Small molecules such as oxygen and water can pass freely through the membrane,
without the need of energy
c. Large molecules such as glucose and amino acids pass through the membrane with the
help of transport proteins. This process is passive because it uses energy
d. Small molecules such as oxygen use energy to pass freely through the selectively
permeable membrane
e. Large molecules such as oxygen can freely pass through the membrane with the help of
a transport protein
20. Choose the statements that describe endocytosis
a. It is a type of active transport
b. It allows large molecules or particles to enter the cell
c. It is used by water molecules
d. It uses transport proteins
e. It requires the use of energy
21. Choose the statements that describe exocytosis
a. It is a type of active transport
b. It allows large molecules or particles to enter the cell
c. It allows large molecules or particles to leave the cell
d. It uses transport proteins
e. It requires the use of energy
Date 17/9/23 | Level J | 12
22. Which of the following statements relate to the size of the cell in order to perform its
proper function?
a. Cells are small so that the surface area to volume ratio is high enough for materials to
pass into and out of the cell
b. Cells are large enough to have a high surface area allowing the diffusion of substances
across the membrane
c. As a cell grows, it increases in size and its volume increases much faster than its
surface area does. The cell’s surface area becomes too small to bring in materials
needed by the cell.
d. As a cell grows, its volume decreases and its surface area increases in order to allow
diffusion across the membrane
e. Cells are small so that surface area to volume ratio is too small, which allows materials
to pass in and out of the cell.
23. What will happen when a red blood cell is placed in a drop of pure water?
a. It will shrink
b. It will become turgid
c. Water will move into the cell
d. It will swell and may burst
e. Nothing happens
24. Which 2 cell characteristics determine how much material can enter and leave?
a. Mass
b. Color
c. Volume
d. Age
e. Surface area
25. How will this molecule leave the cell by exocytosis? Arrange the steps of exocytosis
The vesicle moves to the cell membrane
The contents of the vesicle are released outside the ell
Large molecules of waste are enclosed in a vesicle
The vesicle fuses with the cell membrane
26. The table below shows few molecules. Some of these molecules pass through
the cell membrane while others do not.
Molecules Passes by diffusion through the cell membrane
Date 17/9/23 | Level J | 13
Oxygen/carbon dioxide
glucose
ions
Vitamins
27. Fish living in the ocean might absorb excessive salt due to the higher salt
concentration in seawater compared to their cells. How do these fish manage to
survive in such environment?
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
28. Fish rely on oxygen for their survival. What happens to a fish when the oxygen
concentration in the water decreases?
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
29. Compare and contrast endocytosis and exocytosis
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Reference: Level J Cells and Genetics Chapter 2 Section 2
1. The following figure shows a chloroplast.
Date 17/9/23 | Level J | 14
a) In which type of organisms is a chloroplast found?
……………………….
b) Which reaction is carried out by a chloroplast?
………………………….
c) Write the chemical equation for this reaction.
….……+……… …………..……+………………….
d) Name the sugar produced in this reaction?
…………………..
e) How does this sugar store energy?
…………………………………….
f) Label A, B, C, D from the figure above
A:……………….
B:……………….
C:……………….
D:………………..
g) In what form does the tree store sugar for later use
…………………………………….
h) Name a plant part that stores sugar for later use?
…………………………………….
Date 17/9/23 | Level J | 15
2. Grasshoppers are animals that feed on plants. Many grasshoppers are green in
color. Is a green grasshopper considered a photoautotroph? Explain.
………………………………………………………………………
3. Where is the site of photosynthesis?
…………………………………
4. What happens in part 1 of photosynthesis?
……………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………
5. What happens in part 2 of photosynthesis?
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
6. What is the main function of stomata?
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………
7. When does the stomata open? Why?
………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………
8. When does stomata close? Why?
……………………………………………………………………
9. How does each of carbon dioxide and water enter the plant?
…………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………
10. What happens to the sugars that are made during photosynthesis?
Can be converted into:
-Amino acids for ……………………
-Stored as …………………………….
Date 17/9/23 | Level J | 16
-Wood in ……………………………….
