Professional Documents
Culture Documents
English Tenses Made Easy1
English Tenses Made Easy1
Uploaded by
shannia rOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
English Tenses Made Easy1
English Tenses Made Easy1
Uploaded by
shannia rCopyright:
Available Formats
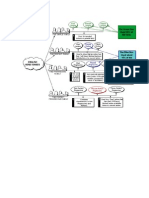
In most grammar books they will teach you that there are three forms to a verb (infinitive: V1,
Past: V2,
Past Participle: V3) whereas there are in fact six. Look at the table below.
Table 1
Base Infinitive Present simple Present Participle Past simple Past Participle
(V1) (V2) (V3)
be to be am/is/are being was/were been
continue to continue continue(s) continuing continued continued
think to think think(s) thinking thought thought
In order to form all tenses there are just five rules you should remember. Look at the list below.
Table 2
1: Future Will + Base (V1)
2: Perfect Have + Past Participle (V3)
3: Continuous Be + Present Participle
4: Passive Be + Past Participle (V3)
5: Modals Can, could, should, would, etc… + Base (V1)
Once you have remembered these five rules, more complex tenses can easily be constructed without
having to think very hard. Imagine you need to use the Future Perfect Continuous. A lot of students will say:
‘will be doing’, ‘will have doing’ or ‘will have been’ but very rarely find the correct answer. Therefore by
making the following table students can easily find the correct answer.
(Source: ‘English Tenses Made Easy’ by W. Shearmur)
Table 3
Future will base
(V1)
Perfect + have Past participle
(V3)
Continuous + be Present Part.
Future Perfect = will have been Present
Continuous (V1) (V3) Participle
Example: I will have been swimming when you arrive.
Now Go swimming you arrive
| | | |
The result when you arrive is that I will have started and finished to swim. As swimming is a long process
the continuous is used.
(Source: ‘English Tenses Made Easy’ by W. Shearmur)
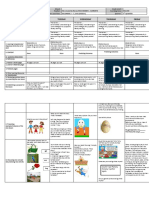
The main problem then is trying to remember how to use each tense. The following table will help you do
this.
Table 4
Tense Time Past Present Future
Three rules: Two rules: Two rules:
1: Definite past time. 1: Habits. 1: Future facts.
------------------- -------------------- -------------------
- 2: Timetables. -
Simple 2: Chronological order. 2: Unplanned future
-------------------- actions.
------------------- -------------------
-
3: Historical events.
Three rules:
1: Time up to now.
------------------- -------------------- -------------------
- 2: Present result at the -
Past result at a given present time. Future result at a given
Perfect
past time. future time.
--------------------
------------------- 3: Indefinite past time. -------------------
- -
Three rules:
1: Action happening at
time of speaking
------------------- -------------------- -------------------
- 2: Action happening -
Continuous Action happening around the present time. Action happening around
around a past time. -------------------- a future time.
------------------- 3: Future planned action. -------------------
- -------------------- -
4: Something that is
about to happen.
Action that continued Action that has continued Action that will have
Perfect Continuous for some time before up to the present time. continued for some time
another action. before a future time.
Something to notice is that in all three times (past, present, future) the perfect is used to talk about
results at a given time. The same goes for the continuous, which is used to describe an action happening
around a given past, present or future time.
