Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pure Competitive Market
Uploaded by
Chris Danielle FuentesCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pure Competitive Market
Uploaded by
Chris Danielle FuentesCopyright:
Available Formats
Managerial Economics AC 4102
Pure Competitive Market
Problem Set
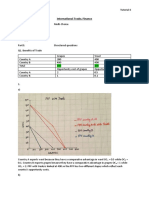
A. The market for leche flan in the city of Panderia is competitive and has the following demand schedule
Price Quantity Demanded
50 1,200
100 1,100
150 1,000
200 900
250 800
300 700
350 600
400 500
450 400
500 300
550 200
600 100
650 0
Each producer in the market has fixed costs of Php 450 and the marginal cost schedule:
Quantity Marginal Cost
1 Php 100
2 200
3 300
4 400
5 500
6 600
a. Compute each producer's total cost and average total cost for each quantity from 1 to 6 leche
flan.
b. The price of leche flan is now at 11. How many leche flans are sold? How many leche flan does
each producer make?
c. Is the situation described in part (b) a long run equilibrium? Why or Why not?
d. Suppose that in the long run there is free entry and exit. How much profit does each producer
earn in the long run equilibrium? What is the market price? How many leche flan does each
producer make? How many leche flan are sold in the market? How many leche flan producers are
operating?
B. Lingin Liggid Inc., faces costs of production as follows:
Quantity ( cases ) Total Fixed Cost Total Variable Cost
0 5000 0
1 5000 2500
2 5000 3500
3 5000 4500
4 5000 7000
5 5000 10000
6 5000 18000
a. Calculate the company’s average fixed cost, average variable cost, average total cost, and
marginal cost at each level of production.
b. The price of a case of ball bearings is Php 2500. Seeing that he can’t make a profit, the chief
executive officer (CEO) decides to shut down operations. What is the firm’s profit/loss? Is shutting down
a wise decision? Explain.
c. Vaguely remembering his introductory economics course, the chief financial officer tells the
CEO it is better to produce 1 case of ball bearings because marginal revenue equals marginal cost at that
quantity. What is the firm’s profit/loss at that level of production? Is producing 1 case the best decision?
Explain.
You might also like
- MicroEcons Practice Questions by SKDocument8 pagesMicroEcons Practice Questions by SKdadaudaNo ratings yet
- Course Assignment Due On 5 December Part I: Essays QuestionsDocument4 pagesCourse Assignment Due On 5 December Part I: Essays QuestionsAbdo Salem9090No ratings yet
- Manecon Assignment #5Document3 pagesManecon Assignment #5tygurNo ratings yet
- CVP 2Document18 pagesCVP 2priyanshu kumariNo ratings yet
- Suggested Solution: BHMH2002 Introduction To Economics Individual Assignment II (S2, 2021)Document3 pagesSuggested Solution: BHMH2002 Introduction To Economics Individual Assignment II (S2, 2021)Chi Chung LamNo ratings yet
- Micro Econs-Tutorial Three and FourDocument8 pagesMicro Econs-Tutorial Three and Fourvc854146No ratings yet
- Class Room Exercise 10Document5 pagesClass Room Exercise 10aiperikulushevaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Exercises 7: Perfect Competition: Essential Readings: Chapter 7Document18 pagesTutorial Exercises 7: Perfect Competition: Essential Readings: Chapter 7tahmeemNo ratings yet
- Economics Practice QuestionsDocument6 pagesEconomics Practice QuestionsEve PomeNo ratings yet
- Break Even AnalysisDocument4 pagesBreak Even AnalysisRachit DixitNo ratings yet
- CVP1Document36 pagesCVP1Pankaj SahaniNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Questions On AccountingDocument6 pagesTutorial Questions On AccountingEve PomeNo ratings yet
- Assignment 01 Managerial Economics - Saturday, 6:30-9:30: Due Date: April15, 2020Document3 pagesAssignment 01 Managerial Economics - Saturday, 6:30-9:30: Due Date: April15, 2020Mahek Anwar AliNo ratings yet
- BMME5103 Assignment QuestionDocument7 pagesBMME5103 Assignment Questionsheyen choongNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Asna202309001Document3 pagesAssignment 2 Asna202309001Rameez KhanNo ratings yet
- Mix VarianceDocument1 pageMix VarianceClaire BarrettoNo ratings yet