11. Identify the form in which plants store starch
………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………
12. A large molecule made up of thousands of glucose subunits linked together is
A. water.
B. carbon dioxide.
C. oxygen.
D. granule.
E. starch.
13. choose the correct answers: the rate of photosynthesis increases in
A. dim sunlight
B. bright sunlight
C. warm temperatures
D. small quantity of carbon dioxide
E. large quantity of carbon dioxide
14. What is photosynthesis?
……………………………………………………………………
15. What is the role of the chloroplast in photosynthesis?
……………………………………………………………………
16. What are the 4 needs and the end products of photosynthesis?
Needs: ……………………………………………………………………
end products: ……………………………………………………………………
17.Arrange the sequence of the events taking place during photosynthesis.
Choose the answer.
Chlorophyll absorbs energy from sunlight.
Chemical energy that powers the second part of photosynthesis
is produced.
The energy from the sun is used to split water molecules into
hydrogen and oxygen.
The cell uses the energy, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide to
produce sugars.
18. The magnified picture below shows some starch granules found in potatoes
that were photographed through a microscope.
Date 17/9/23 | Level J | 17
Which two statements are true about these starch granules?
a) They are made of lipid molecules.
b) They are the form in which excess sugars are stored.
c) They are mainly used to store water.
d) They are formed from a chain of glucose linked together.
e) They help capture sunlight energy.
19. After taking good care of a poinsettia plant, Sam removed one of its leaves
on which he placed a few drops of iodine solution. A few minutes later, the
orange-brown color of the iodine solution turned dark blue.
Which substance caused the change in the color of the iodine solution?
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..
-
Sam places the same poinsettia plant in the dark until its leaves turn red. Then he adds
a few drops of the same iodine solution.
What is the expected color of the drops of iodine after a while?
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..
20. Circle the organisms that obtain energy from the food that they make
and underline the
organisms that obtain energy from the food that they eat.
Cactus tree dog frog
Reference: Level J Cells and Genetics Chapter 2 Section 3
1. The following figure shows a cell containing a structure X.
Date 17/9/23 | Level J | 18
a) Label the
following parts:
A. ……..
B. …………..
C. …………………
D. …………..
F. …………….
X. ……………….
b) Which reaction is carried out by a structure X?
……………………………………………………………………
c) Write the chemical equation for this reaction.
……………………………………………………………………
2. Where does part 1 of cellular respiration take place?
……………………………………………………………………
3. What events take place in part 1 of cellular respiration?
…………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………
4. Where does part 2 of cellular respiration take place?
……………………………………………………………………
5. What events take place in part 2 of cellular respiration?
…………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………
6. Compare how do plants and animals obtain their glucose to perform cellular
respiration.
Date 17/9/23 | Level J | 19
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………
7. Anna’s mother was baking bread. She put the dough in a warm place to rise.
Alcohol and Carbon dioxide were produced during this phase. After baking the
dough, Anna noticed small holes in the bread.
a) What caused the dough to rise and the bread holes to appear?
…………………………..
b) What happens to alcohol when the dough is baked? ……………………………….
c) Name the process that produced alcohol and carbon dioxide.
…………………………………
8. Compare photosynthesis and cellular respiration.
………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………
9. The cells in your body rely on cellular respiration and not lactic acid
fermentation to fuel your activities. Explain why.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………
10. A) Name the process that your body uses to provide your muscle cells with
energy when oxygen is missing.
………………………………………………………………………………………………
b) What causes muscle pain?
…………………………………………………………………………………………………
c) How can you remove lactic acid from your muscle cells?
……………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………
11. Yeast is usually added to the mixture of flour, water, and sugar to bake bread.
After a few minutes of adding the ingredients, bubbles of carbon dioxide start
appearing. Choose the process that leads to the gas release knowing that
oxygen is absent.
a) Photosynthesis
b) Cellular respiration
c) Alcoholic respiration
d) Acid fermentation
Date 17/9/23 | Level J | 20
12. The diagram below shows the cellular respiration and photosynthesis
photosynthesis
produces: A+ B
Cellular respiration
produces C+D
Identify A, B, C and D
A: ………….