(Source: ‘English Tenses Made Easy’ by W. Shearmur)
You might also like
- Slackers Guide To Physics: Electricity and MagnetismDocument39 pagesSlackers Guide To Physics: Electricity and Magnetismkhers_zalNo ratings yet
- Monroe TechniqueDocument5 pagesMonroe Techniquesimion100% (2)
- Ever Deeper HonestyDocument1,193 pagesEver Deeper HonestySara Azizi100% (1)
- English For Tourism: Students' WorkbookDocument98 pagesEnglish For Tourism: Students' WorkbookLarisa100% (1)
- German QuicklyDocument453 pagesGerman QuicklykashochualanNo ratings yet
- Ode To AutumnDocument16 pagesOde To AutumnNishita SankhalaNo ratings yet
- Verben Mit PraepositionenDocument4 pagesVerben Mit Praepositionenpaul george100% (1)
- Angol NyelvtanDocument17 pagesAngol Nyelvtaninvisiblevision4No ratings yet
- Toyota Kata - 5Q - CardDocument11 pagesToyota Kata - 5Q - CardJesus Alarcon Z CantuNo ratings yet
- ملخص شامل لقواعد الانجليزية - الوحدة الأولى- للشعب الأدبيةDocument14 pagesملخص شامل لقواعد الانجليزية - الوحدة الأولى- للشعب الأدبيةYoona Kim100% (4)
- Student - Simple Present Verb To BeDocument4 pagesStudent - Simple Present Verb To Beluz areli diaz meneses100% (2)
- Wichtige Grammatikbereiche. Englisch 7. Klasse und für Erwachsene: Übungs- und Trainingsbuch mit Lösungen für das 3. EnglischjahrFrom EverandWichtige Grammatikbereiche. Englisch 7. Klasse und für Erwachsene: Übungs- und Trainingsbuch mit Lösungen für das 3. EnglischjahrNo ratings yet
- FILE - 20211127 - 121827 - NG Pháp 2 - K5 - 2019 - 2TCDocument52 pagesFILE - 20211127 - 121827 - NG Pháp 2 - K5 - 2019 - 2TCNi CaoNo ratings yet
- Consolidation 1Document3 pagesConsolidation 1Toan TranNo ratings yet
- Consolidation 4Document3 pagesConsolidation 4Toan TranNo ratings yet
- Academic Writing Course Future Tenses ReviewDocument9 pagesAcademic Writing Course Future Tenses ReviewjorghelaldoNo ratings yet
- Classwork and Homework - Future EventsDocument1 pageClasswork and Homework - Future Eventsnarko baronasNo ratings yet
- Assessment 2LPHDocument1 pageAssessment 2LPHkitty AndersonNo ratings yet
- ملخص شامل في اللغة الإنجليزية للشعب العلمية1649968630Document80 pagesملخص شامل في اللغة الإنجليزية للشعب العلمية1649968630SabrinaNo ratings yet
- Course For L1 ASSRI & MIAGEDocument19 pagesCourse For L1 ASSRI & MIAGEkoffiabonouan290No ratings yet
- اللغة الإنجليزية - المحطة النظرية الشاملة للتحضير الممتاز - نافع بكالوريا 2024Document60 pagesاللغة الإنجليزية - المحطة النظرية الشاملة للتحضير الممتاز - نافع بكالوريا 2024Oum YoussefNo ratings yet
- Modulo InglesDocument44 pagesModulo InglesZayra Rico100% (1)
- Life As A Youtuber - WorksheetDocument4 pagesLife As A Youtuber - WorksheetNicole ScheferNo ratings yet
- General GrammarDocument2 pagesGeneral GrammarRodrigo HidalgoNo ratings yet
- First Law of Motion 8 20-8 21 Independent Tasks 2Document5 pagesFirst Law of Motion 8 20-8 21 Independent Tasks 2api-372548146No ratings yet
- Edu303 Quiz 1Document3 pagesEdu303 Quiz 1Xia AlliaNo ratings yet
- ملخص قواعد الانجليزية الشعب العلمية المشتركة 1Document31 pagesملخص قواعد الانجليزية الشعب العلمية المشتركة 1Youcef BrahimiNo ratings yet
- Verb Tenses Mind MapDocument27 pagesVerb Tenses Mind MapArt Scot100% (1)
- CC TPA Unit 1 LanguageDocument3 pagesCC TPA Unit 1 LanguagenoureddinemsylyaNo ratings yet