- Taranveer-Wk 1-Quiz 1-Man EcoDocument16 pagesTaranveer-Wk 1-Quiz 1-Man EcoaksNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Kim Jubilee Casencia Flordeliza Nanoy Irish Cayao Erman Dave Sabuya Edrian Carejon Jelyn Paredes Jessica GajetoDocument18 pagesGroup 1 Kim Jubilee Casencia Flordeliza Nanoy Irish Cayao Erman Dave Sabuya Edrian Carejon Jelyn Paredes Jessica GajetoPrincess Di BaykingNo ratings yet
- Ama Set 25Document5 pagesAma Set 25uroojfatima21299No ratings yet
- Drill#1Document5 pagesDrill#1Leslie BustanteNo ratings yet
- MAS - 1416 Profit Planning - CVP AnalysisDocument24 pagesMAS - 1416 Profit Planning - CVP AnalysisAzureBlazeNo ratings yet
- 7 2010 Jun QDocument8 pages7 2010 Jun QWeezy360No ratings yet
- Accept or Reject Special OrderDocument6 pagesAccept or Reject Special OrderLex100% (1)
- MARGINAL COSTIN1 Auto SavedDocument6 pagesMARGINAL COSTIN1 Auto SavedVedant RaneNo ratings yet
- 02 CVP Analysis PDFDocument5 pages02 CVP Analysis PDFJunZon VelascoNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics: Production Process and Cost AnalysisDocument44 pagesManagerial Economics: Production Process and Cost AnalysisNicole Anne Villanueva PacificoNo ratings yet
- Pacific Southbay College, Inc: Purok Carmenville, Calumpang, General Santos CityDocument3 pagesPacific Southbay College, Inc: Purok Carmenville, Calumpang, General Santos CityItss Louie'sNo ratings yet
- I. Elasticity: Q Q Q Q P P P PDocument6 pagesI. Elasticity: Q Q Q Q P P P PAIREEN DEIPARINENo ratings yet
- April 2012Document3 pagesApril 2012Derick cheruyotNo ratings yet
- Homework 5 - Part - I - AKDocument14 pagesHomework 5 - Part - I - AKBagus SaputroNo ratings yet
- Questions For ReviewDocument13 pagesQuestions For Reviewنور عفيفهNo ratings yet
- Problem 1: Solution Guide - Requirement 1Document4 pagesProblem 1: Solution Guide - Requirement 1Lerma MarianoNo ratings yet
- EBE1063 LU7 8 Practise QuestionsDocument5 pagesEBE1063 LU7 8 Practise Questions史迪奇No ratings yet
- MBA 542 Inventory Exercise IIIDocument5 pagesMBA 542 Inventory Exercise IIISinem DüdenNo ratings yet
- Logistics and Supply Chain ManagementDocument3 pagesLogistics and Supply Chain ManagementSatchidananda TripathyNo ratings yet
- Cost Management Problems CA FinalDocument266 pagesCost Management Problems CA Finalksaqib89100% (1)
- Badm 560 - Firm and Industry Analysis Problem Set Two QuestionsDocument2 pagesBadm 560 - Firm and Industry Analysis Problem Set Two QuestionsRoger federerNo ratings yet
- SS3 DRDocument4 pagesSS3 DRabdulramon2023No ratings yet
- Performance Management: March/June 2016 - Sample QuestionsDocument13 pagesPerformance Management: March/June 2016 - Sample QuestionsBảo BốiNo ratings yet
- CVP ComputationsDocument2 pagesCVP ComputationsEnp Gus AgostoNo ratings yet
- Quizzer - Cost Volume Profit AnalysisDocument8 pagesQuizzer - Cost Volume Profit AnalysisJethro Gutlay100% (3)
- Mid-Term MAKEUP Exam (Open Book) : Near East UniversityDocument2 pagesMid-Term MAKEUP Exam (Open Book) : Near East UniversityAhmet ErolNo ratings yet
- Econ130 Tutorial 06 International Trade, FinanceDocument3 pagesEcon130 Tutorial 06 International Trade, FinanceGurkiran KaurNo ratings yet
- Accounting 14 Assignment To HahahaDocument14 pagesAccounting 14 Assignment To HahahaRampotz Ü EchizenNo ratings yet
- MANECO Week-2Document28 pagesMANECO Week-2mackyberriesNo ratings yet
- SolutionDocument6 pagesSolutionmailrahulrajNo ratings yet
- Kuis - Financial Lab ModelingDocument2 pagesKuis - Financial Lab Modelingalexandersur9No ratings yet
- Break Even Analysis Final Term Lesson Activity 1Document53 pagesBreak Even Analysis Final Term Lesson Activity 1温埃德No ratings yet
- Pom Mock ExamDocument3 pagesPom Mock ExamManzar HussainNo ratings yet
- Mock Reviewer in Management AccountingDocument6 pagesMock Reviewer in Management AccountingJA VicenteNo ratings yet
- Mock Deparmentals MASQDocument6 pagesMock Deparmentals MASQHannah Joyce MirandaNo ratings yet
- Preparing Financial Forecasts Alternative Assessment Outcome 01Document5 pagesPreparing Financial Forecasts Alternative Assessment Outcome 01piumiNo ratings yet
- MICRO Ass. 4Document3 pagesMICRO Ass. 4Sidramushtaq IoBMNo ratings yet
- Break-Even Analysis Template (Excel)Document4 pagesBreak-Even Analysis Template (Excel)MicrosoftTemplates100% (1)
- Chapter 1 Cost-Volume-Profit RelationshipsDocument51 pagesChapter 1 Cost-Volume-Profit Relationshipspamela dequillamorteNo ratings yet