B: ……………
C: ……………
D: ……………
Describe the 2 processes:
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………
Date 17/9/23 | Level J | 21
13. label the below diagram
16. What is cellular respiration? (Grid)
………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………
17. What is fermentation? (Grid)
………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………
18. compare Aerobic and Anaerobic respiration
………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………
Date 17/9/23 | Level J | 22
19. give one condition necessary for lactic acid fermentation:
………………………………………………………………………………………………
Reference: Level J Cells and Genetics Chapter 4 Section 1
1. Which three statements are true about scars and dyed hair?
a. They are not controlled by genes.
b. They are present since birth.
c. They are acquired traits.
d. They are inherited traits.
e. They cannot be passed to offspring.
2. Label the figure using: Gene, Chromosome, DNA, Nucleotides.
A ………….
B …………..
C…………..
D …………….
3. Consider the following two figures:
a. Which process is shown by figure a?
………………………
Date 17/9/23 | Level J | 23
b. Which process is shown by figure b?
………………………..
c. Where does process a take place?
………………..
d. Where does process b take place?
……………………………..
e. What are these two processes used for in the cell?
……………………….
f. What is the function of tRNA?
………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………
g. What is the function of mRNA? How many mRNA nucleotide code for one amino
acid?
………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………
4. Identify whether each of the following steps belongs to the process
of transcription or translation. Choose the answer.
a. The genetic information in DNA is copied onto a
………………..
molecule of messenger RNA.
b. DNA molecule unzips and forms a single strand …………………..
c. In the cytoplasm, molecules of transfer RNA pick up
…………….
amino acids and carry them to the ribosome.
d. Genetic information is converted into protein
………………
information.
Date 17/9/23 | Level J | 24
5. Label the following diagram
A= …………………….
B= …………………………
6. Order the following steps of transcription.
___ Nucleotides of mRNA pair with exposed DNA bases
___ The DNA molecule unzips and forms a single strand
___ The mRNA molecule carries the information put of the nucleus to the ribosome
___ The mRNA attaches to the ribosomes which is where protein synthesis takes place
7. Identify whether each of the below properties
describes dominant or recessive alleles. Choose the answer.
a. cannot be covered up ………………….
b. represented by a capital letter ……………………
c. homozygous and heterozygous individuals have
…………………….
the same phenotype
d. homozygous and heterozygous individuals have
….…………
different phenotypes
Date 17/9/23 | Level J | 25
6. The diagram below shows different processes that cause genetic variations
within living things. Complete this diagram using words from the box below.
Fertilization – meiosis – multiple gene traits – multiple alleles
• Union of human sperm and egg cell ……………….
• Several genes controlling one trait …………………..
• Different sets of alleles for the same gene ……………
• Production of different gametes ……………….
7. Compare and contrast a DNA and a RNA molecule. Complete the following Venn
diagram with terms from the box below.
Single stranded – made up of nucleotides – has the base uracil – double
stranded – involved in protein synthesis – has the base thymine
DNA RNA
8. The chain below shows nucleotides of a nucleic acid molecule.
ACGGUUGCAAUG
A: ………..
G:………..
C: …………..
U:………………..
a) Does the given chain represent a part of a DNA or RNA molecule? Explain
your answer.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Date 17/9/23 | Level J | 26
b) How many amino acids can be assembled by this chain? Explain your
answer.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………..
9) Answer the following questions
1) What is an inherited trait? Grid
…………………………………………………………………………………………….
2) What is an acquired trait? Grid
…………………………………………………………………………………………….
3) What is a gene? Grid
…………………………………………………………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………………………………………….
4) What is an allele? Grid
…………………………………………………………………………………………….
5) What is a dominant allele? Grid
…………………………………………………………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………………………………………….
6) What is a recessive allele? Grid
…………………………………………………………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………………………………………….
7) What are the sex chromosomes found in human gametes? Grid
…………………………………………………………………………………………….
8) How are traits passed from parents to offspring? Grid
…………………………………………………………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………………………………………….
9) How do both parents contribute to the genetic makeup of their offspring? Grid
…………………………………………………………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………………………………………….
Reference: Level J Cells and Genetics Chapter 4 Section 2
1. Why did Mendel use pea plants for his experiment?
…………………………………………………………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………………………………………….