- Writing - Task 1 - Processess - Manufacturing WSDocument5 pagesWriting - Task 1 - Processess - Manufacturing WSNhi LêNo ratings yet
- اللغة الإنجليزية - الباقة النظرية الشاملة للتحضير الممتاز - نافع - بكالوريا 2022Document77 pagesاللغة الإنجليزية - الباقة النظرية الشاملة للتحضير الممتاز - نافع - بكالوريا 2022G23No ratings yet
- Worksheet On Elon MuskDocument3 pagesWorksheet On Elon MuskCecilia EscobarNo ratings yet
- Trevor Ling PresentationDocument28 pagesTrevor Ling Presentationapi-271883875No ratings yet
- 5Q - Card KataDocument14 pages5Q - Card Katacharles.fotsoNo ratings yet
- Present PerfectDocument2 pagesPresent PerfectLink CornerNo ratings yet
- The Causative: Have / GetDocument5 pagesThe Causative: Have / Getmonaatta444No ratings yet
- Reflexive Verbs 1Document3 pagesReflexive Verbs 1Aignard Krijger GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Actividades - Unidad 1-4 - InglesIVDocument14 pagesActividades - Unidad 1-4 - InglesIVMariel ValdezNo ratings yet
- Course For L1 ASSRI & MIAGEDocument18 pagesCourse For L1 ASSRI & MIAGEarielkoliaNo ratings yet
- TemplateDocument7 pagesTemplateHector ZavaletaNo ratings yet
- Science Practice 1Document5 pagesScience Practice 1Naufal IlhamNo ratings yet
- PSY348 Lab 5Document7 pagesPSY348 Lab 5Kirana Rista PutriNo ratings yet
- Workbook 2Document24 pagesWorkbook 2srishti.bhattacharyya2021No ratings yet
- Unit 1 Health: Grammar Present Simple and Adverbs of FrequencyDocument5 pagesUnit 1 Health: Grammar Present Simple and Adverbs of FrequencyvictorNo ratings yet
- Review Exercises For Baccalaureate StudentsDocument8 pagesReview Exercises For Baccalaureate StudentsSaida MokhtariNo ratings yet
- ملف مراجعة الإنجليزي (المعسكر) مع الأستاذ شادي الرمحيDocument13 pagesملف مراجعة الإنجليزي (المعسكر) مع الأستاذ شادي الرمحيMohammad AburummanNo ratings yet
- AERO174 Report 5Document4 pagesAERO174 Report 5Asif Karim OrnobNo ratings yet
- Newtons Second Law of Motion 9 5-9 6 Independent TasksDocument5 pagesNewtons Second Law of Motion 9 5-9 6 Independent Tasksapi-372548146No ratings yet
- Detailes English GrammerDocument25 pagesDetailes English GrammerJbour LaithNo ratings yet
- 340workbook PDFDocument130 pages340workbook PDFas_5kNo ratings yet
- Tarea InglesDocument7 pagesTarea InglesredcoreanNo ratings yet
- Newenterpriseb2 Grammar PLDocument10 pagesNewenterpriseb2 Grammar PLmailhorizontetecnoNo ratings yet
- Elementary CalculusDocument77 pagesElementary CalculusJoseph TabulinaNo ratings yet
- English Ii: SubjectDocument8 pagesEnglish Ii: SubjectSerx RobertNo ratings yet
- NURS280 Questions 7Document3 pagesNURS280 Questions 7HealthybatcheYNo ratings yet
- Y C NC en Ncy Cy Cy Cy en E: First Term English ExamDocument2 pagesY C NC en Ncy Cy Cy Cy en E: First Term English ExamDjamila SekhriNo ratings yet
- E-Book Puzzle of TensesDocument40 pagesE-Book Puzzle of TenseshmkNo ratings yet
- The Moving Target Kettlebell Complex Strongfirst PDFDocument13 pagesThe Moving Target Kettlebell Complex Strongfirst PDFAntonioNo ratings yet
- 'Providing That / Provided That / As Long As 'Document17 pages'Providing That / Provided That / As Long As 'alaa daysNo ratings yet
- Comparative TemplateDocument6 pagesComparative TemplateCARLOS FRANCISCO IZQUIERDO PRIETONo ratings yet
- Time ExercisesDocument5 pagesTime Exercisessabrina harrakNo ratings yet