- 22 - Mtest - Management Accounting Morning 1st HalfDocument4 pages22 - Mtest - Management Accounting Morning 1st HalfZohaib NasirNo ratings yet
- Venture Capital Valuation, + Website: Case Studies and MethodologyFrom EverandVenture Capital Valuation, + Website: Case Studies and MethodologyNo ratings yet
- Life-Cycle Costing: Using Activity-Based Costing and Monte Carlo Methods to Manage Future Costs and RisksFrom EverandLife-Cycle Costing: Using Activity-Based Costing and Monte Carlo Methods to Manage Future Costs and RisksNo ratings yet
- Strategy, Value and Risk: A Guide to Advanced Financial ManagementFrom EverandStrategy, Value and Risk: A Guide to Advanced Financial ManagementNo ratings yet
- Beyond Earnings: Applying the HOLT CFROI and Economic Profit FrameworkFrom EverandBeyond Earnings: Applying the HOLT CFROI and Economic Profit FrameworkNo ratings yet
- Spike Magazine Cup PackDocument5 pagesSpike Magazine Cup PackBungle MarleyNo ratings yet
- PLX Model OfficialDocument105 pagesPLX Model OfficialBảo Ngọc LêNo ratings yet
- C305 - QTO Workshop PDFDocument90 pagesC305 - QTO Workshop PDFJason SecretNo ratings yet
- 10 Problem For The Topic 9 & 10 Hicao GroupDocument4 pages10 Problem For The Topic 9 & 10 Hicao GroupArvin ArmojallasNo ratings yet
- APS PresentationDocument32 pagesAPS PresentationRozack Ya ZhackNo ratings yet
- (AVA Academia) Lorraine Farrelly - The Fundamentals of architecture-AVA Academia (2012) - Trang-137-161Document25 pages(AVA Academia) Lorraine Farrelly - The Fundamentals of architecture-AVA Academia (2012) - Trang-137-161Thảo VyNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mathematics Questions and AnswersDocument9 pagesEngineering Mathematics Questions and AnswersZaky Muzaffar100% (1)
- Et200sp Im 155 6 PN ST Manual en-US en-USDocument47 pagesEt200sp Im 155 6 PN ST Manual en-US en-USayaz officeNo ratings yet
- Corporate Profile of Multimode GroupDocument6 pagesCorporate Profile of Multimode GroupShaheen RahmanNo ratings yet
- Appendicitis Case StudyDocument6 pagesAppendicitis Case StudyKimxi Chiu LimNo ratings yet
- Auburn Bsci ThesisDocument5 pagesAuburn Bsci Thesisafksaplhfowdff100% (1)
- FE 208 Lab #4 - Profile Leveling: CrewDocument4 pagesFE 208 Lab #4 - Profile Leveling: CrewJefferson Himson0% (1)
- Automatic Coconut Dehusking MachineDocument12 pagesAutomatic Coconut Dehusking MachineKumaresh Salem0% (1)
- Advanced Packaging Polymers: Product Selection GuideDocument12 pagesAdvanced Packaging Polymers: Product Selection GuideDKNo ratings yet
- Stitch2421 1 Kit PDFDocument8 pagesStitch2421 1 Kit PDFJoshua Robertson100% (1)
- Architech 06-2016 Room AssignmentDocument4 pagesArchitech 06-2016 Room AssignmentPRC Baguio100% (1)
- Handbook - European Choral AssociationDocument24 pagesHandbook - European Choral AssociationMonica SaenzNo ratings yet
- Digital ThermometerDocument12 pagesDigital Thermometershahpatel19No ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter SUMMATIVE TEST in MAPEHDocument3 pages3rd Quarter SUMMATIVE TEST in MAPEHzaile felineNo ratings yet
- Why Do Kashmiris Need Self-Determination?: UncategorizedDocument16 pagesWhy Do Kashmiris Need Self-Determination?: UncategorizedFarooq SiddiqiNo ratings yet
- Bell Single-Sleeve Shrug Crochet PatternDocument2 pagesBell Single-Sleeve Shrug Crochet PatternsicksoxNo ratings yet
- AR Financial StatementsDocument281 pagesAR Financial StatementsISHA AGGARWALNo ratings yet
- p1632 eDocument4 pagesp1632 ejohn saenzNo ratings yet
- RSM222.f22.CourseOutline v3 2022-09-05Document9 pagesRSM222.f22.CourseOutline v3 2022-09-05Kirsten WangNo ratings yet
- Statement of Cash Flows AnswerDocument3 pagesStatement of Cash Flows Answeranber mohammadNo ratings yet
- Drill Bit Classifier 2004 PDFDocument15 pagesDrill Bit Classifier 2004 PDFgustavoemir0% (2)
- SOP For Operation & Calibration of PH Meter - QualityGuidancesDocument9 pagesSOP For Operation & Calibration of PH Meter - QualityGuidancesfawaz khalilNo ratings yet
- Titus Selection of DiffuserDocument14 pagesTitus Selection of DiffuserhanyassawyNo ratings yet
- Essential Study SkillsDocument86 pagesEssential Study SkillsFady NgunyuNo ratings yet
- Simple Love Spells That WorkDocument14 pagesSimple Love Spells That Workagg24ankitNo ratings yet