2. How did Mendel produce the F2 generation of pea plants?
a) He allowed purebred pea plants to self-pollinate
b) He crossed purebred pea plants with purebred corn plants
c) He allowed the F1 generation to self-pollinate
d) He allowed purebred plants to cross-pollinate
Date 17/9/23 | Level J | 27
3. A____ plant is a plant that has two different alleles for a trait
a) Purebred
b) Hybrid
c) Homozygous
d) Dominant
4. Round seeds are dominant over wrinkled seed.
Which two statements are true about the resulting offspring of a cross between
two pea plants with wrinkled seeds?
a) They cannot have round seeds.
b) They only have homozygous genotypes.
c) No offspring can be produced.
d) They have both round and wrinkled seeds.
e) They only have round seeds.
5. The diagram below shows a cross between two purebred plants.
Parents Green pod purebred X yellow pod
purebred
F1 generation green pod
a) Which trait is dominant?
……………………………………………….
Explain your answer.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
b) If plants of F1 generation are self- pollinated, what is the phenotypic ratio of the
offspring in the F2 generation?
…………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………
c) give symbols that represents each allele
Green: ………
Yellow: ………
Date 17/9/23 | Level J | 28
6. Explain why two parents with type AB blood cannot have a child with type O
blood. Drag and drop.
………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………
7. Given that short hair is dominant over long hair in cats, what is the probability of
two cats with homozygous long hair having a kitten with short hair?
a) 100%
b) 50%
c) 75%
d) 0%
8. Chicken with white and black checkered feather pattern are the offspring of a
crossing between a white feathered rooster and a black feathered hen.
BW is the genotype of the offspring
a. What is the pattern of inheritance of the given trait? Explain
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………
b. Write the genotype of each parent.
…………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………
9. Which two statements are true about Mendel's hybrid plants?
a) They showed a recessive genotype.
b) They showed a recessive phenotype.
c) They were heterozygous for the trait.
d) They showed a dominant phenotype.
e) They had two identical alleles for the trait.
10. P represents the allele for purple flowers in peas that is dominant over p that
represents the allele for white flowers. The below Punnett square shows a cross
between two pea plants.
PP PP
Pp Pp
a. One parent has the gene combination Pp while the genotype of the other
parent is: ………
b. The phenotype of both parents is: ………….
c. All the offspring have ……………….. as a phenotype.
Date 17/9/23 | Level J | 29
11. The table below shows a cross between a male and a female dog
x x
B x xx xx
y XY XY
What do X and Y represent? ……………………
which of A and B is the female dog, and which is the male dog?
A-…………
B-………….
12. choose the correct answer about phenotype
a. it refers to the way a trait appears
b. it refers to the allele combinations in the cells
c. it involves expressed gene only.
d. it can be determined just by observations
13. What is phenotype? Grid
……………………………………………………………………………………………………
14. What is genotype? Grid
……………………………………………………………………………………………………
15. What is homozygous? Grid
……………………………………………………………………………………………………
16. What is a heterozygous? Grid
……………………………………………………………………………………………………
Date 17/9/23 | Level J | 30
17. A mouse with brown fur mates with another brown mouse
the allele brown is recessive with a symbol “b”
a) what is the phenotype of offspring? why
……………………………………………………………………………………………………
b) what is the genotype of offspring
……………………………………………………………………………………………………
18. Purebred dog with black hair crossed with purebred yellow hair. all offspring had
……………………………………………………………………………………………………
which allele can be represented by capital B? why?
……………………………………………………………………………………………………
what is the genotype of parent?
black hair : …………..
yellow hair: ……….
what is the genotype of offspring? ………….