- GrammarDocument7 pagesGrammarmahsa.goodarzNo ratings yet
- Simple Past Vs Past Continuous & Past Perfect Vs Past Perfect ContinuousDocument4 pagesSimple Past Vs Past Continuous & Past Perfect Vs Past Perfect ContinuousJocelynNo ratings yet
- Limba Engleză: Curs Pentru Învăţământ La DistanţăDocument79 pagesLimba Engleză: Curs Pentru Învăţământ La DistanţăTatiana MolociNo ratings yet
- B2 First ConditionalsDocument7 pagesB2 First ConditionalsVanessaNicole14391No ratings yet
- DLL - English 1 - Q3 - W6Document6 pagesDLL - English 1 - Q3 - W6JOHAIMAH CABUGATANNo ratings yet
- Kcse Prediction 2 Class of March 2022Document207 pagesKcse Prediction 2 Class of March 2022Jeddah TroyNo ratings yet
- Essay Ronggeng Dukuh ParukDocument8 pagesEssay Ronggeng Dukuh ParukJoni BudiantoNo ratings yet
- Pragmatics - BRUDocument129 pagesPragmatics - BRUAnnie LeNo ratings yet
- Ow Ame Ev Placement General Ak 0 3Document3 pagesOw Ame Ev Placement General Ak 0 3Aleksei KhomutovNo ratings yet
- English Checklist by Nimisha Mam (3, May, 2022,)Document31 pagesEnglish Checklist by Nimisha Mam (3, May, 2022,)RajendraNo ratings yet
- Week1 (Sitthathan Seesangum & 63102010173)Document4 pagesWeek1 (Sitthathan Seesangum & 63102010173)Sitthathan SeesangumNo ratings yet
- Exemplars Final 1EN0 Paper 1Document62 pagesExemplars Final 1EN0 Paper 1Innova Anna konthiamadom AnilNo ratings yet
- DL English 6Document11 pagesDL English 6jerwindeleon260No ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Anticipating Questions About DialogsDocument5 pagesLesson 1: Anticipating Questions About DialogsInas Rizky HumairahNo ratings yet
- Countable and Uncountable NounsDocument6 pagesCountable and Uncountable NounsJoahaNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Writing Is Where The Author Uses Details To Paint A Picture With Their WordsDocument1 pageDescriptive Writing Is Where The Author Uses Details To Paint A Picture With Their WordsJada KnightsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document31 pagesChapter 2CA Pham KhaiNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Plan English Language Year 6Document5 pagesDaily Lesson Plan English Language Year 6aishah abdullahNo ratings yet
- FCE Listening Practice Test 3Document4 pagesFCE Listening Practice Test 3Lê Mai Bảo VyNo ratings yet
- SSC CGL 2011 To 2019 Direct & Indirect SpeechDocument37 pagesSSC CGL 2011 To 2019 Direct & Indirect SpeechSandeep MudgilNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Plan Year 2Document18 pagesDaily Lesson Plan Year 2Nurul AinNo ratings yet
- Ruth and The Green Book RubricDocument1 pageRuth and The Green Book Rubricapi-264643152No ratings yet
- Foreign Language ReviewerDocument7 pagesForeign Language ReviewerIson, Marc Ervin A.No ratings yet
- Basics of Writing For RadioDocument11 pagesBasics of Writing For RadioBrandon JohnNo ratings yet
- S VCRDocument16 pagesS VCRPriscila JodasNo ratings yet
- Test Taker GuideDocument79 pagesTest Taker GuideVinit ParakhNo ratings yet
- Семінар 10Document4 pagesСемінар 10nastya14.12.shNo ratings yet
- French Grammar - III: Course Title: Credit Units: 2 Course Code: FREN123 UG (Semester-8)Document3 pagesFrench Grammar - III: Course Title: Credit Units: 2 Course Code: FREN123 UG (Semester-8)Athul Jayaram0% (1)