19. Smooth hair is dominant over curly hair.
a) Give symbols for each allele
……………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………
b) A heterozygous Smooth air is crossed with another heterozygous Smooth
I. Give the genotypes of each the parents ……………………………
II. Give the genotype of offspring with curly hair? …………….
III. Give the genotype of heterozygous offspring: …………………
IV. Give the phenotype of heterozygous offspring: ………………….
V. What is the percentage of heterozygous for smooth hair: ………….
Date 17/9/23 | Level J | 31
You might also like
- ENTRANCE TEST - BIOLOGY For 2018/2019 Academic Year at Medical Faculty, Trakia University, Stara ZagoraDocument6 pagesENTRANCE TEST - BIOLOGY For 2018/2019 Academic Year at Medical Faculty, Trakia University, Stara ZagoraNia BoyadzhievaNo ratings yet
- S.5 Cell Biology Questions..Document11 pagesS.5 Cell Biology Questions..mober jonNo ratings yet
- Final Revision U4 m3Document10 pagesFinal Revision U4 m3Pioneers FoundationNo ratings yet
- مراجعة ساينس - 6 ب - أكتوبر - ذاكروليDocument257 pagesمراجعة ساينس - 6 ب - أكتوبر - ذاكروليNada MeselhyNo ratings yet
- Botany Exam PDFDocument9 pagesBotany Exam PDFanon_262141250No ratings yet
- Cell Revision WorksheetDocument3 pagesCell Revision WorksheetCally Chew100% (4)
- CAIE 7 - Biology - U1 - SLS - HWSH1ADocument5 pagesCAIE 7 - Biology - U1 - SLS - HWSH1AKshitij SoniNo ratings yet
- EI 9G BIO Cell-Revision-WorksheetDocument3 pagesEI 9G BIO Cell-Revision-WorksheetNaghul MxNo ratings yet
- Cellular Basis of Life and Cell DivisionDocument14 pagesCellular Basis of Life and Cell DivisionrameesmohamedjrNo ratings yet
- Cell Process QuestionsDocument17 pagesCell Process Questionsmofid monirNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document2 pagesUnit 2Camila Paula Mendoza ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Mock Cells TestDocument5 pagesMock Cells TestDavid LeechNo ratings yet
- IB Style Test Topic 1: Cell Biology: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument8 pagesIB Style Test Topic 1: Cell Biology: Multiple Choice QuestionsSneha Kumari100% (1)
- Screenshot 2023-06-17 at 3.13.00 PMDocument19 pagesScreenshot 2023-06-17 at 3.13.00 PMPlazom rlNo ratings yet
- Sci g7 pt1Document4 pagesSci g7 pt1Syed Athiq PashaNo ratings yet
- Cell Revision WorksheetDocument3 pagesCell Revision WorksheetXu Tianlong DanielNo ratings yet
- Plant Structure & Functio-1 - 2023Document3 pagesPlant Structure & Functio-1 - 2023wadimaNo ratings yet
- Cover Page - 3rd Mid Term Tests - 2023 NewDocument2 pagesCover Page - 3rd Mid Term Tests - 2023 Newanuhasfernando000No ratings yet
- REVISON WORKSHEET Class 9 DocxDocument2 pagesREVISON WORKSHEET Class 9 DocxAaratrika DasNo ratings yet
- Cells Worksheet: Name: . DateDocument5 pagesCells Worksheet: Name: . DateMuhammadNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2: Cell Structure and FunctionDocument12 pagesCHAPTER 2: Cell Structure and FunctionKhairul NizamNo ratings yet
- Bio Module 1 WorksheetsDocument11 pagesBio Module 1 WorksheetsKevin100% (2)
- Full download Biology Concepts And Connections Campbell 6Th Edition Test Bank pdfDocument43 pagesFull download Biology Concepts And Connections Campbell 6Th Edition Test Bank pdfrobert.scott362100% (10)
- c72b3eed21e042d34c60565ad049eda54eed0280-1662434460979Document17 pagesc72b3eed21e042d34c60565ad049eda54eed0280-1662434460979Tarun PatelNo ratings yet
- Biology Grade 9 t3 Revision Sheet With Answer KeyDocument6 pagesBiology Grade 9 t3 Revision Sheet With Answer KeyFatima AlmuheiriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Sections 1 and 2Document10 pagesChapter 3 - Sections 1 and 2laxolazo99No ratings yet
- Edexcel Biology A-level cell organelles questionsDocument22 pagesEdexcel Biology A-level cell organelles questionsIsa KhanNo ratings yet
- S1 Biology1Document13 pagesS1 Biology1izomadman392No ratings yet
- Question Paper: Sections Type of Questions Marks Allocated Marks Scored Tutor SignDocument7 pagesQuestion Paper: Sections Type of Questions Marks Allocated Marks Scored Tutor SignAbdul MalikNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 Science Topical Revision QuestionsDocument9 pagesGrade 6 Science Topical Revision Questionshiss turn100% (1)
- ICSE Class 10 Biology Important QuestionsDocument87 pagesICSE Class 10 Biology Important QuestionsMahimna SinghNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 - Biology October Exam (Key Answers)Document2 pagesGrade 9 - Biology October Exam (Key Answers)HisokagenNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 - Biology October ExamDocument2 pagesGrade 9 - Biology October ExamHisokagenNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 - Biology October ExamDocument2 pagesGrade 9 - Biology October ExamHisokagenNo ratings yet
- Cells Unit TestDocument9 pagesCells Unit TestDanna SchererNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology PDFDocument97 pagesCell Biology PDFashish sahuNo ratings yet
- The Biology of CellsDocument4 pagesThe Biology of Cellsnawel dekNo ratings yet
- Test CH 1 To 5-1Document3 pagesTest CH 1 To 5-1umamhumaira86No ratings yet
- October Biology ExamDocument2 pagesOctober Biology ExamHisokagenNo ratings yet
- Questions For Chapter 3Document7 pagesQuestions For Chapter 33bdallah.mseNo ratings yet
- Attachment 2Document217 pagesAttachment 2Badmind JnrNo ratings yet
- Exam Paper Sample BioDocument9 pagesExam Paper Sample Bioaarizonline2000No ratings yet
- Summative Assessement Criterion ADocument6 pagesSummative Assessement Criterion Aapi-484776271No ratings yet
- TL Gonzalez Sala ValeriaDocument26 pagesTL Gonzalez Sala ValeriagloriaNo ratings yet
- Year 1 Revision Handout 26.11Document8 pagesYear 1 Revision Handout 26.11r7yu46No ratings yet
- BVCCT 1st Sem WorkbookDocument8 pagesBVCCT 1st Sem WorkbookShivani Yadav75% (4)
- Biology-foodchain worksheet gradde 6Document8 pagesBiology-foodchain worksheet gradde 6aim instituteNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Science 2NDDocument3 pagesWeek 4 Science 2NDDIANE BORROMEO,No ratings yet
- MCQS From Ebito-WPS OfficeDocument24 pagesMCQS From Ebito-WPS Officeadebiyibisola2020No ratings yet
- Cell MCQDocument12 pagesCell MCQFave EsperanzaNo ratings yet
- Instructions To Students: Information For CandidatesDocument6 pagesInstructions To Students: Information For CandidatesMukhtaar CaseNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - Cell - ReviewDocument4 pagesWorksheet - Cell - Reviewapi-270403367No ratings yet
- 17Th International Biology Olympiad JULY 9-16, 2006 Río Cuarto - República ArgentinaDocument38 pages17Th International Biology Olympiad JULY 9-16, 2006 Río Cuarto - República ArgentinamartynapetNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Inte-Science Paper 1Document5 pagesForm 2 Inte-Science Paper 1saajid hafizNo ratings yet
- S.Y.B.sc. Microbiology (MB-211 - 212 - 221 - 222) Question BankDocument33 pagesS.Y.B.sc. Microbiology (MB-211 - 212 - 221 - 222) Question BankaadhanNo ratings yet
- Year 9cells DPDocument12 pagesYear 9cells DPVaidile JonikasNo ratings yet
- First Pu Model Paper PDFDocument5 pagesFirst Pu Model Paper PDFMujeeb KhanNo ratings yet
- Bio-Vision - SSLC Biology em Sample QN 2019Document12 pagesBio-Vision - SSLC Biology em Sample QN 2019anandkrishnaNo ratings yet
- Bio F110 1001Document2 pagesBio F110 1001AmanNo ratings yet
- Assignment-2 XII Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocument2 pagesAssignment-2 XII Molecular Basis of InheritanceJai Bharat0% (1)
- 1 A 2 AfcDocument6 pages1 A 2 AfcMahina WongNo ratings yet
- Radiotherapy Inlung Cancer PDFDocument539 pagesRadiotherapy Inlung Cancer PDFStefania CarboneNo ratings yet
- Dna Extraction and SpoolingDocument4 pagesDna Extraction and SpoolingHas AlqisNo ratings yet
- Homosexuality and The Scientific Evidence PDFDocument274 pagesHomosexuality and The Scientific Evidence PDFanon_113431634No ratings yet
- DNA Structure and Analysis ChapterDocument11 pagesDNA Structure and Analysis Chapteranon_747148947No ratings yet
- Pediatric Genetics Dr. Samed AlsalmiDocument166 pagesPediatric Genetics Dr. Samed AlsalmiabhivnairNo ratings yet
- cDNA Synthesis System: Instruction ManualDocument36 pagescDNA Synthesis System: Instruction ManualmaniiiiiiiiNo ratings yet
- DAVAO MEDICAL SCHOOL FOUNDATION COLLEGE OF MEDICINE BIOCHEMISTRY LIPID EXAMDocument5 pagesDAVAO MEDICAL SCHOOL FOUNDATION COLLEGE OF MEDICINE BIOCHEMISTRY LIPID EXAMVince Cabahug100% (1)
- Assignment Questions Biology Class: XII CHAPTER 1: Reproduction in OrganismDocument14 pagesAssignment Questions Biology Class: XII CHAPTER 1: Reproduction in Organismzach23628No ratings yet
- Capillary ElectrophoresisDocument103 pagesCapillary ElectrophoresisfdlabNo ratings yet
- Blood Bank. Harmening Chapter 2 Review QuestionsDocument2 pagesBlood Bank. Harmening Chapter 2 Review QuestionsMerry GraceNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology Chapter 17Document47 pagesIGCSE Biology Chapter 17Ventus Tan75% (4)
- Microbiology - Bacte, Myco, ViroDocument120 pagesMicrobiology - Bacte, Myco, ViroSogan, MaureenNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 DNADocument19 pagesGrade 9 DNARitchwel FAJARDO100% (1)
- RNADocument13 pagesRNAAgam SharanNo ratings yet
- Dna Vs Rna and Protein Synthesis Updated Recap by Amoeba SistersDocument2 pagesDna Vs Rna and Protein Synthesis Updated Recap by Amoeba SistersJaneNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes - Weeks 1 and 2 BCMB2001Document17 pagesLecture Notes - Weeks 1 and 2 BCMB2001Anushka NeupaneNo ratings yet
- BiochemDocument41 pagesBiochemIram KhanNo ratings yet
- Vaccine Contamination McreardenDocument17 pagesVaccine Contamination McreardenRobert Davidson, M.D., Ph.D.100% (1)
- Soal BimbelDocument3 pagesSoal BimbelAndi Susan Dewi FNo ratings yet
- A Perspective of Synthetic Biology: Assembling Building Blocks For Novel FunctionsDocument10 pagesA Perspective of Synthetic Biology: Assembling Building Blocks For Novel FunctionspharssNo ratings yet
- SGI 2e SBDocument640 pagesSGI 2e SBAnonymous Li3FHiP8TDNo ratings yet
- Cumulative Lab ReportDocument3 pagesCumulative Lab ReportaplesgjskNo ratings yet
- Genetic Analysis An Integrated Approach 2nd Edition Sanders Test BankDocument15 pagesGenetic Analysis An Integrated Approach 2nd Edition Sanders Test Bankmundifycoucheefnhgl100% (19)
- Antiviral Agents Chapter Provides Overview of Classification and BiochemistryDocument26 pagesAntiviral Agents Chapter Provides Overview of Classification and BiochemistryEmily Larissa Saldanha PereiraNo ratings yet
- AP Bio PLUS - Ch. 1-7 Exam ReviewDocument5 pagesAP Bio PLUS - Ch. 1-7 Exam ReviewEmma HeathNo ratings yet
- For Lecture PDF 295074Document12 pagesFor Lecture PDF 295074Rob Robbie RabuelNo ratings yet
- Short Technical ReportDocument5 pagesShort Technical ReportSato ObcianaNo ratings yet